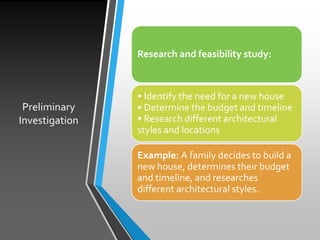
The document illustrates the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) phases using the example of building a new house, starting from the preliminary investigation through to system maintenance. It highlights steps like defining user needs, creating detailed designs, building the house, conducting inspections, and ongoing maintenance. Each phase includes examples reflecting a family's journey in constructing their home.