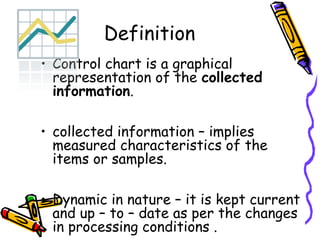
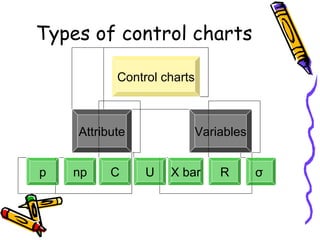
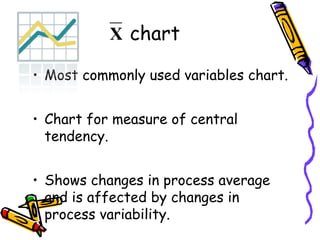
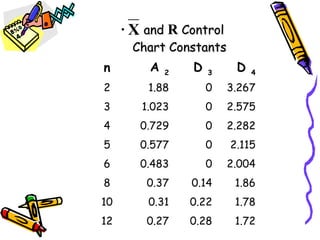
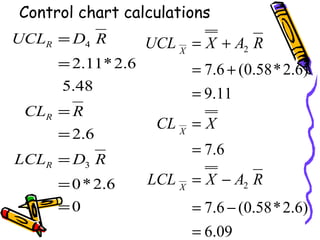
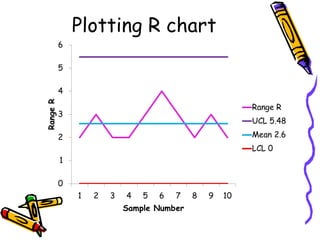
Control charts graphically represent measured characteristics over time to monitor processes for unusual variations. They depict changes in a process average or variability. Control charts determine whether a process is in control or out of control to ensure product quality and reduce scrap. Common types include X-bar and R charts. X-bar charts monitor the central tendency and are affected by variability changes. R charts control general variability. An example calculates control limits for an X-bar and R chart using sample data and constants.