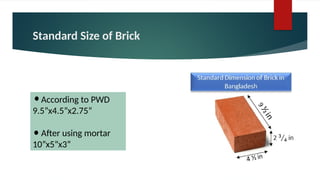
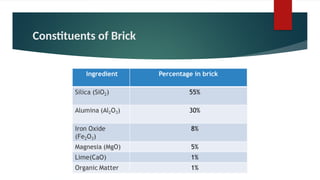
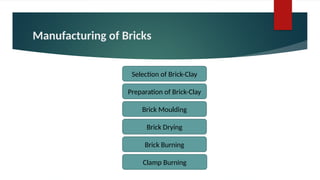
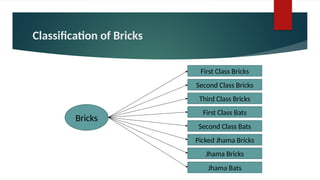
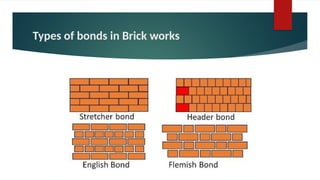
The document provides an overview of bricks, detailing their characteristics, manufacturing process, and classification. It highlights the ideal constituents for quality bricks and discusses harmful materials to avoid. Additionally, it covers field tests to assess brick quality and various uses of bricks in construction.