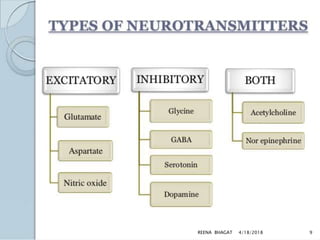
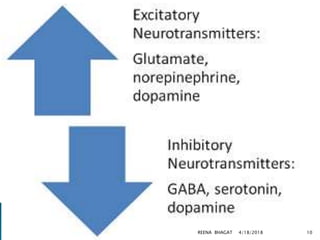
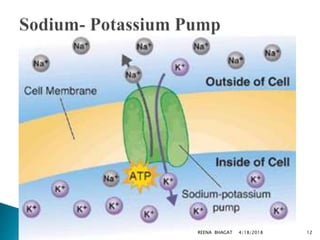
This document presents information on neonatal convulsions. It begins with an introduction and definitions. The causes of convulsions are then discussed, including those related to the early and late neonatal periods. The pathophysiology and signs/symptoms are described. Diagnosis involves history, investigations like blood tests and imaging. Management includes controlling seizures with medications like phenobarbitone and treating the underlying cause. Complications may include cerebral palsy and epilepsy. Prognosis depends on the etiology.