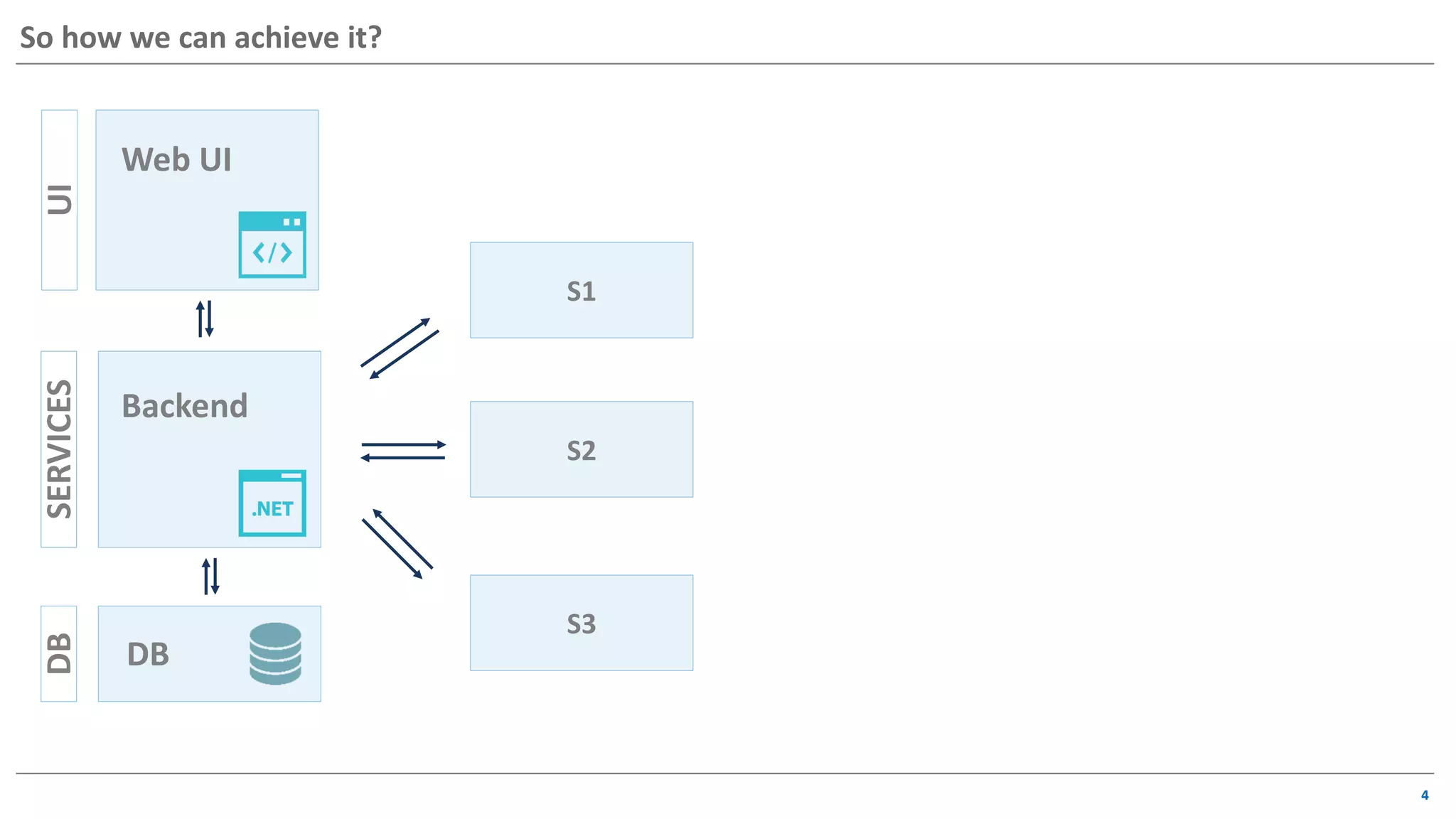
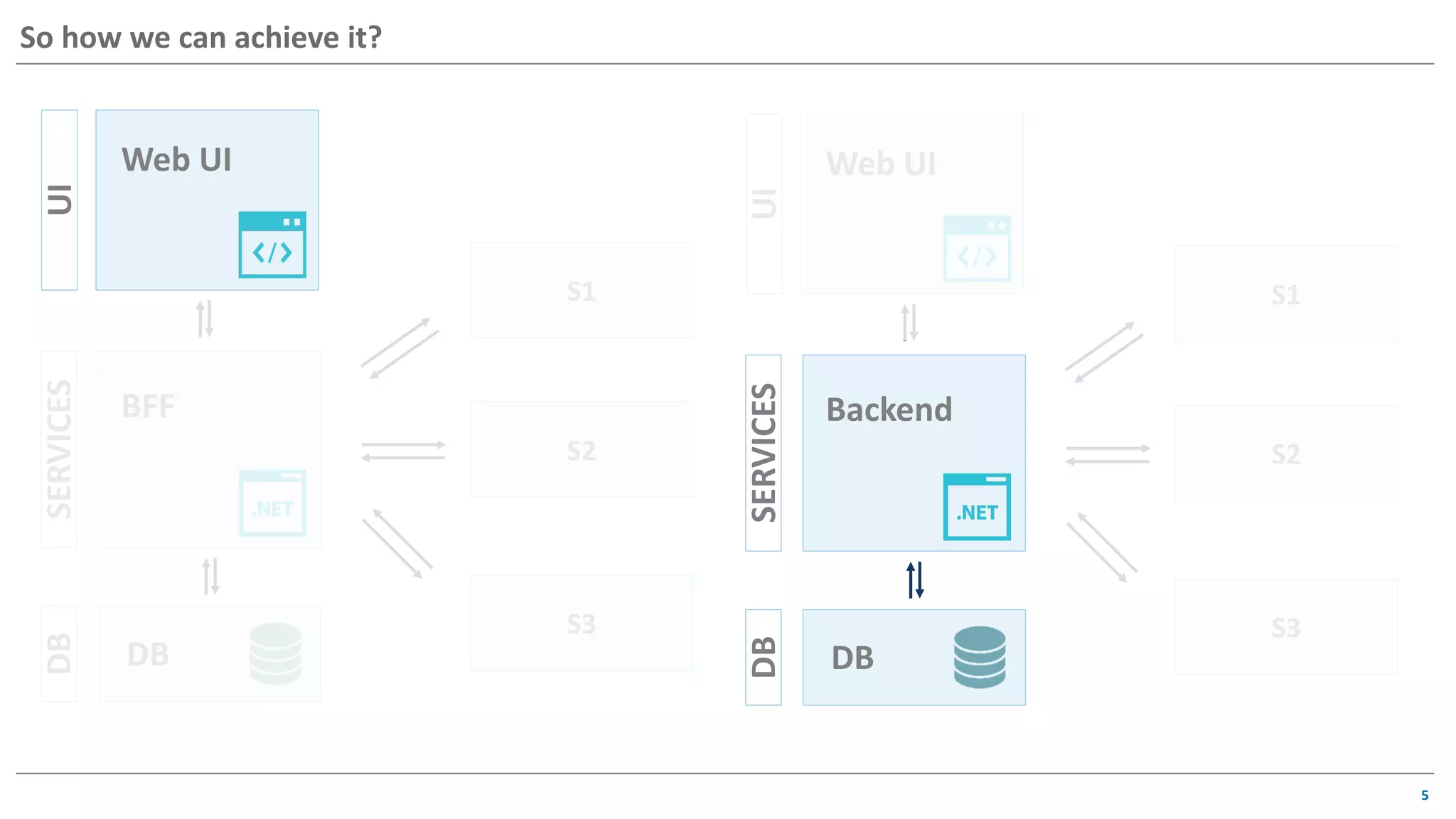
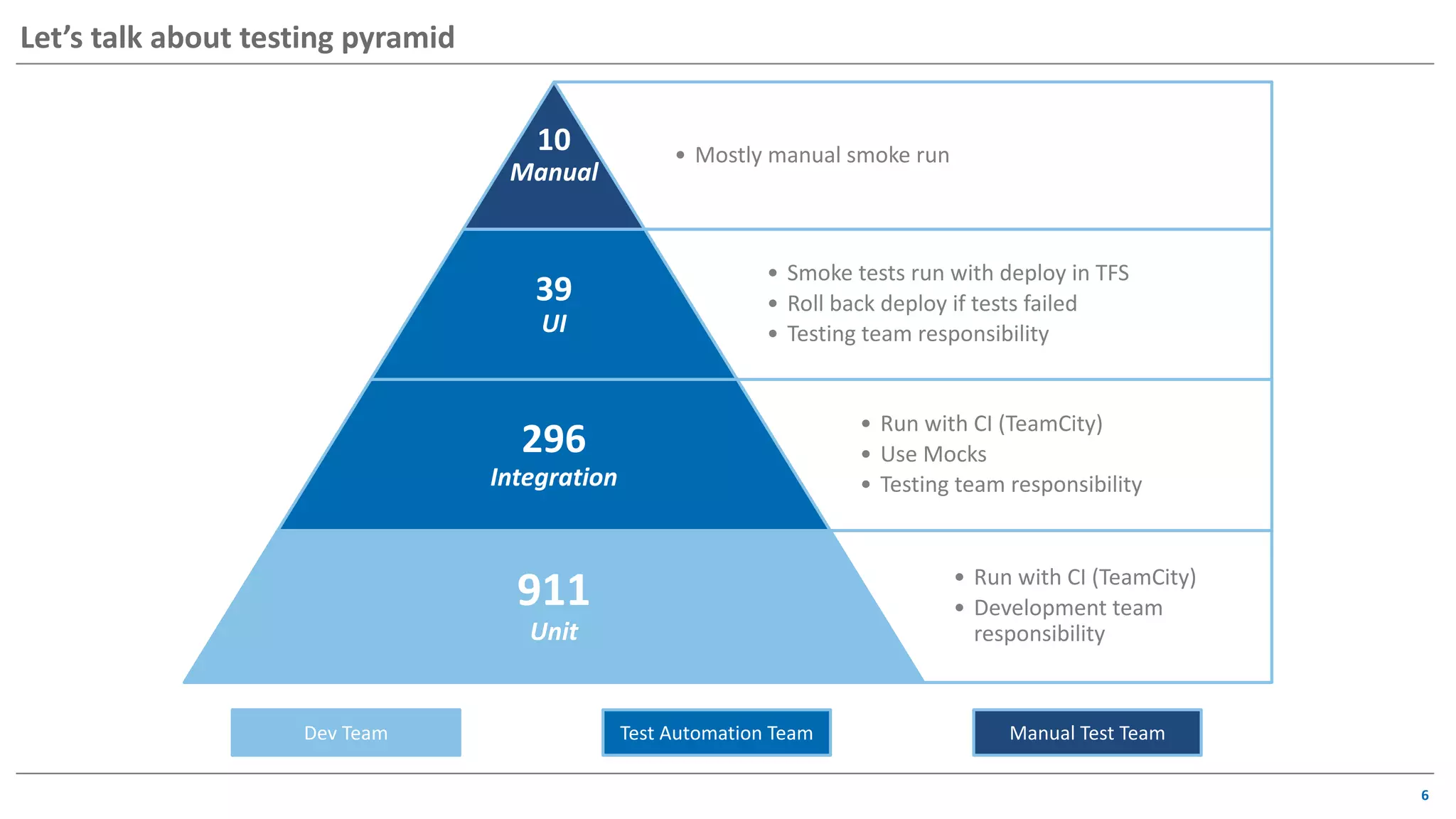
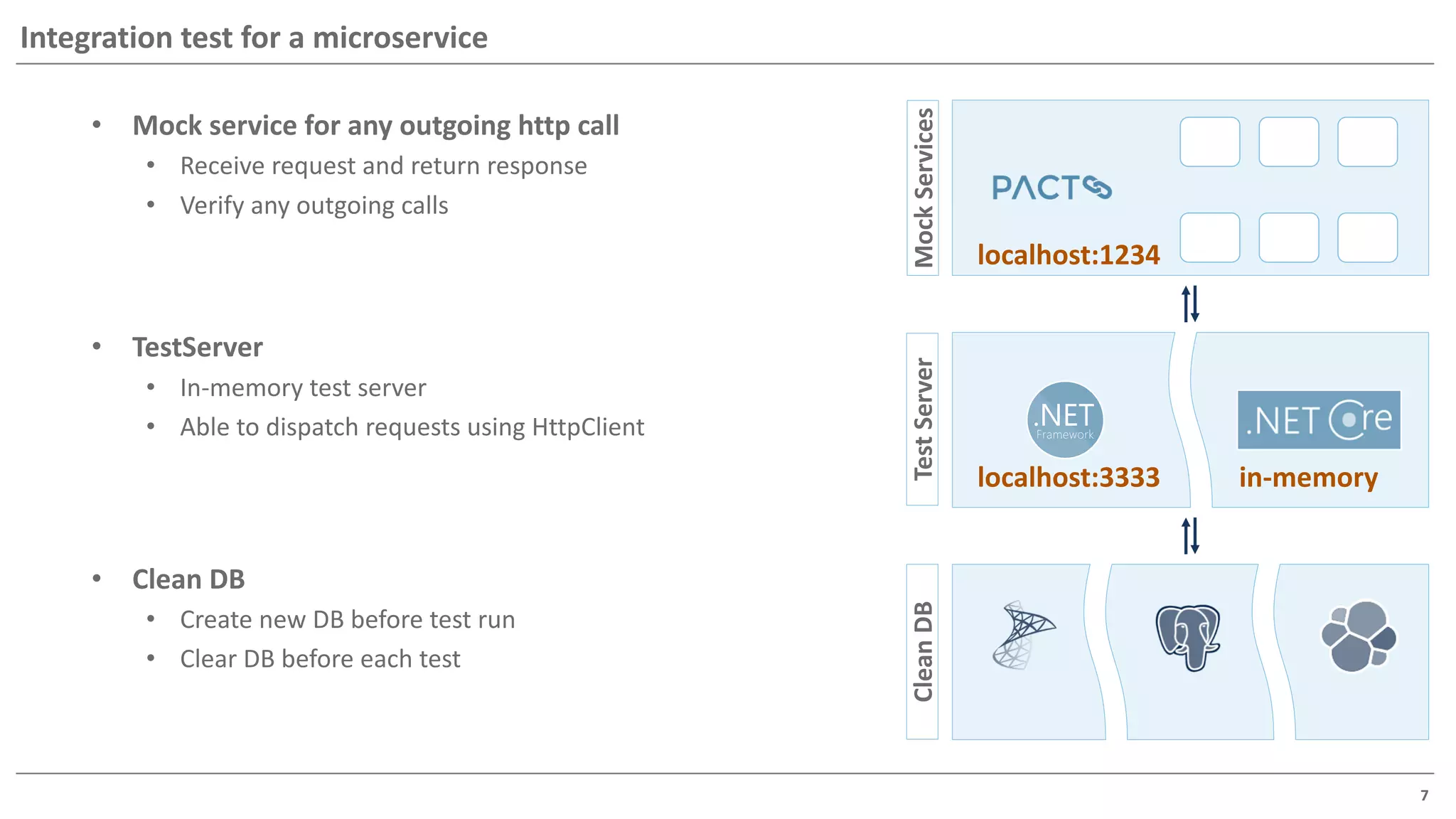
