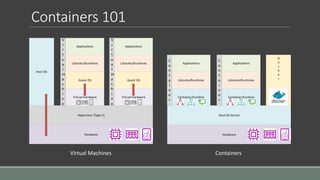
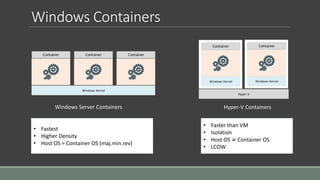
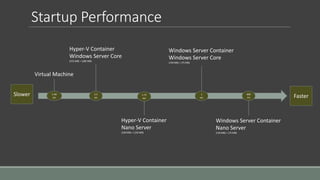
This document provides an introduction to using containers on Windows. It discusses the differences between virtual machines and containers, the two types of containers available on Windows (Windows Server Containers and Hyper-V Containers), and how to install and configure Docker to work with containers on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016, and within a virtual machine. Key steps outlined include enabling container and Hyper-V features, downloading and installing Docker for Windows, and enabling nested virtualization when using Docker in a VM.