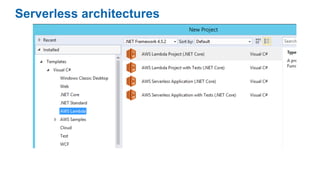
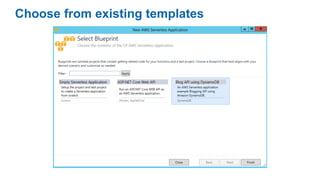
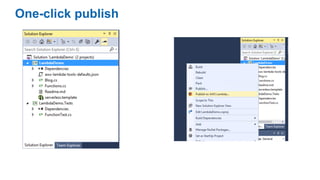
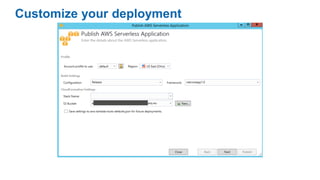
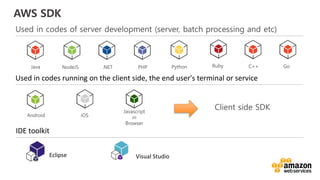
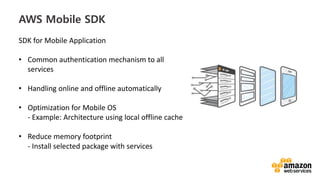
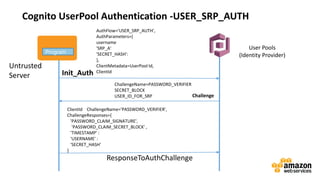
This document discusses DevOps concepts and practices including:
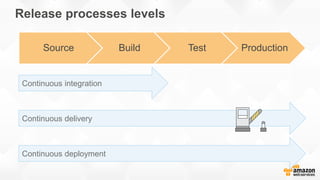
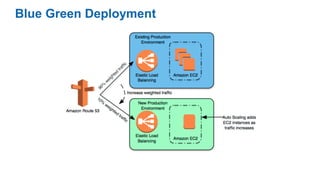
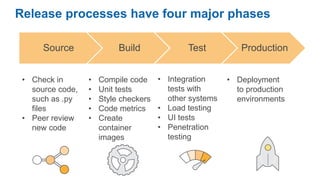
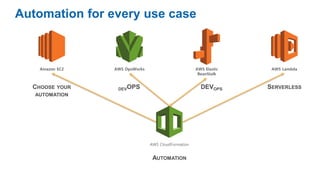
- DevOps aims to improve collaboration between development and operations teams through practices like continuous integration, deployment automation, and infrastructure as code.
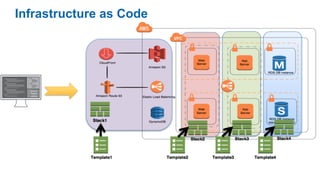
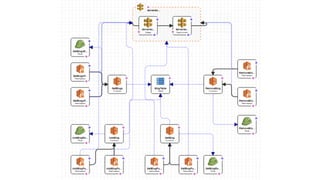
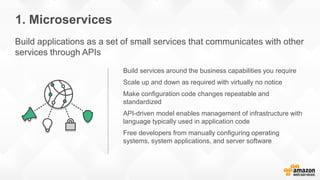
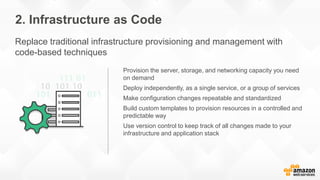
- The five pillars of DevOps are: microservices, infrastructure as code, automation and configuration management, continuous integration and continuous delivery, and logging and monitoring.
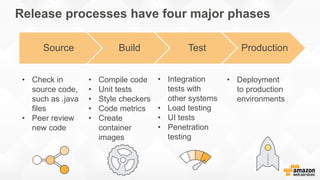
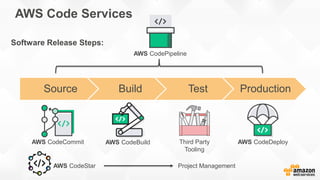
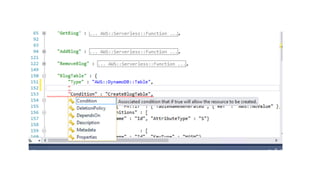
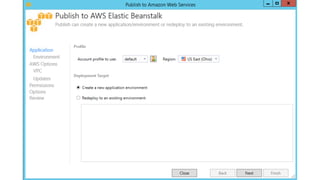
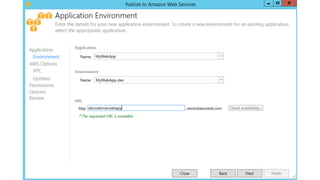
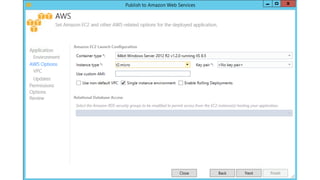
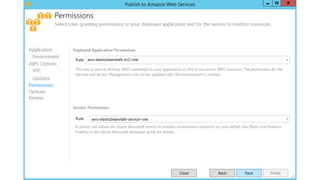
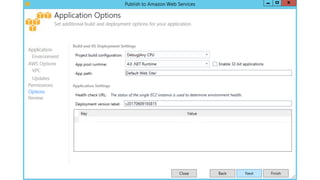
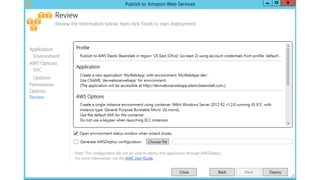
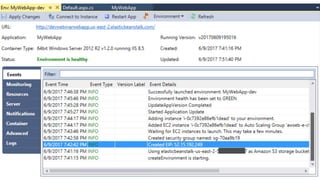
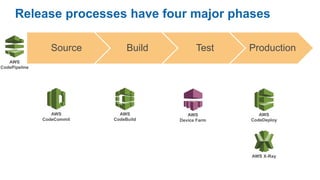
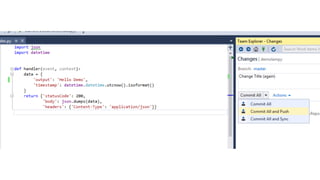
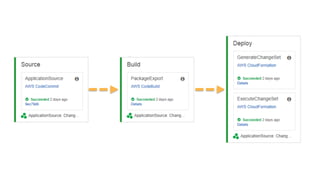
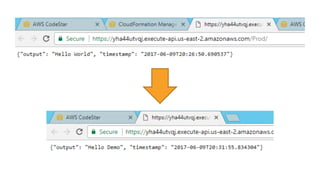
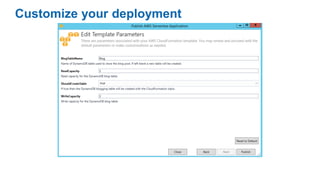
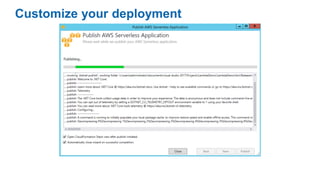
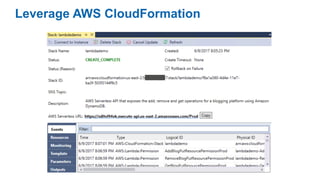
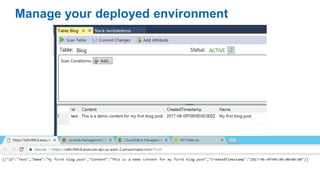
- Specific DevOps practices discussed include building infrastructure templates with CloudFormation, implementing continuous integration and delivery pipelines with CodePipeline/CodeBuild/CodeDeploy, and automating infrastructure provisioning and configuration changes.