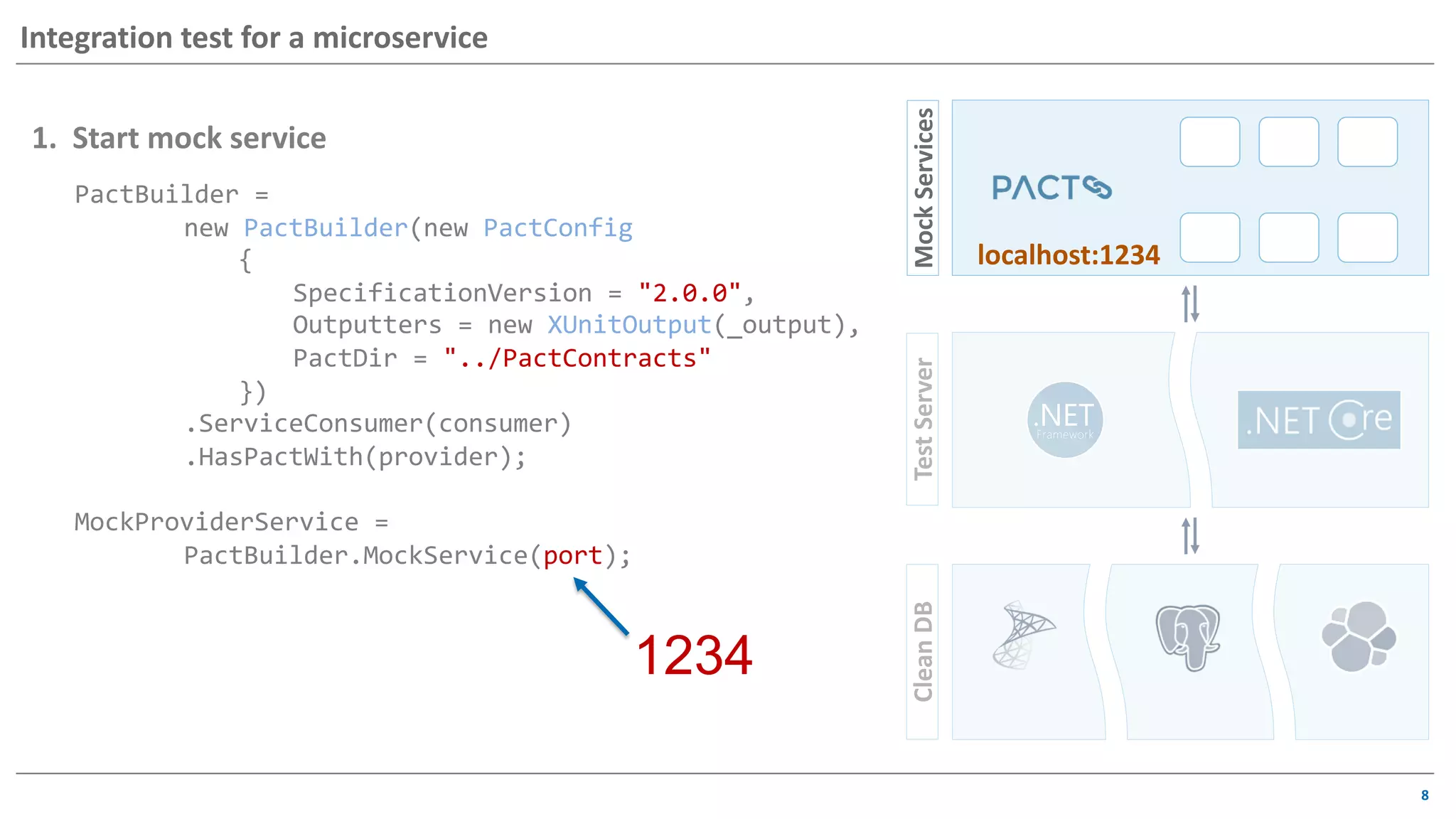
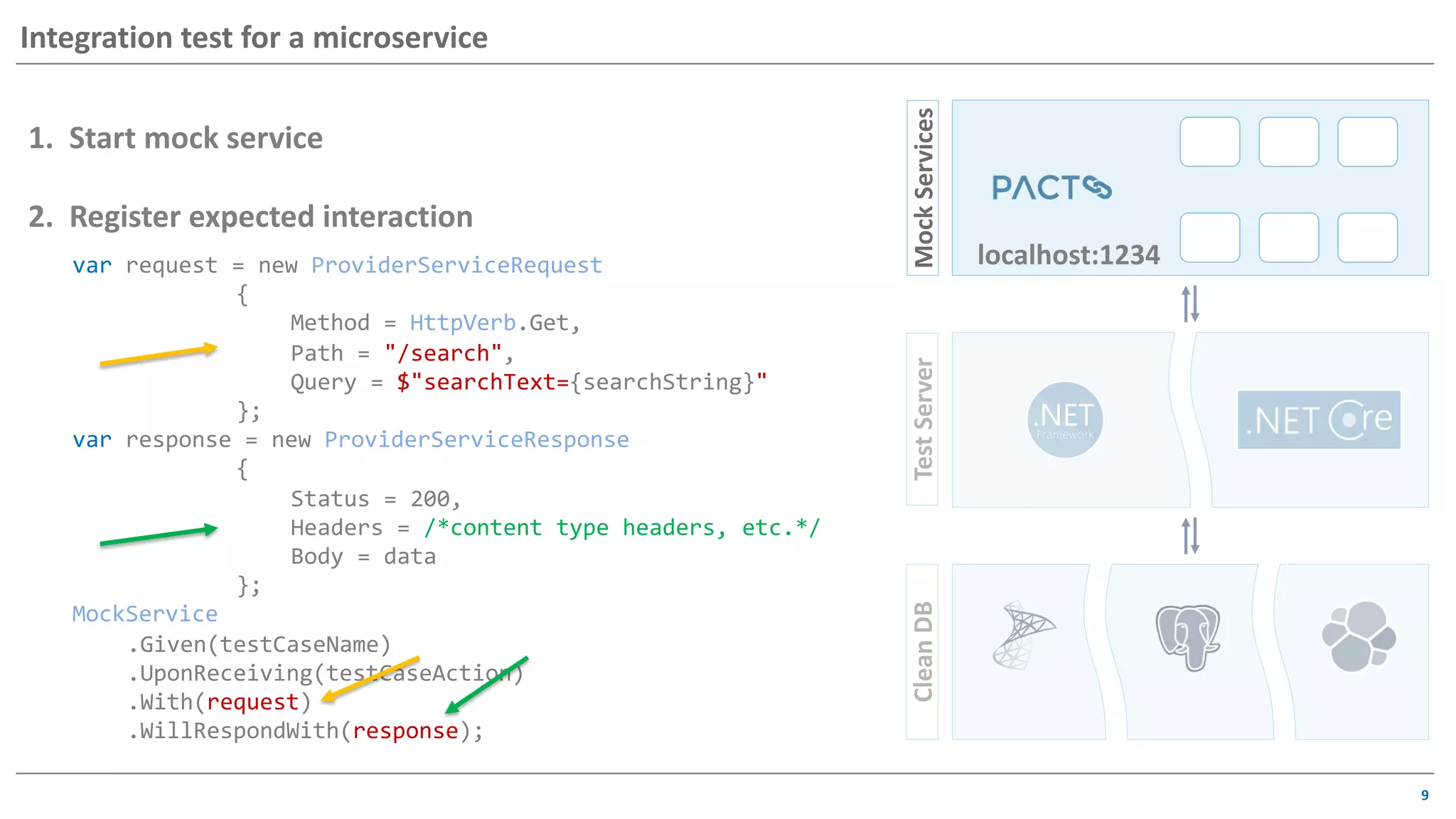
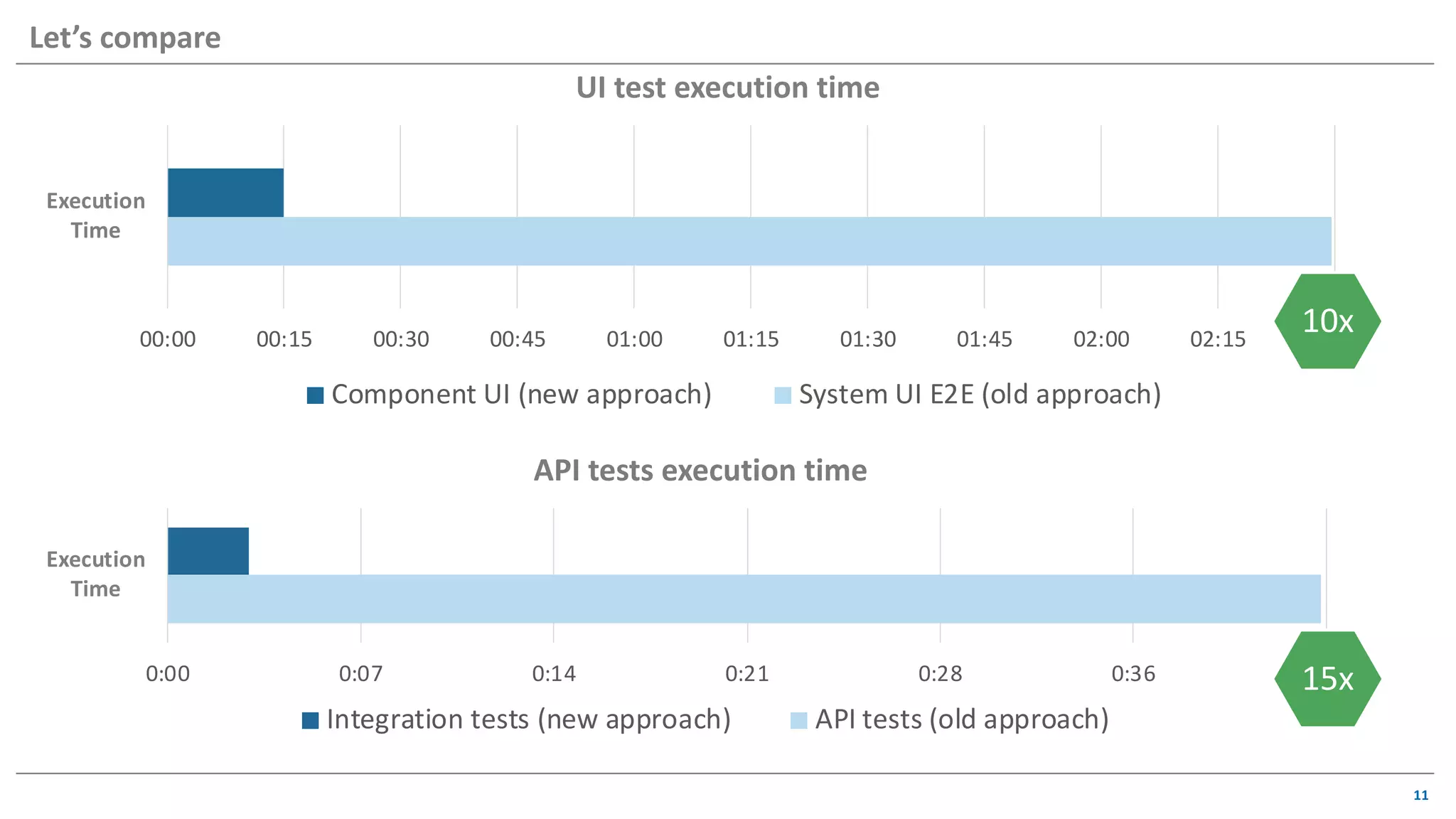
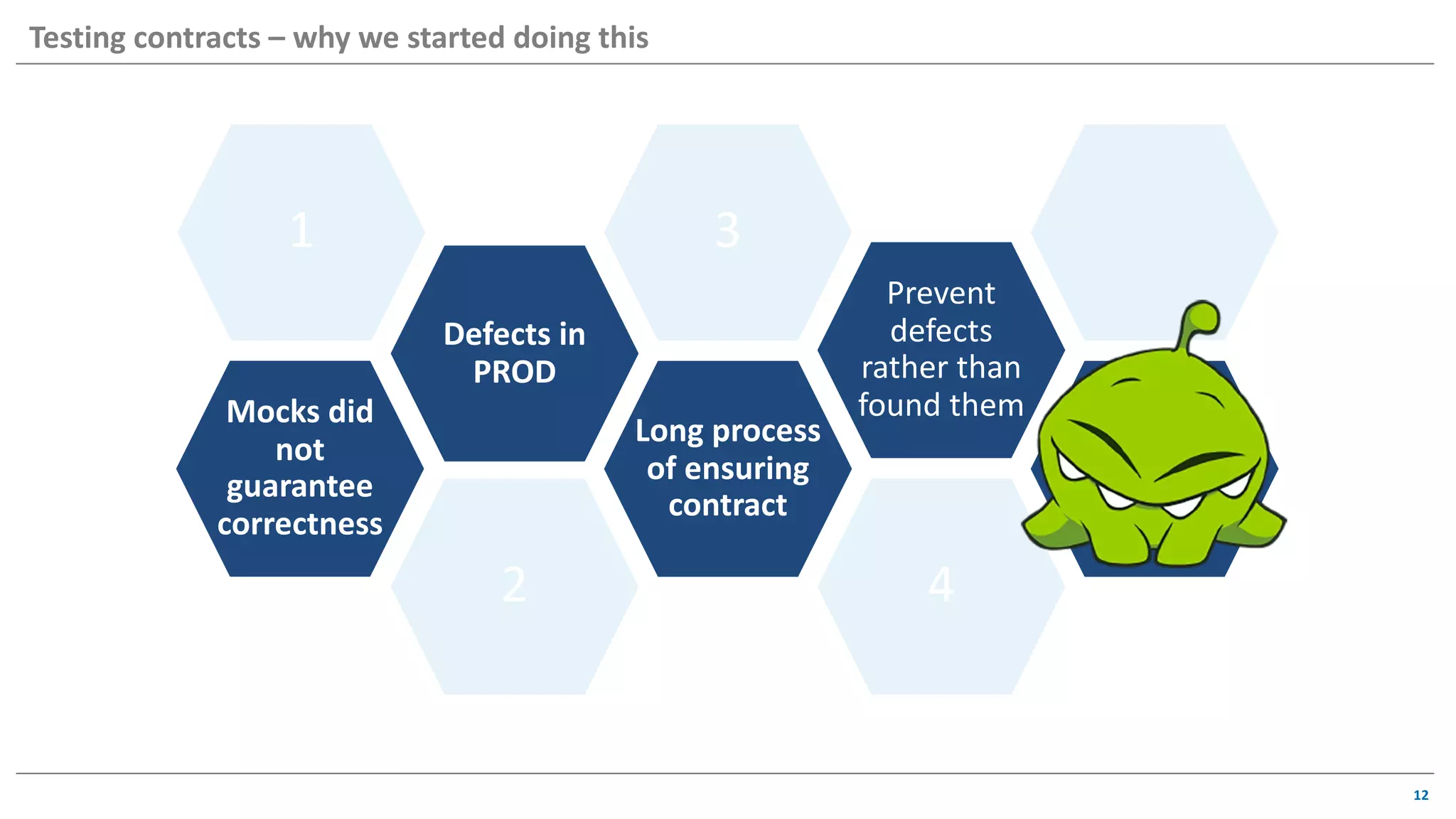
