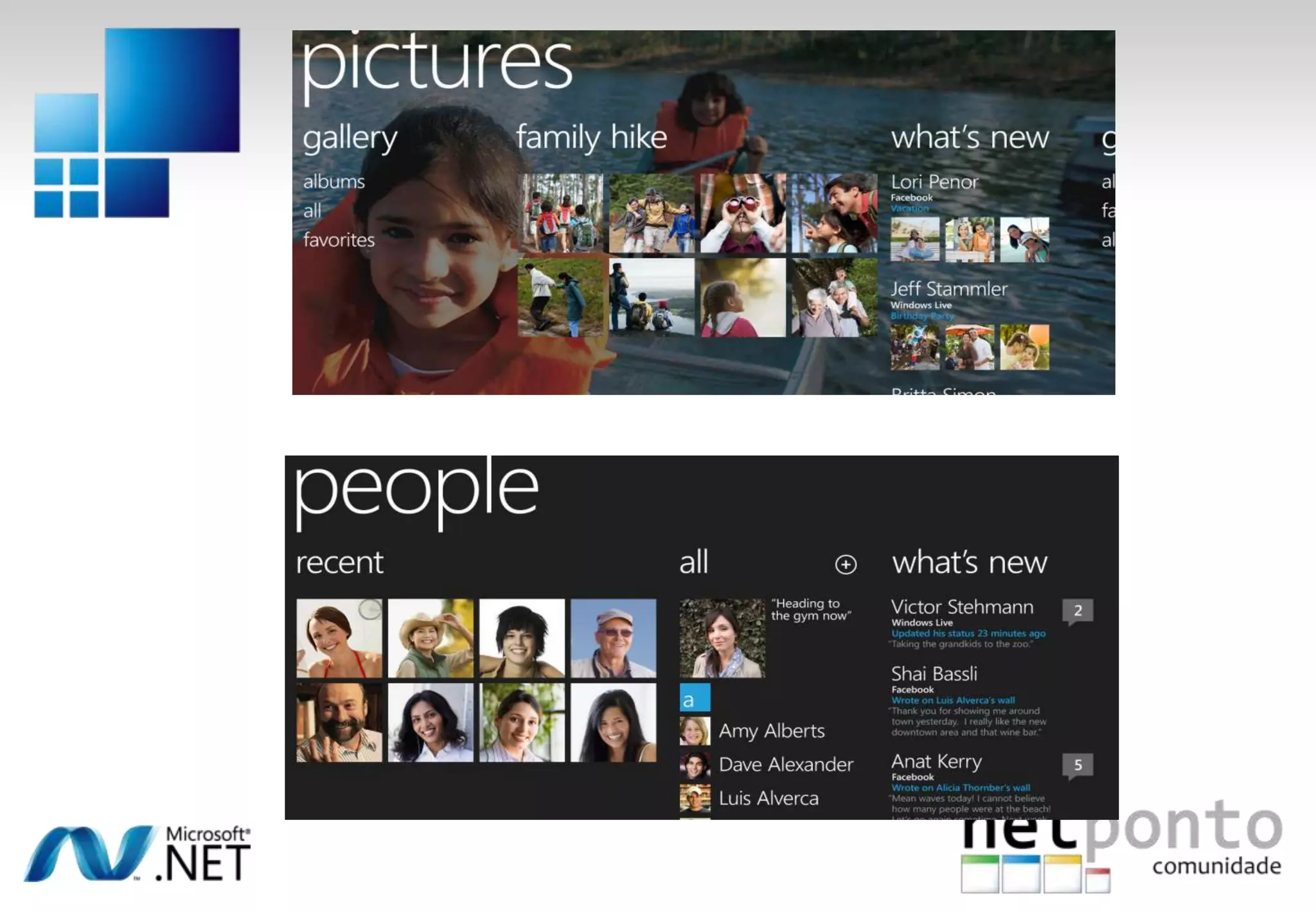
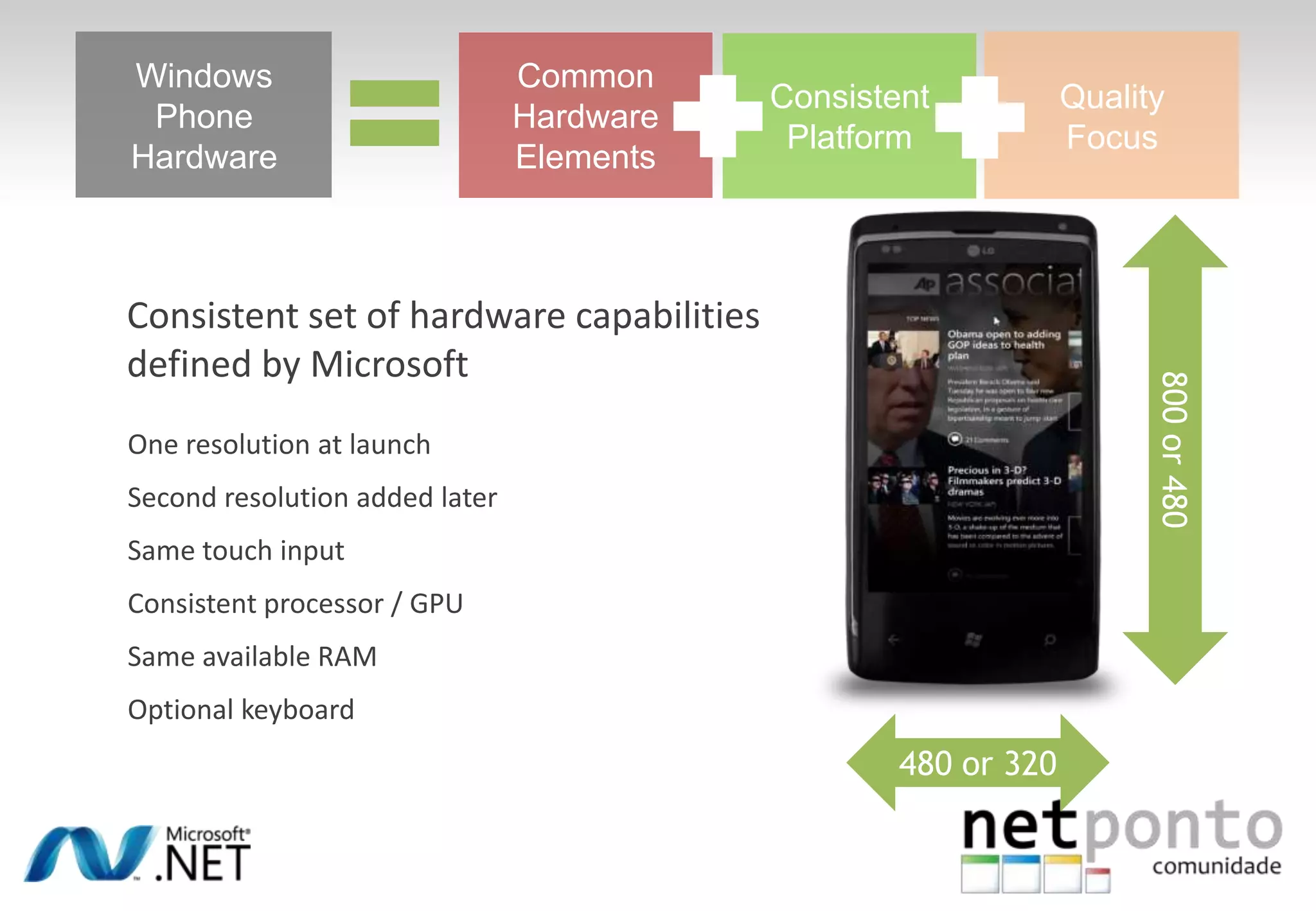
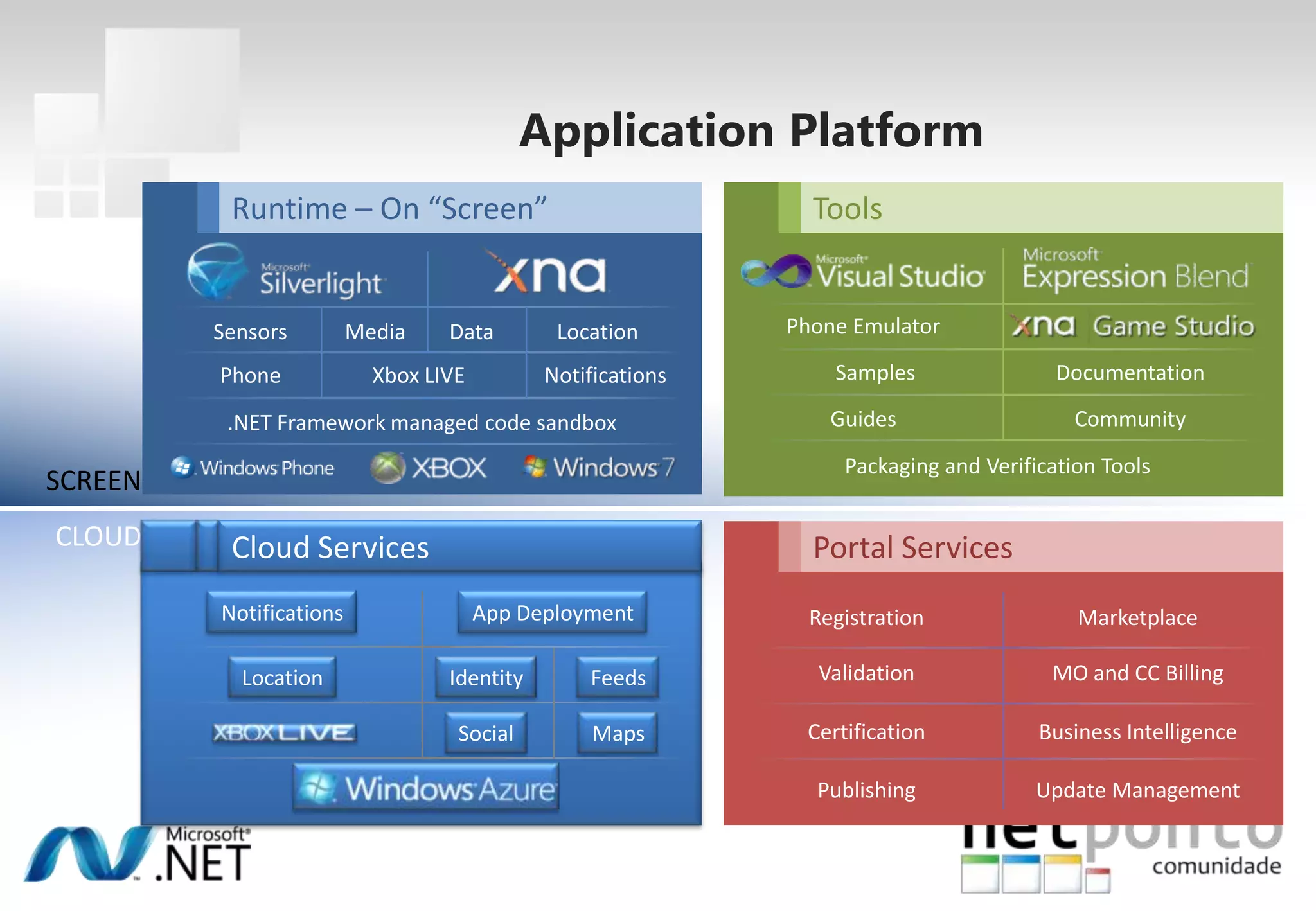
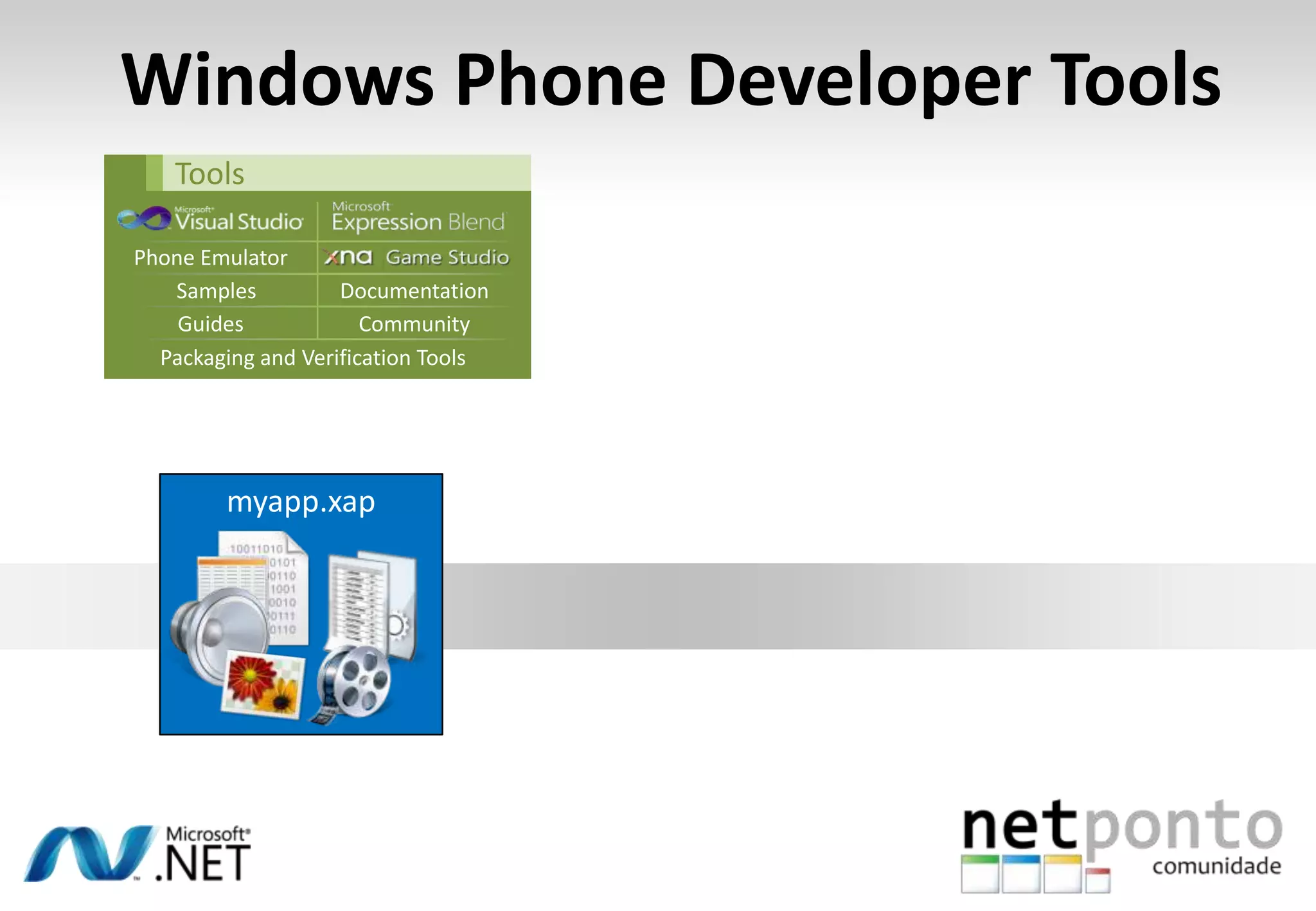
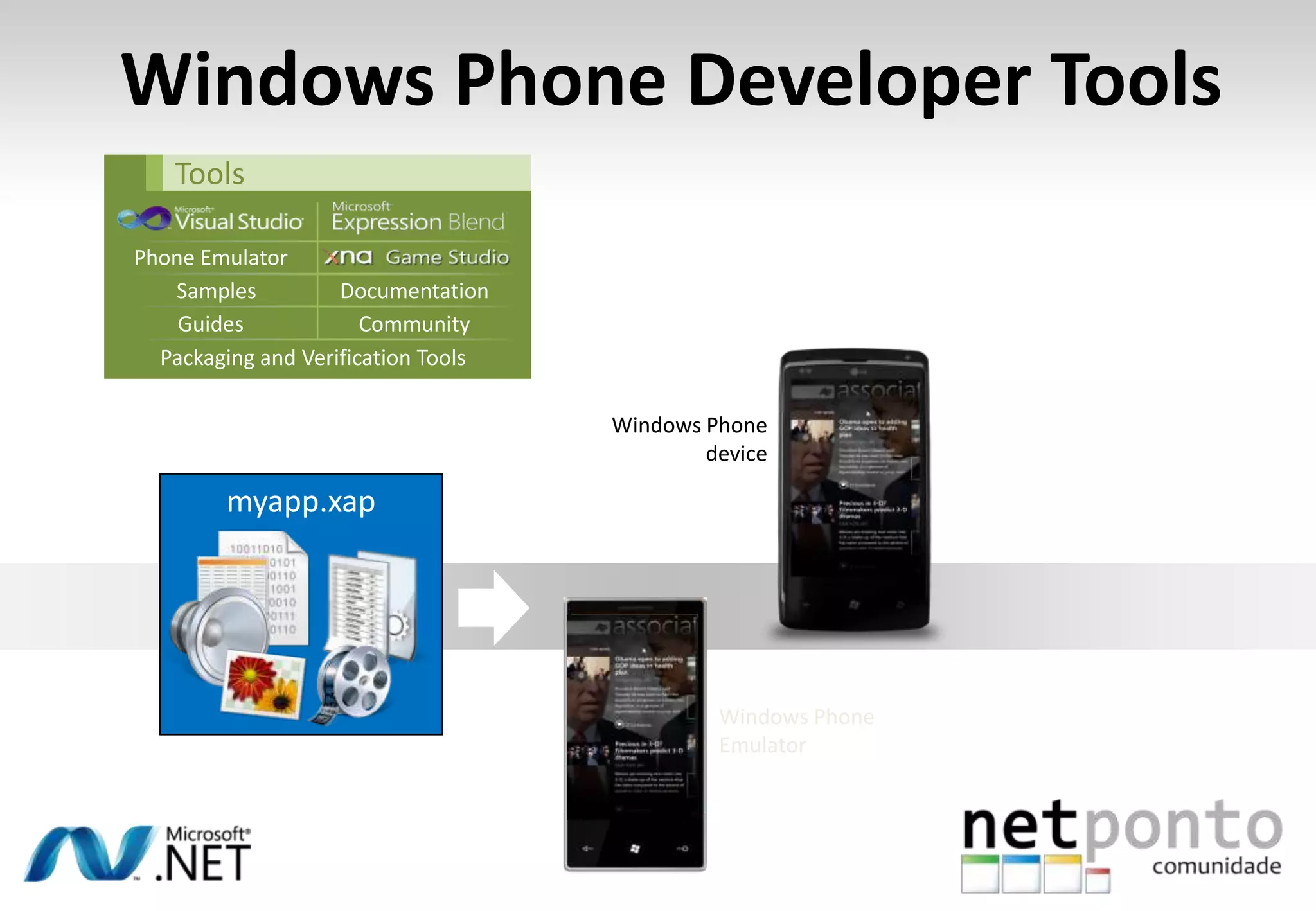
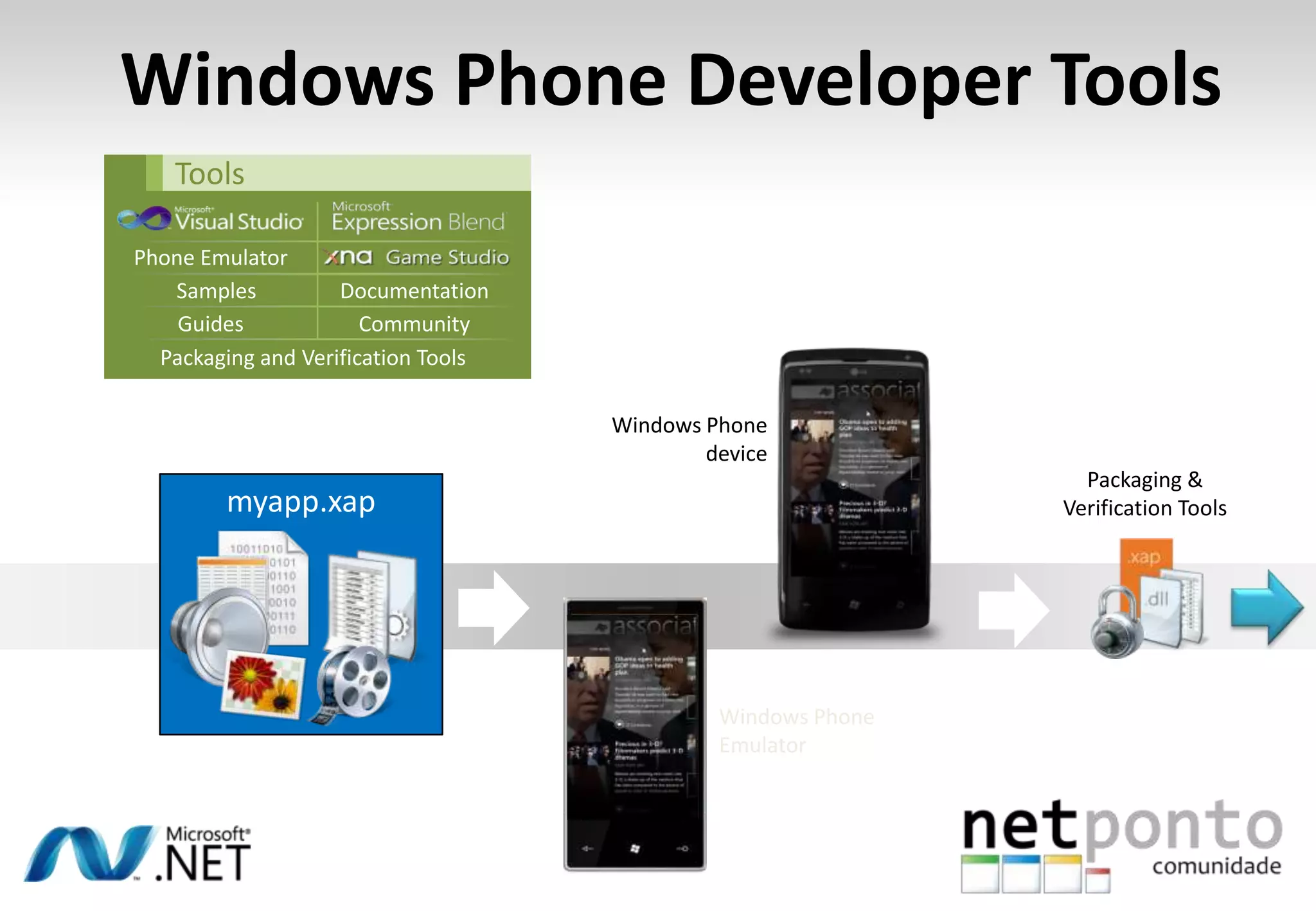
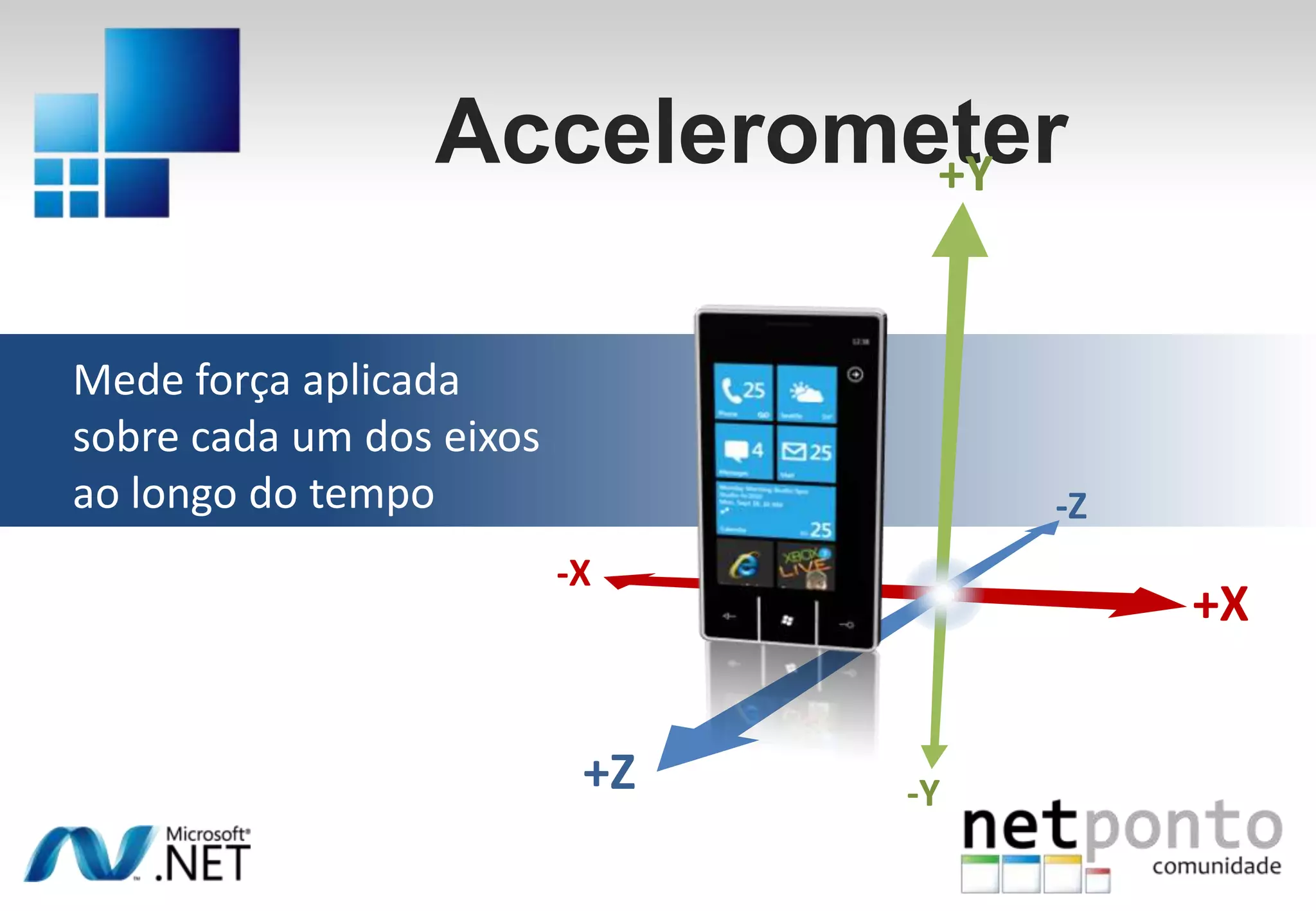
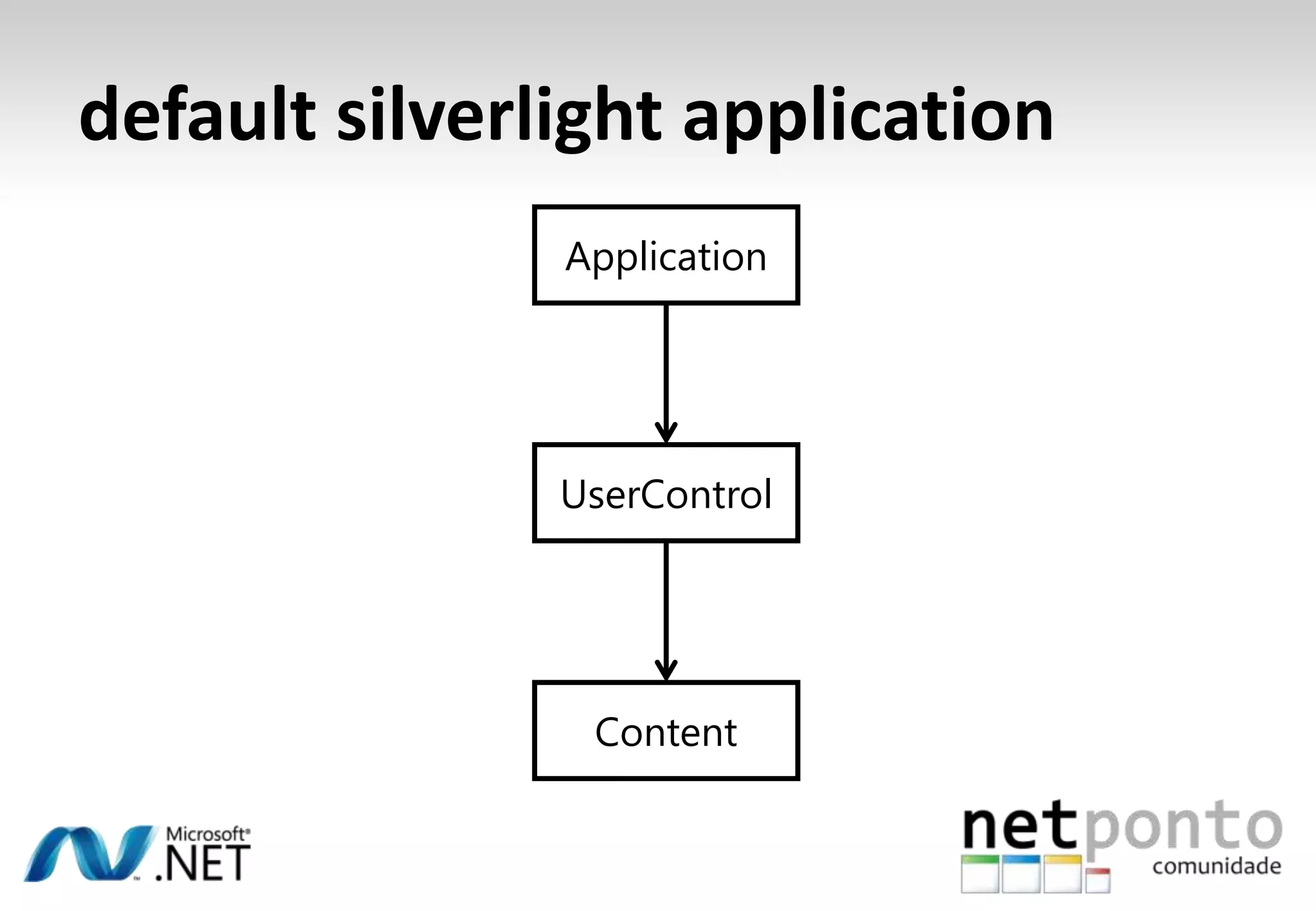
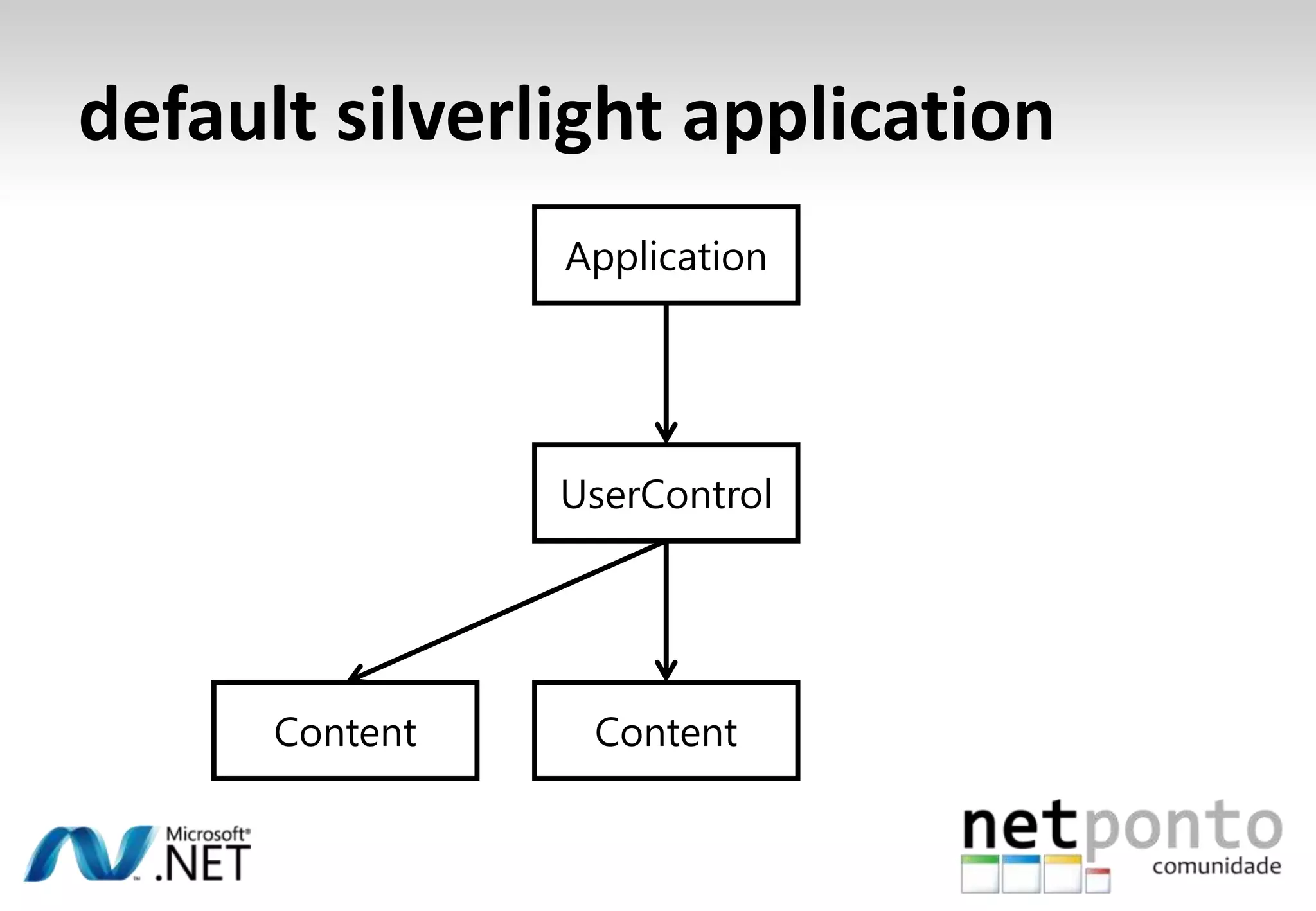
