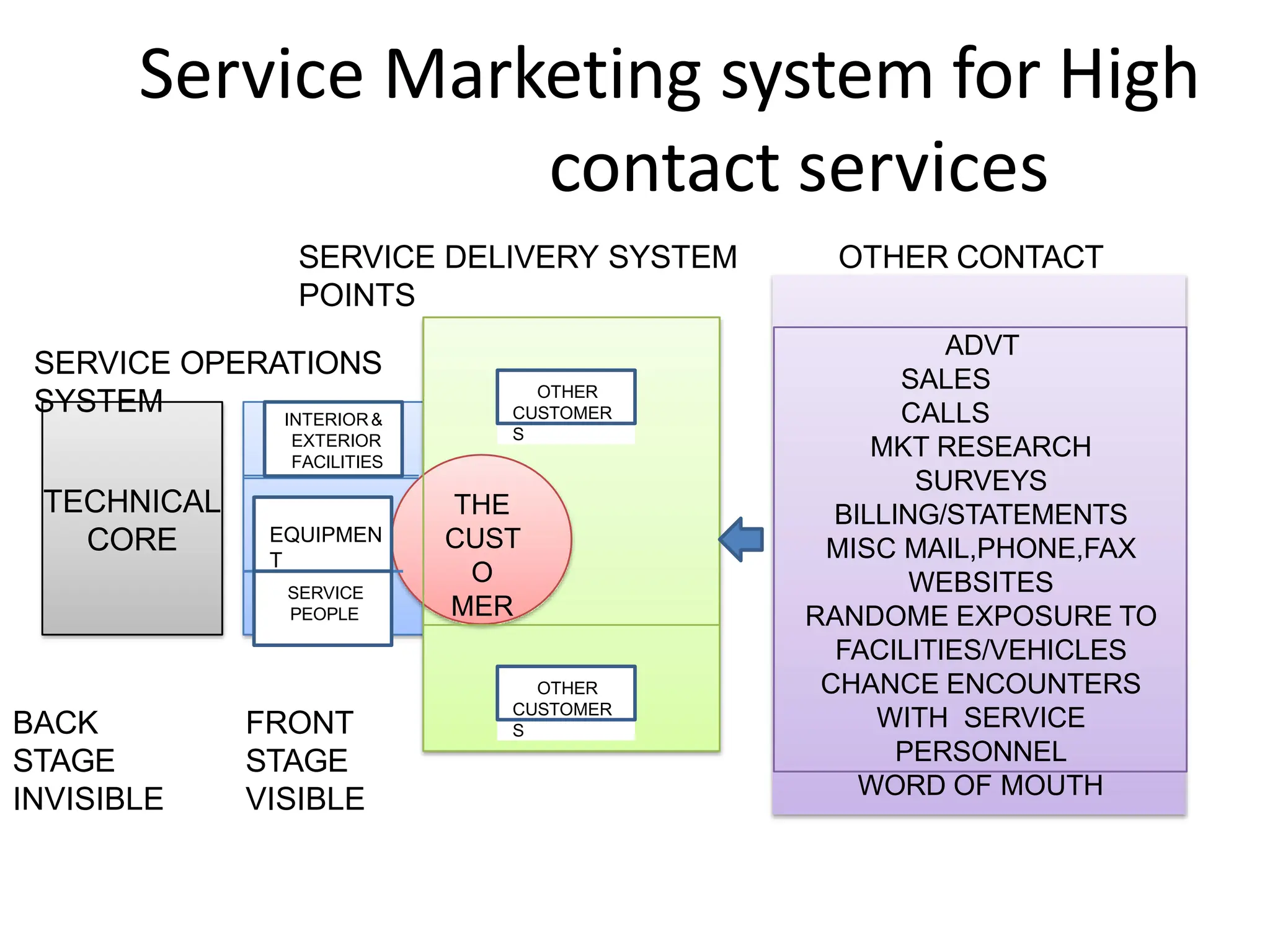
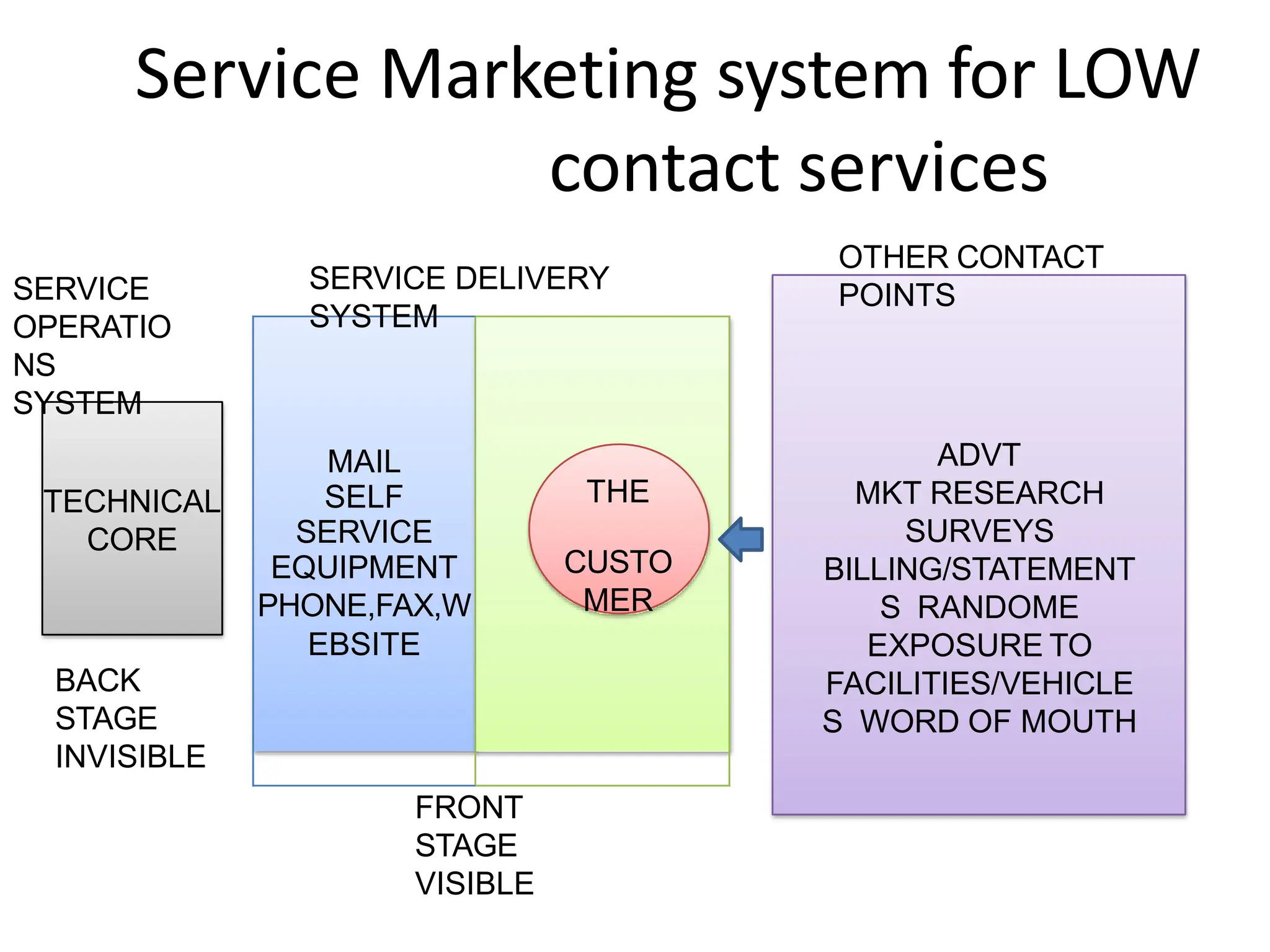
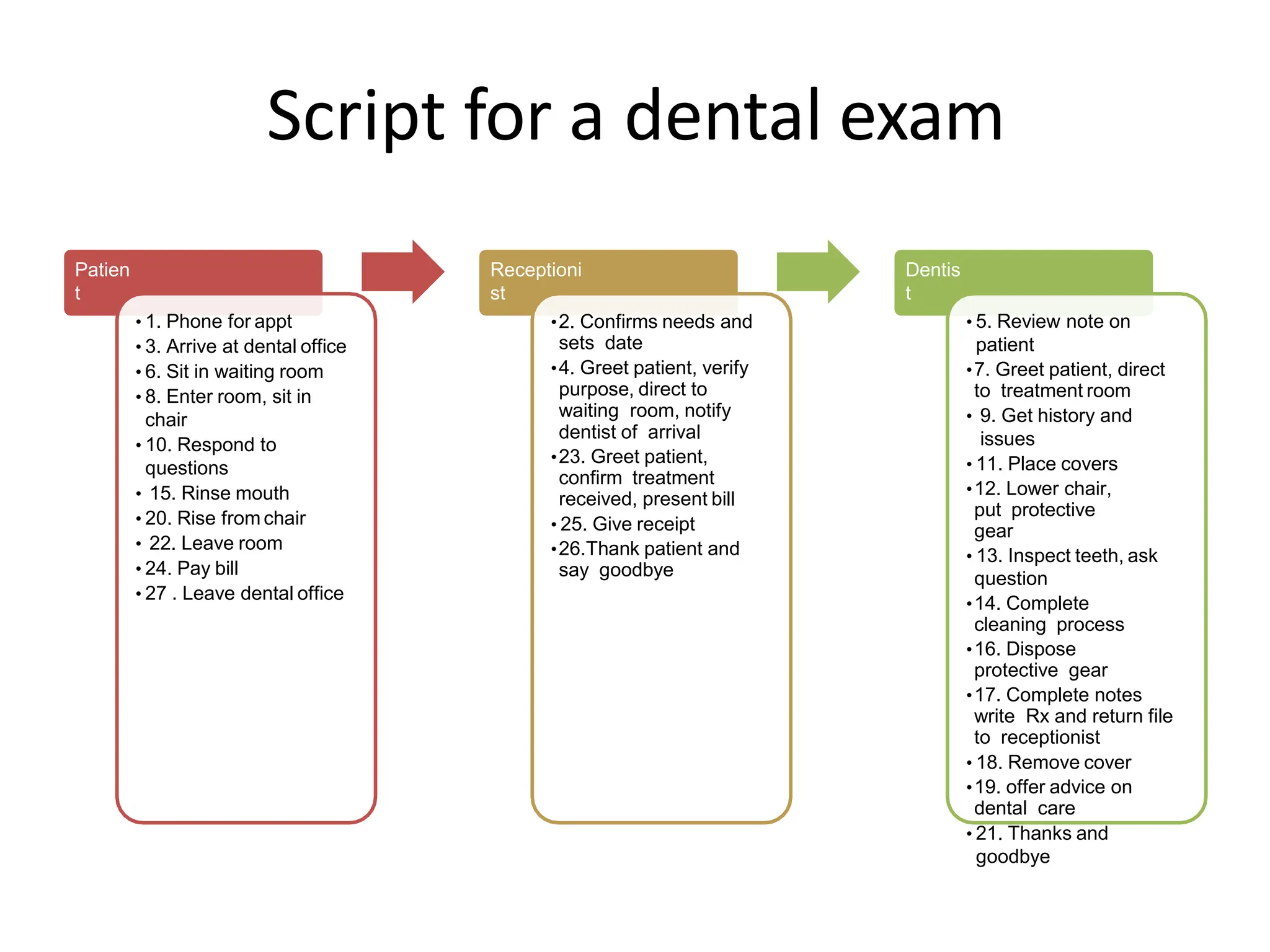
The document discusses consumer behavior in service encounters, emphasizing the service marketing system which varies between high and low contact services. It introduces role and script theories to explain customer and employee interactions during service delivery, highlighting the importance of performing prescribed roles and following scripts to enhance satisfaction. The post-encounter stage addresses how customers compare their expectations with the actual service received and the implications of positive and negative disconfirmation on customer satisfaction.