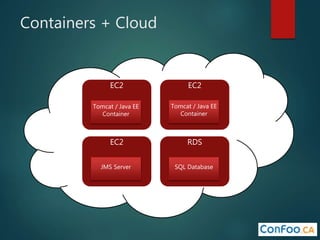
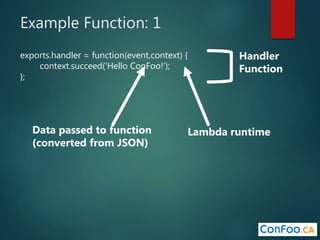
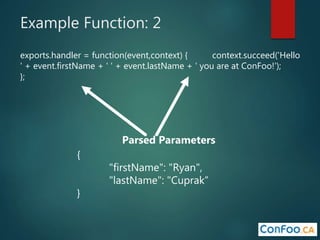
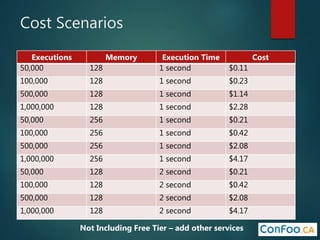
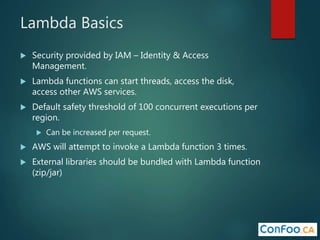
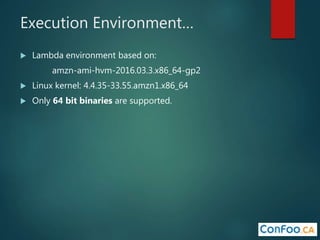
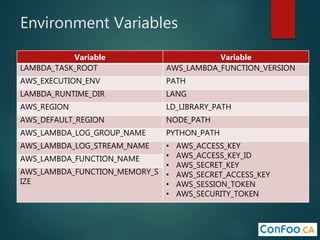
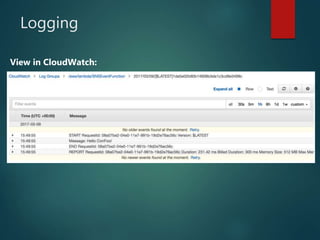
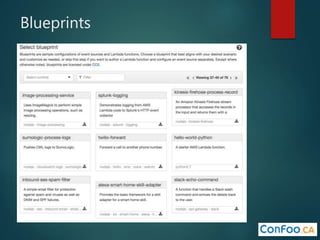
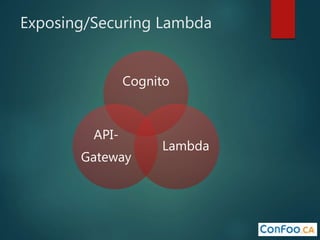
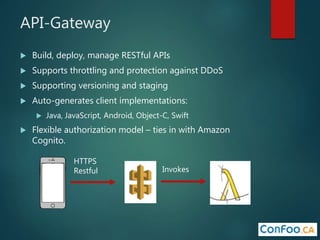
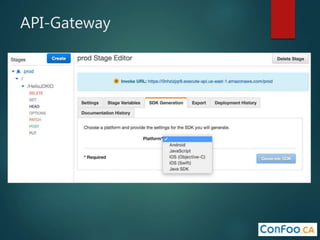
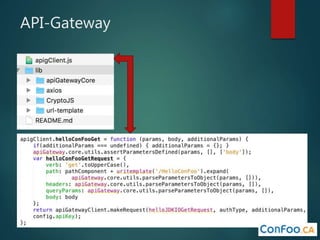
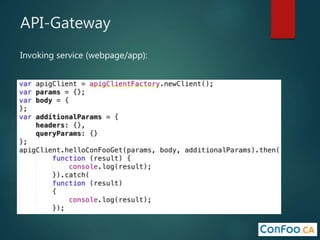
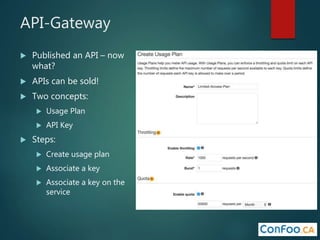
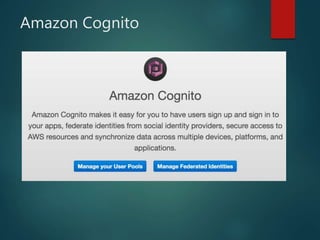
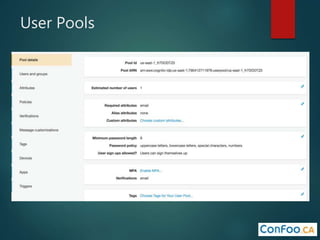
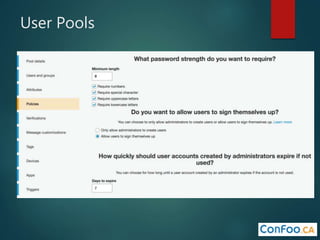
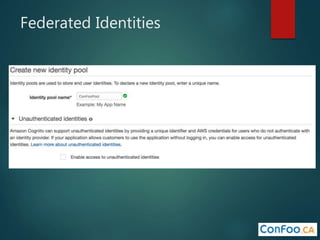
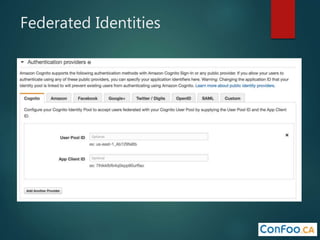
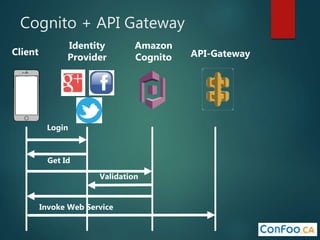
