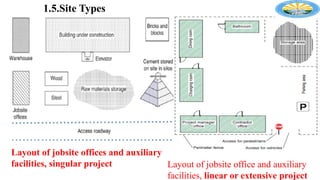
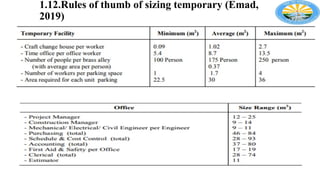
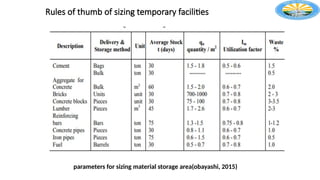
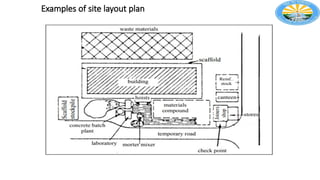
The document outlines the importance of effective construction site planning, emphasizing the coordination of manpower, equipment, and layout to enhance productivity and safety. It details the processes involved in developing site layout plans, identifies common pitfalls in current practices, and discusses factors influencing the organization of jobsite offices and temporary facilities. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of proper material handling, jobsite security, and the characteristics guiding the selection of temporary facilities.