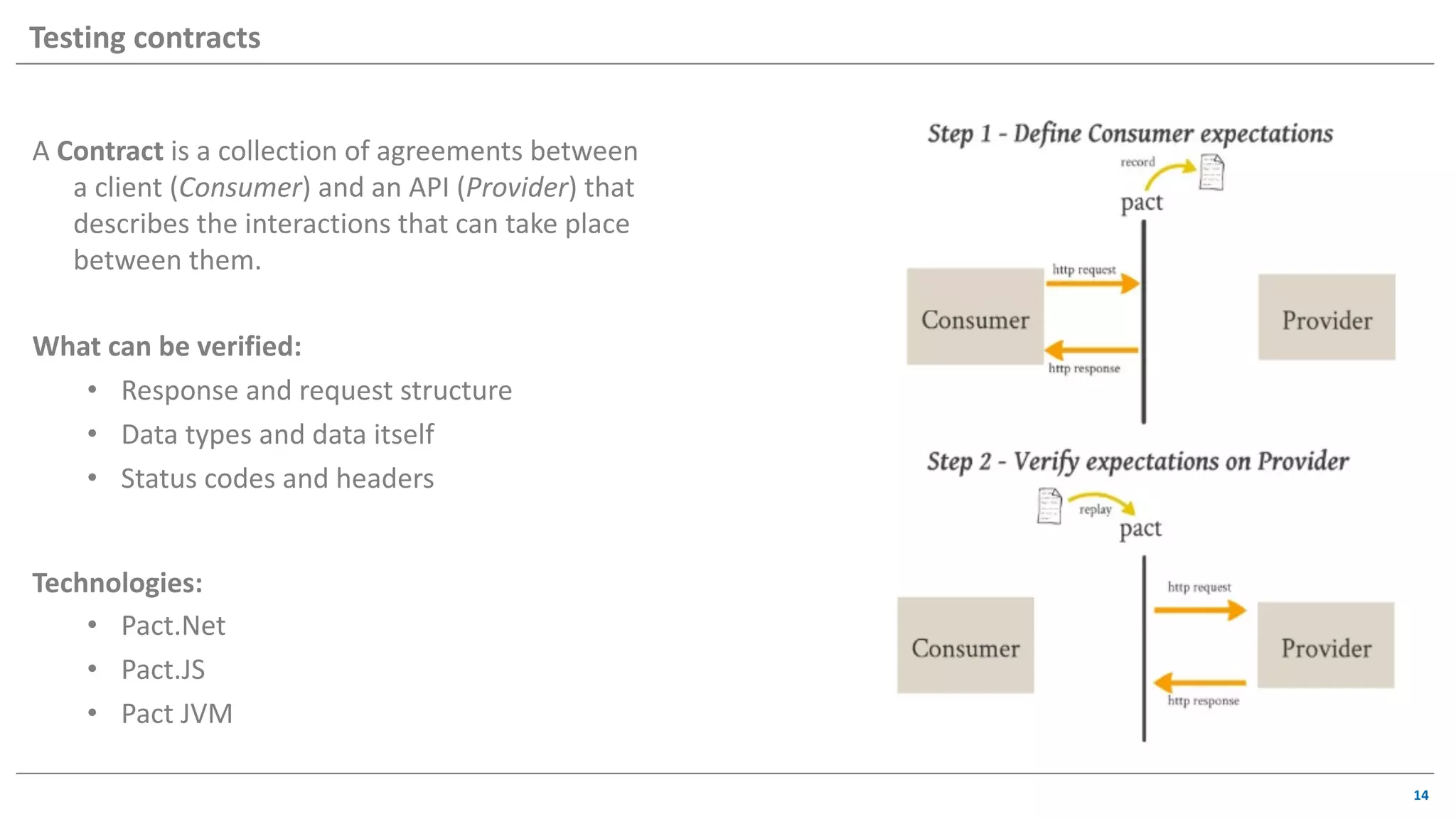
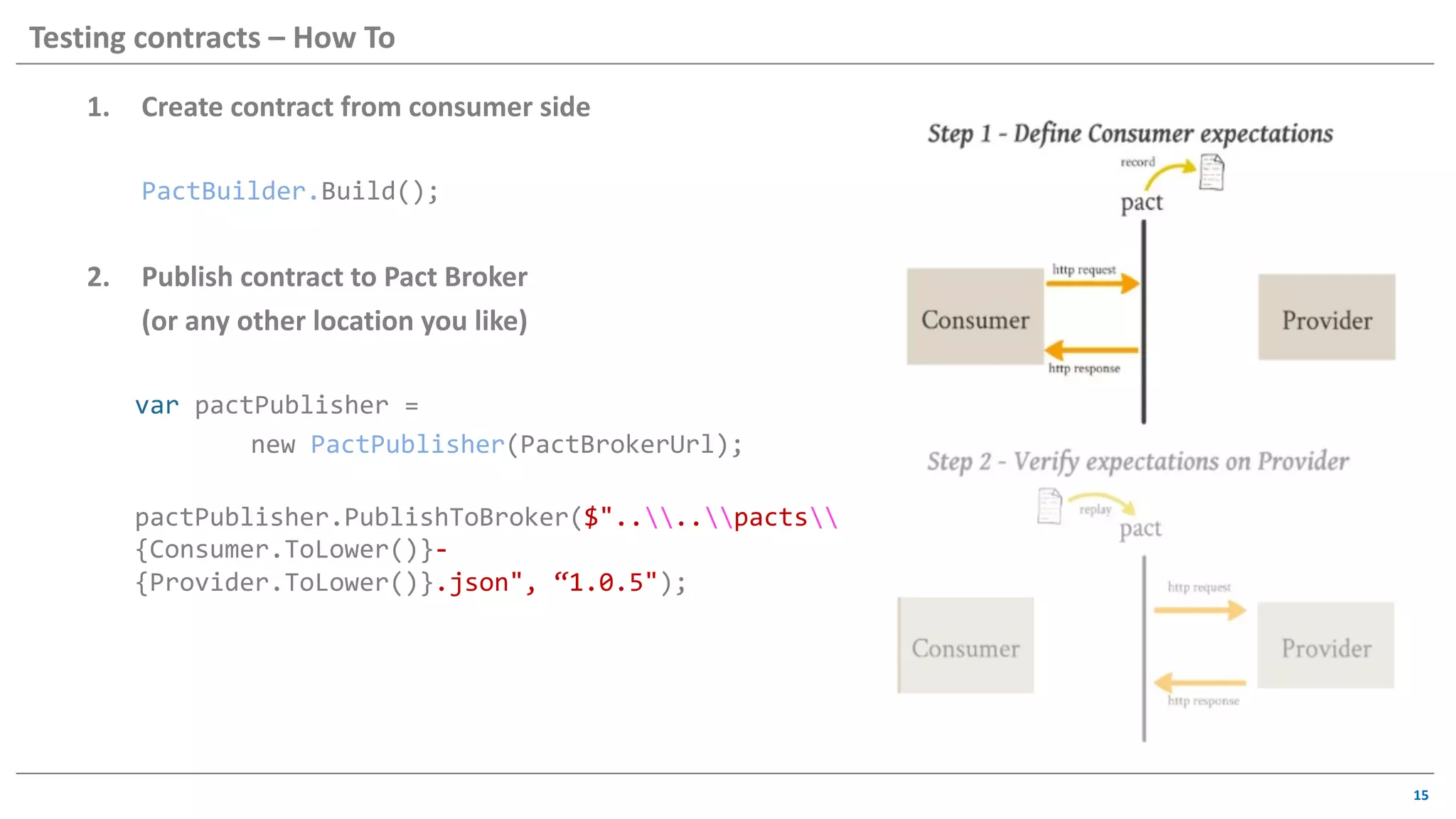
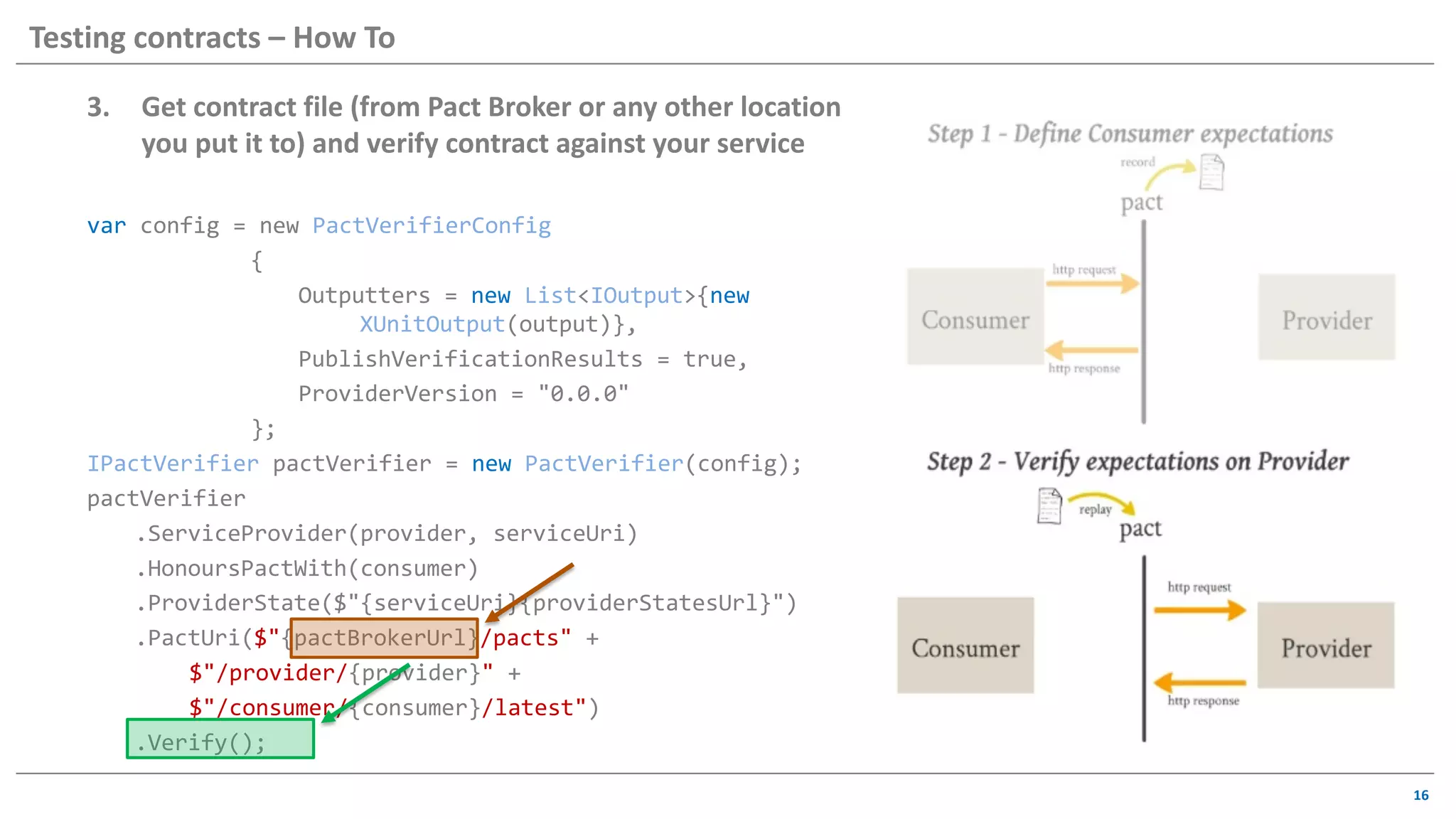
