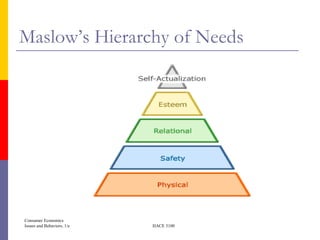
This document provides an overview of key concepts in consumer economics. It defines economics as the study of how society manages its scarce resources. Consumer economics specifically examines how people deal with scarcity by fulfilling needs and selecting among alternatives. The consumption process is discussed as a cycle of awareness of needs/wants, information gathering, planning purchases, implementing purchases, and evaluating the outcomes. Maslow's hierarchy of needs and the distinction between needs and wants are also introduced.