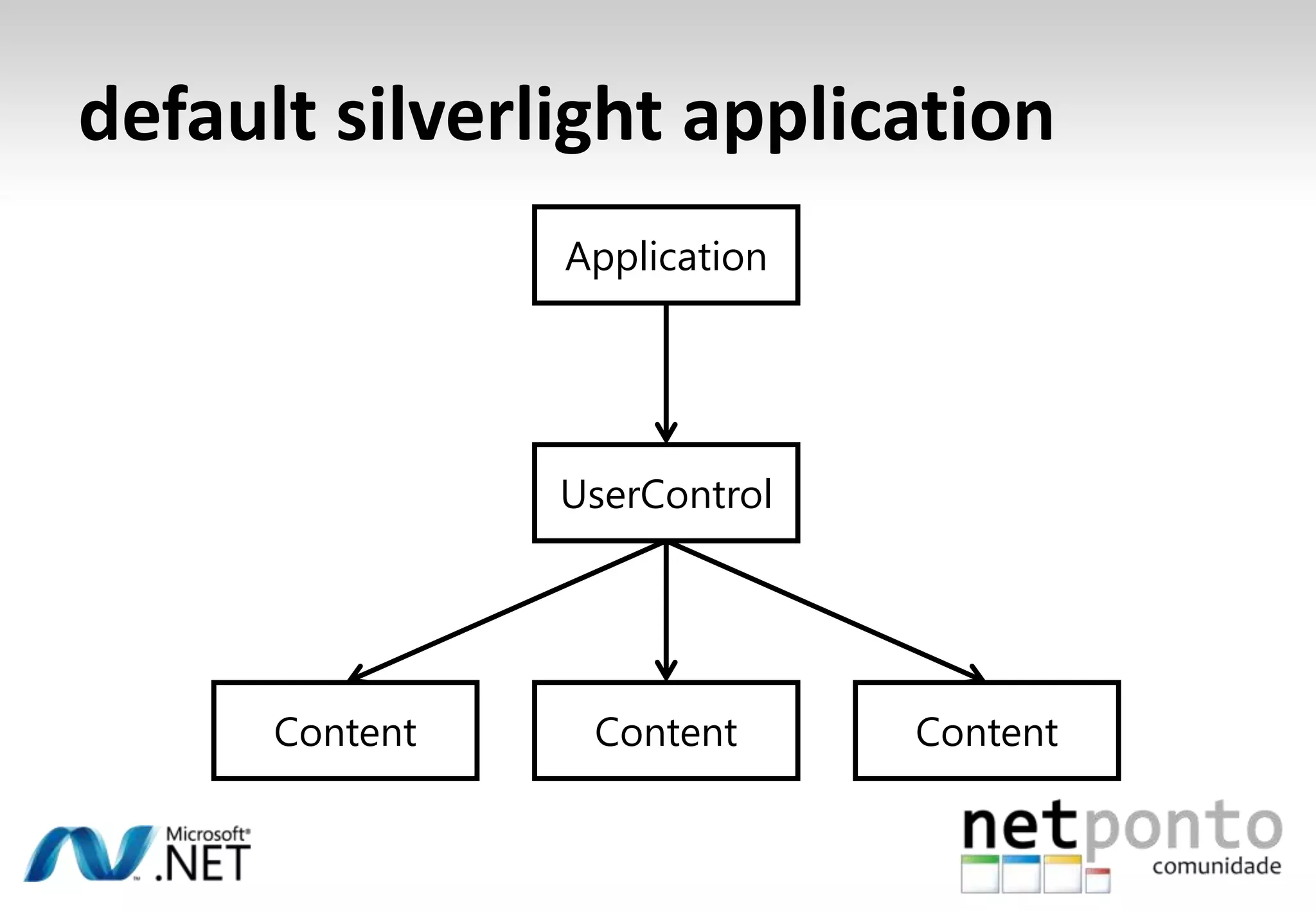
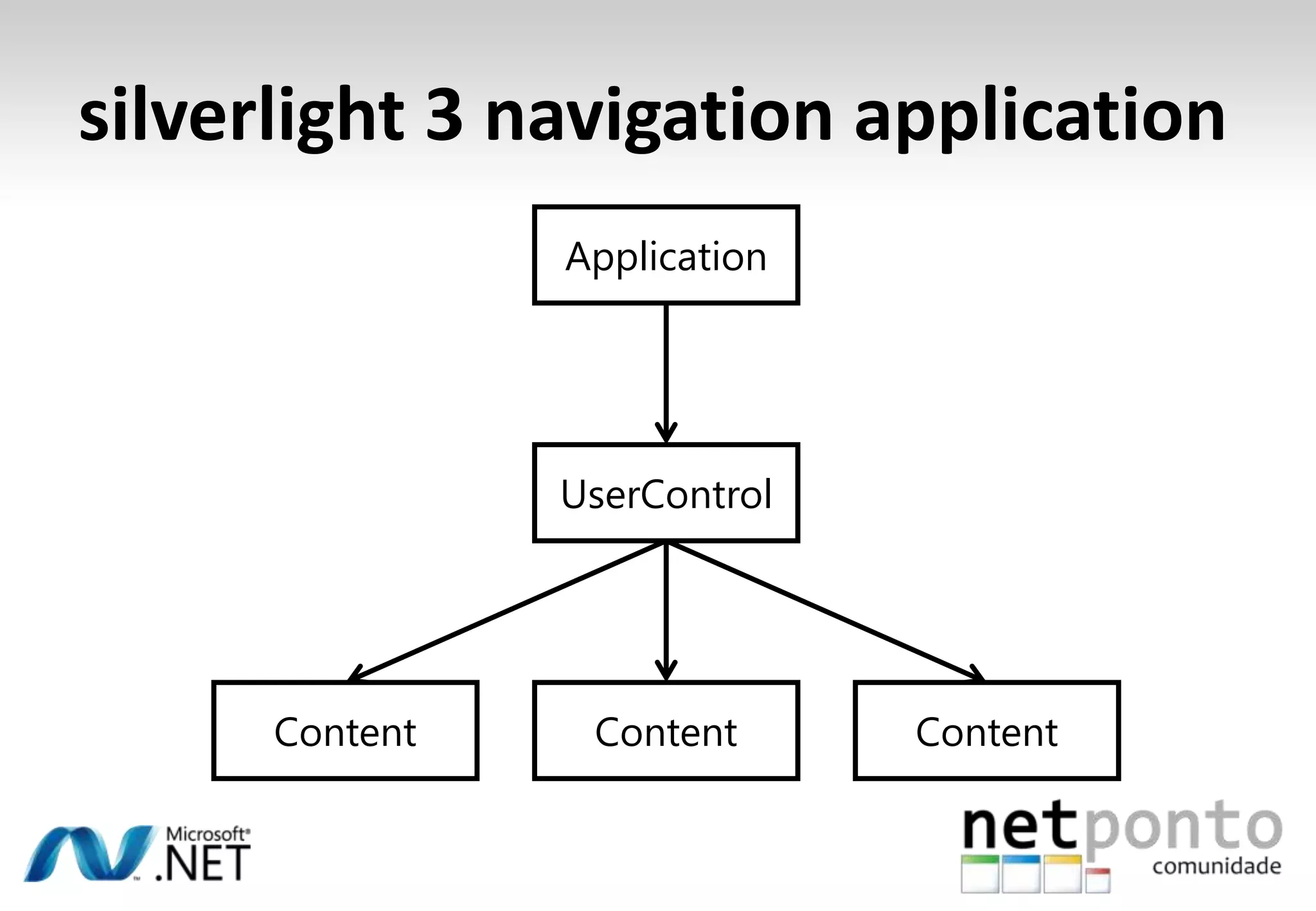
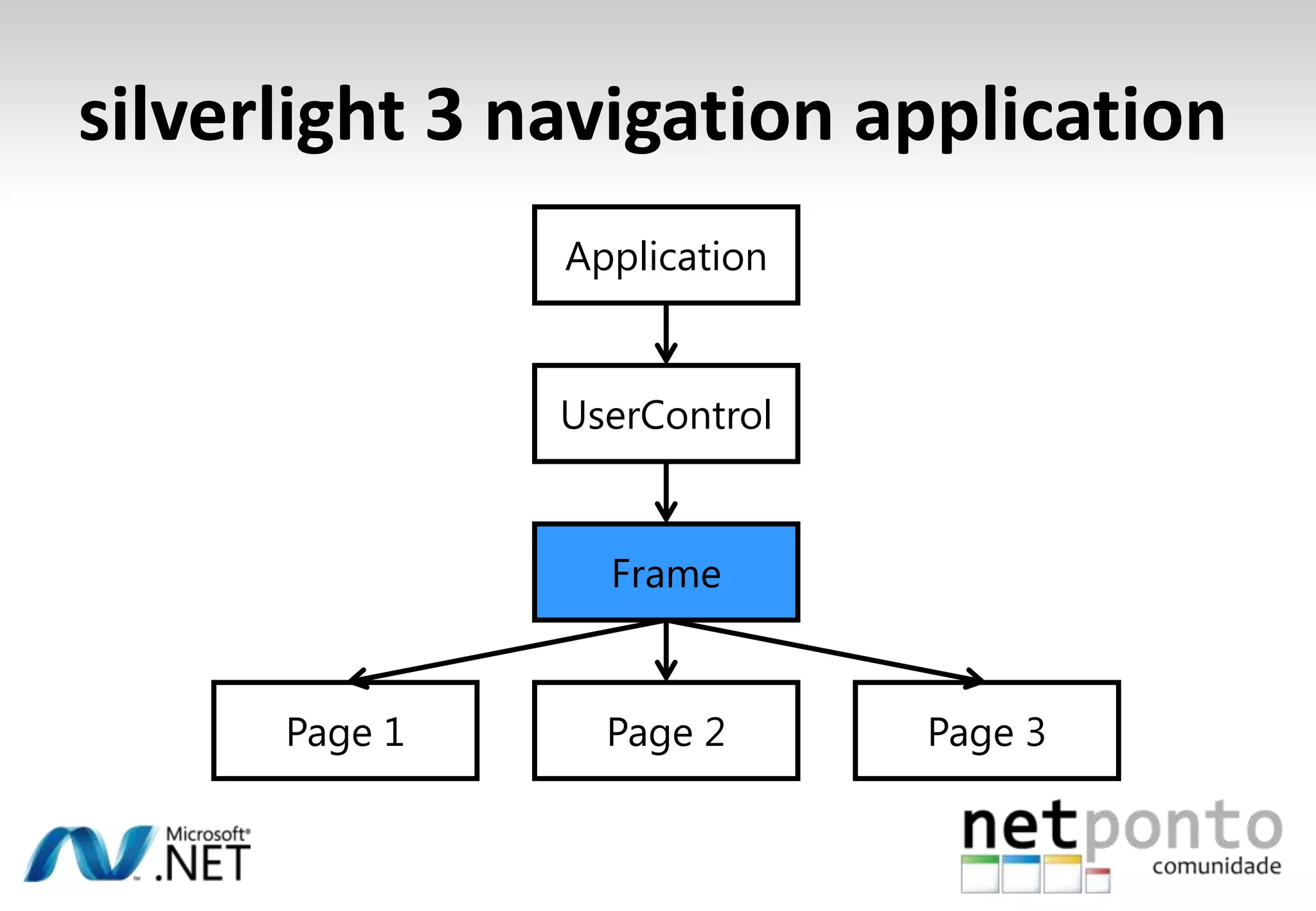
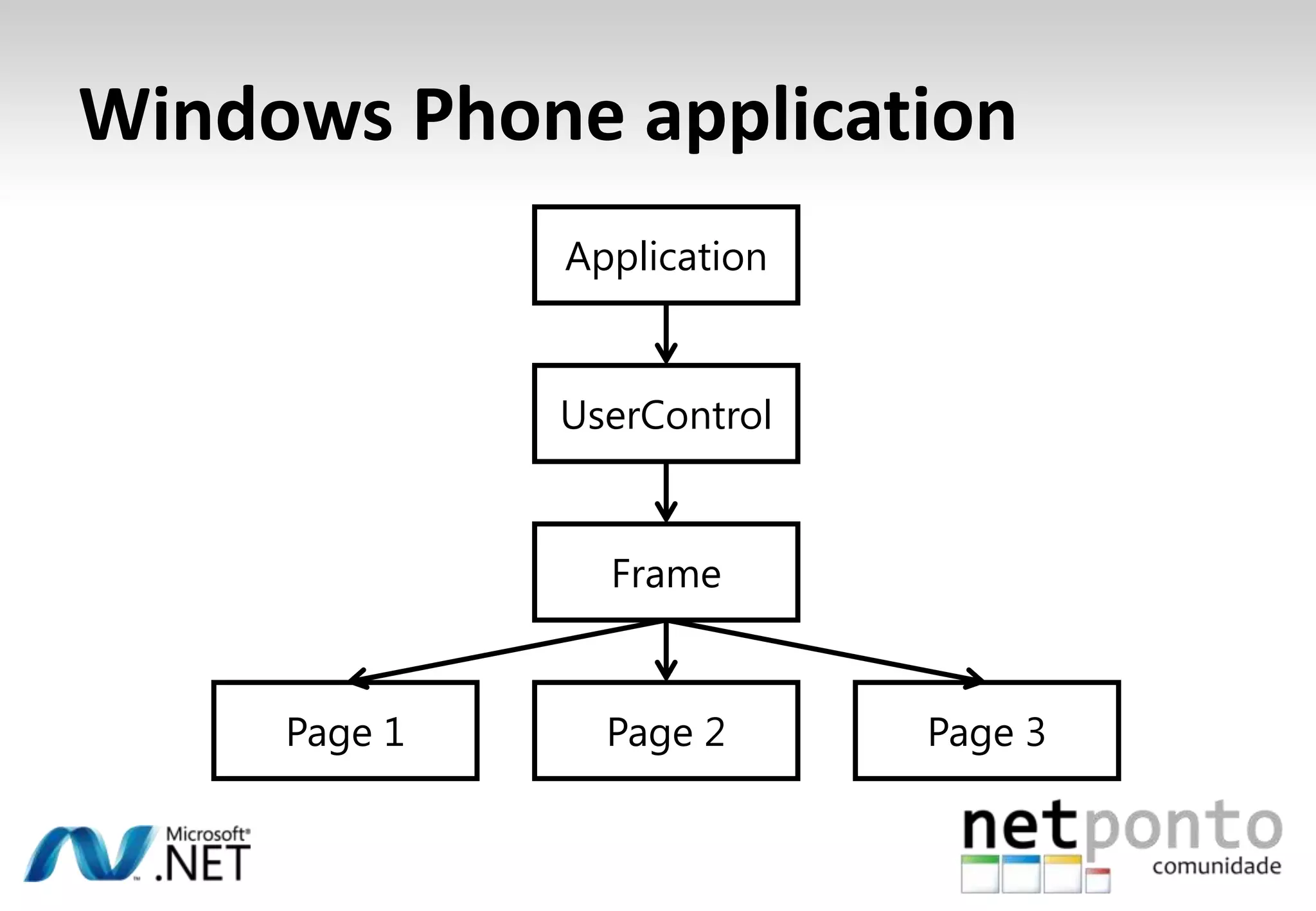
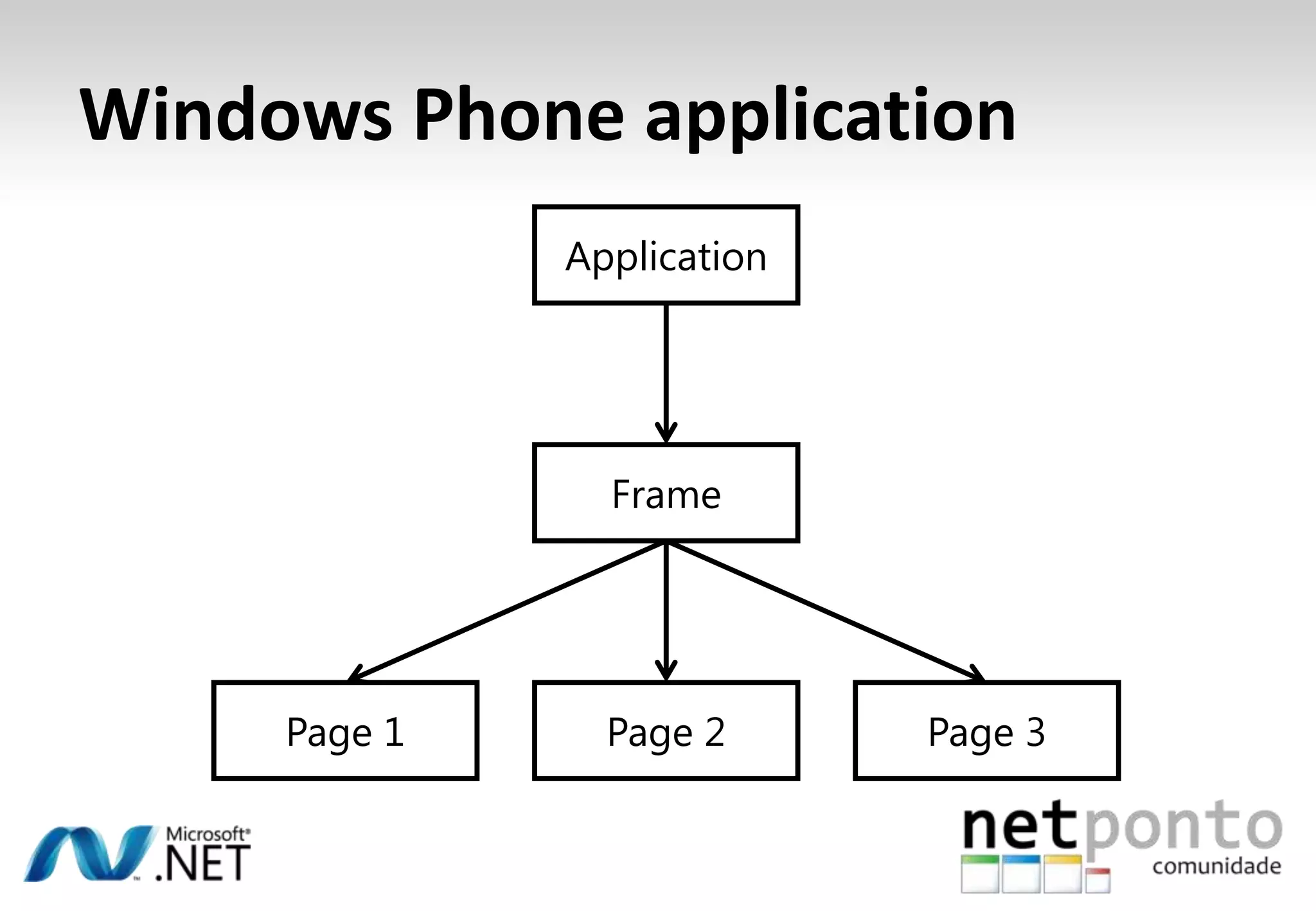
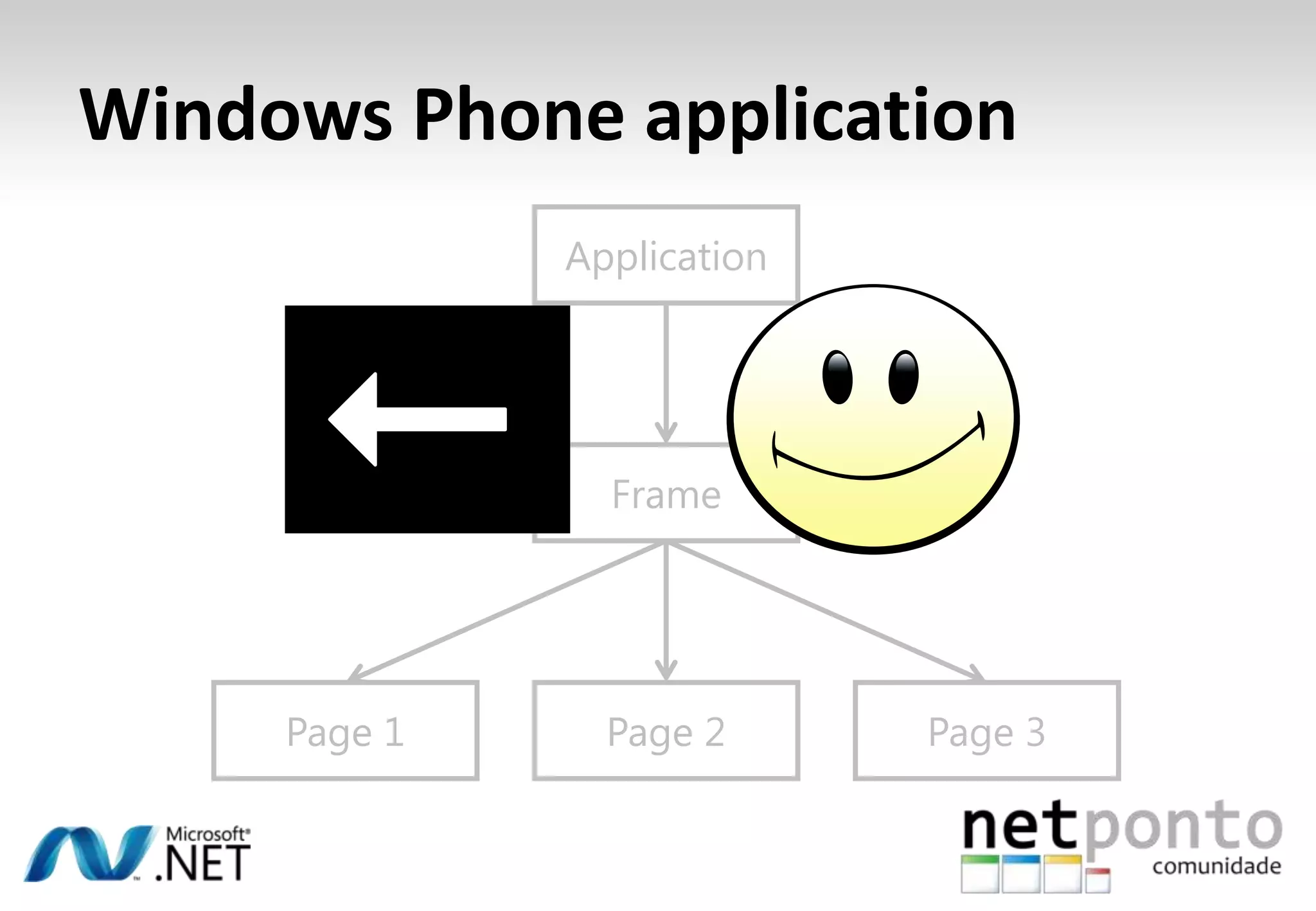
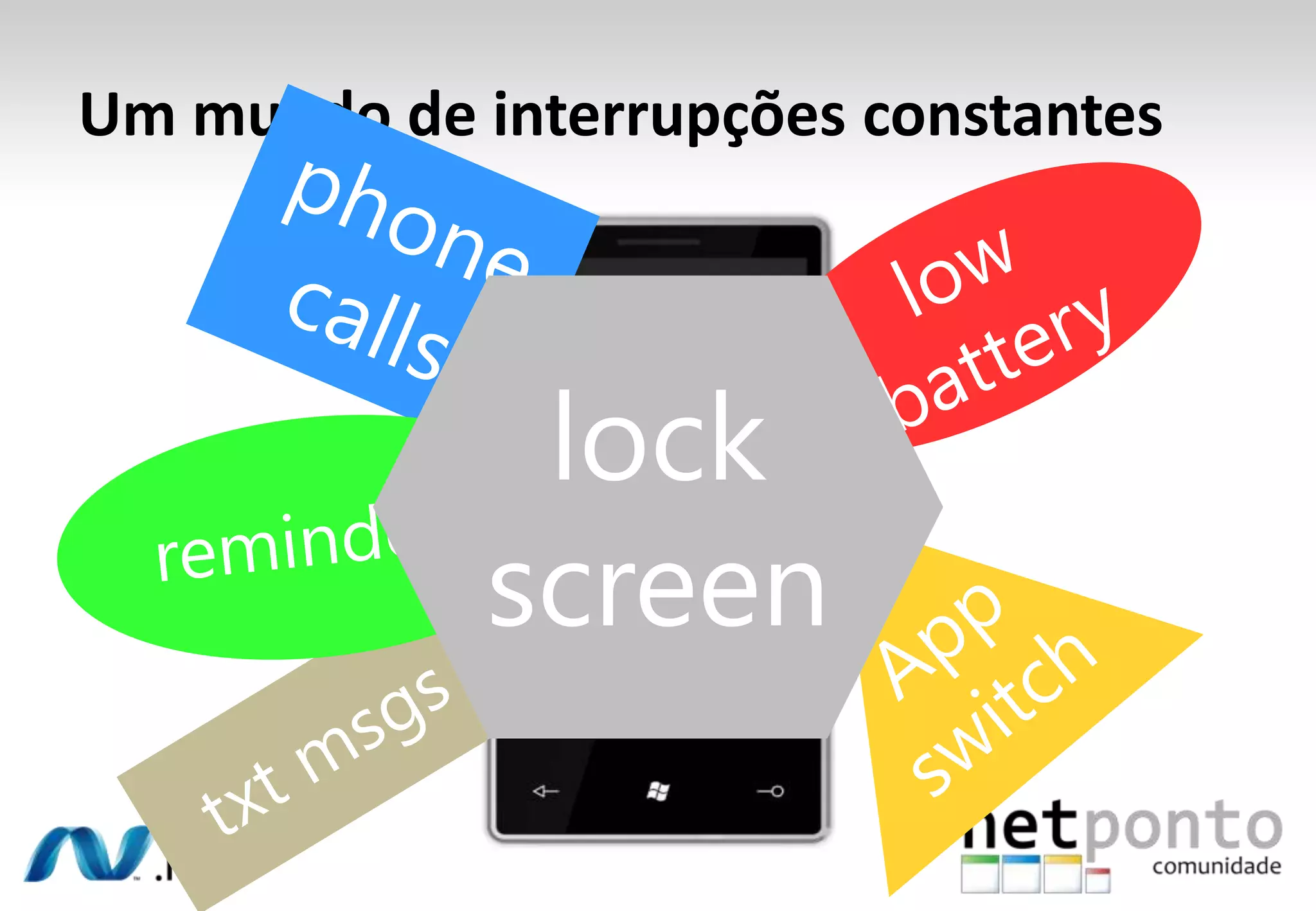
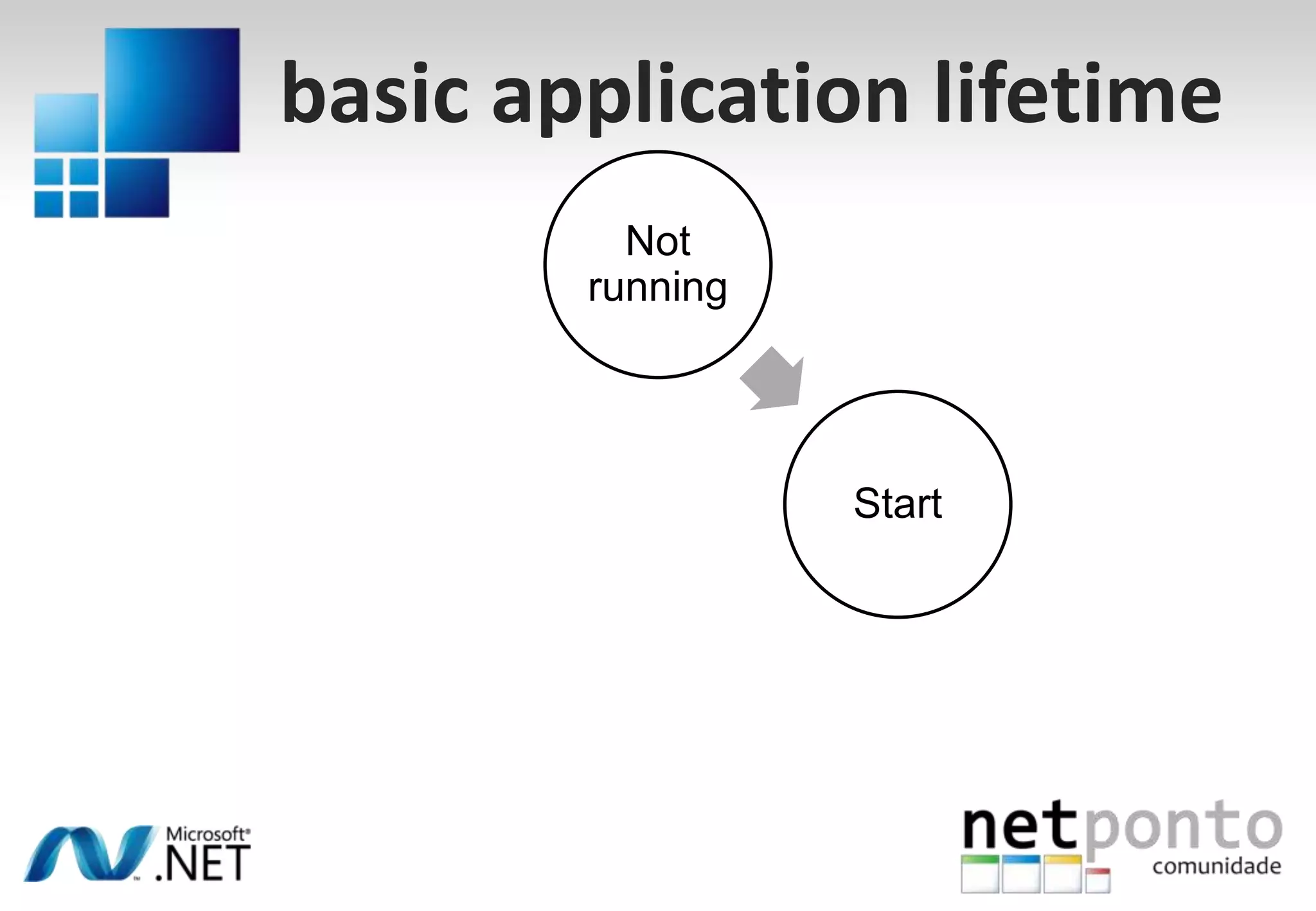