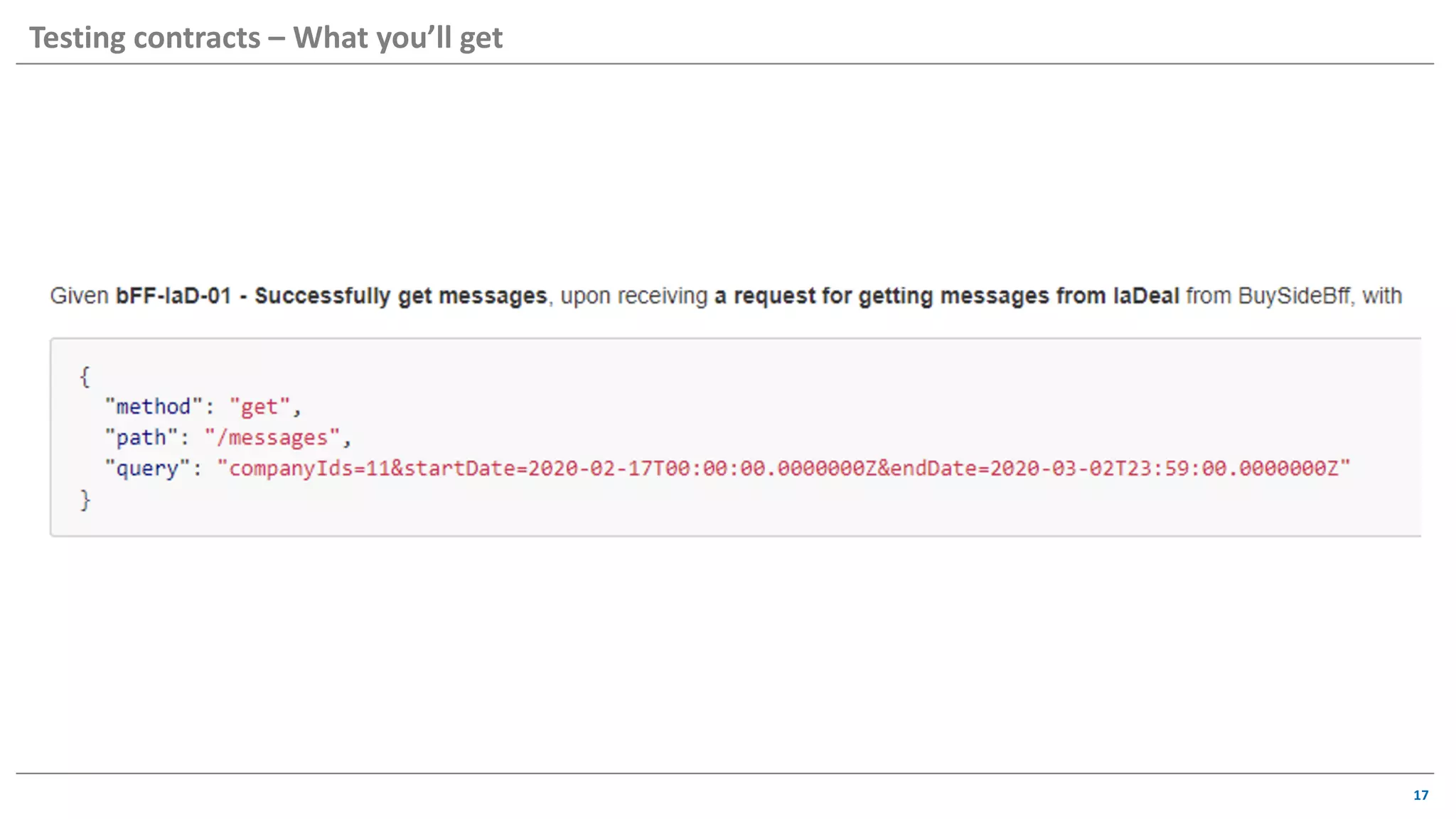
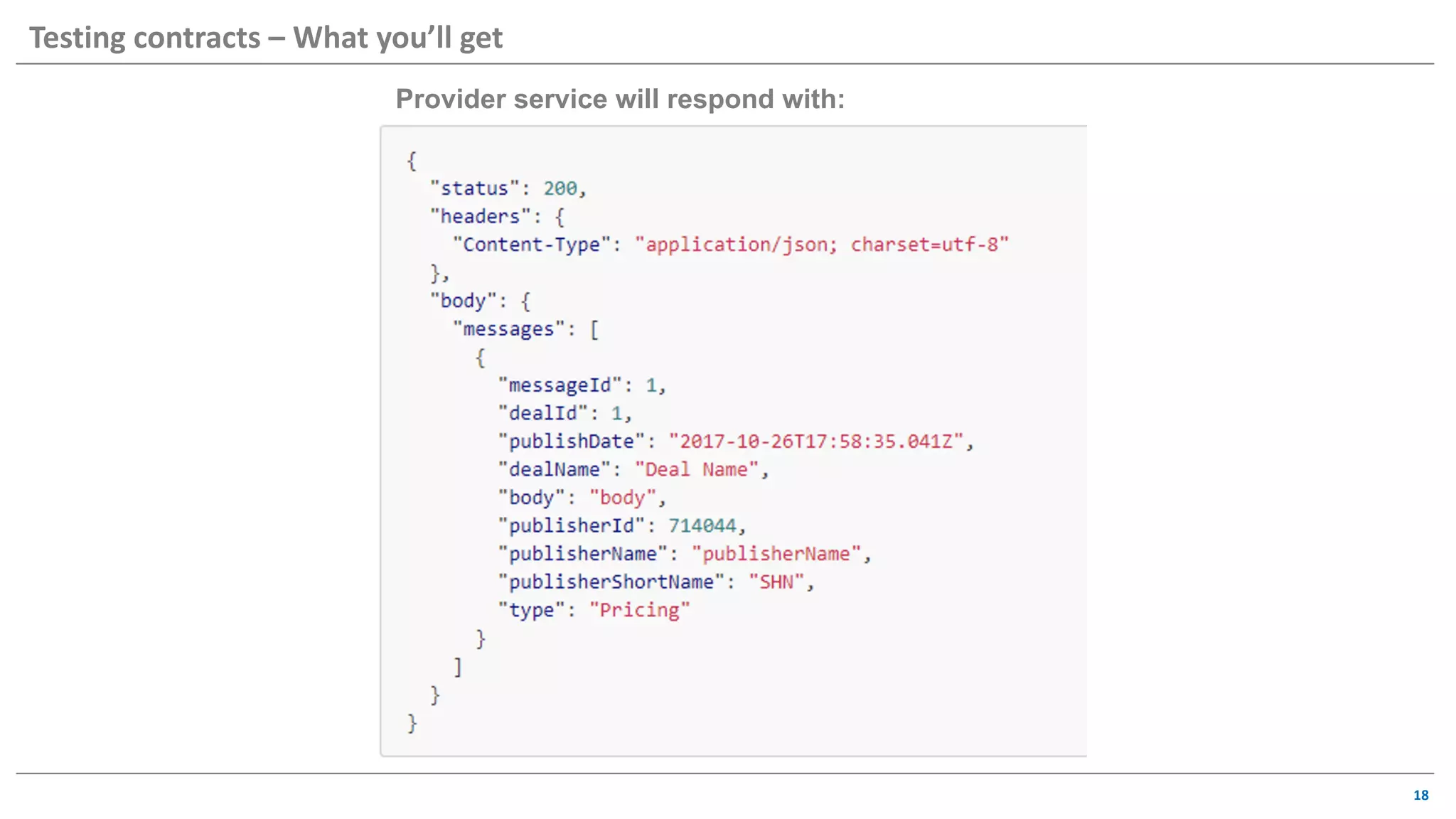
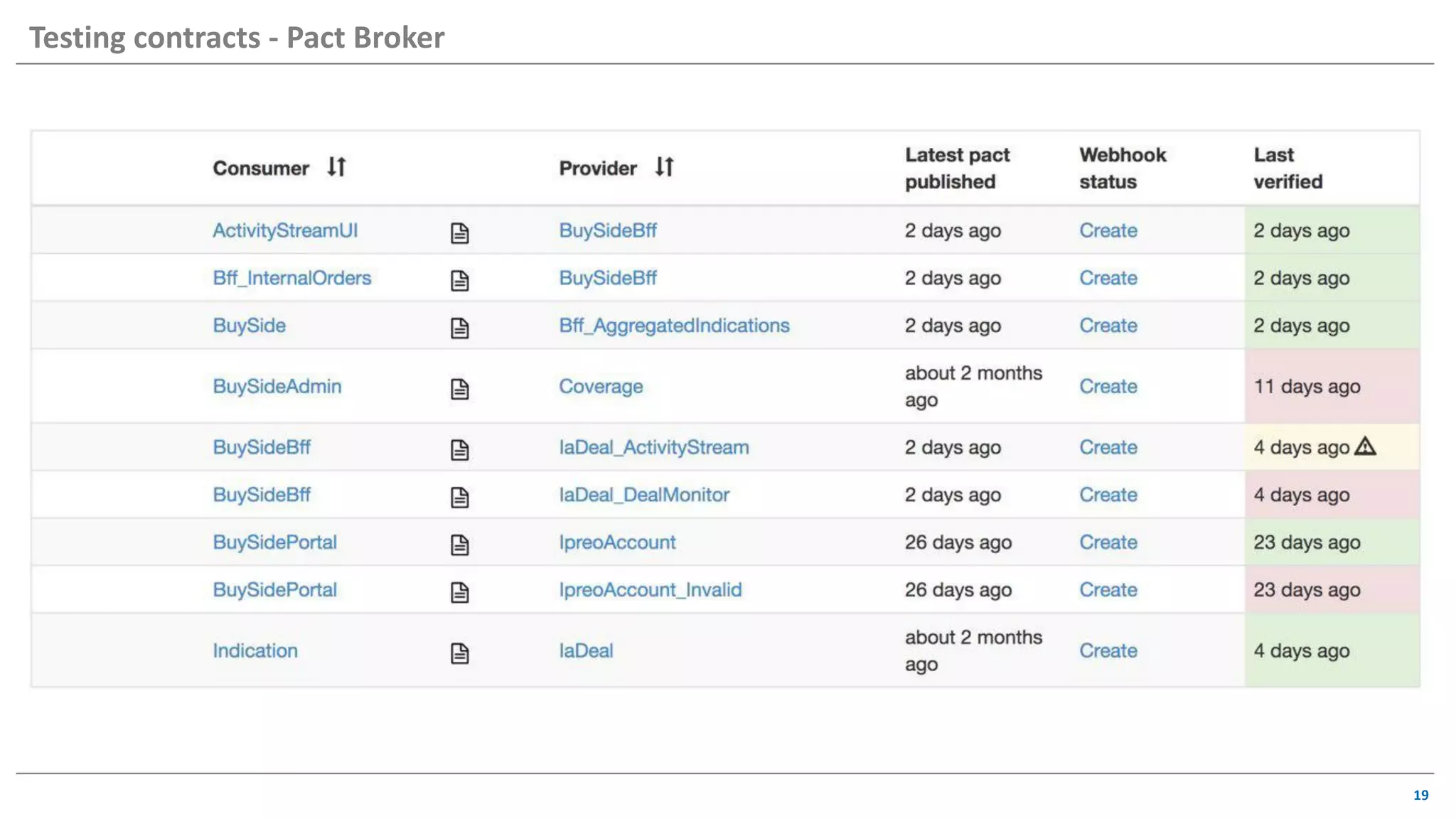
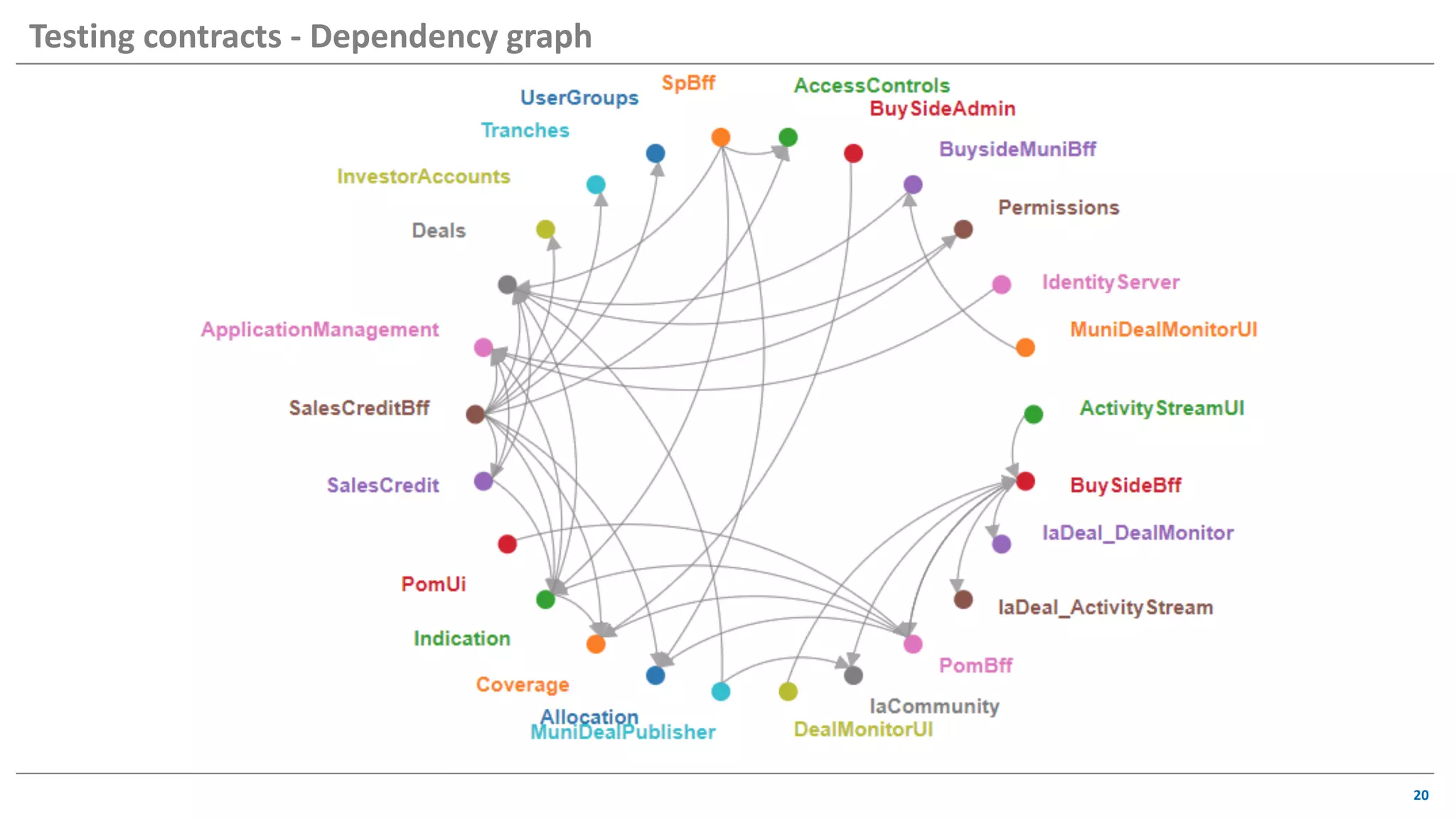