![vv
Loaded from Shared credentials
[default]
aws_access_key_id = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
aws_secret_access_key = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
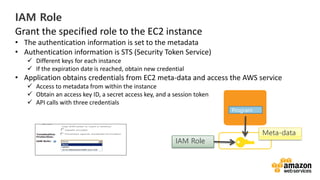
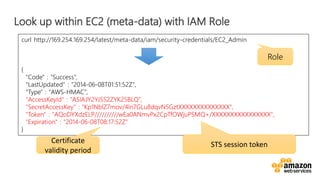
• Prepare a file containing the authentication information in advance
• location
Linux/Mac users: ~/.aws/credentials
Windows users: C:UsersUSER_NAME.awscredentials
• example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-170922074538/85/slide-28-320.jpg)




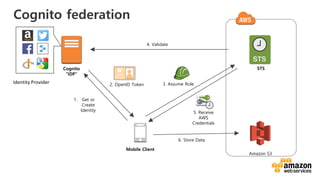
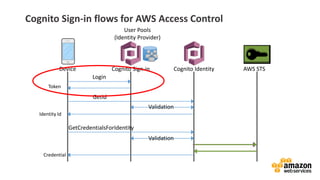
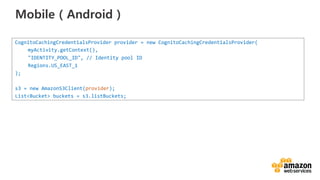

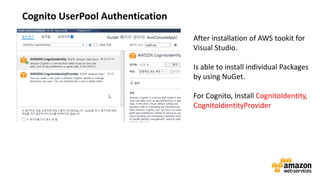








![Here’s some infrastructure as Code
"WebServer": {
"Type": "AWS::EC2::Instance",
"Metadata" : {
"AWS::CloudFormation::Init" : {
"config" : {
"packages" : {
"yum" : {
"httpd" : [],
"php" : [],
"php-mysql" : [],
"php-gd" : [],
"php-xml" : [],
"php-mbstring" : [],
"mysql" : []
}
},
"sources" : {
"/var/www/html" : "http://ftp.drupal.org/files/projects/drupal-7.8.tar.gz",
"/home/ec2-user" : "http://ftp.drupal.org/files/projects/drush-7.x-4.5.tar.gz"
},
AWS
CloudFormation
template](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-170922074538/85/slide-51-320.jpg)