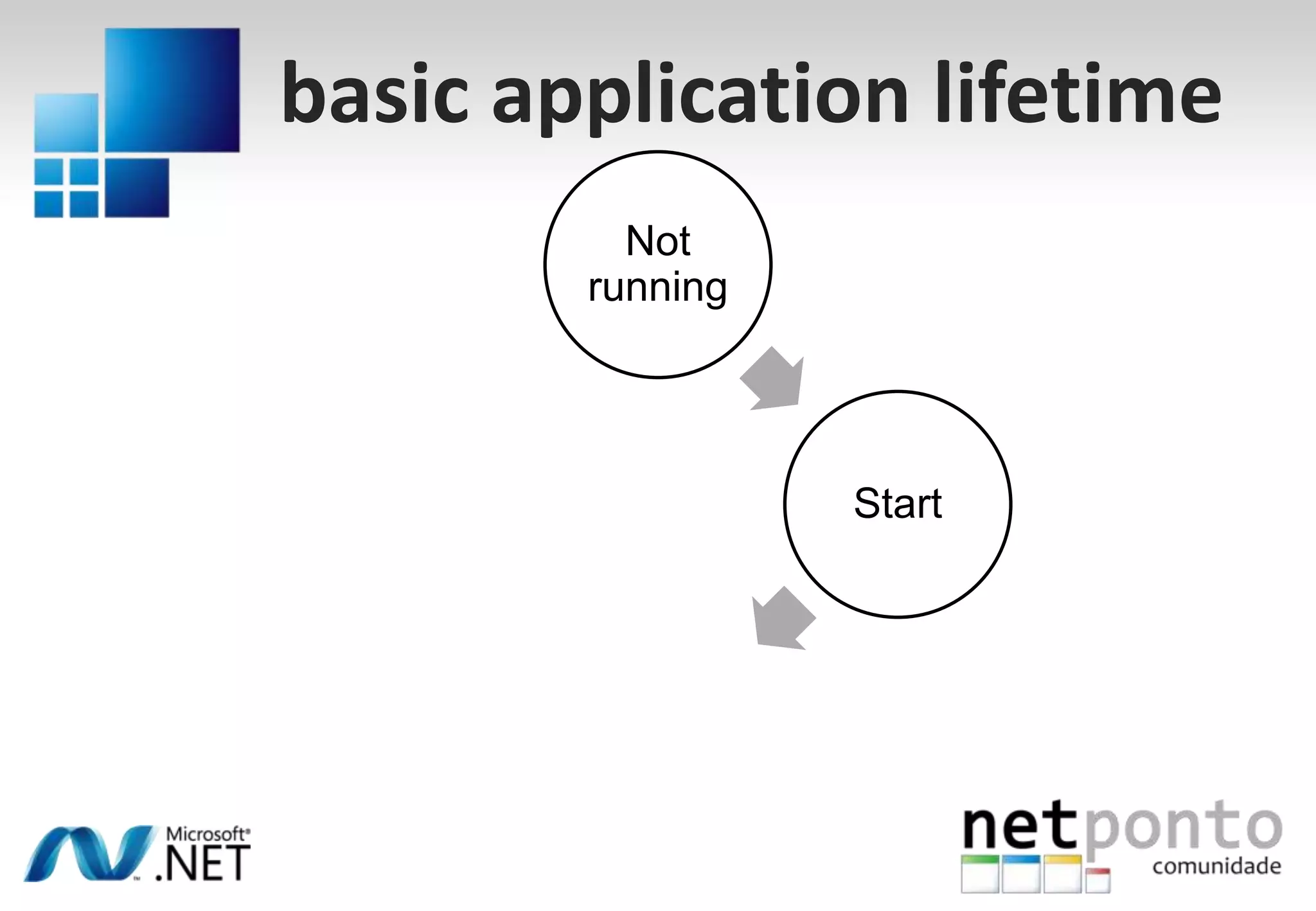
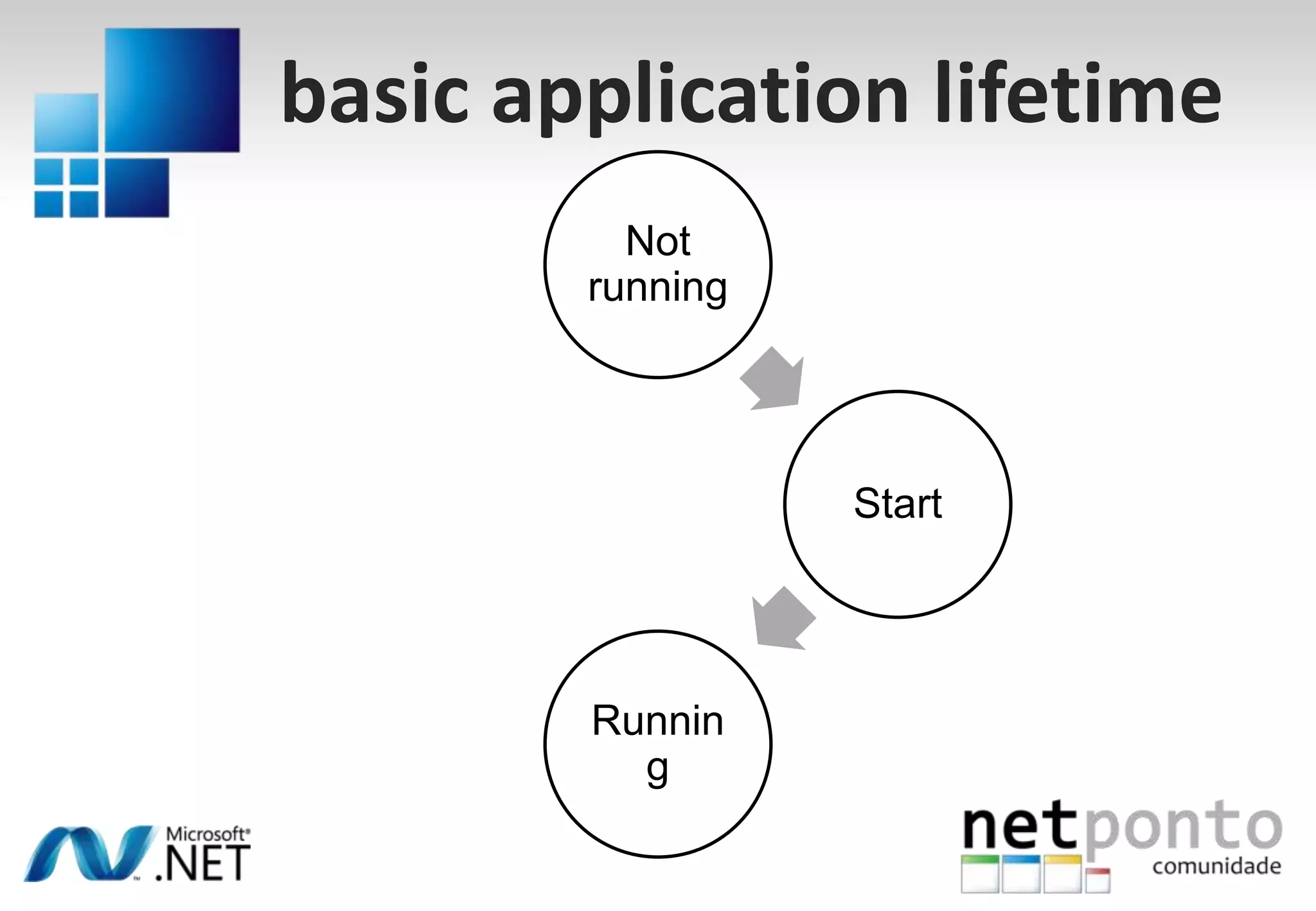
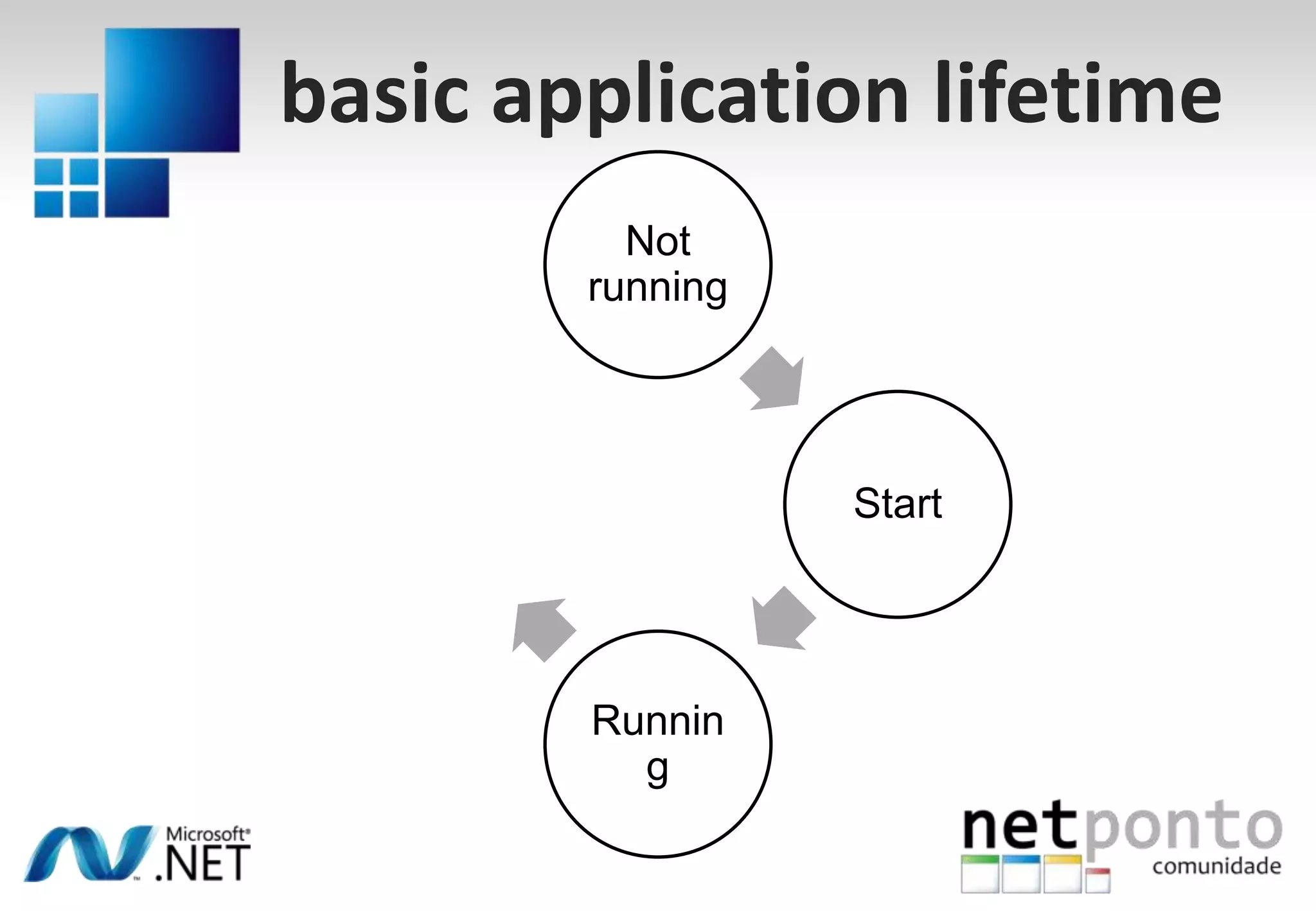
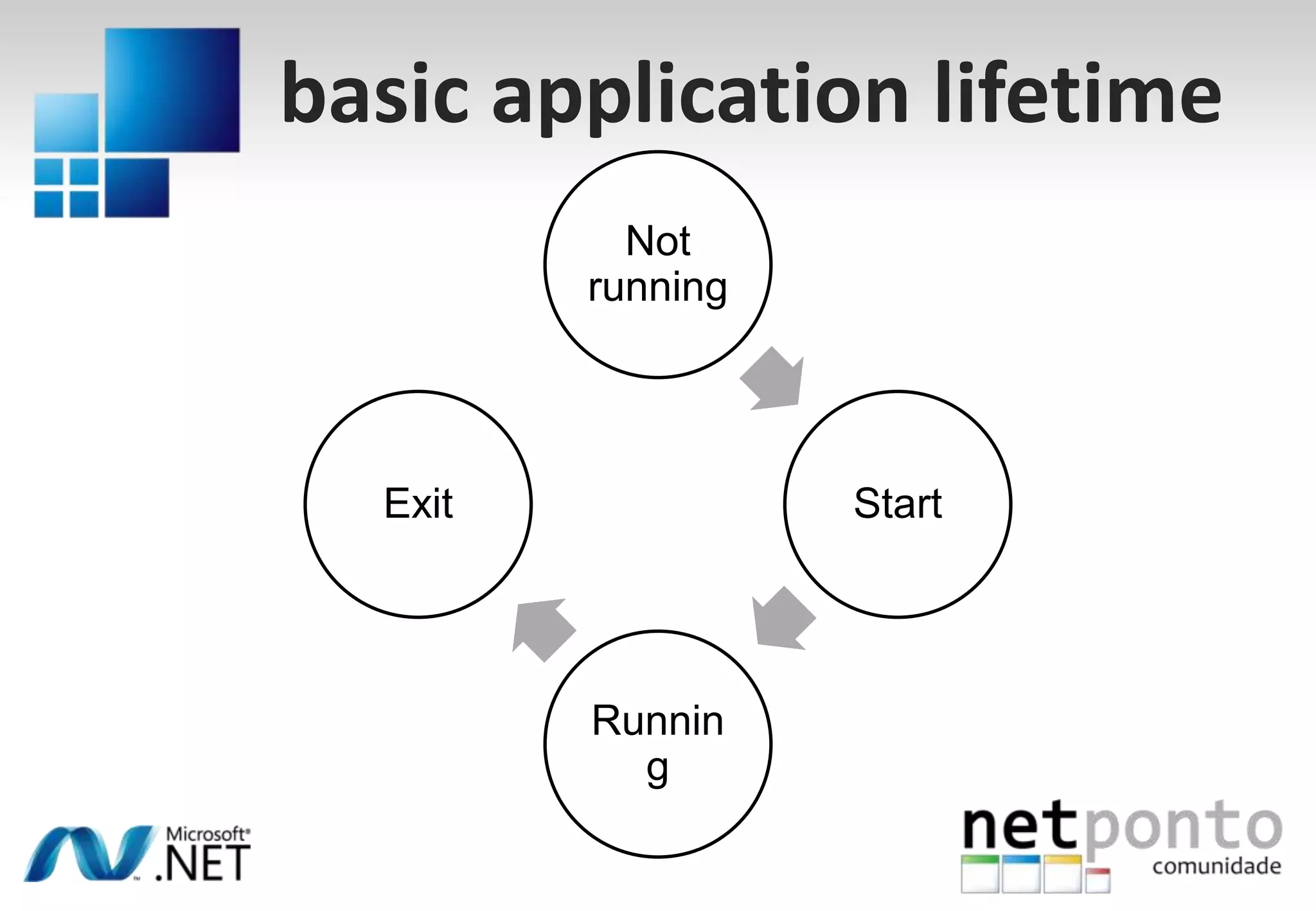
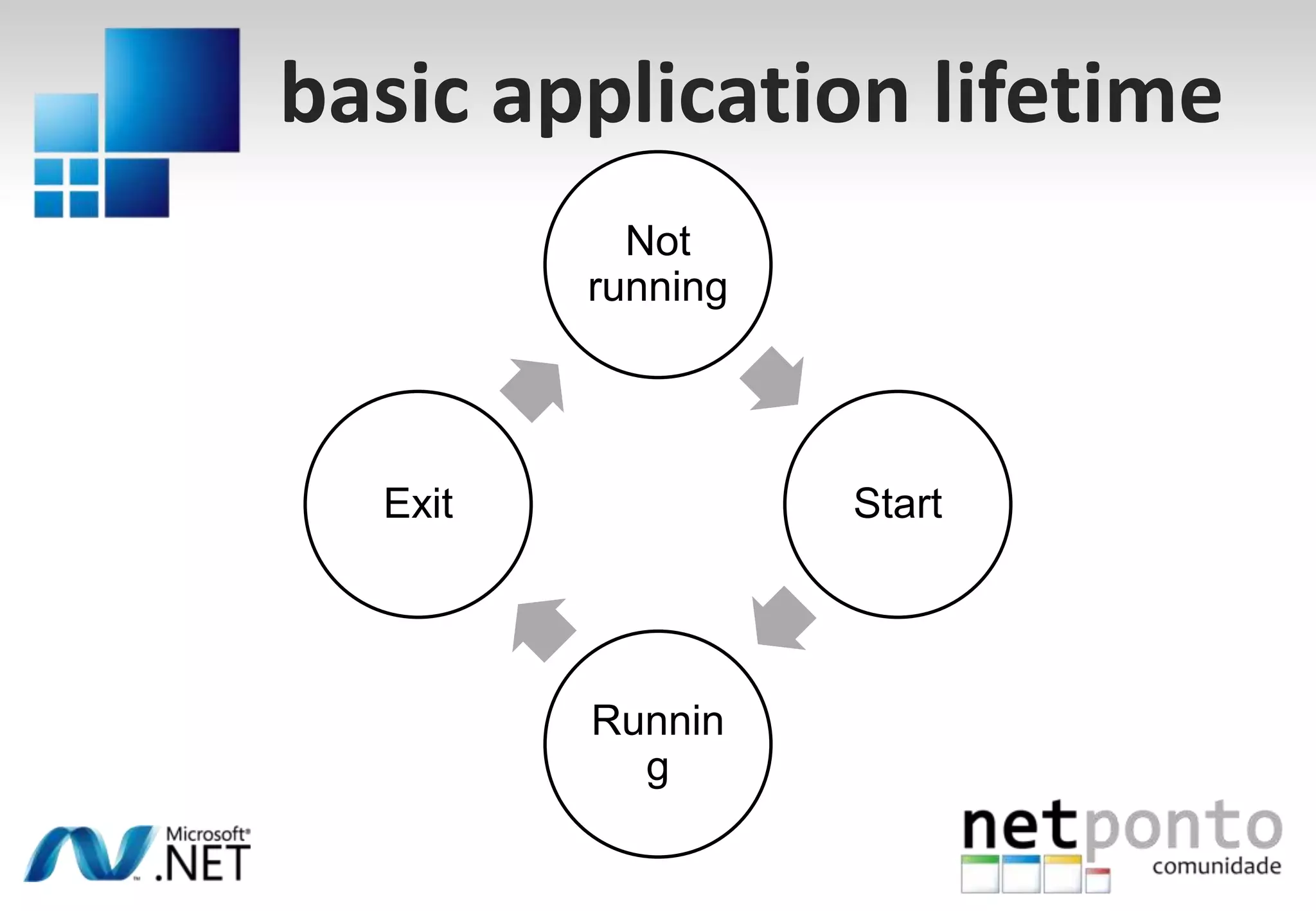
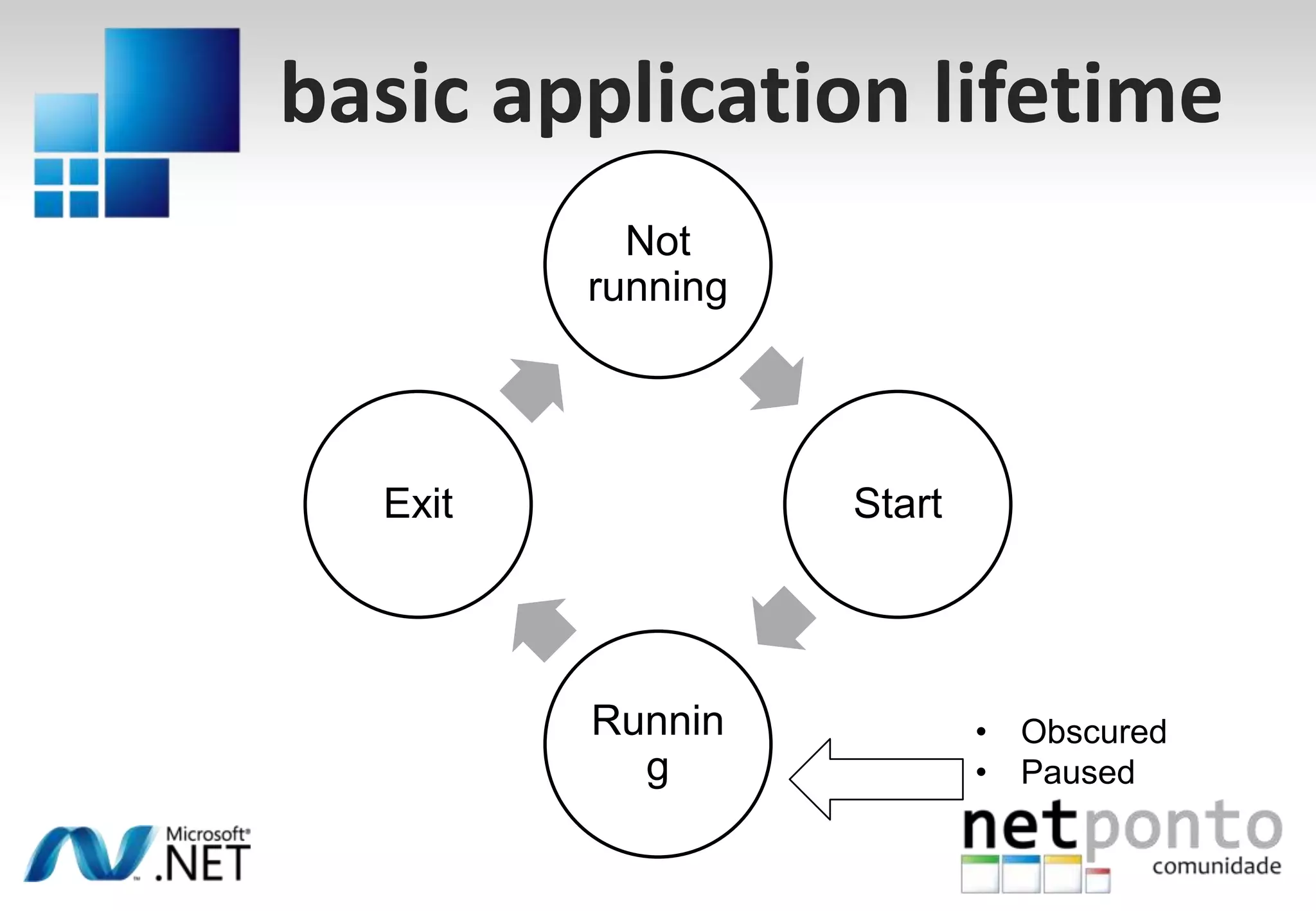
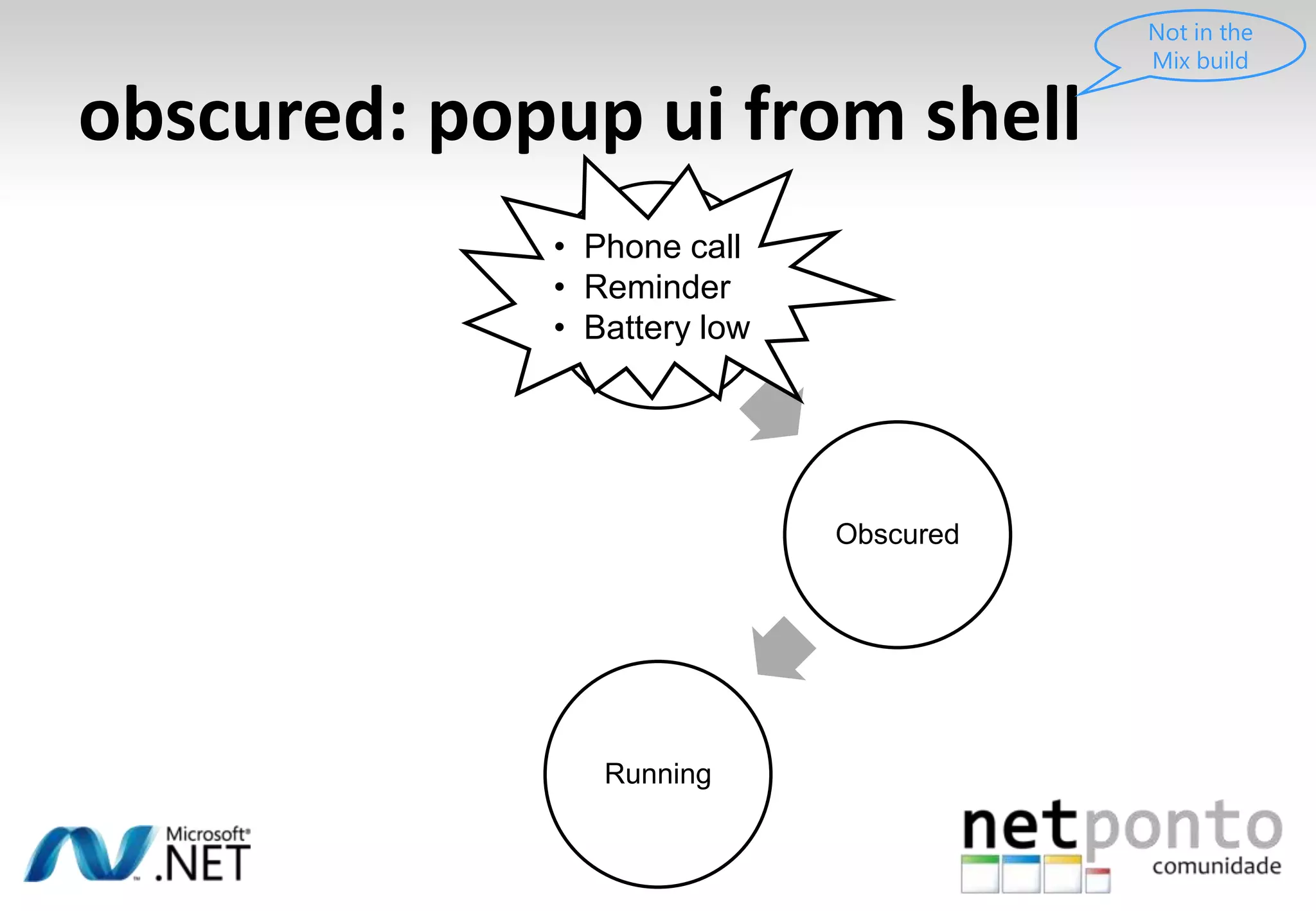
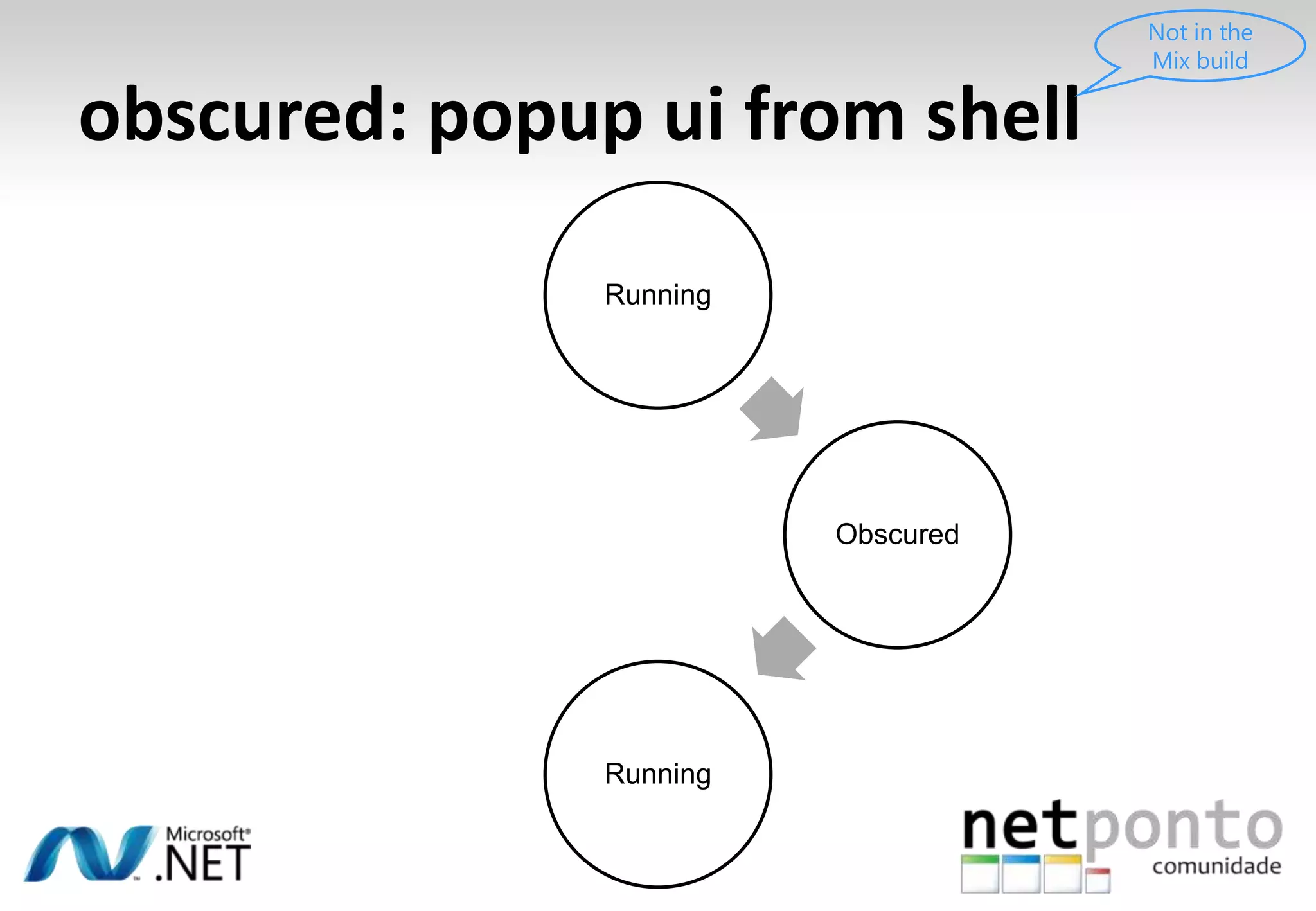
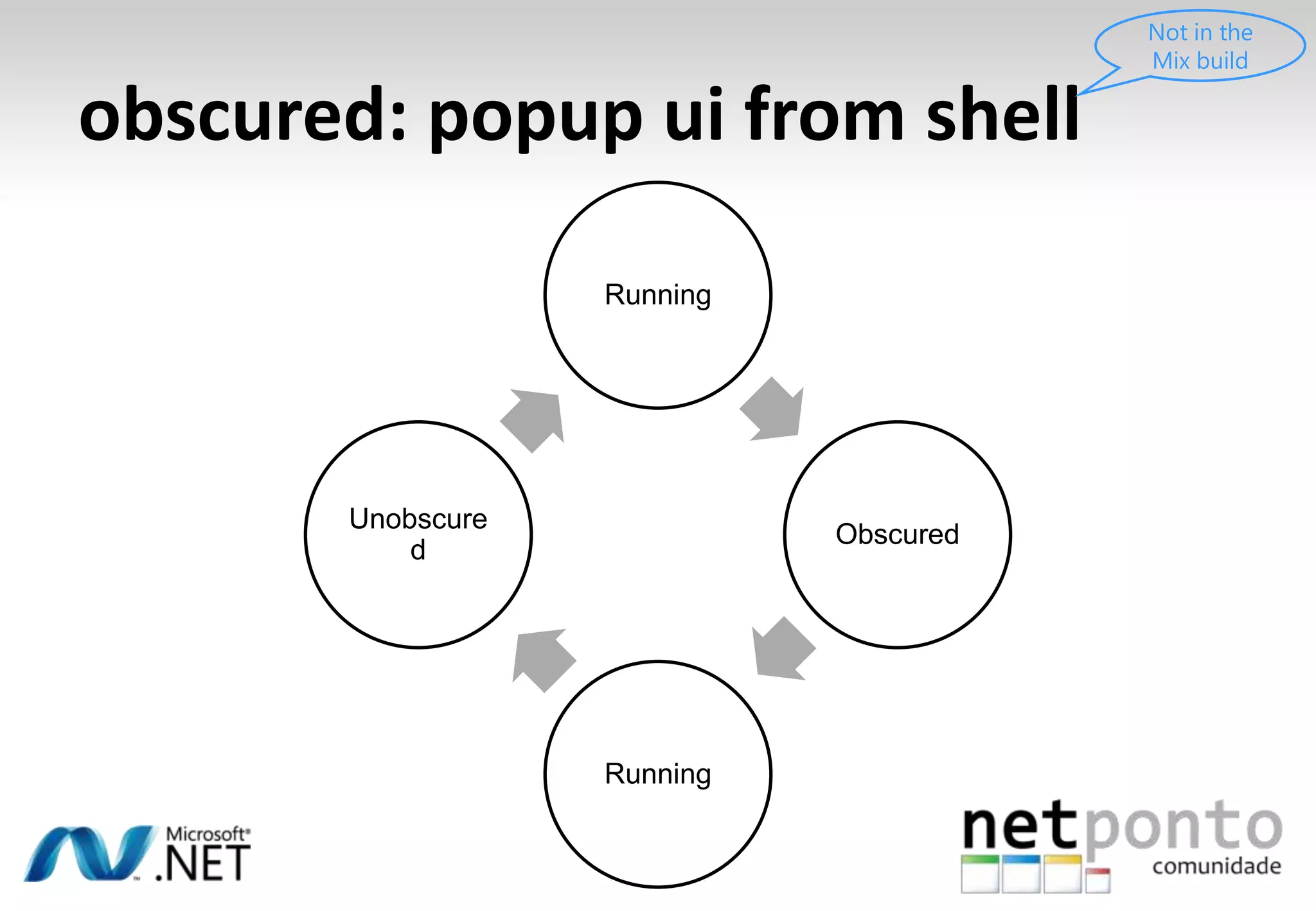