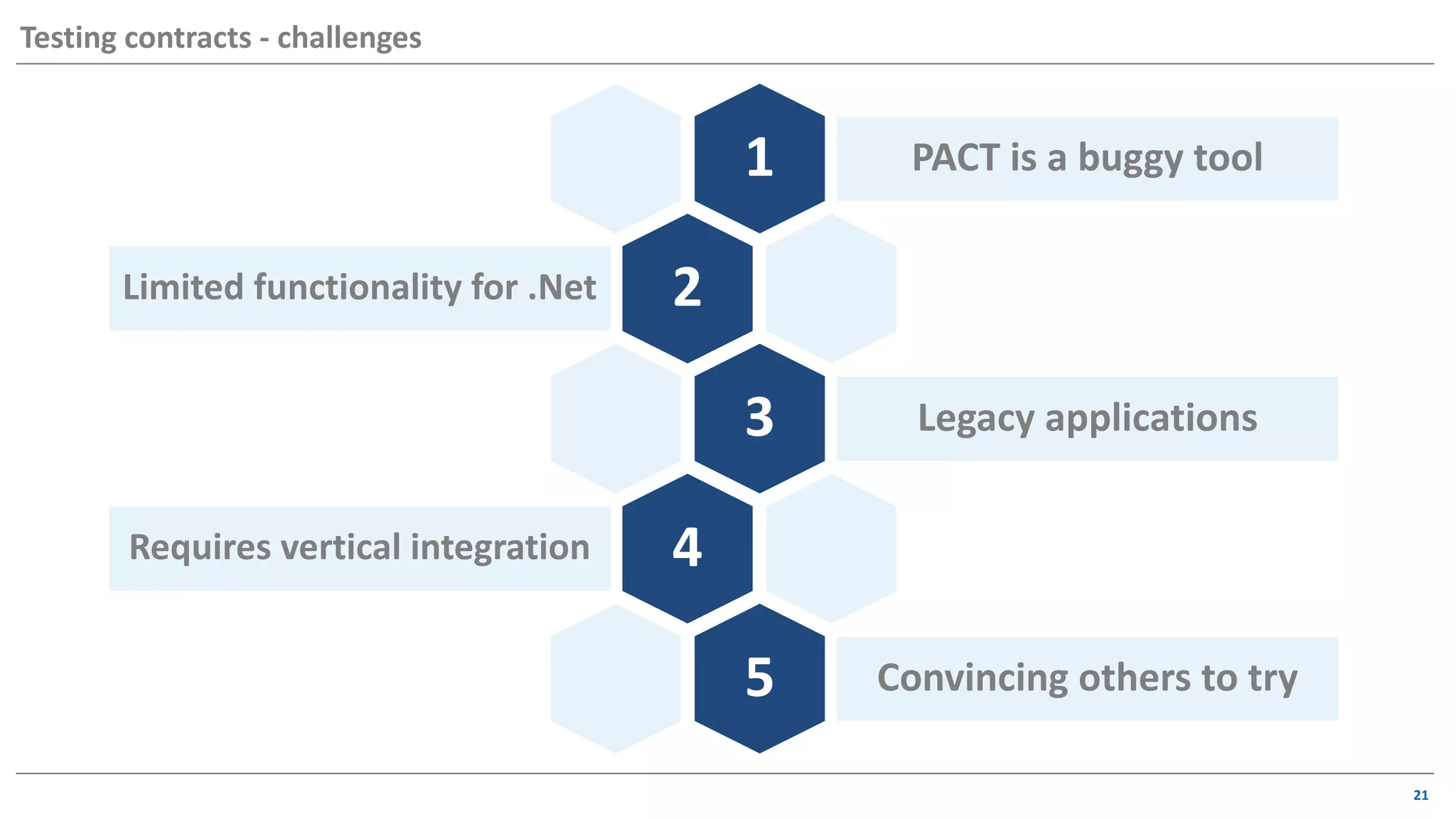
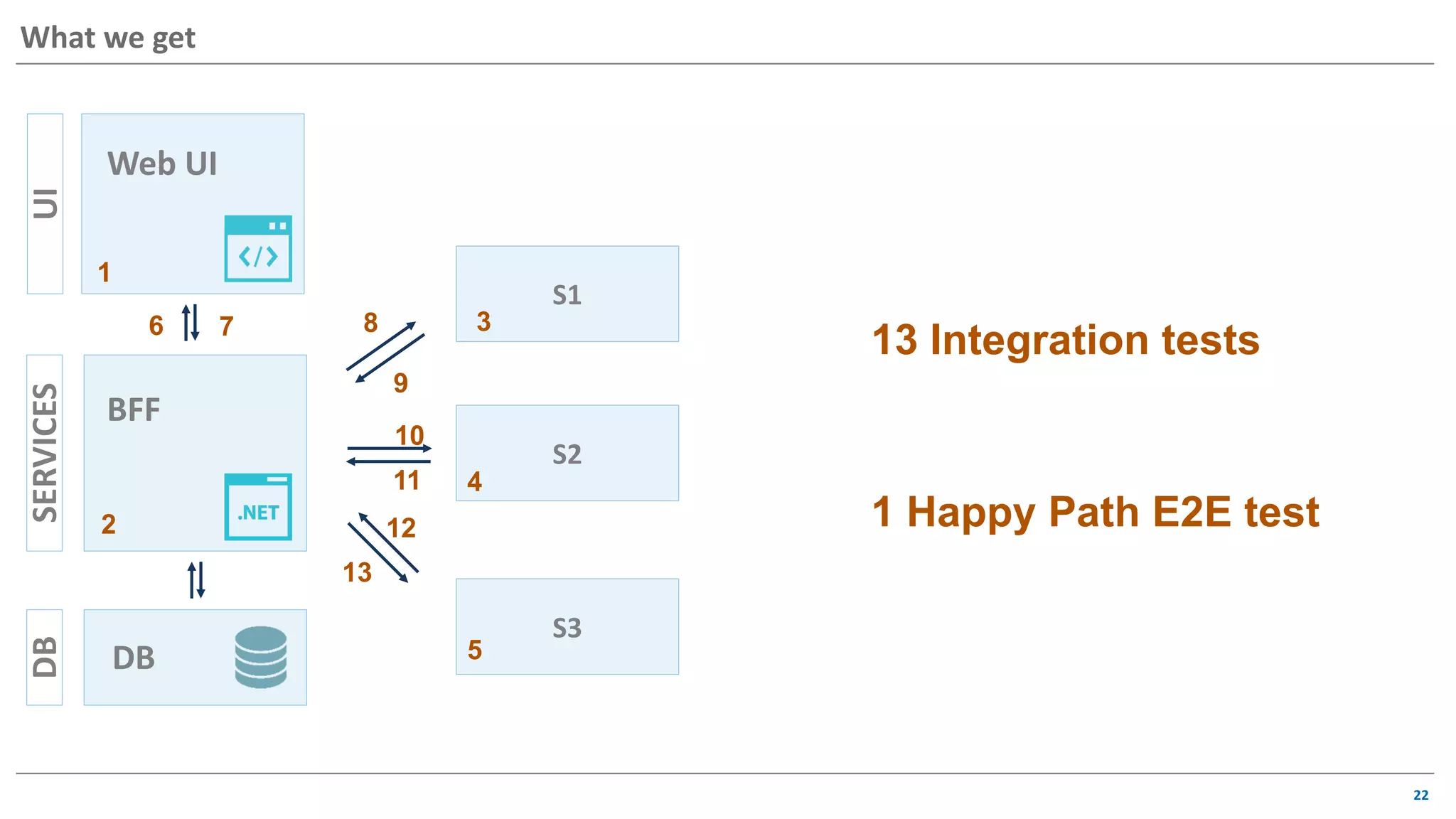
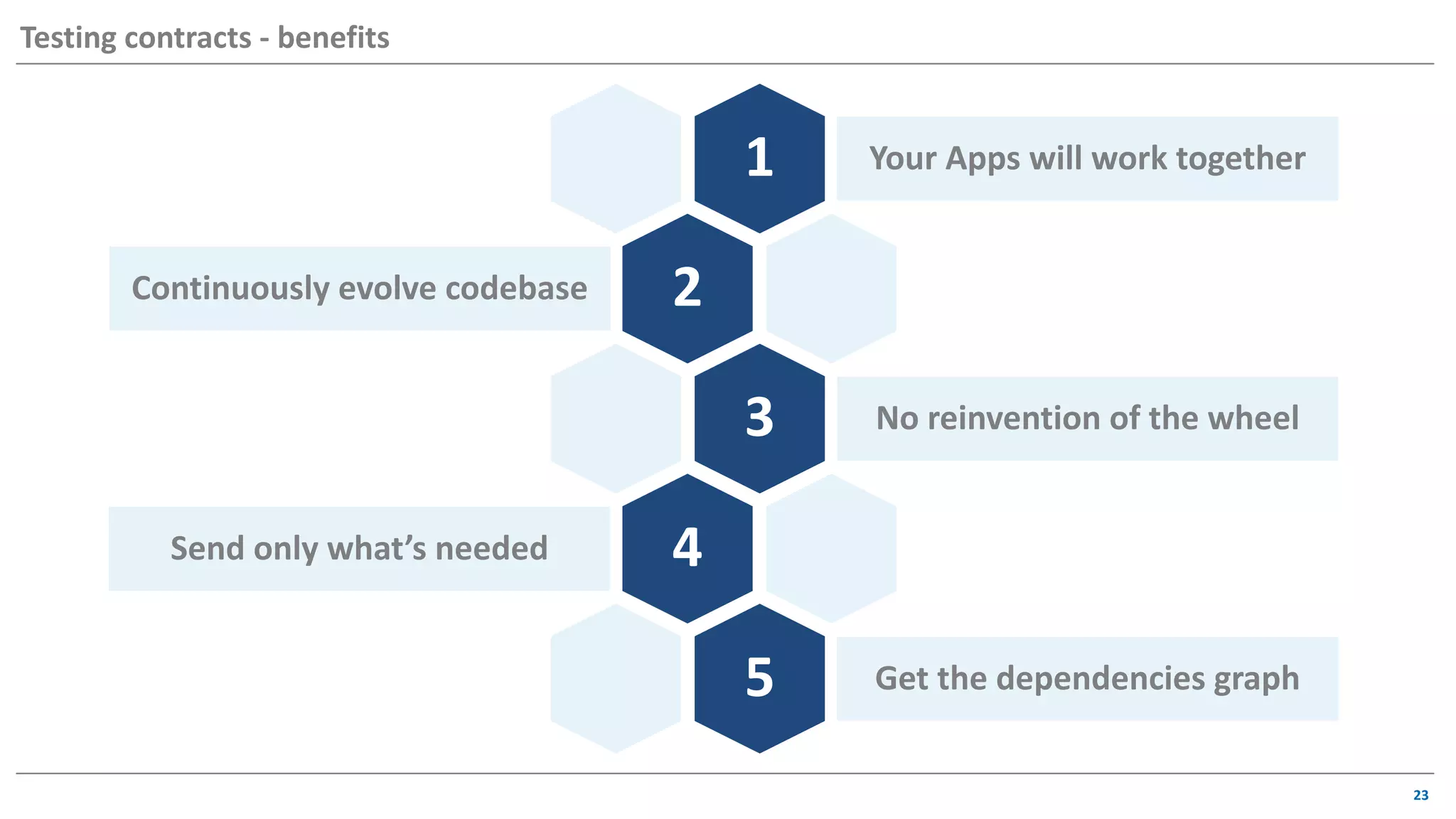
The document discusses contract based testing and shifting testing left. It describes testing at different levels, including UI, integration, and unit testing. It outlines how to implement contract testing between a consumer and provider by creating pacts, publishing them to a broker, and having the provider verify against the pacts. Benefits include apps working together continuously, avoiding duplicative work, and visibility into dependencies. The presentation encourages attendees to try out contract testing.