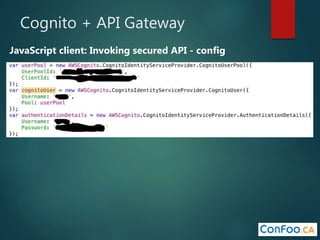
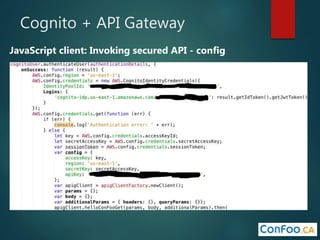
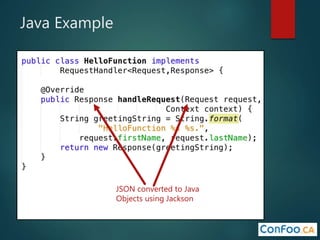
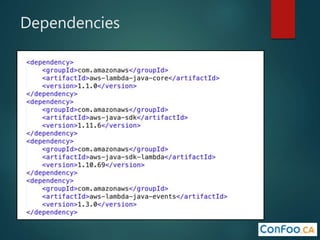
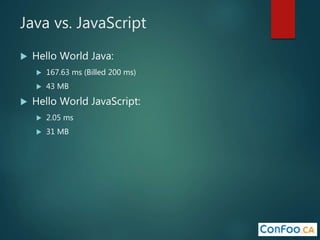
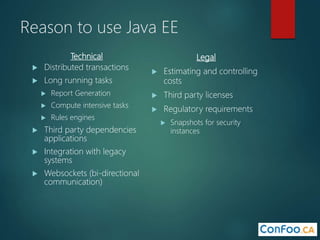
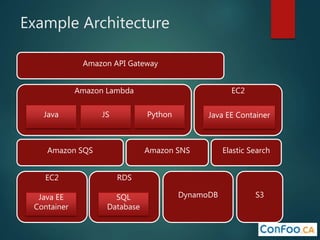
The document provides an in-depth overview of AWS Lambda, a serverless computing service that allows developers to run code in response to events without provisioning servers. It discusses the features of Lambda, including event handling, programming languages supported, pricing models, security measures, and integration with other AWS services like API Gateway and Amazon Cognito. Additionally, it outlines challenges, best practices, and use cases, emphasizing the benefits of a containerless approach in cloud application development.