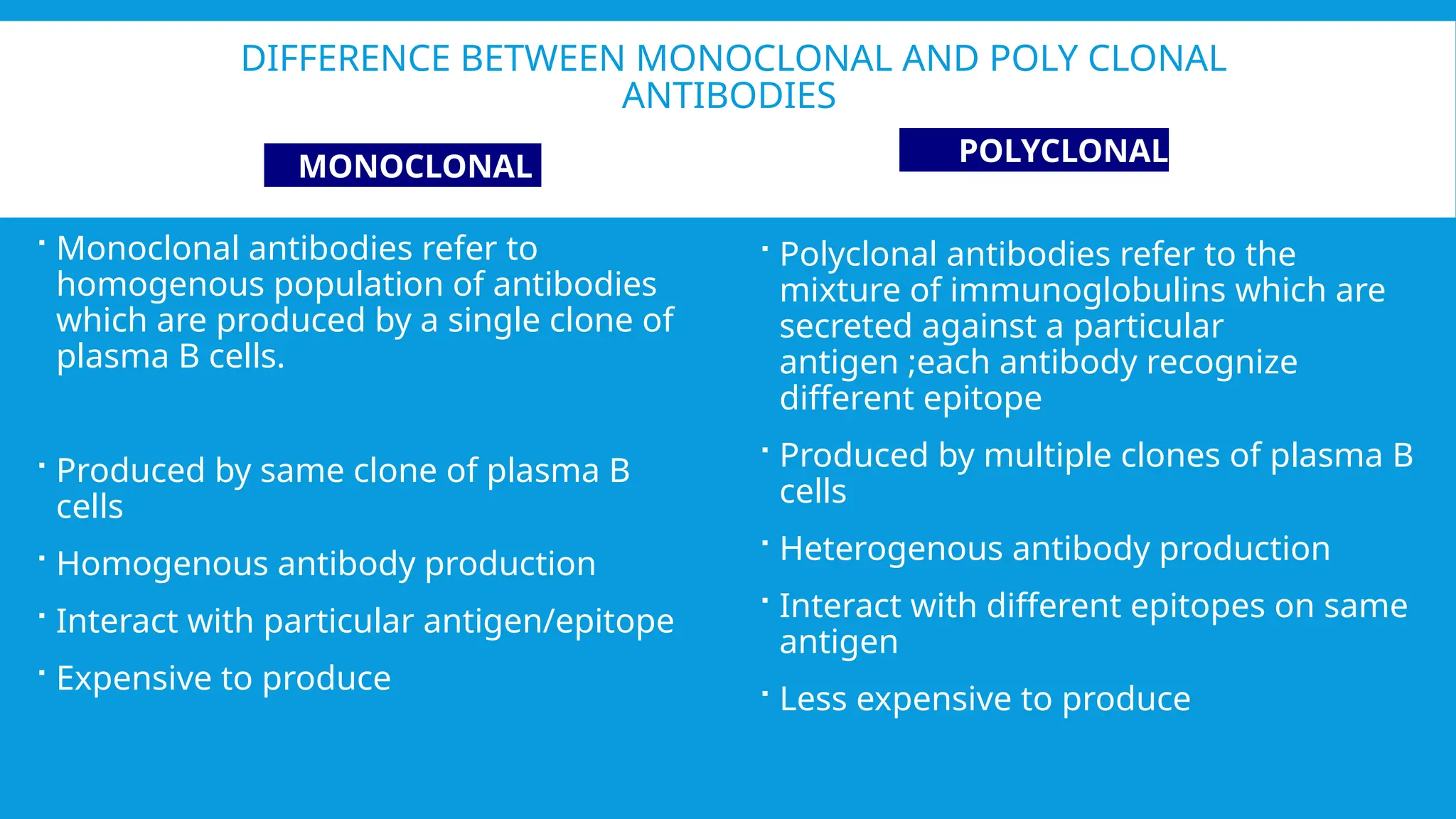
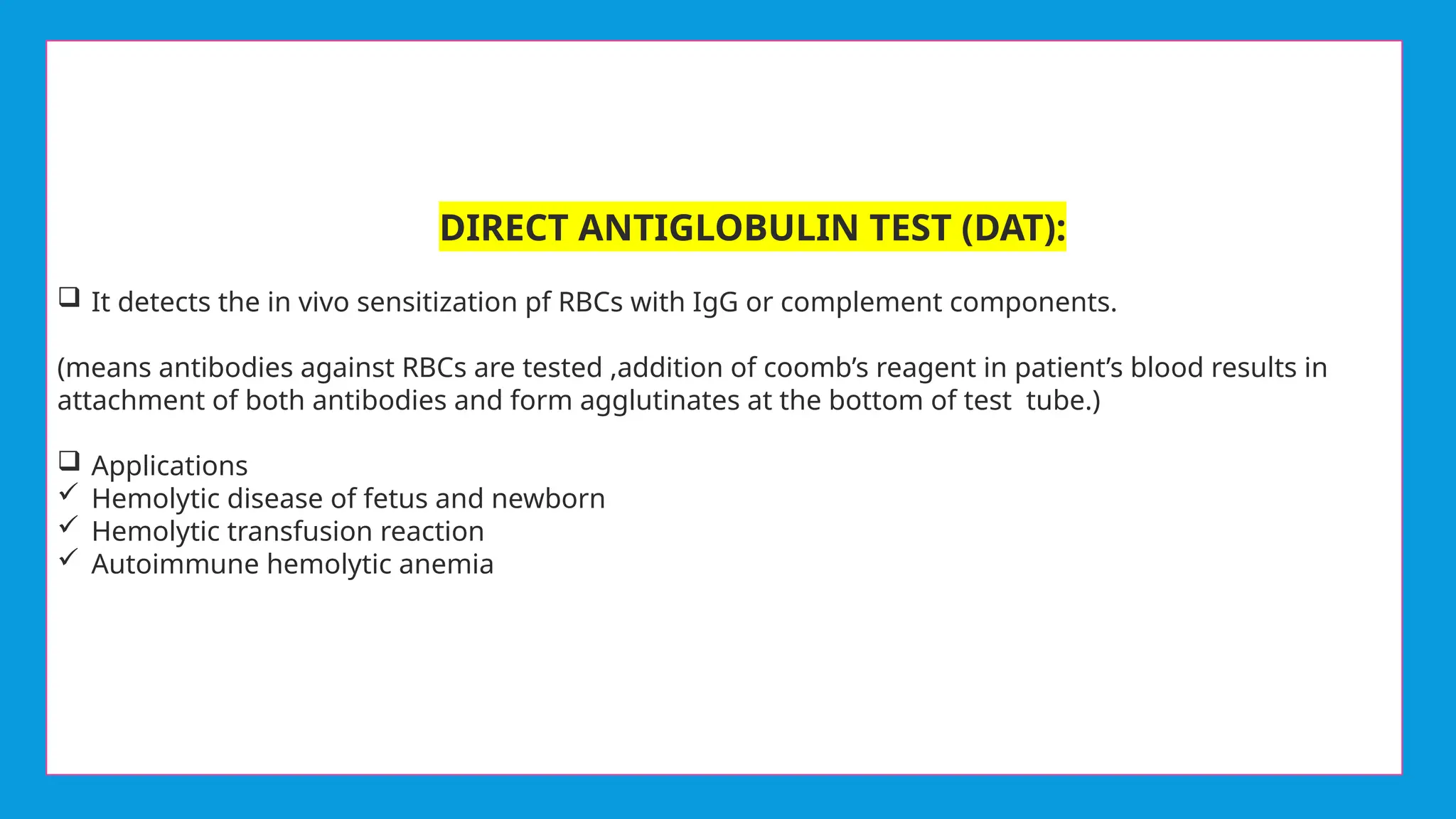
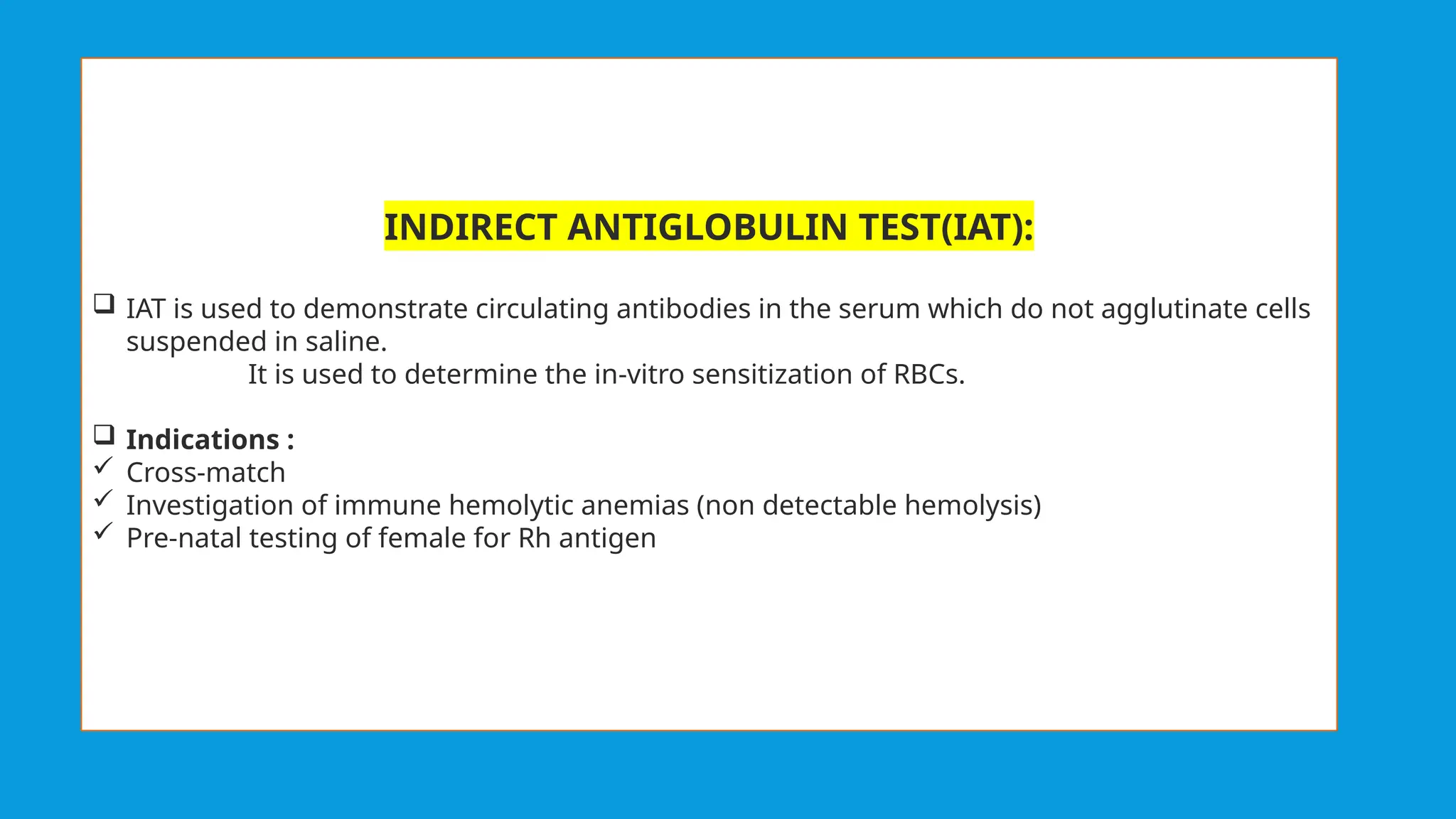
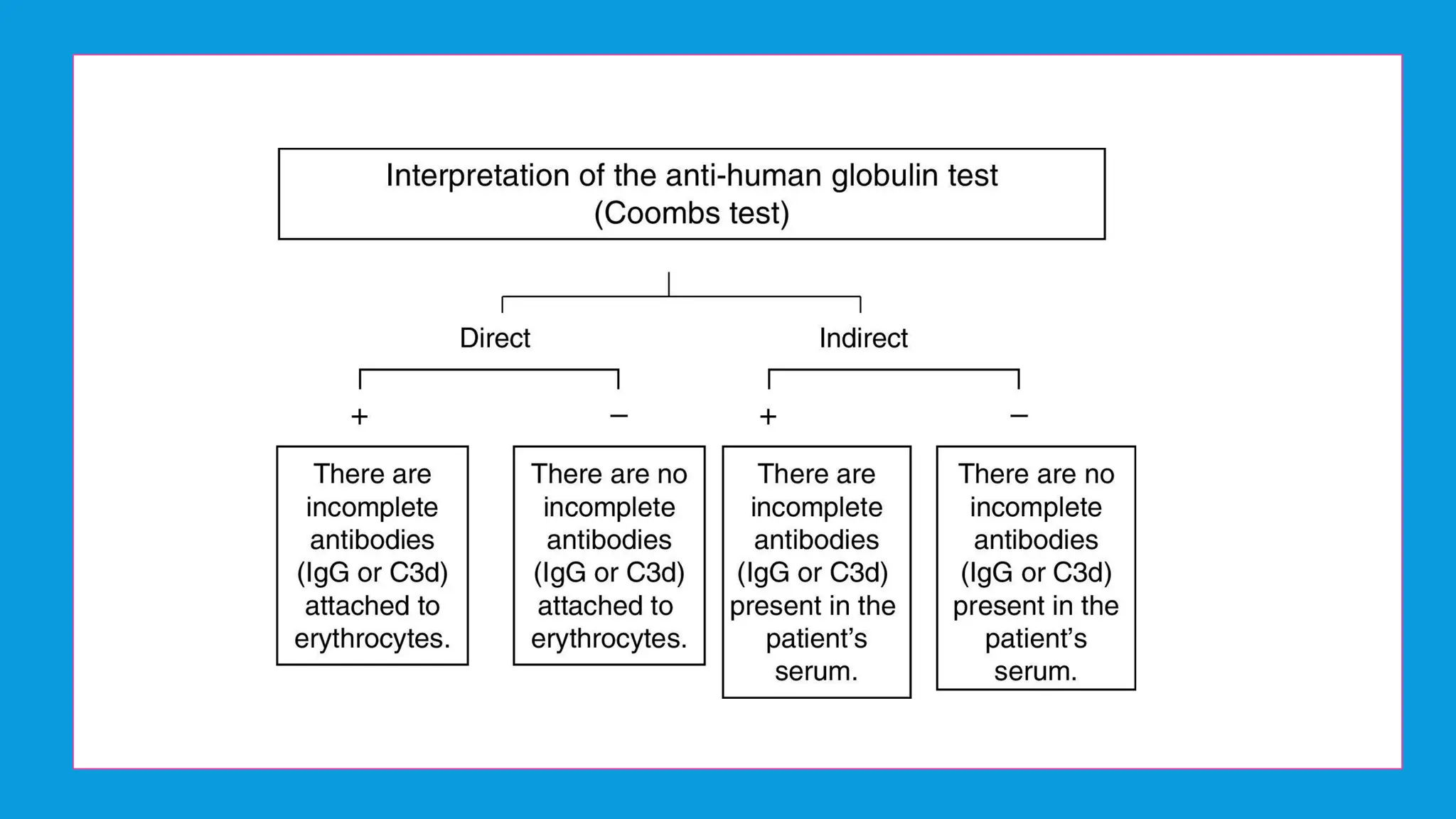
Coombs test is an immunological test to detect anti-RBC antibodies using Coombs reagent, which is produced by injecting human antibodies into rabbits. There are two types of Coombs tests: the Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) that detects in vivo sensitization of RBCs, and the Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT) that identifies circulating antibodies. The document also differentiates between monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, emphasizing their production methods and cost implications.