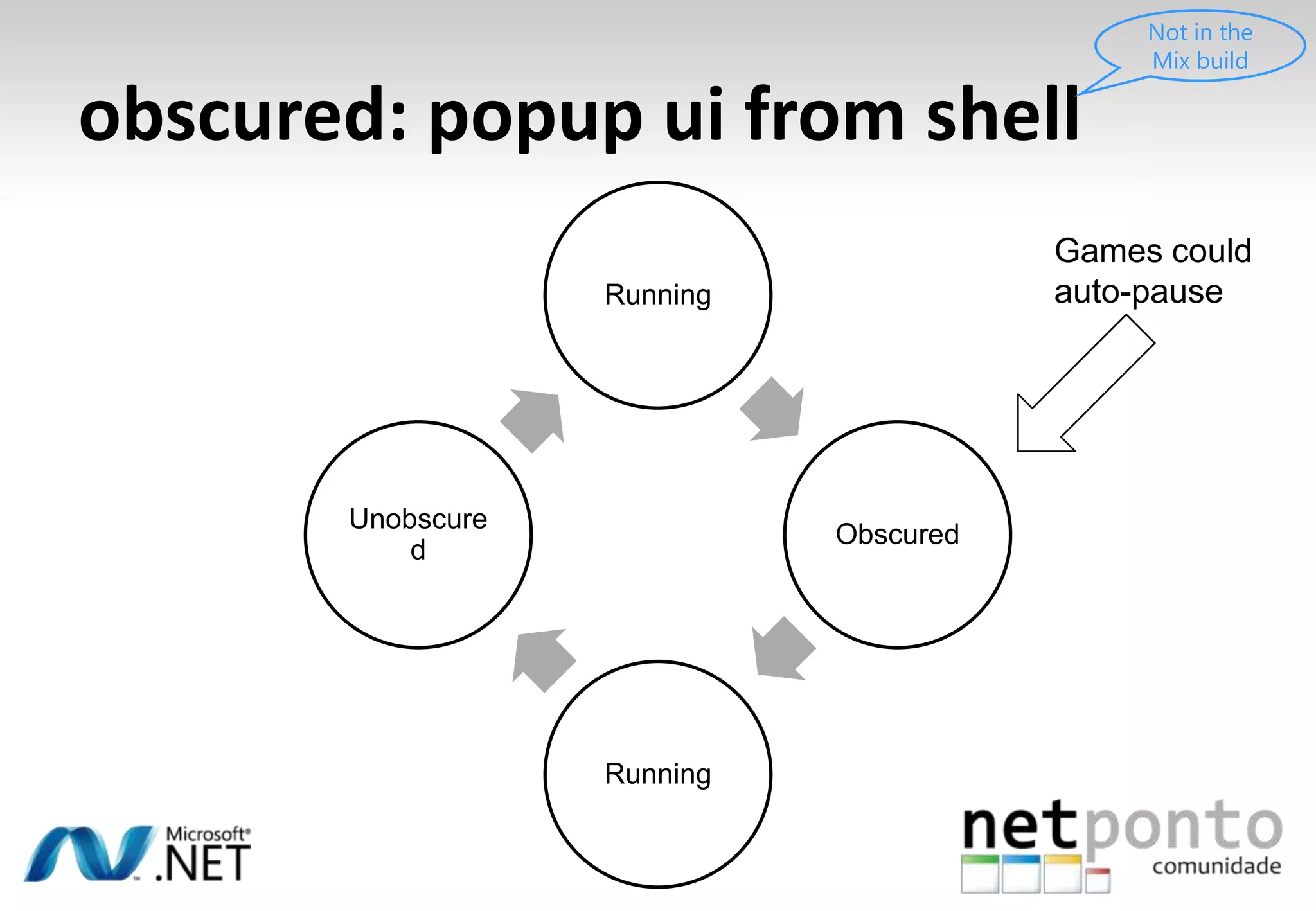
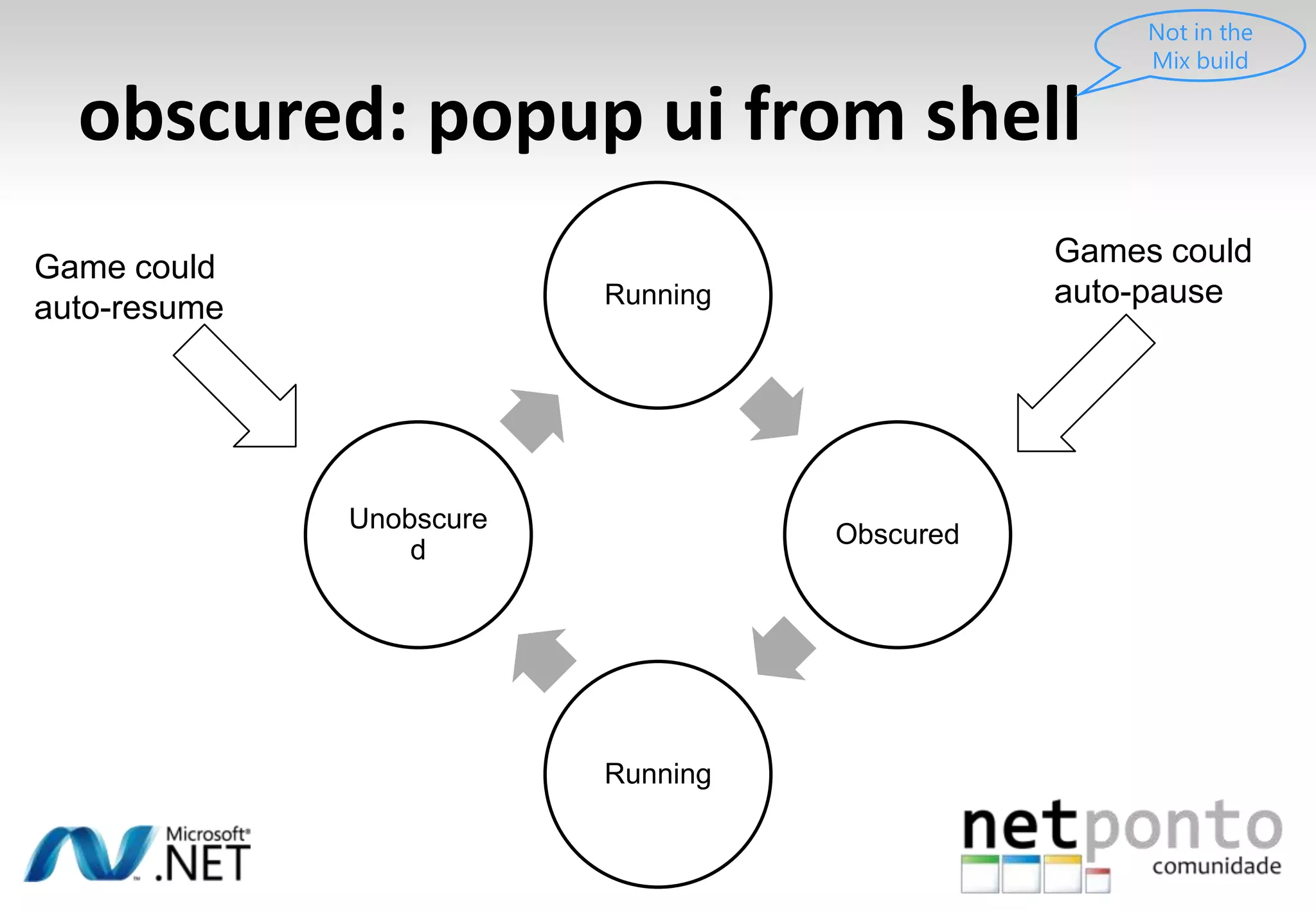
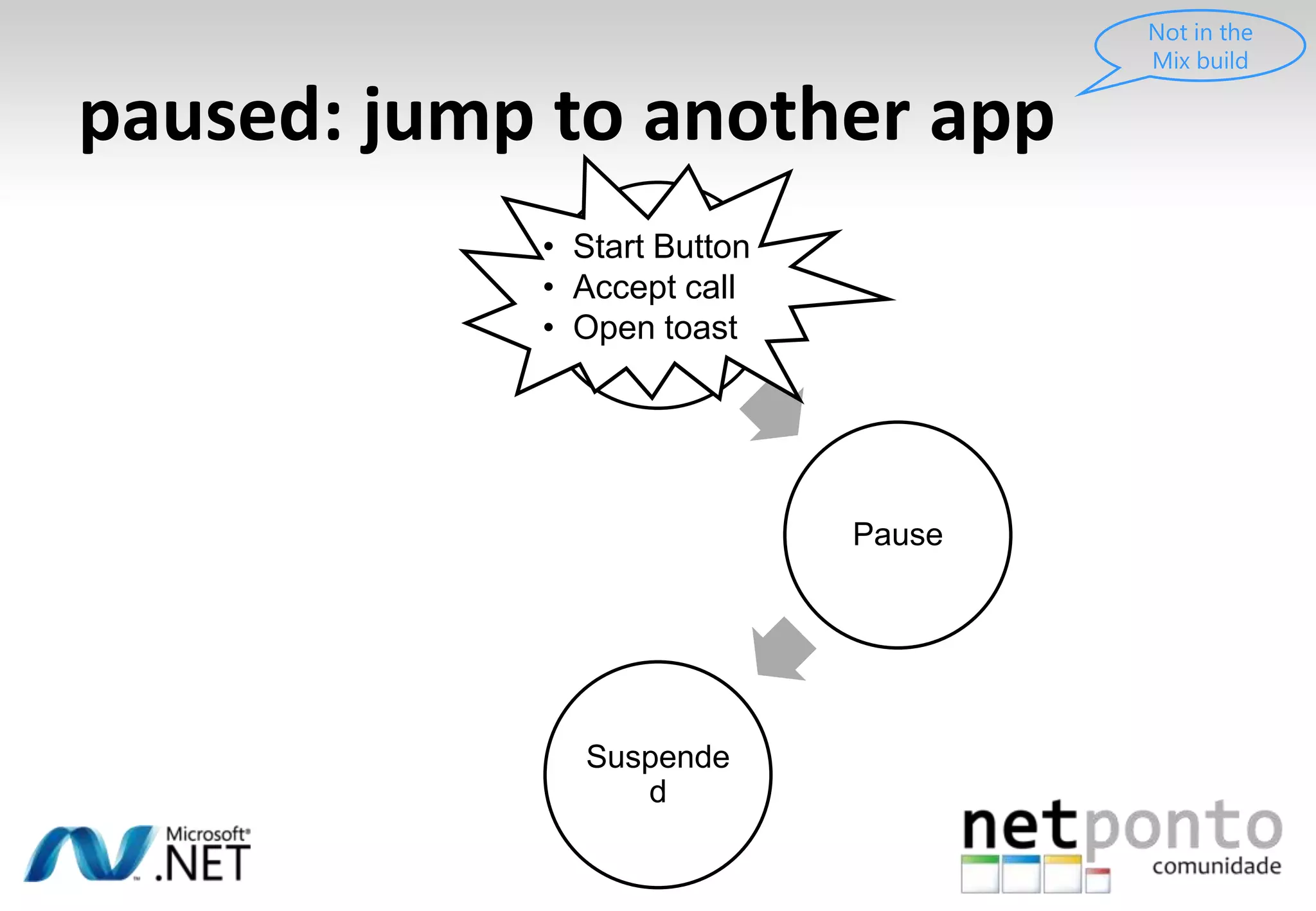
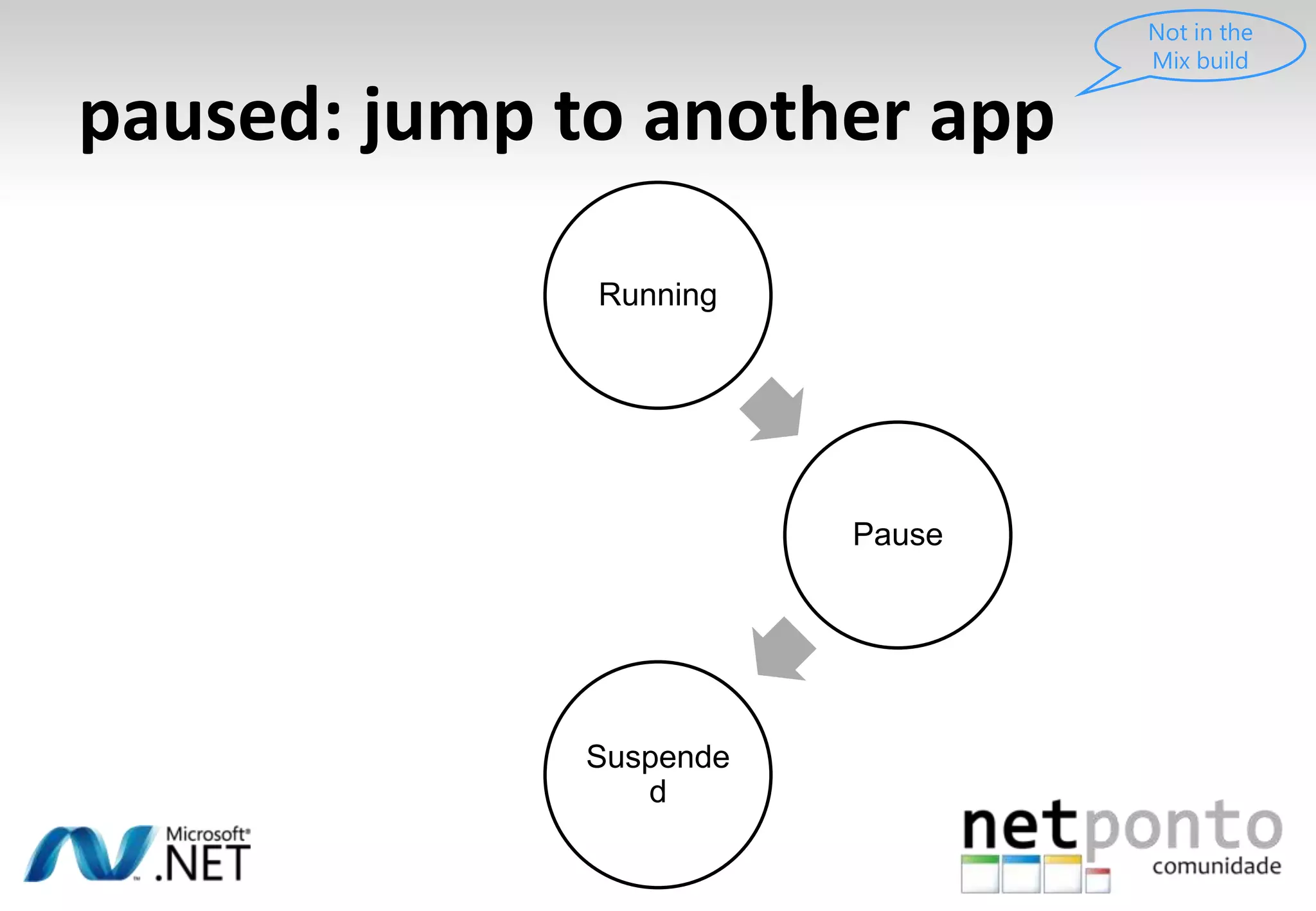
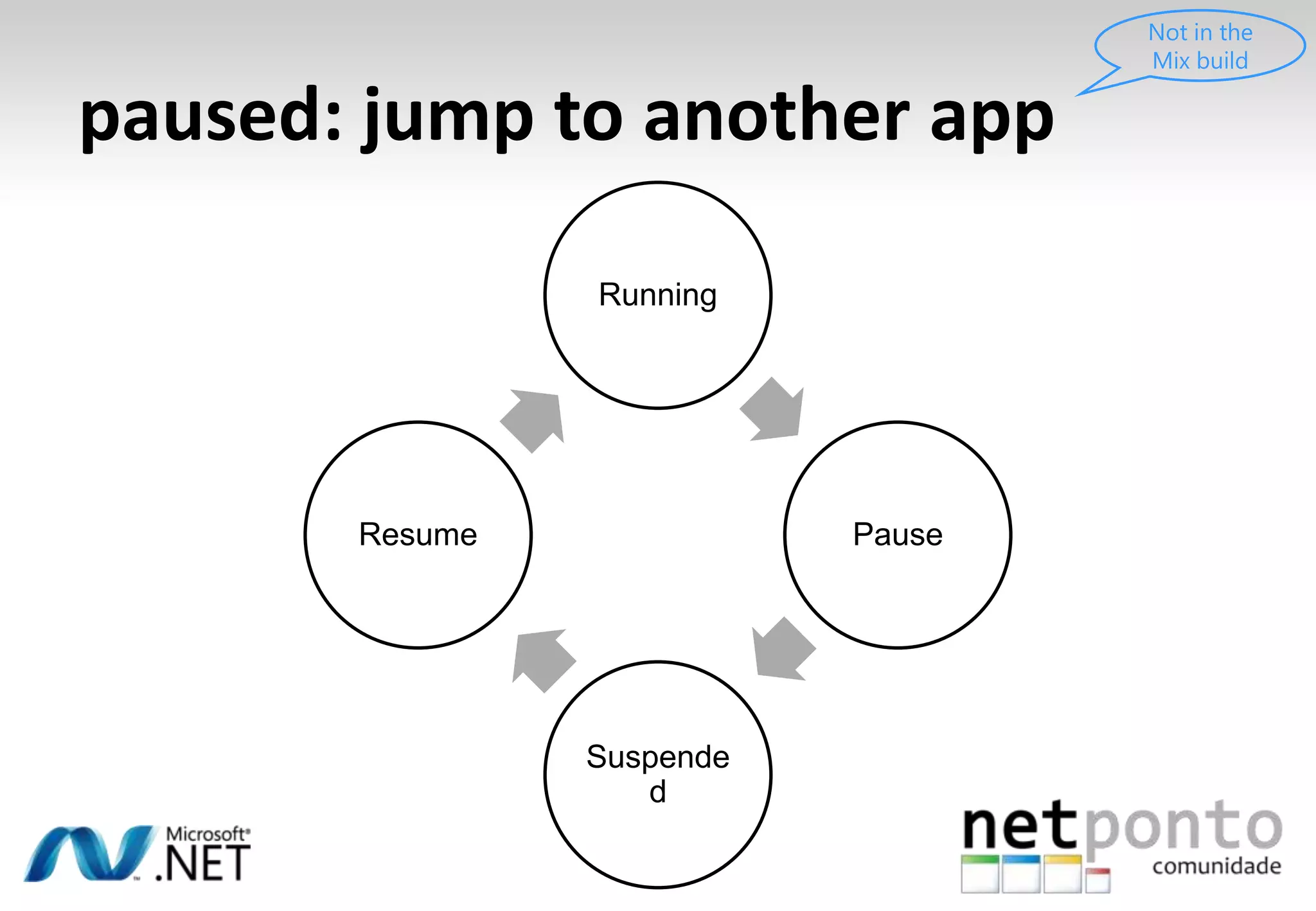
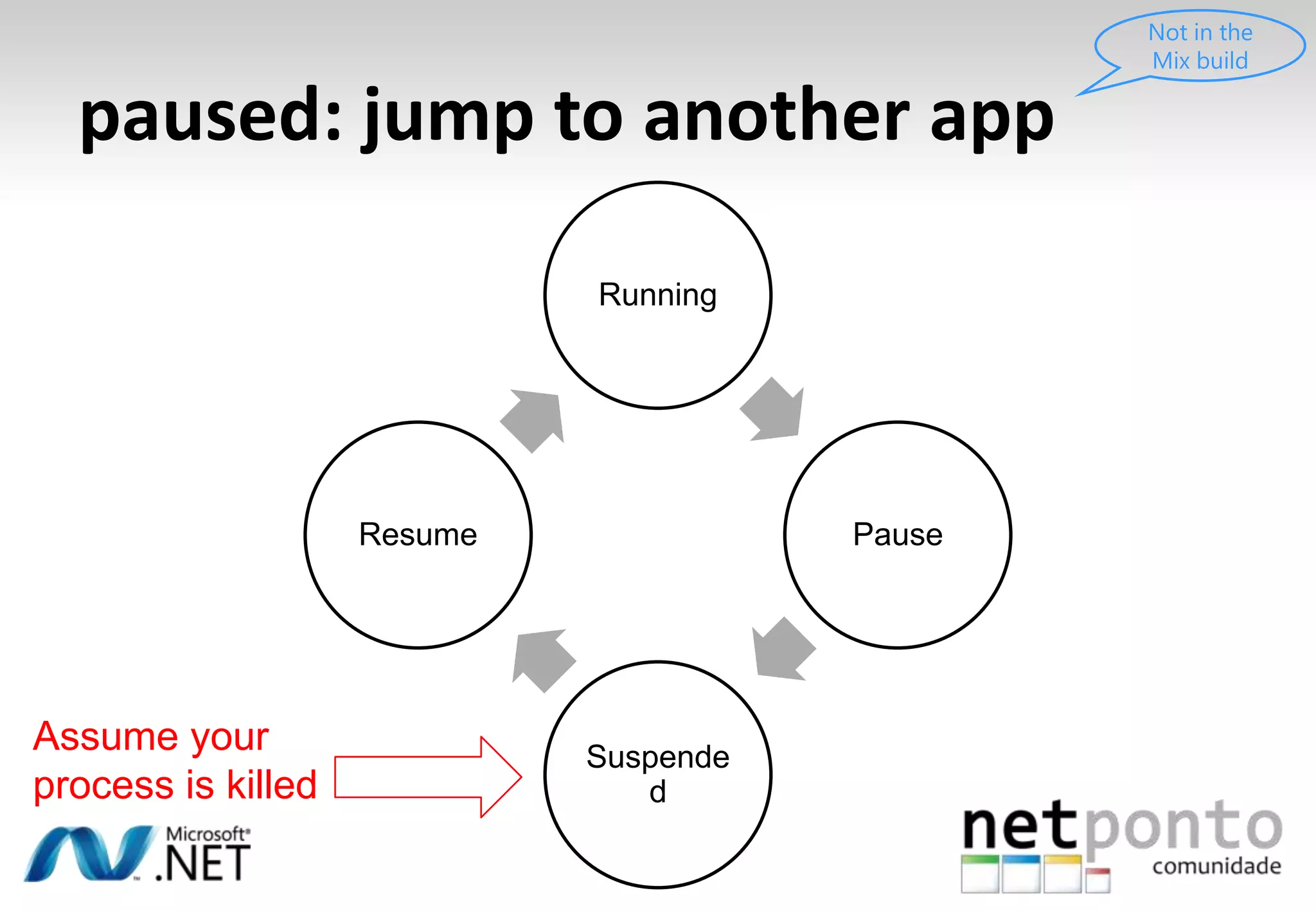
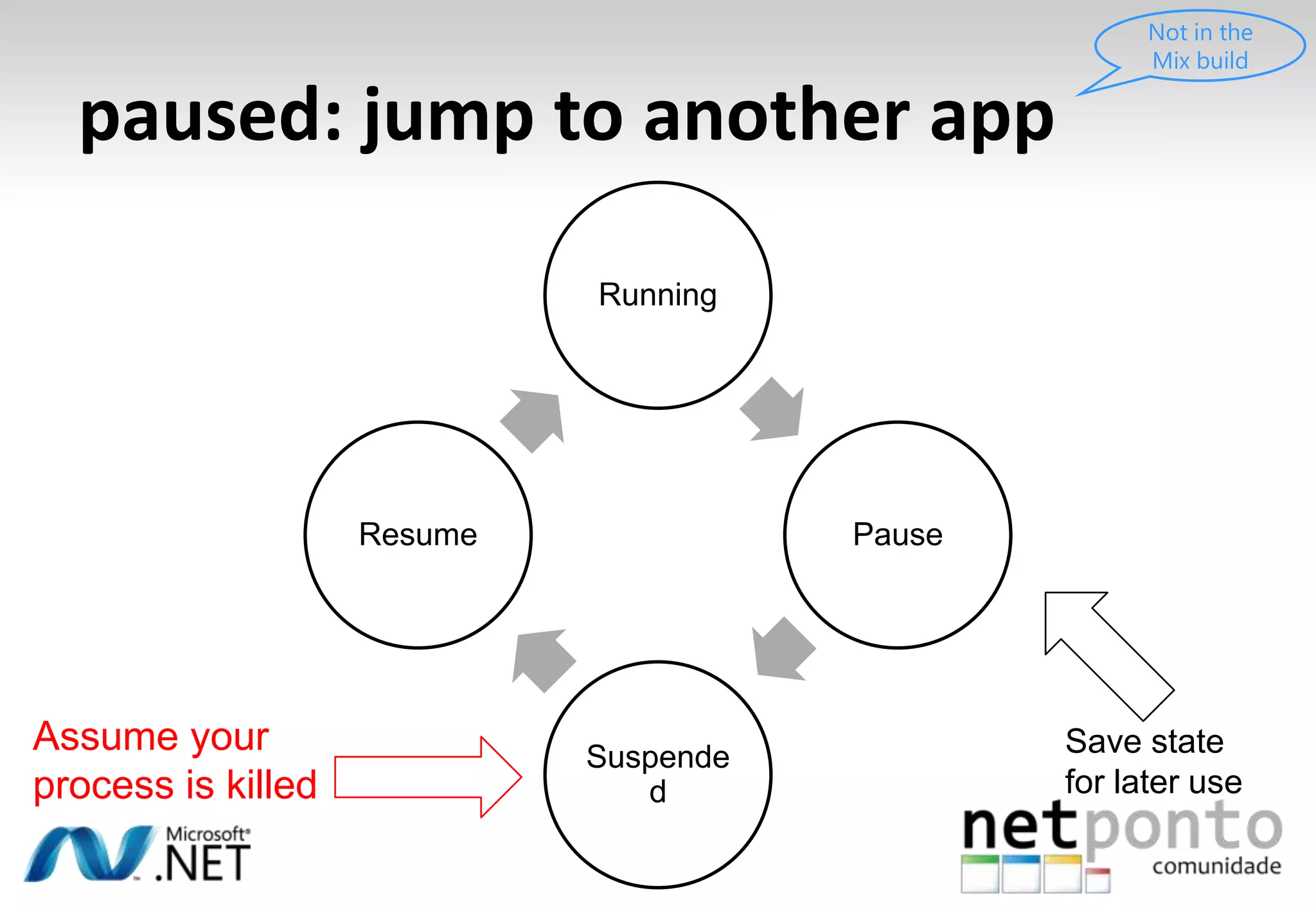
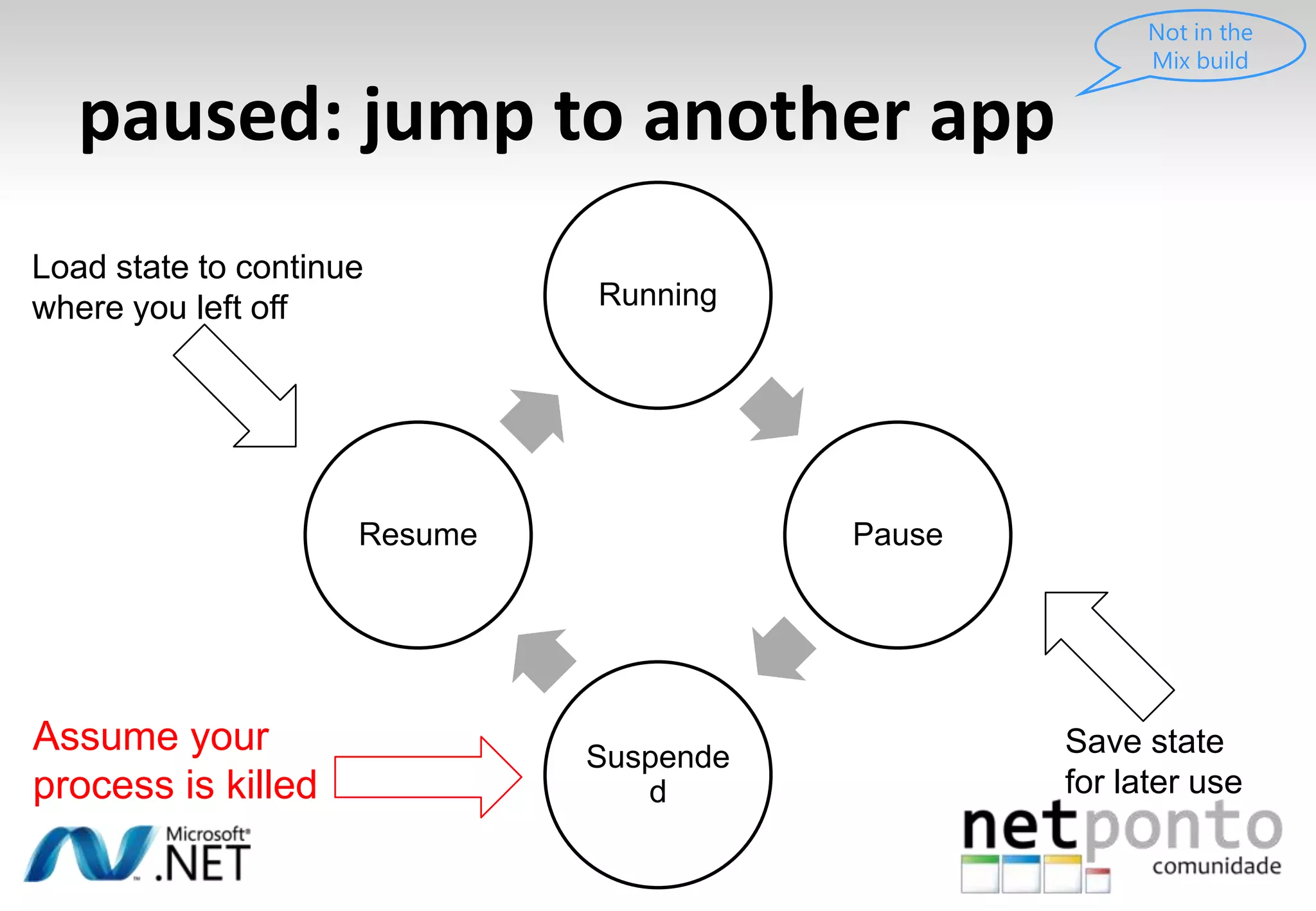
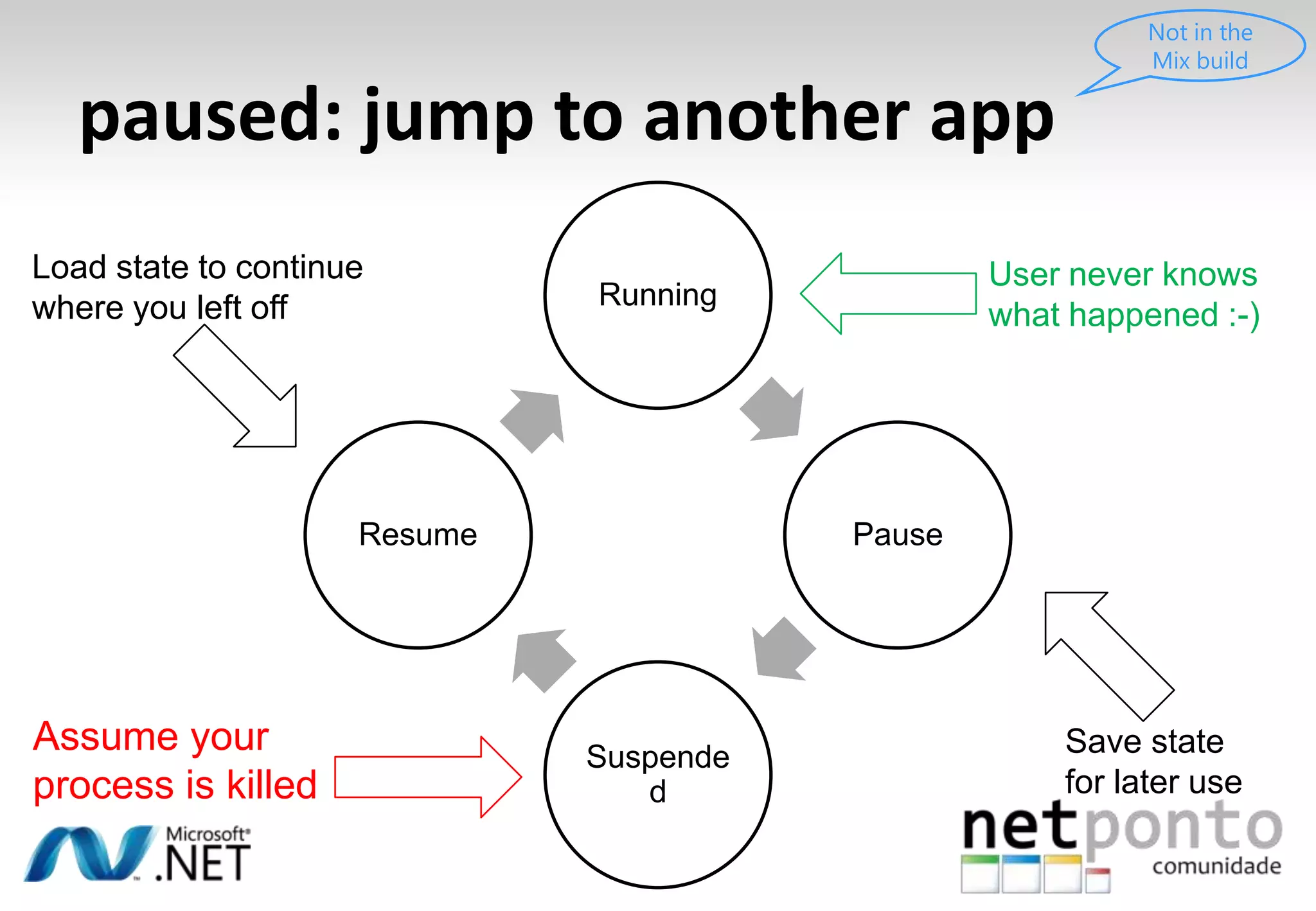
