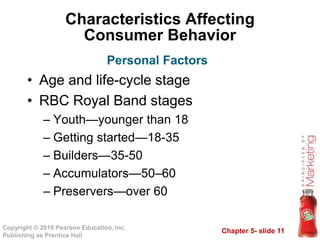
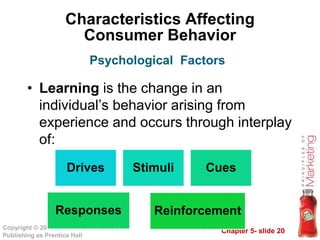
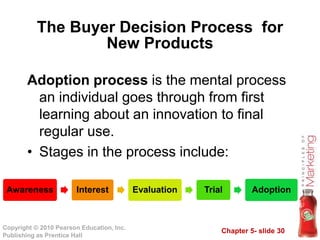
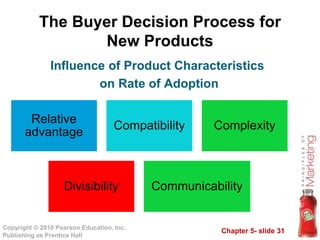
This document outlines key topics in consumer buyer behavior including the model of consumer behavior, characteristics affecting consumer decisions, types of buying behaviors, and the consumer decision process. It discusses how factors like culture, subcultures, social classes, groups, family, age, income and more influence purchasing. It also examines psychological factors, motivation, perception, learning, beliefs and attitudes. Finally, it explores the consumer decision process, sources of information, and the adoption of new products.