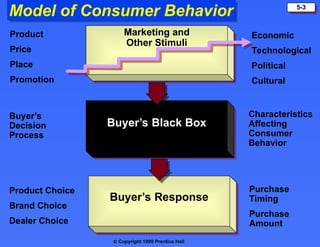
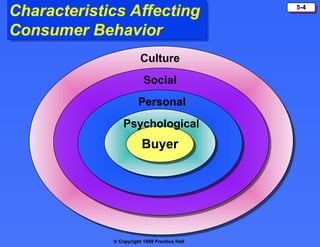
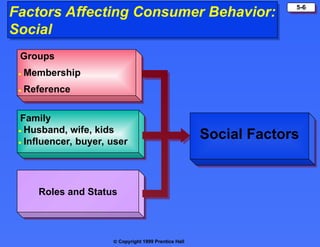
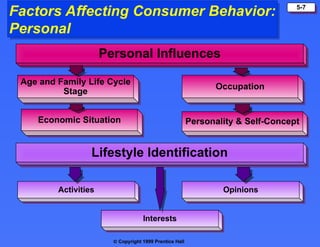
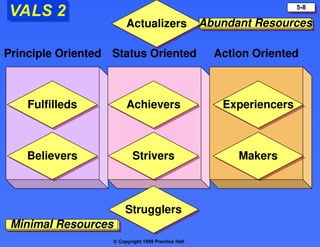
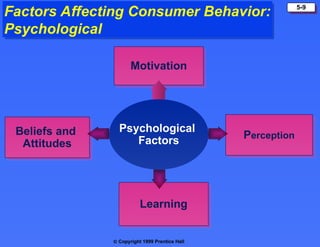
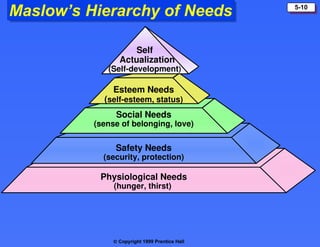
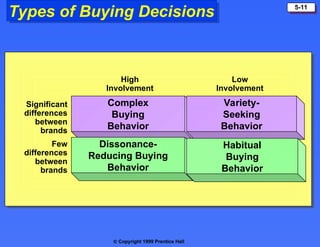
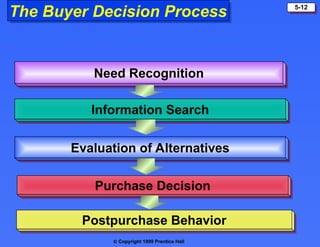
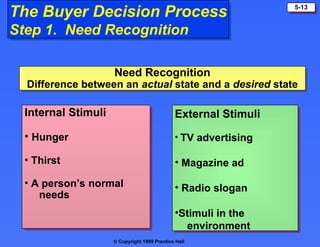
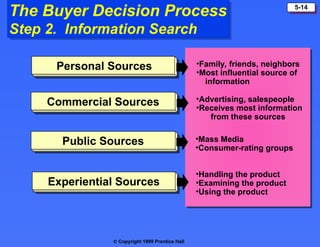
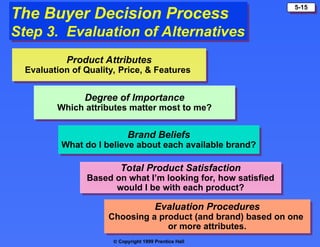
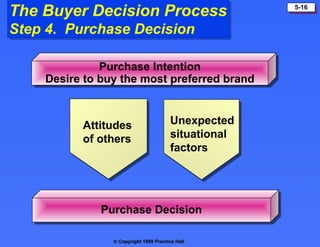
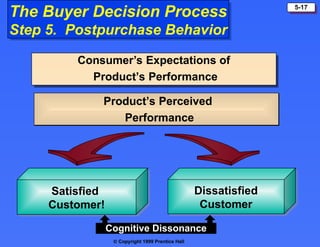
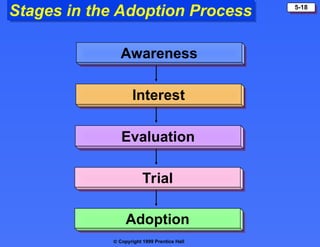
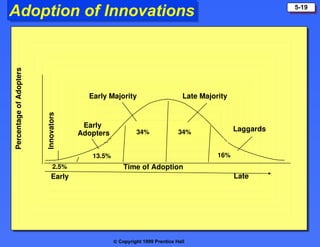
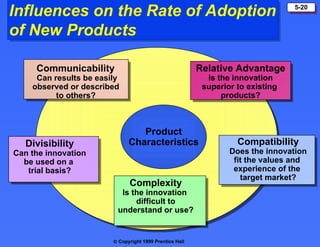
The document discusses consumer buying behavior, defining it as the actions of individuals and households purchasing goods and services for personal use. It outlines various factors influencing this behavior, including cultural, social, personal, and psychological characteristics, and details the buyer decision process from need recognition to postpurchase evaluation. Additionally, it covers the adoption of innovations and factors affecting the rate of adoption of new products.