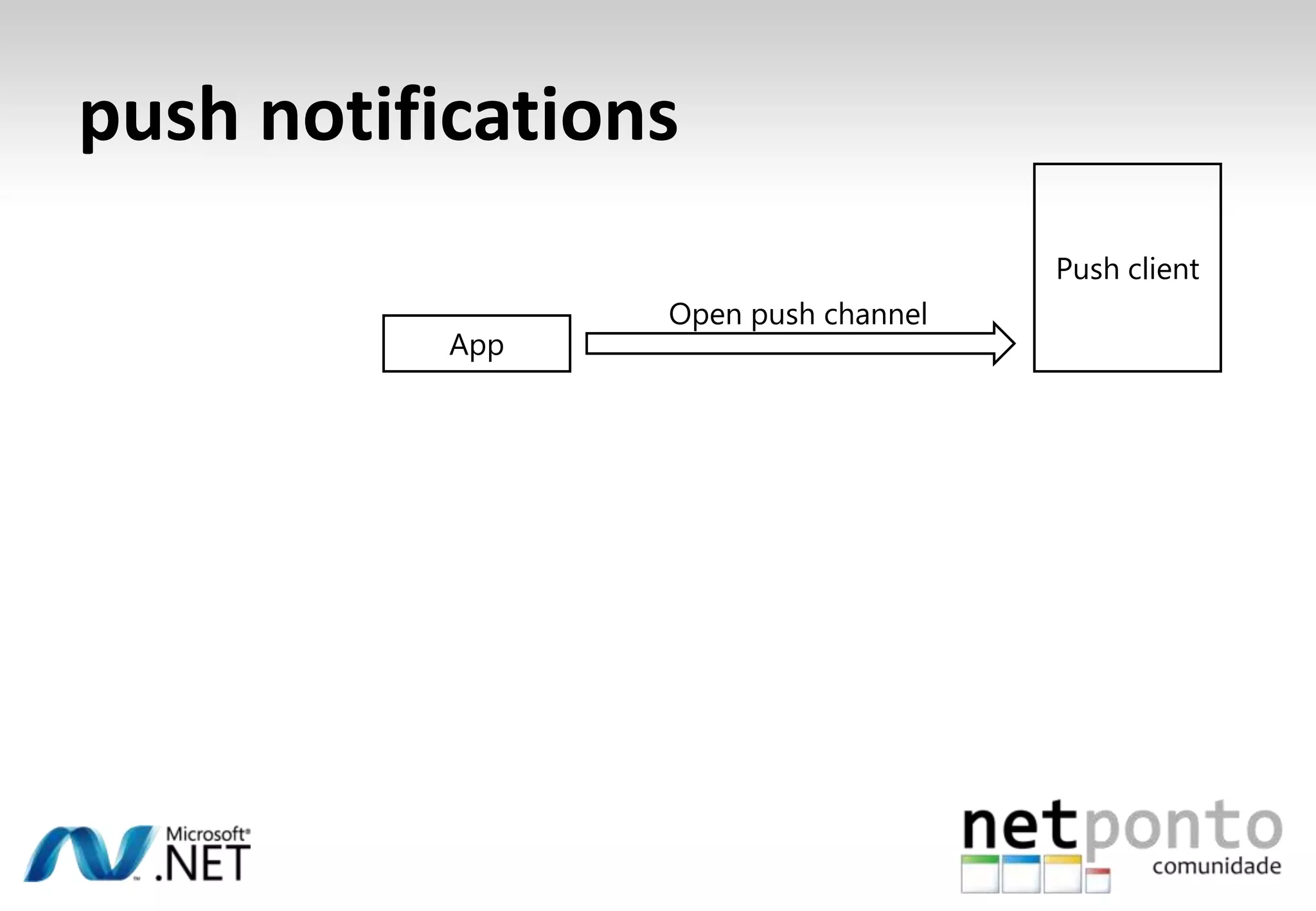
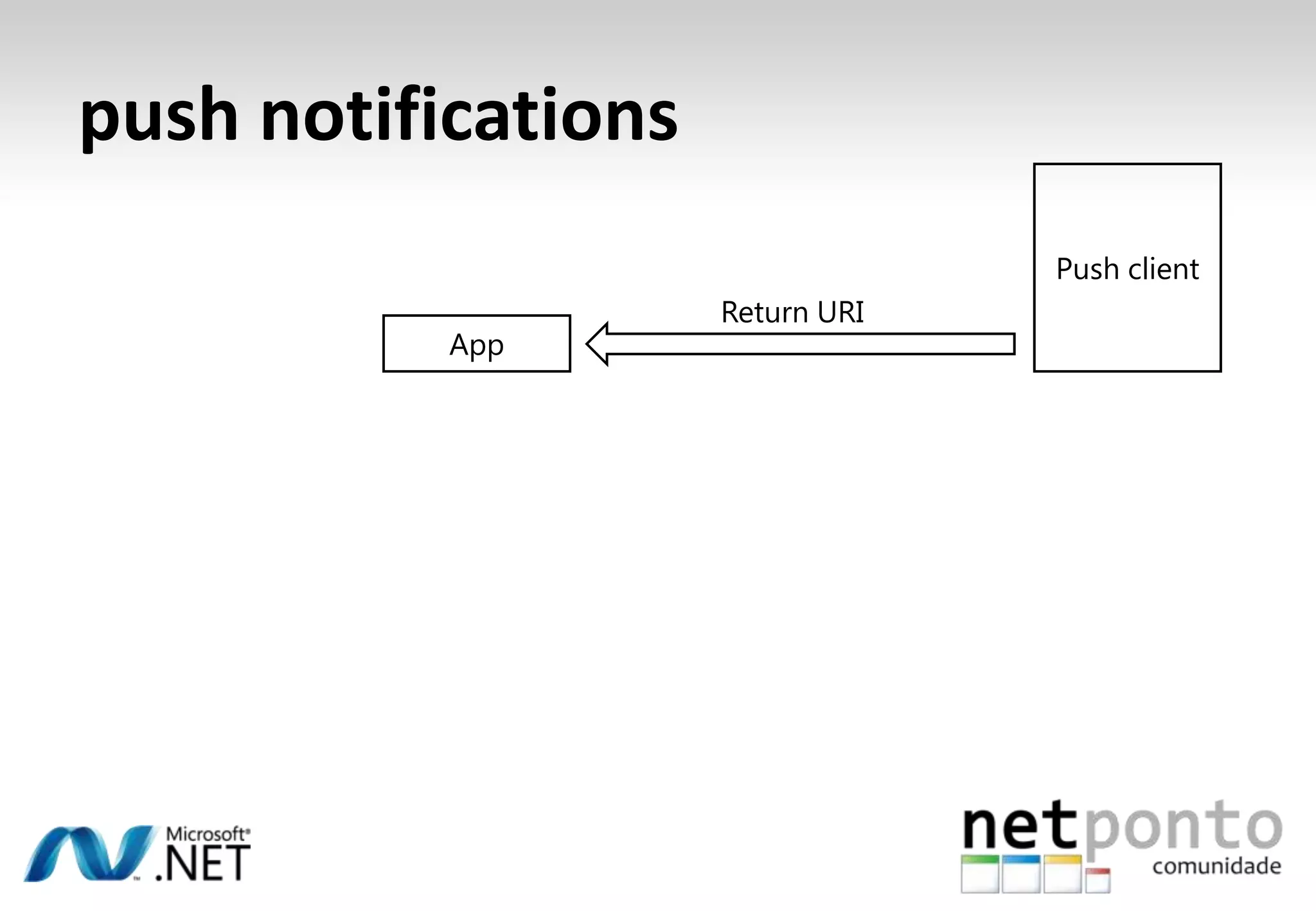
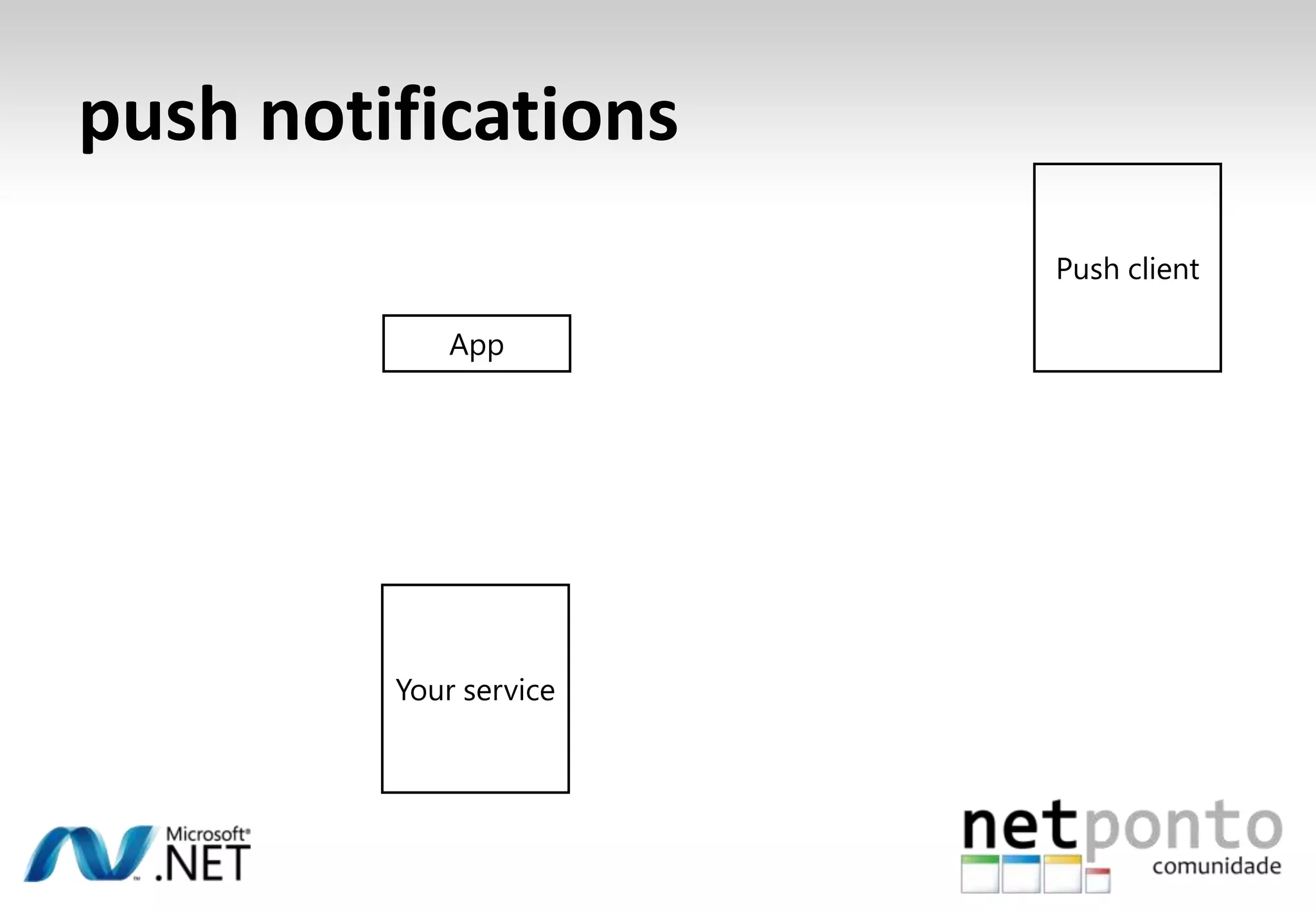
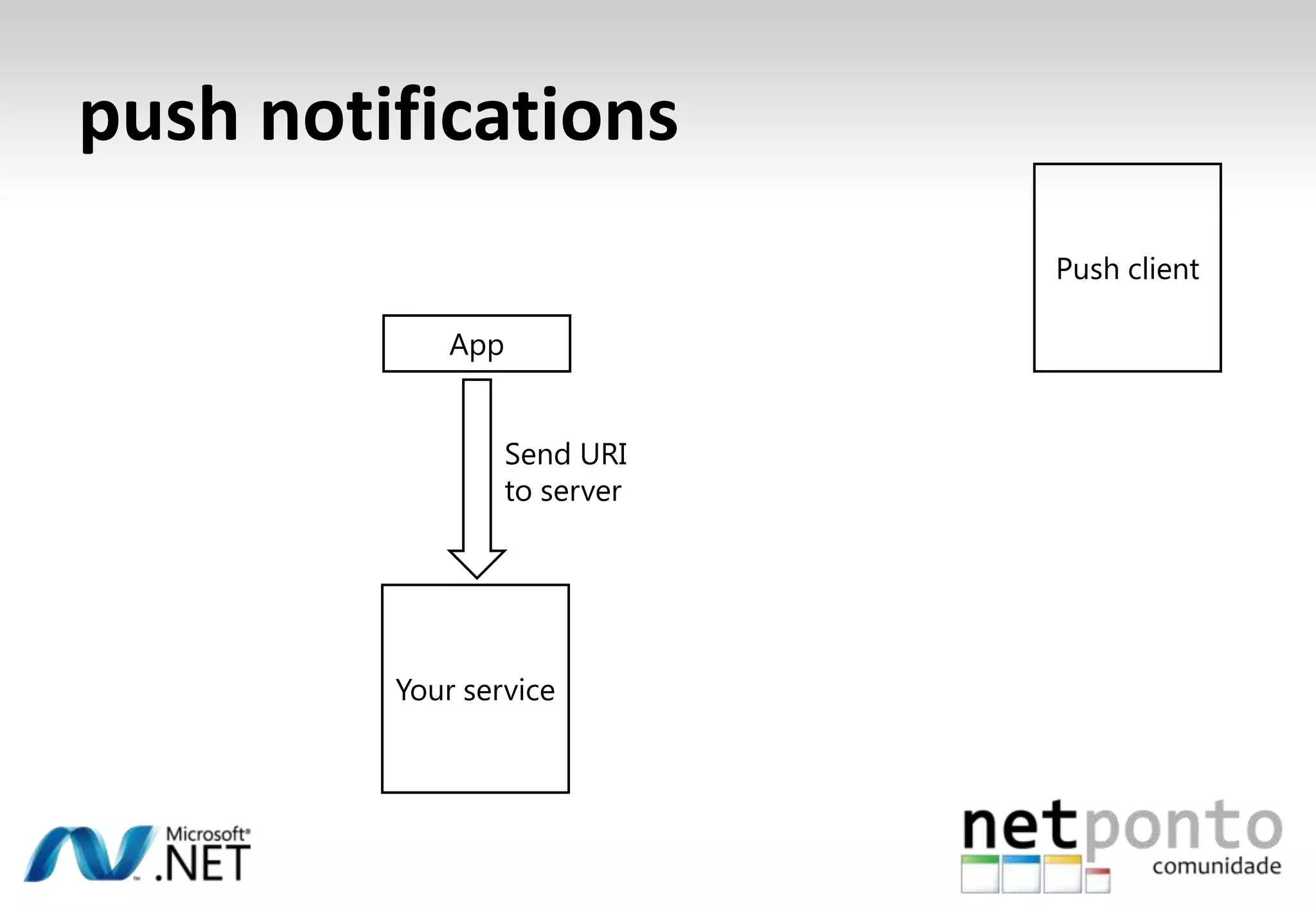
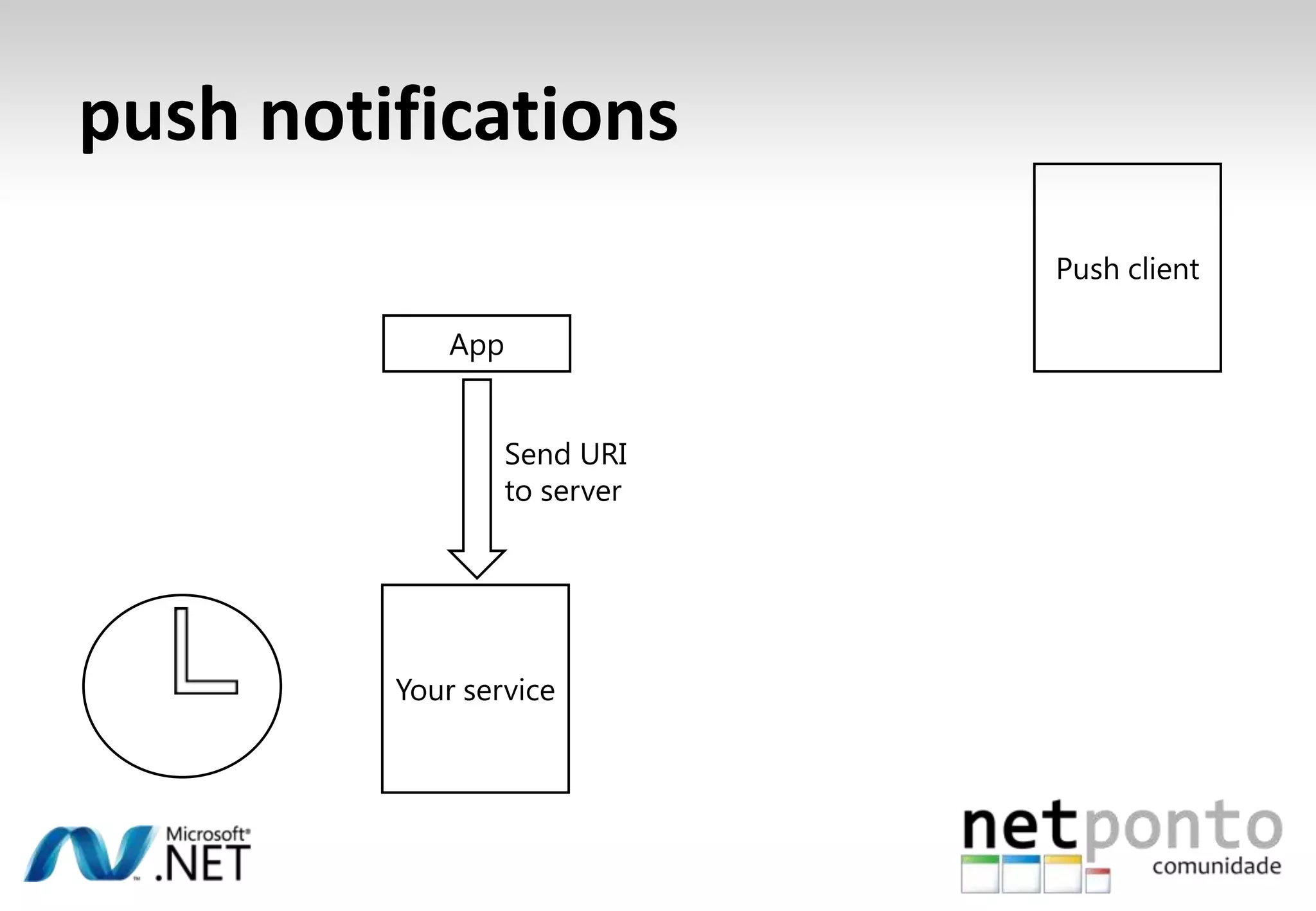
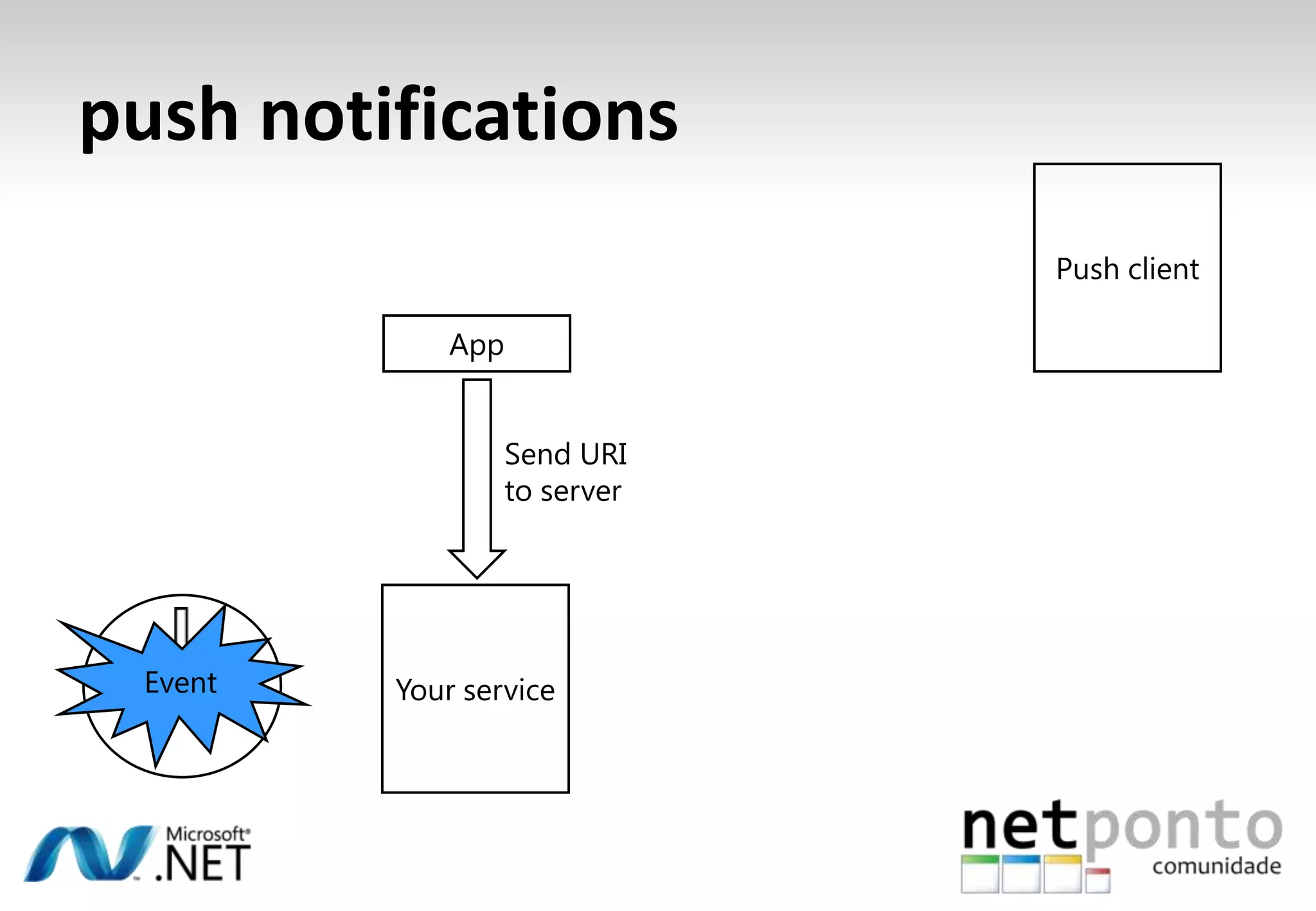
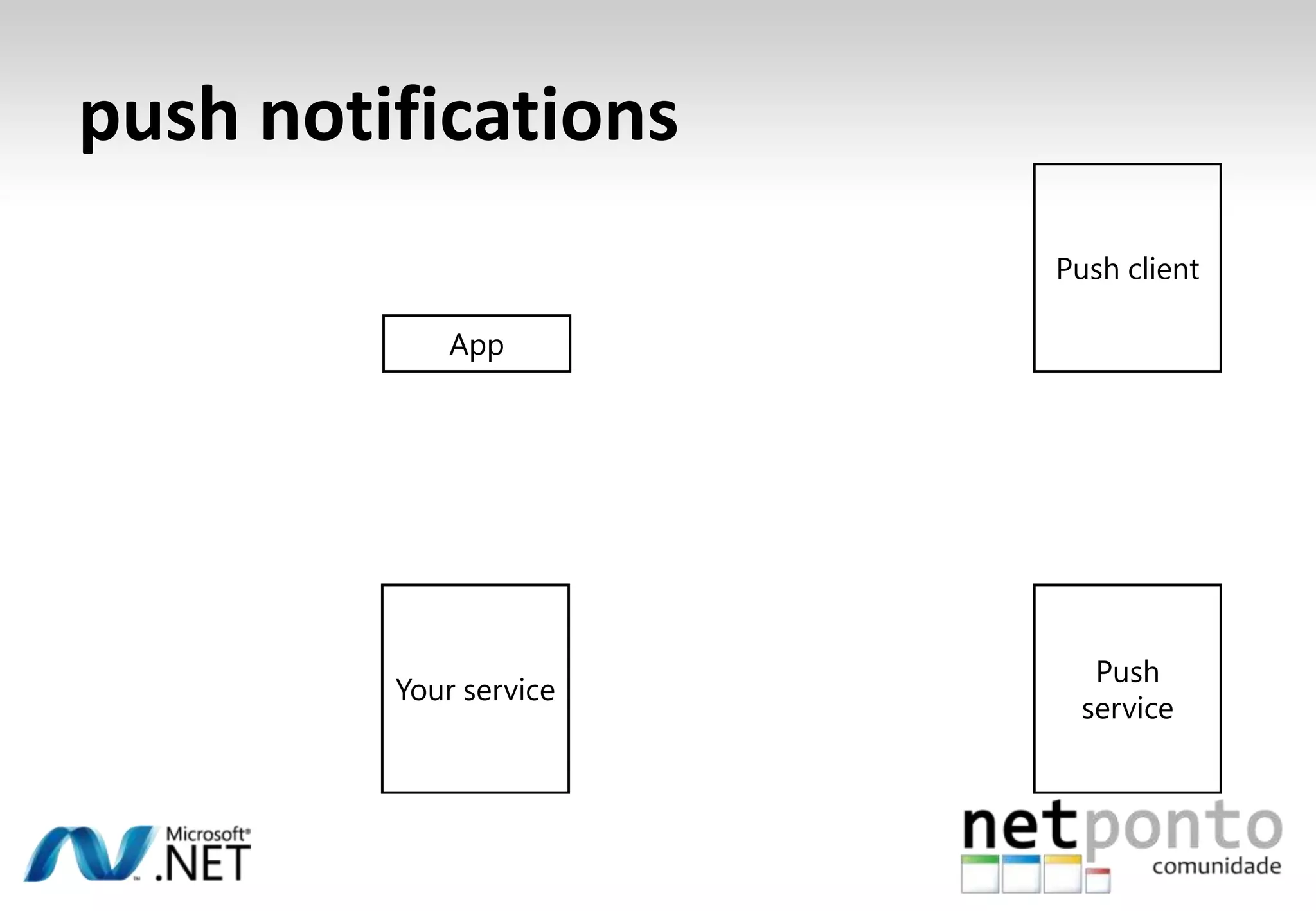
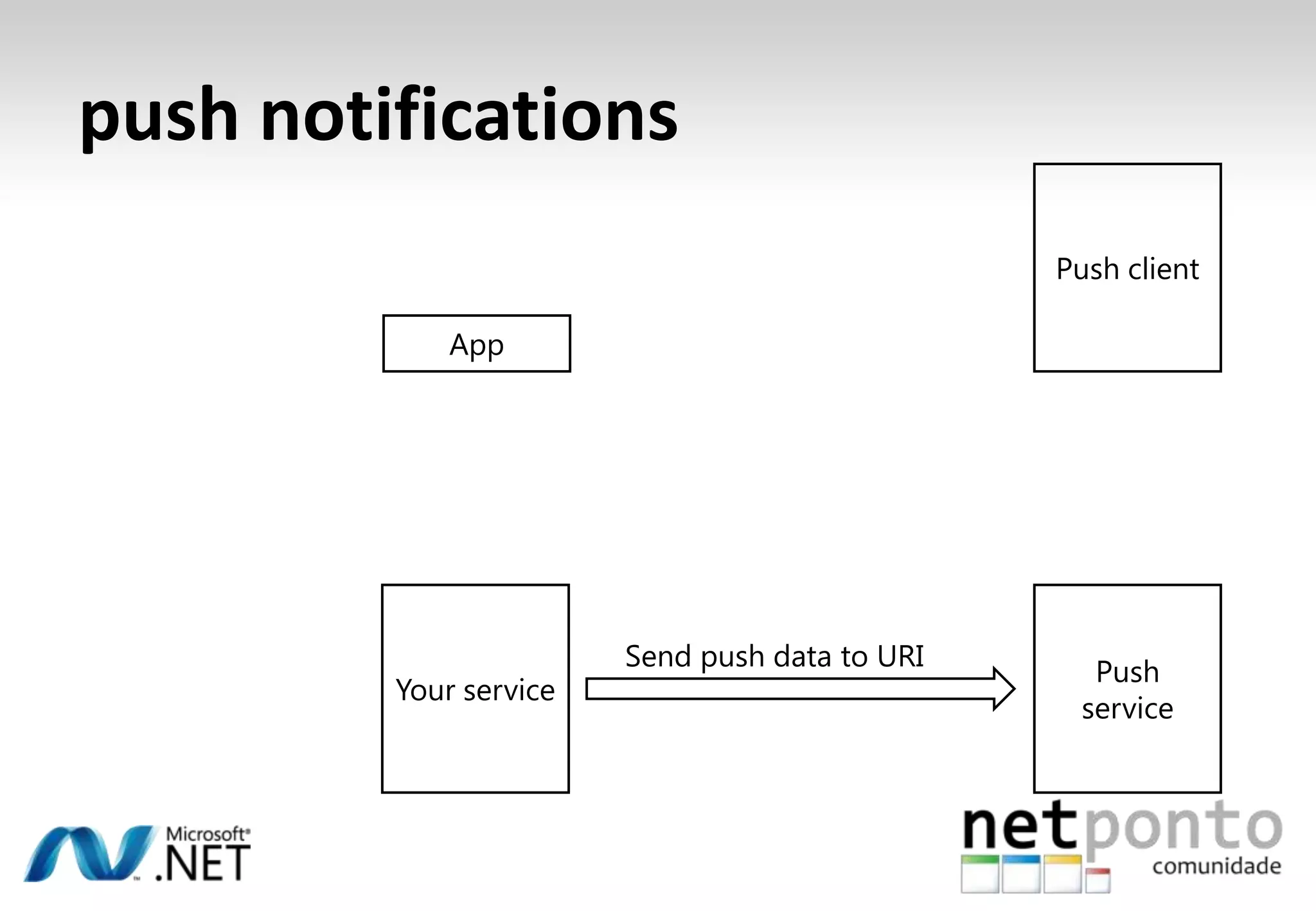
