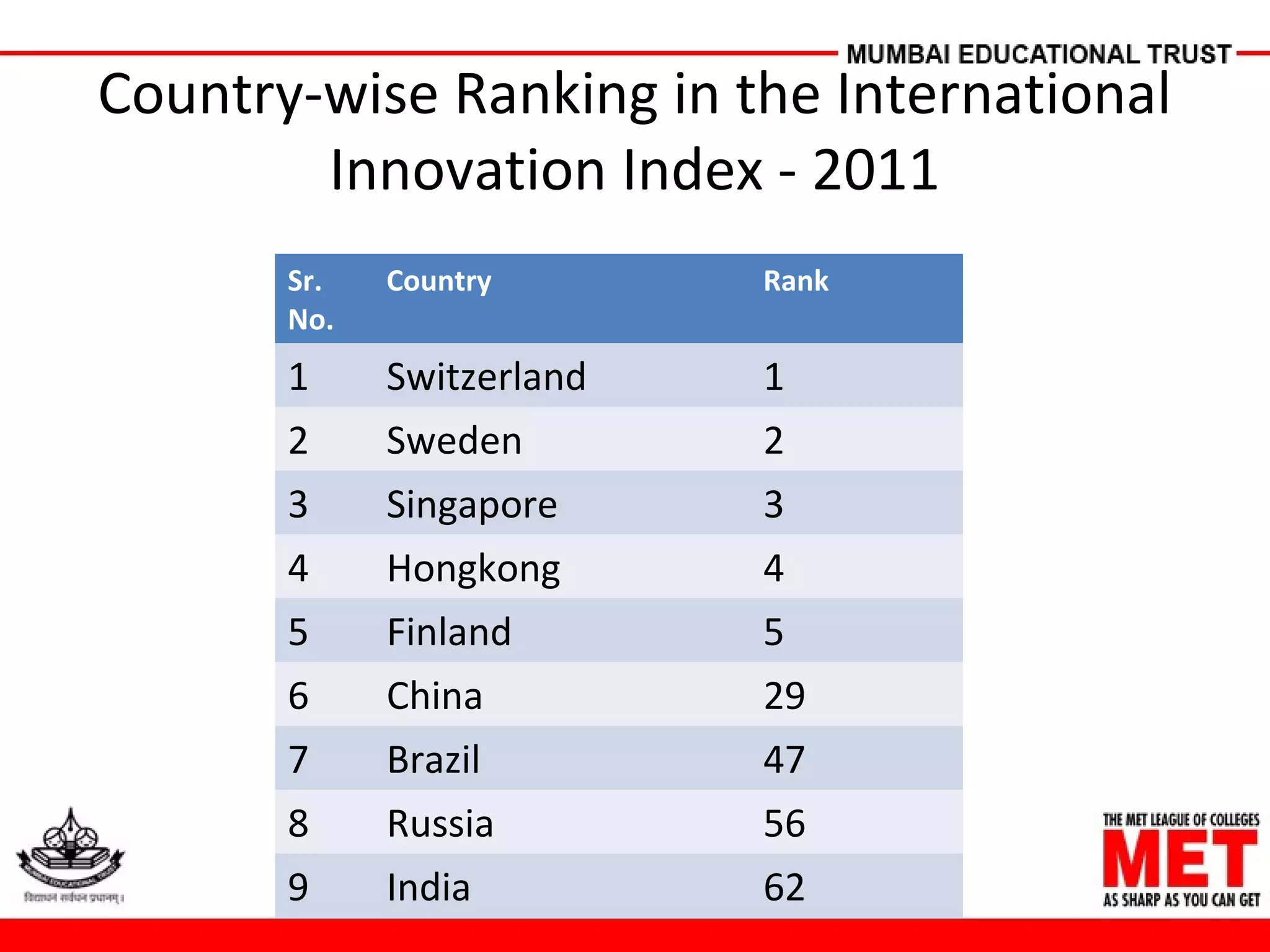
This document summarizes contemporary innovative practices in management. It discusses successful innovations in Western countries and India. It also outlines future areas for innovation like biotechnology, genetics, and artificial intelligence. The document compares country rankings on innovation indexes and distinguishes between invention and innovation. It profiles three models for the future from Venkatakrishnan Balasubramanian, Olivier Serrat, and Gary Hamel that emphasize competitive advantage, customers, and questioning management orthodoxies. The conclusion notes the importance of collaboration between corporations and academia.