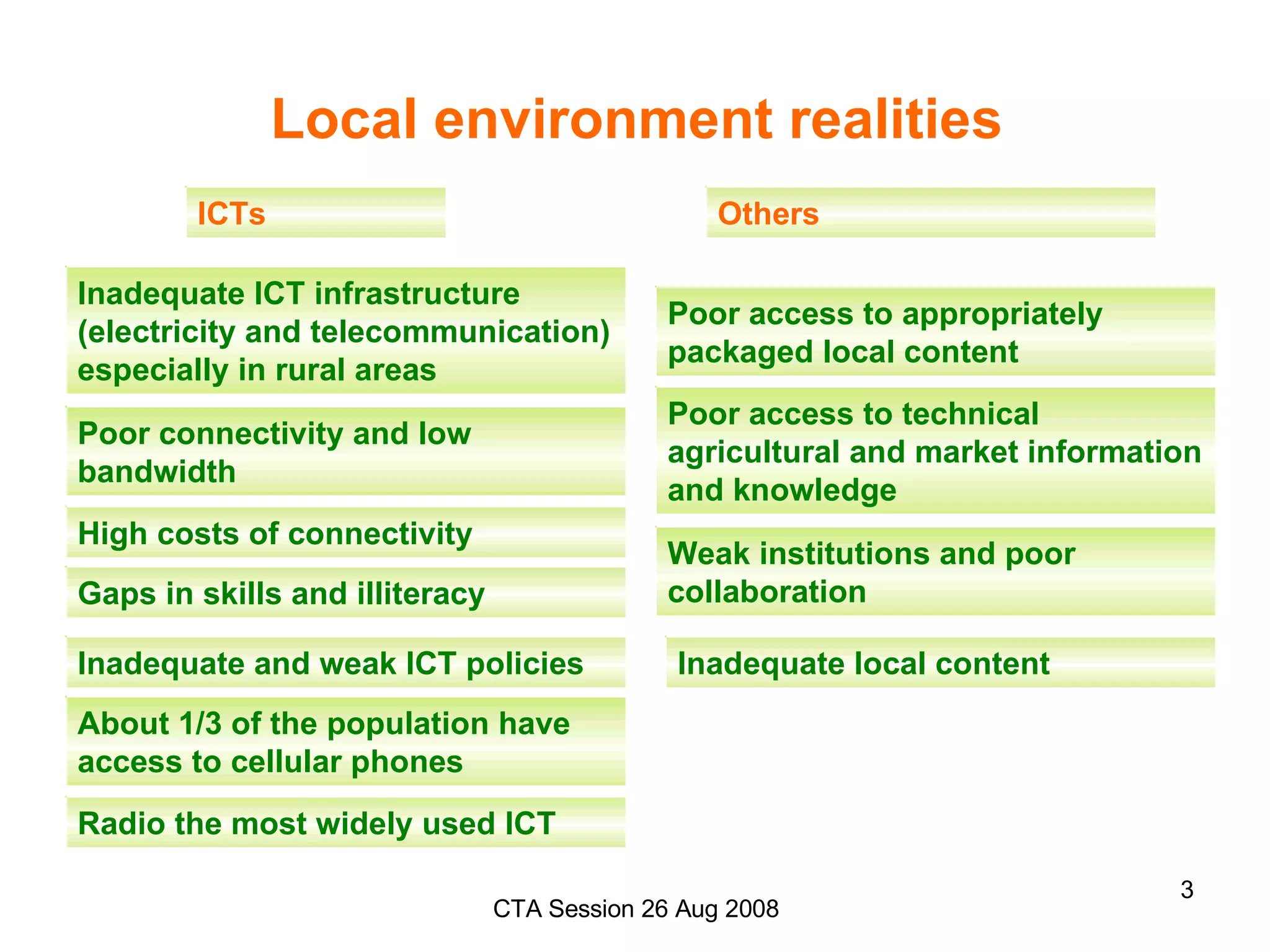
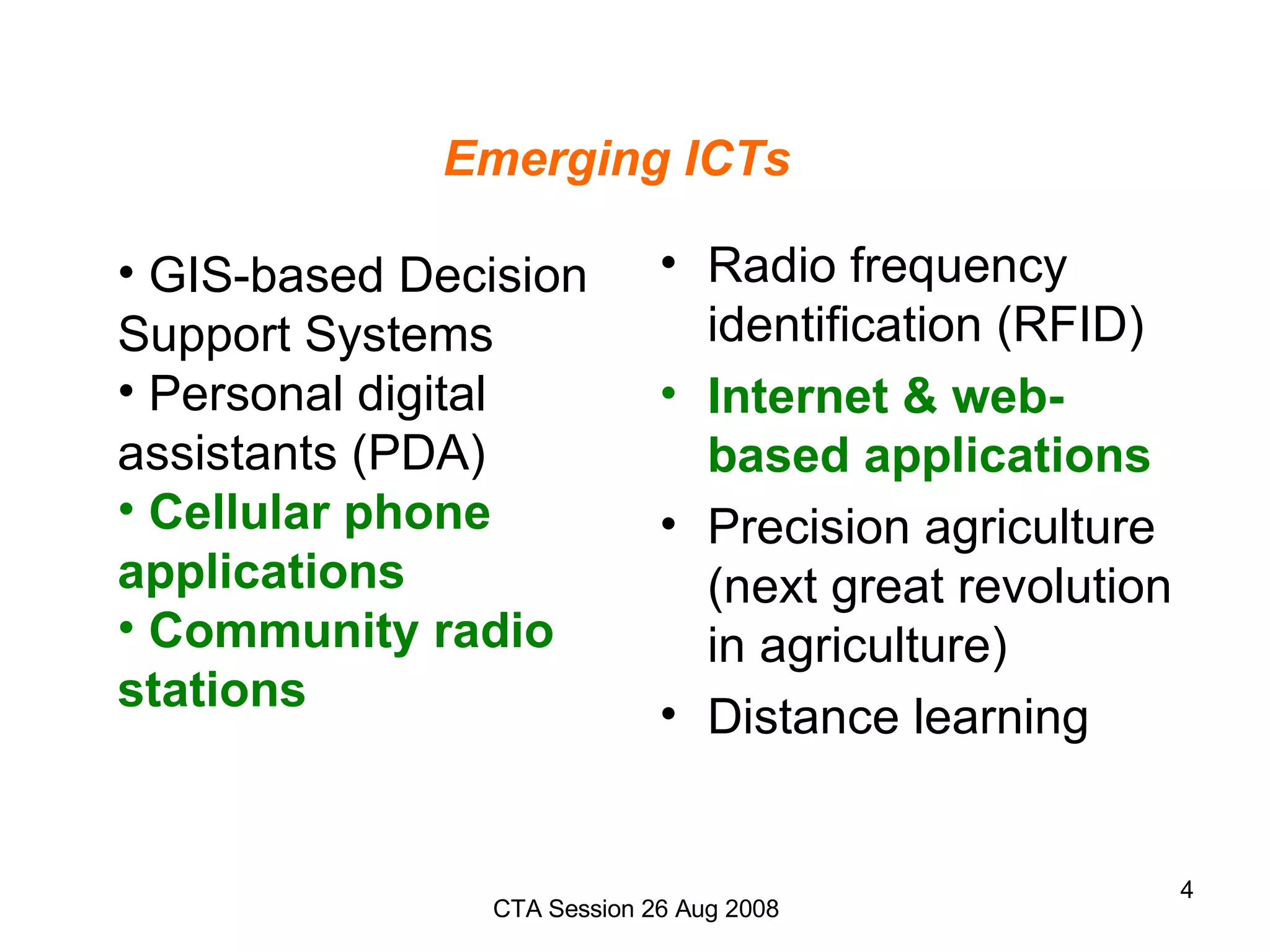
This document discusses opportunities and challenges for using emerging information and communication technologies (ICTs) like web-based applications, radio, and cellular phones in agriculture in Africa. It notes that small-scale farmers have limited access to technologies, markets, and information. However, about a third of Africans now have cell phones, and radio is widely used. Examples from Kenya and Ghana show how ICT platforms can provide farmers timely information on crops and markets via various technologies and languages to address information gaps. Challenges include inadequate infrastructure, skills, and policies across varying development levels in African countries.