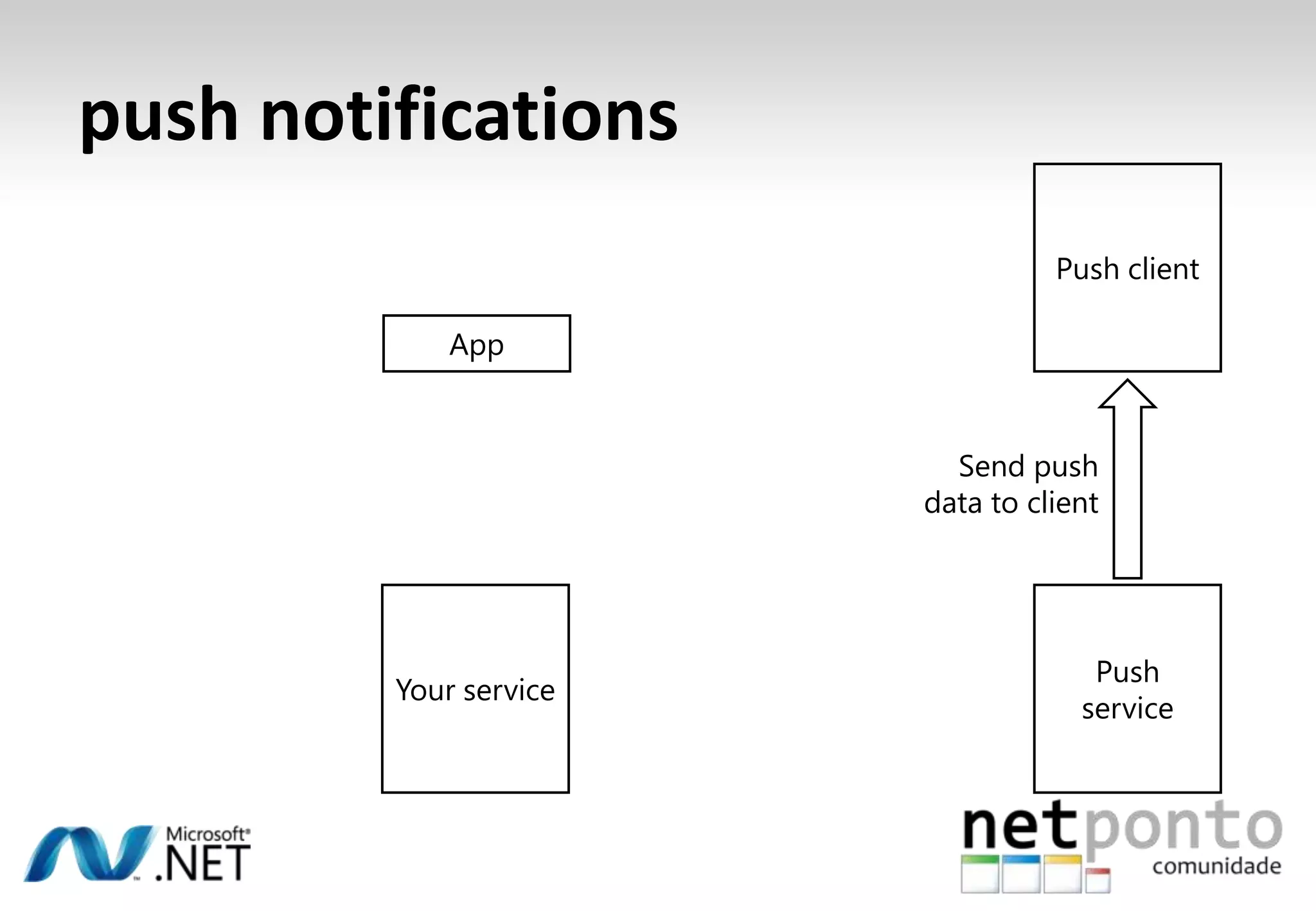
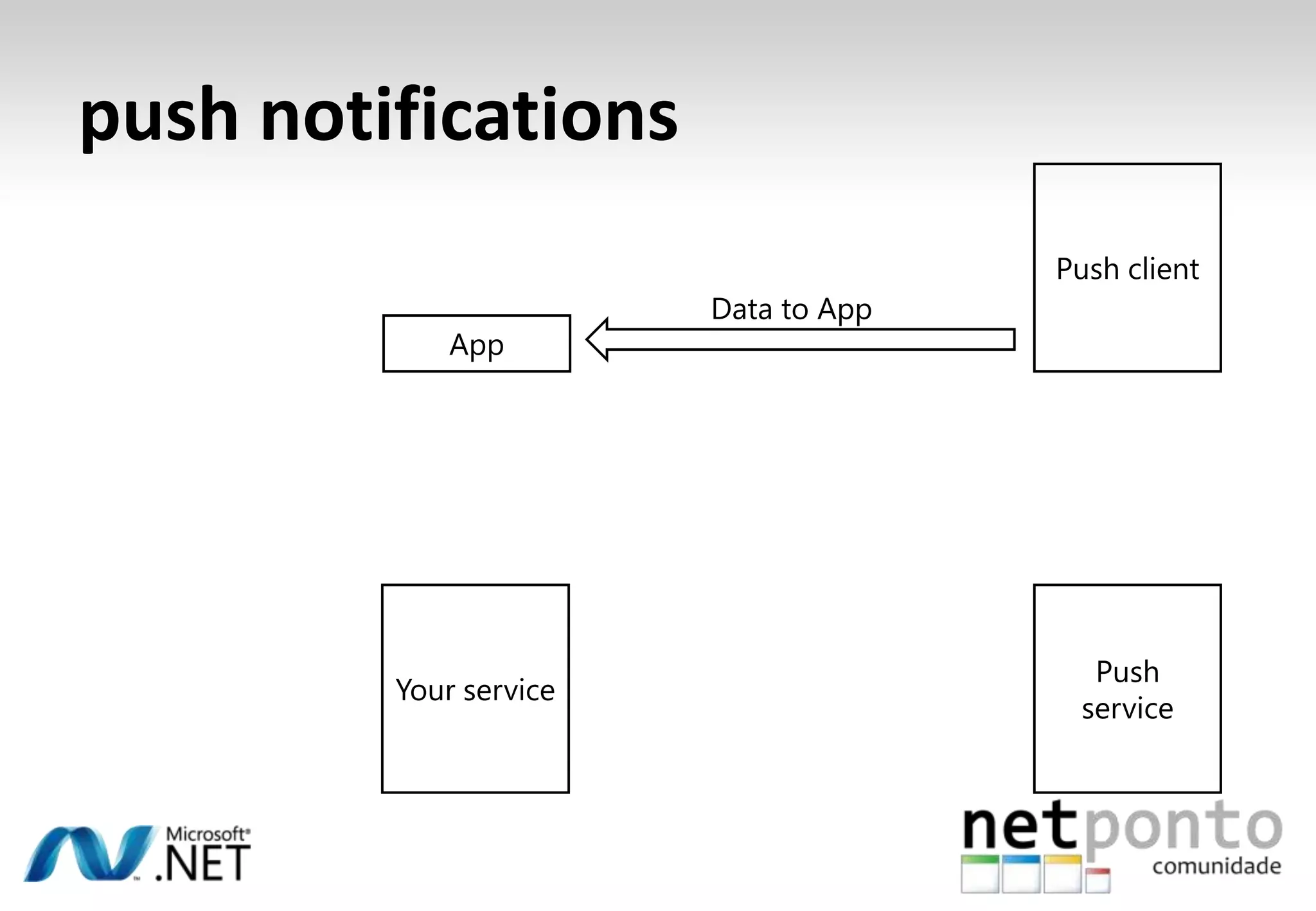
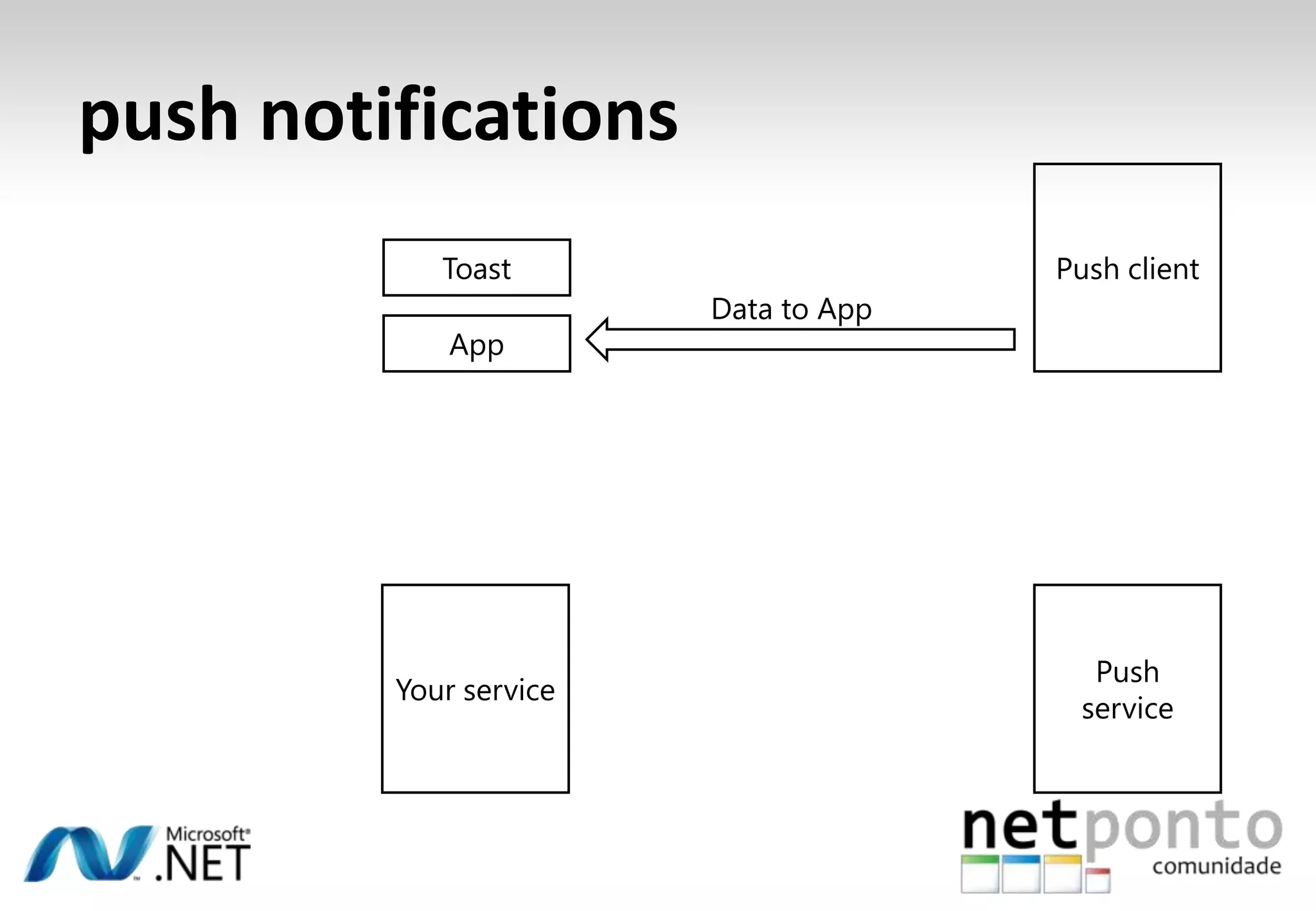
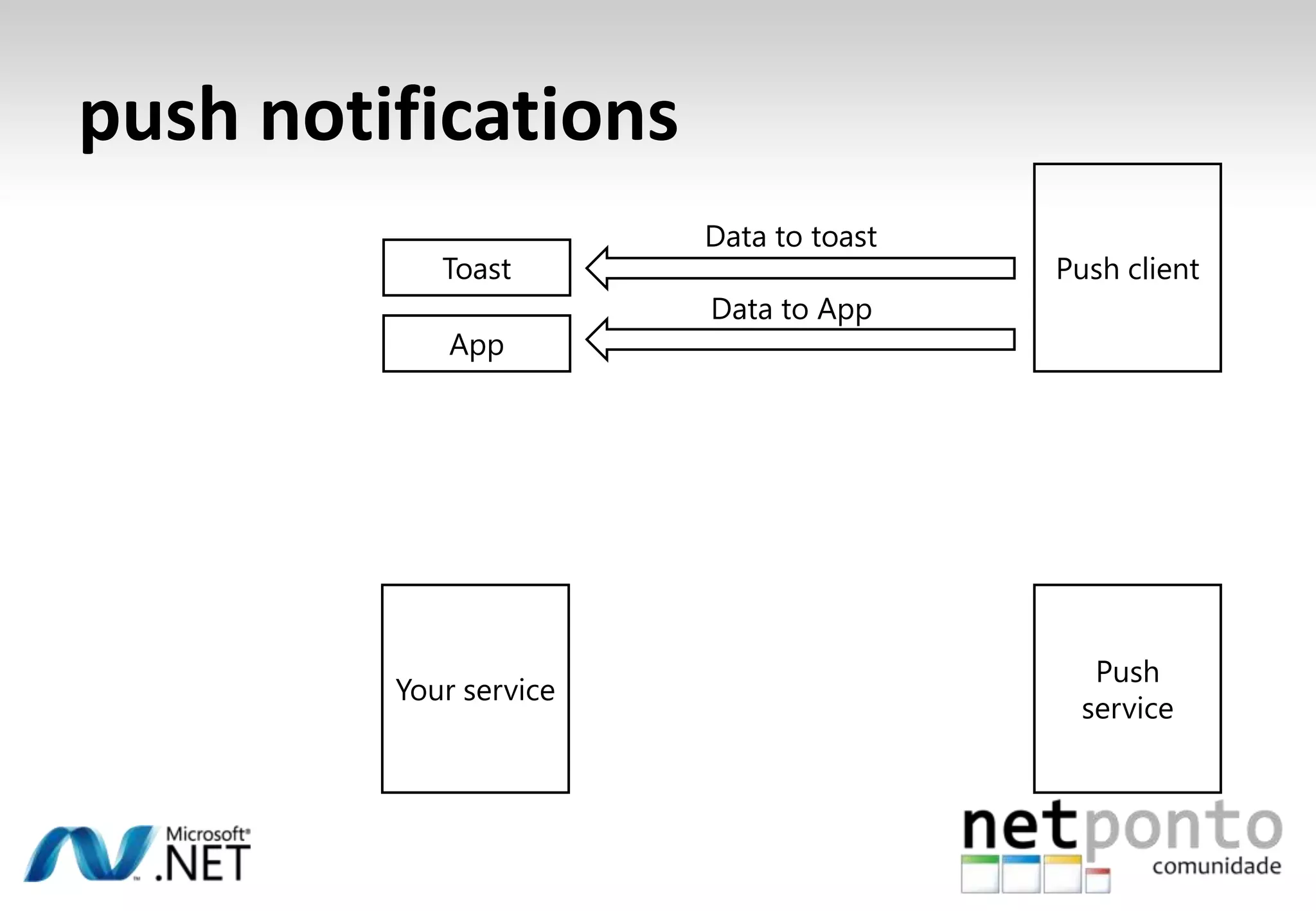
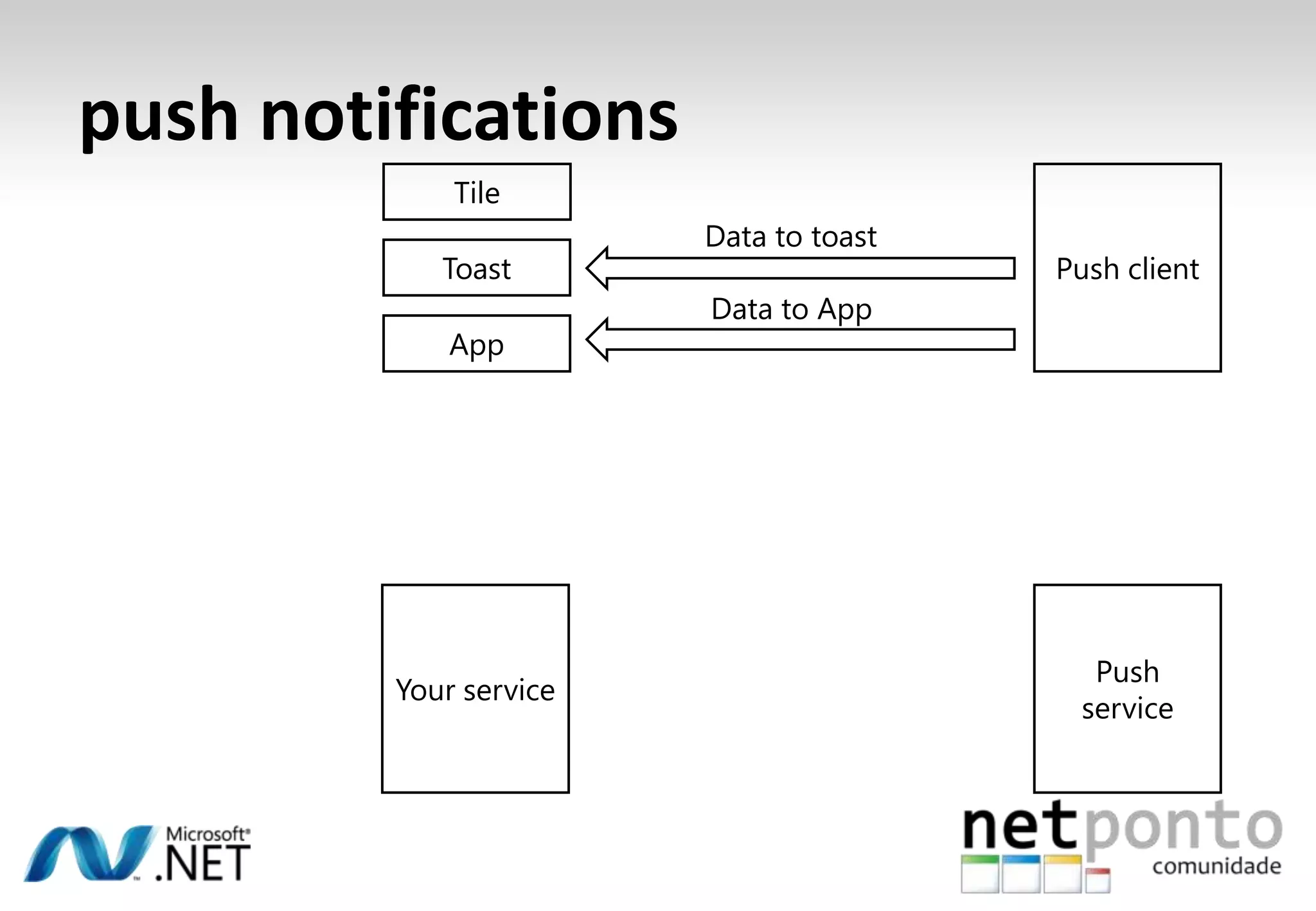
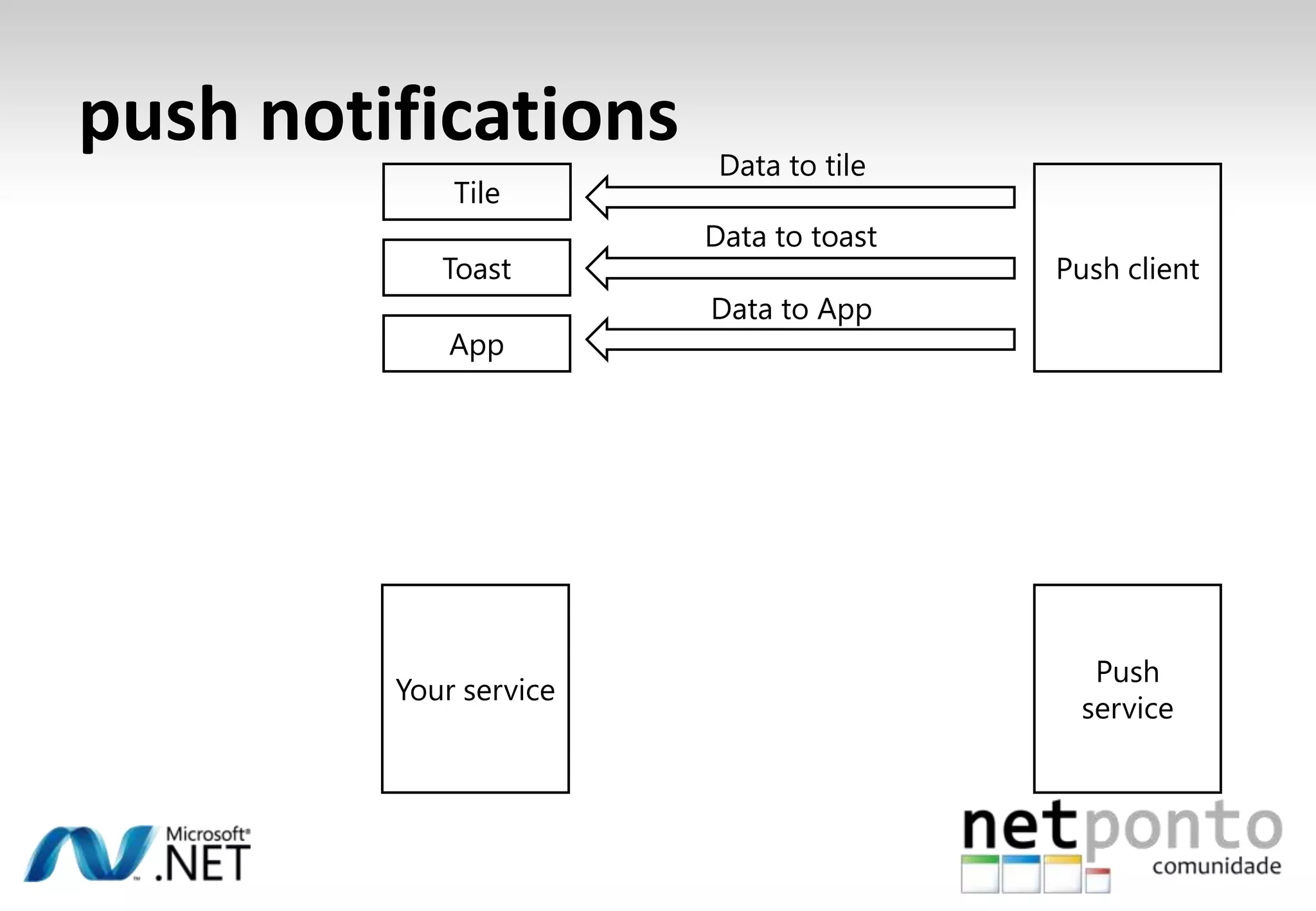
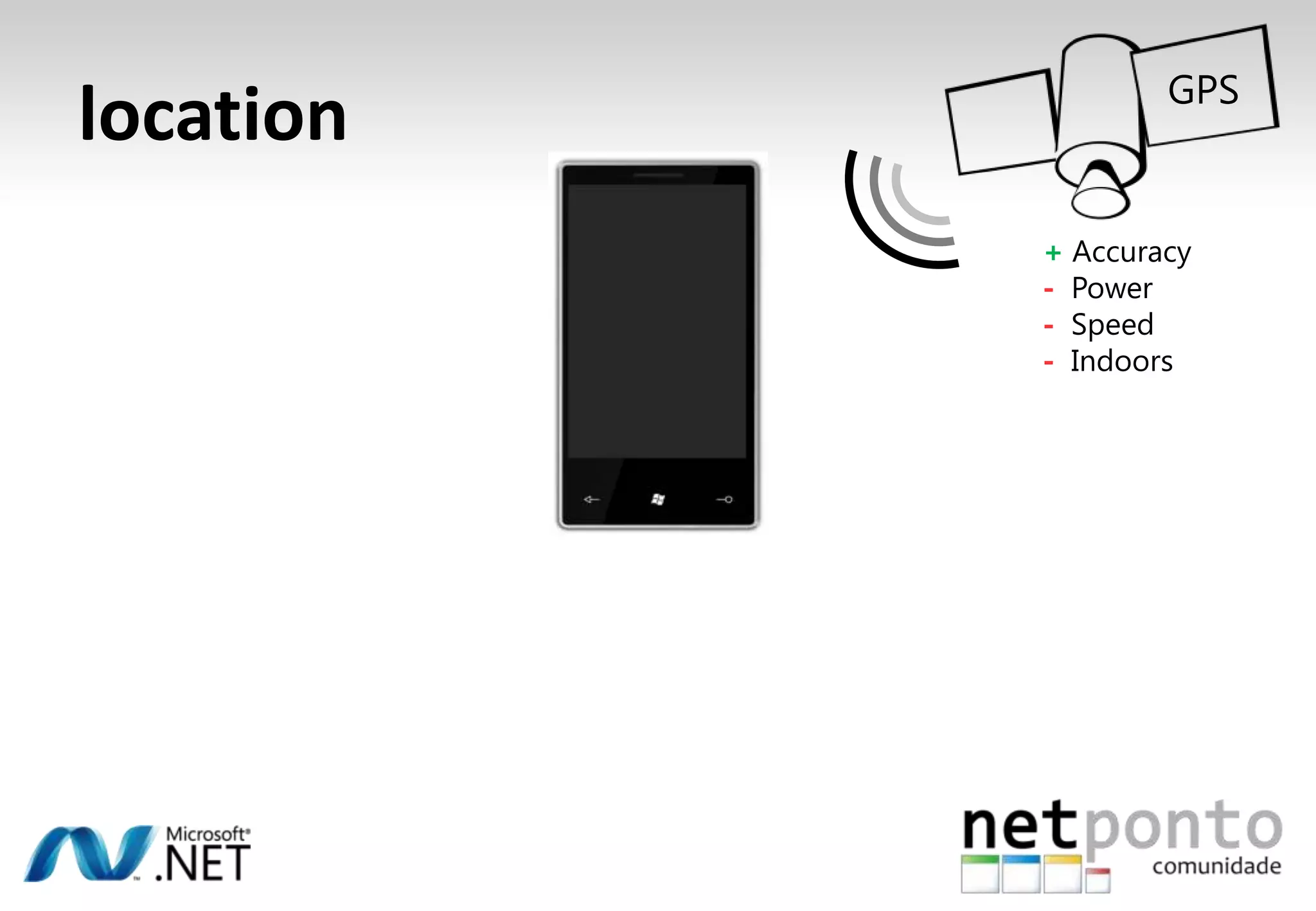
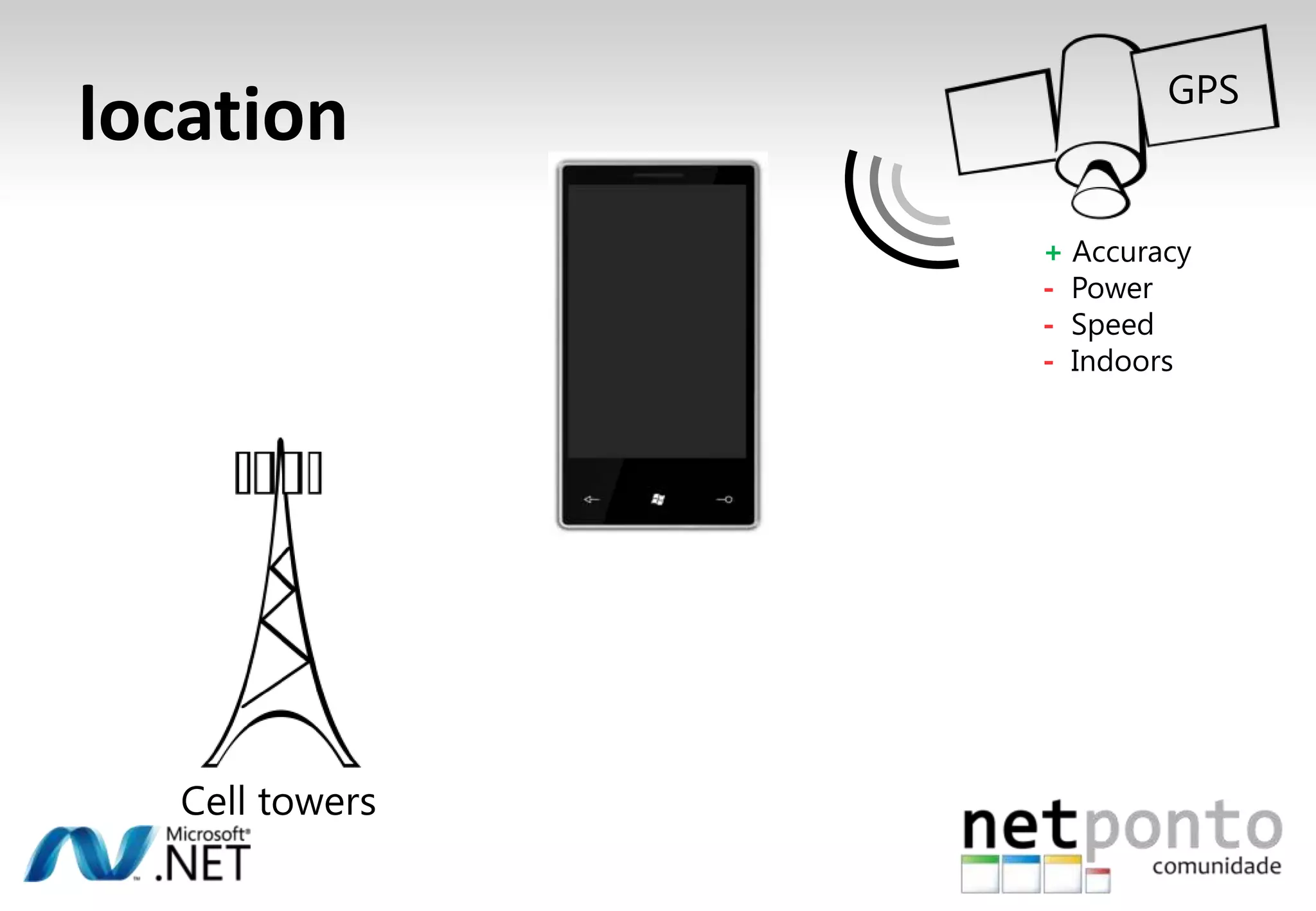
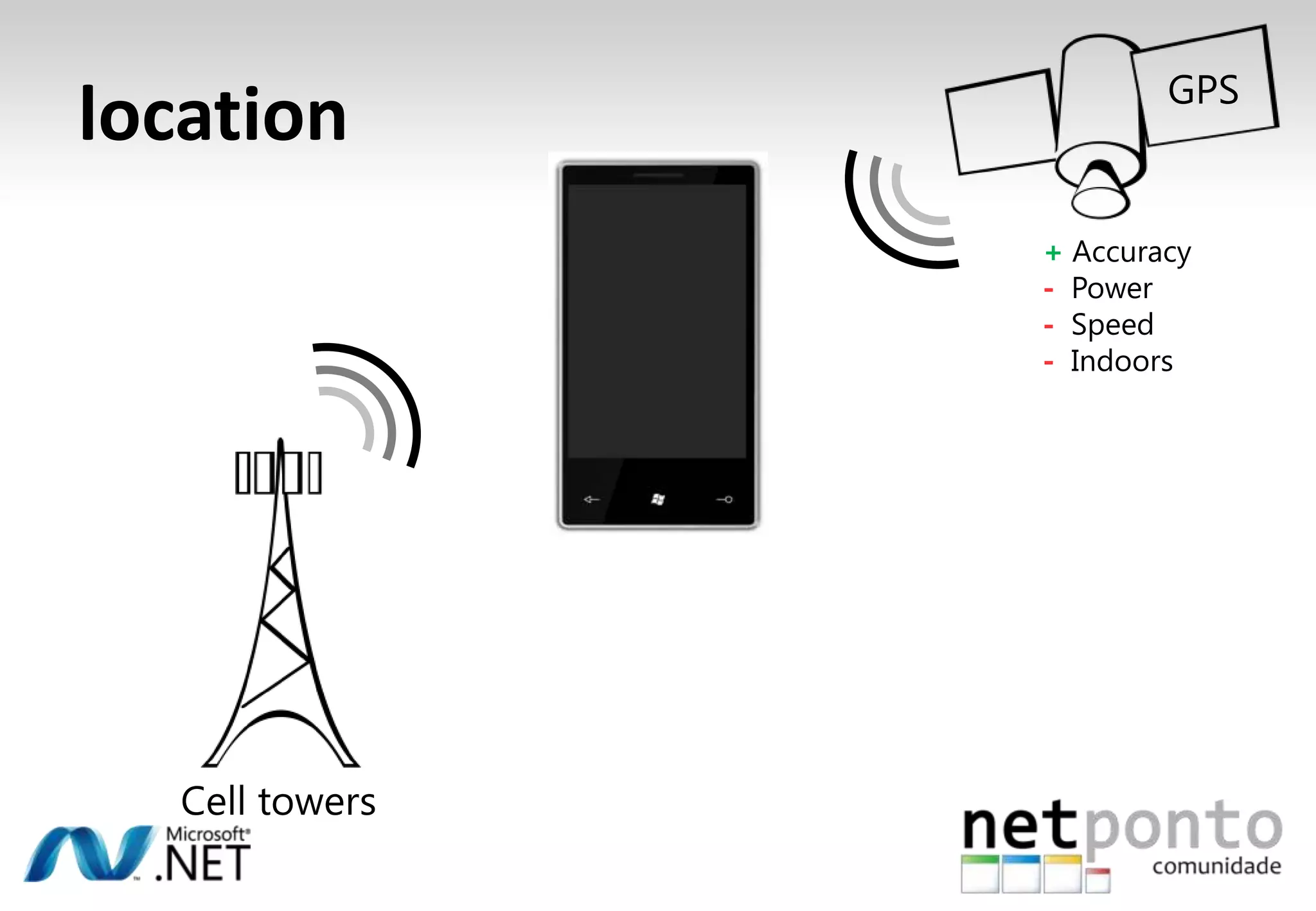
