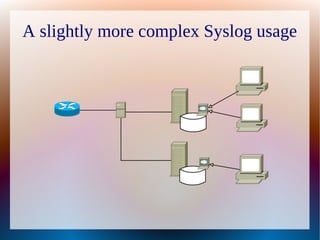
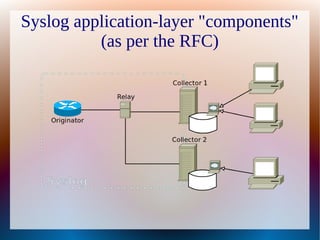
Syslog is a protocol and de facto standard for message logging that allows collection of logs from multiple devices to a central collector. It helps address issues with having to look through logs on individual devices, clocks not being synchronized, and searching logs. Syslog defines message priorities and facilities. The document demonstrates configuring a Cisco router to send logs and an Ubuntu system to collect logs using rsyslog. Questions are welcomed from the audience.