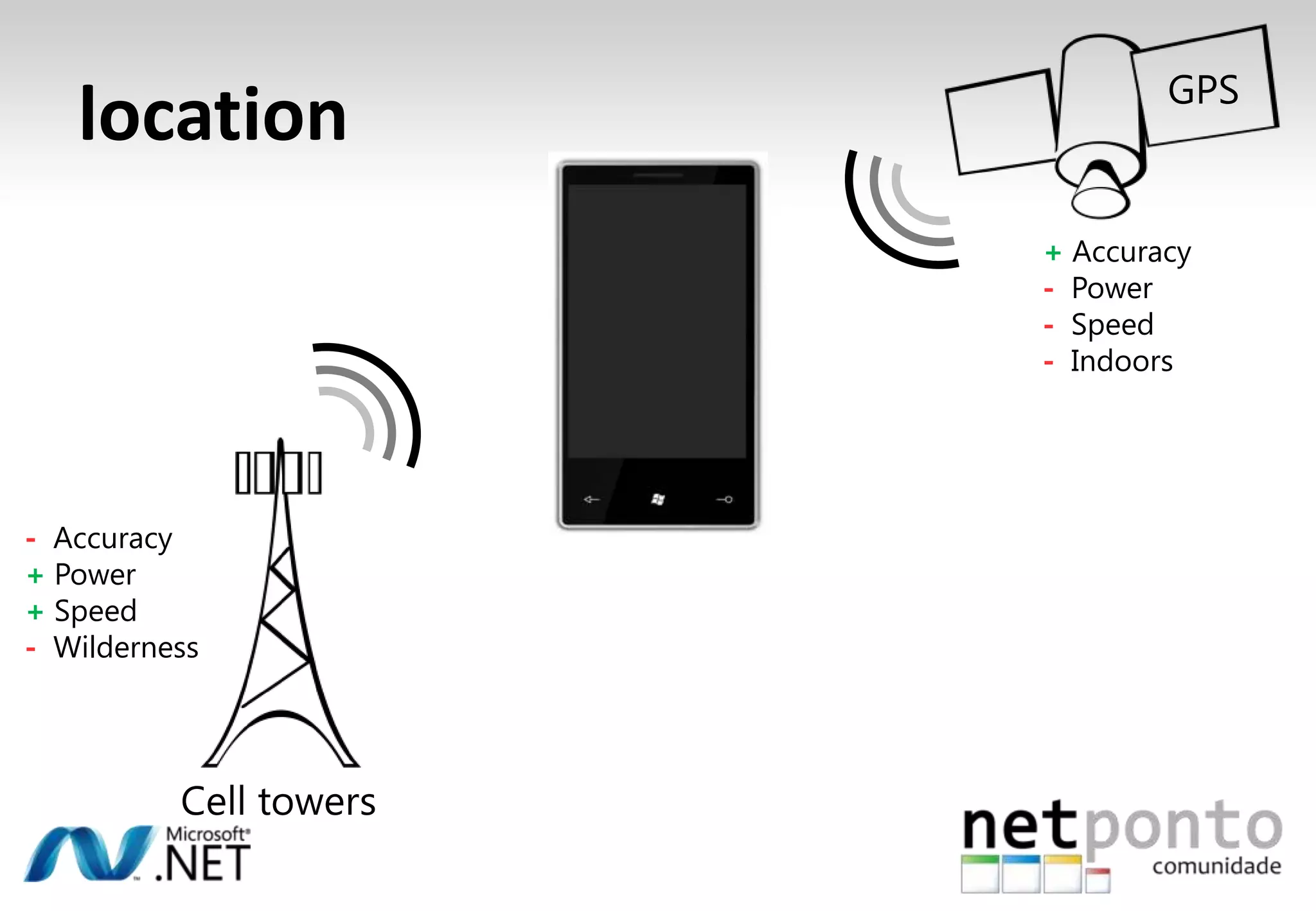
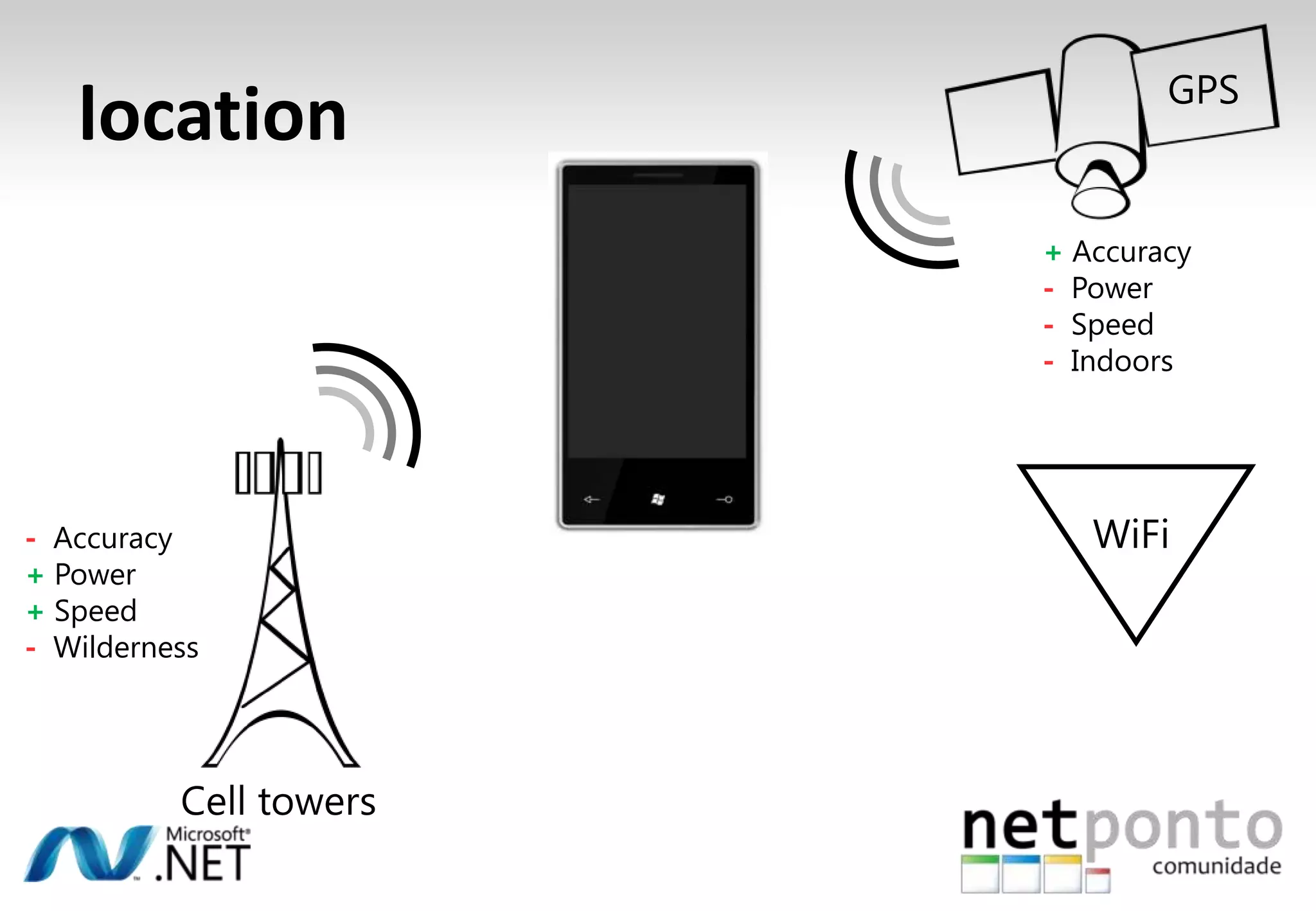
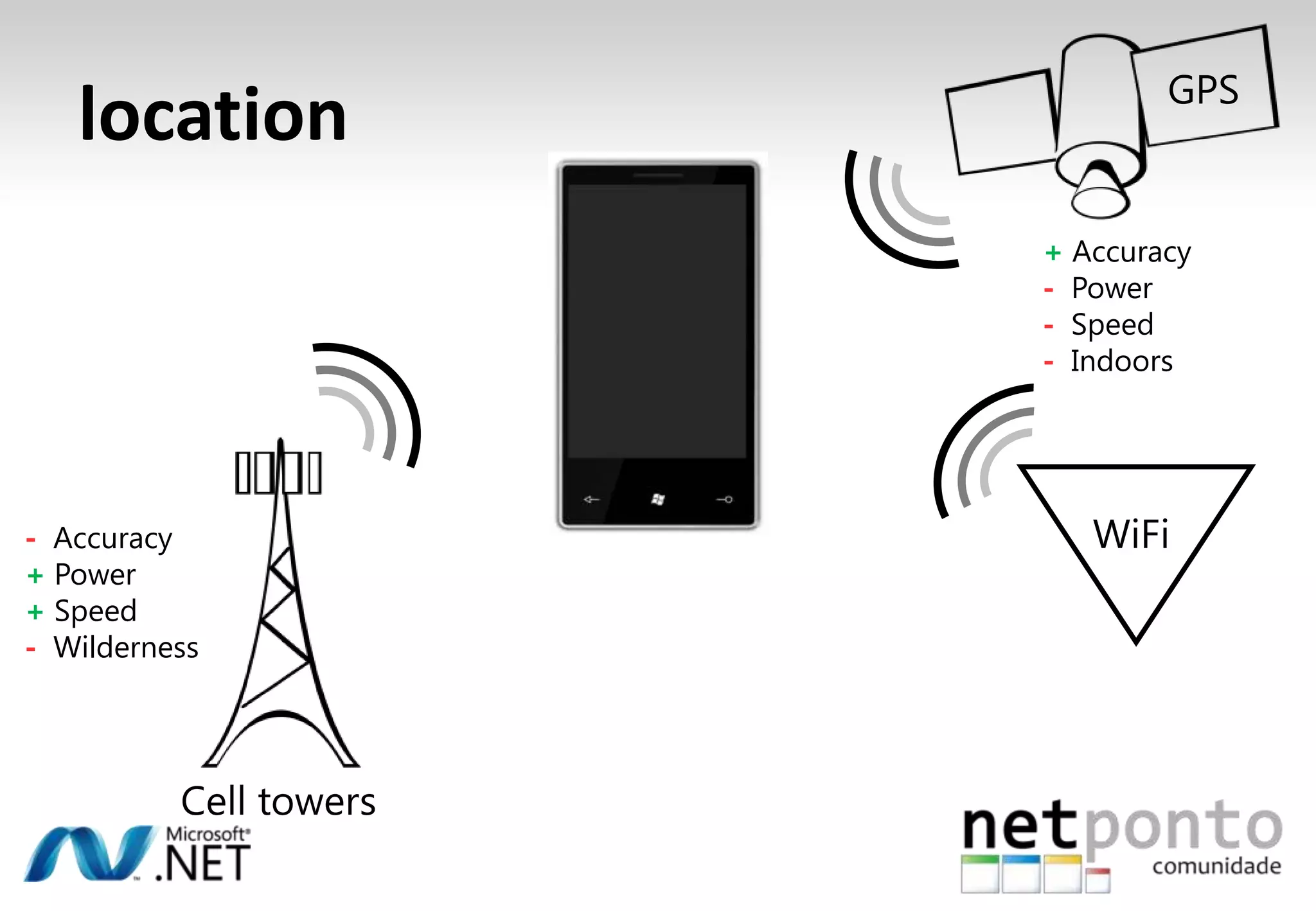
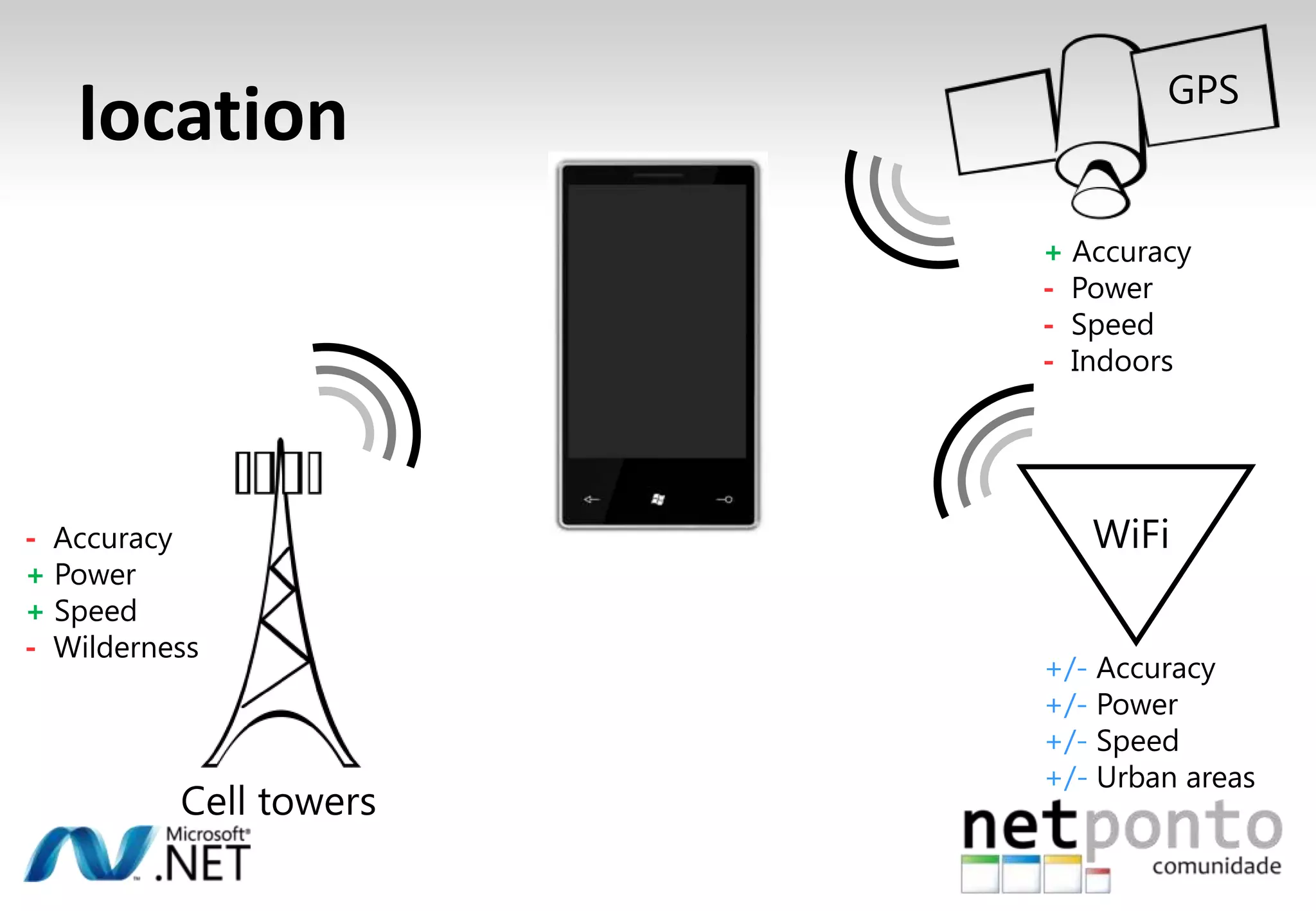
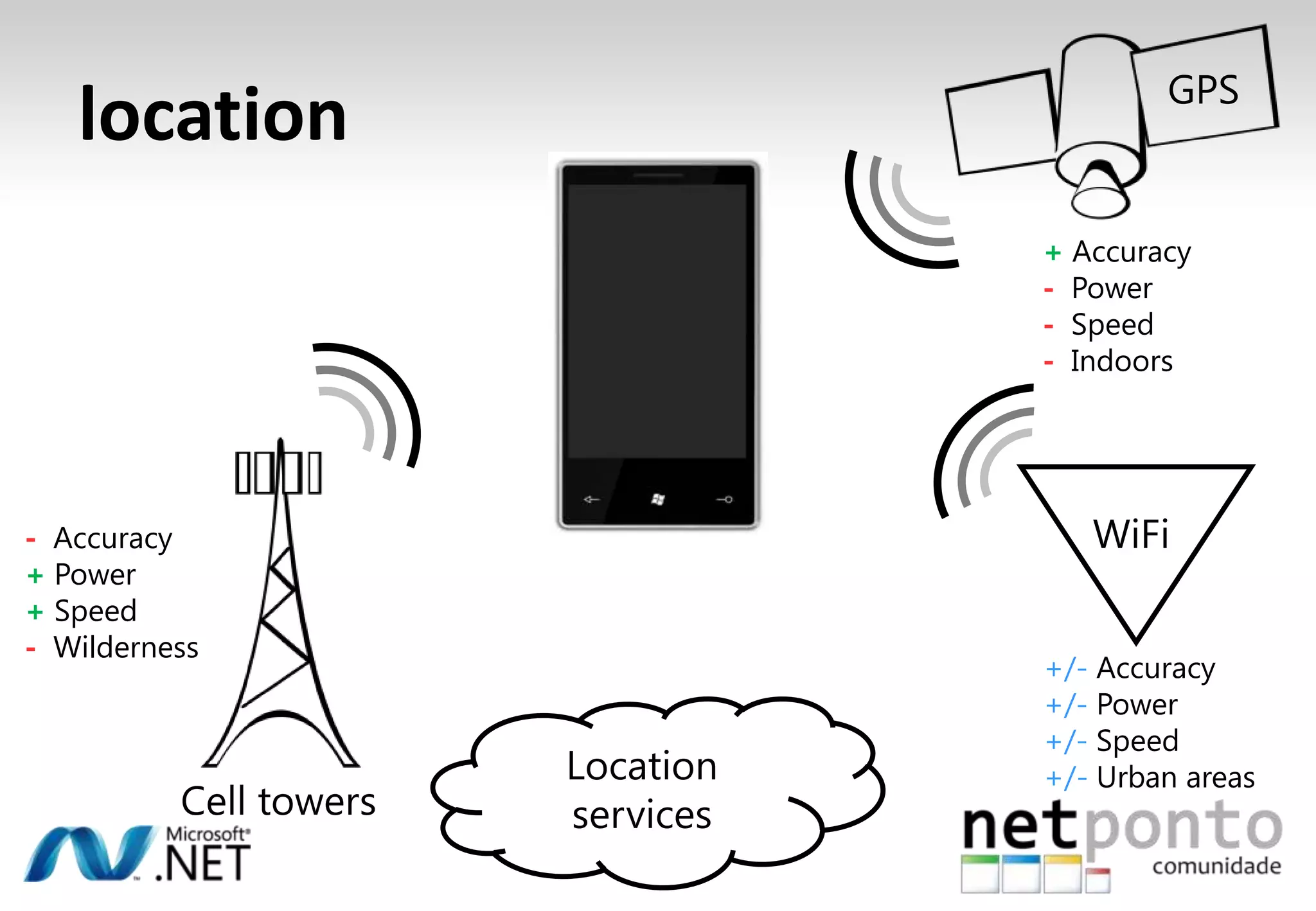
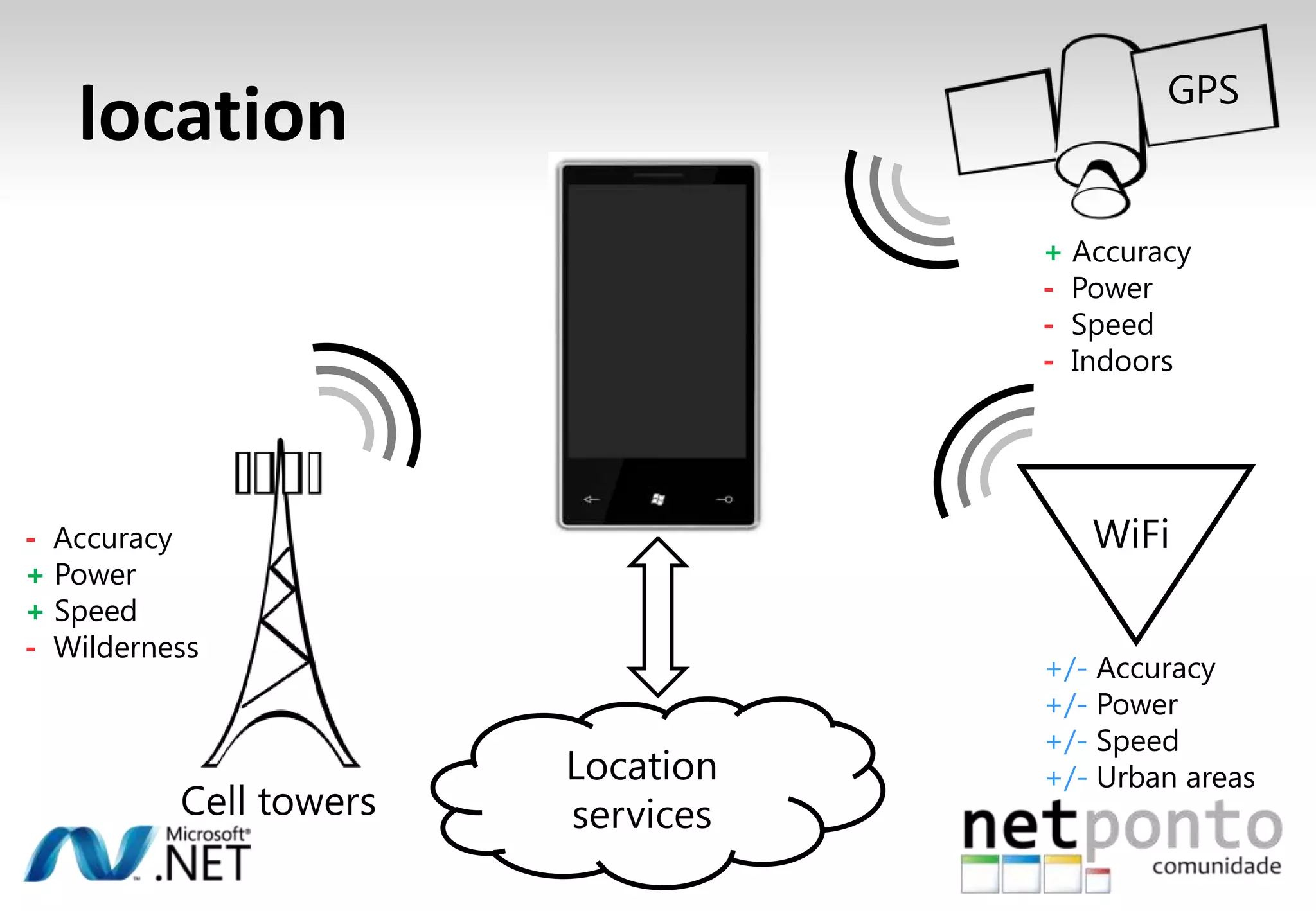
This document discusses a presentation by Nuno Silva on building applications for Windows Phone 7, highlighting the consistent hardware capabilities and developer tools available. It covers the features of the platform, including the modern UI framework, media support, and push notifications, aiming to enhance user experience. Additionally, it outlines the importance of careful application lifecycle management and location services for improved functionality.