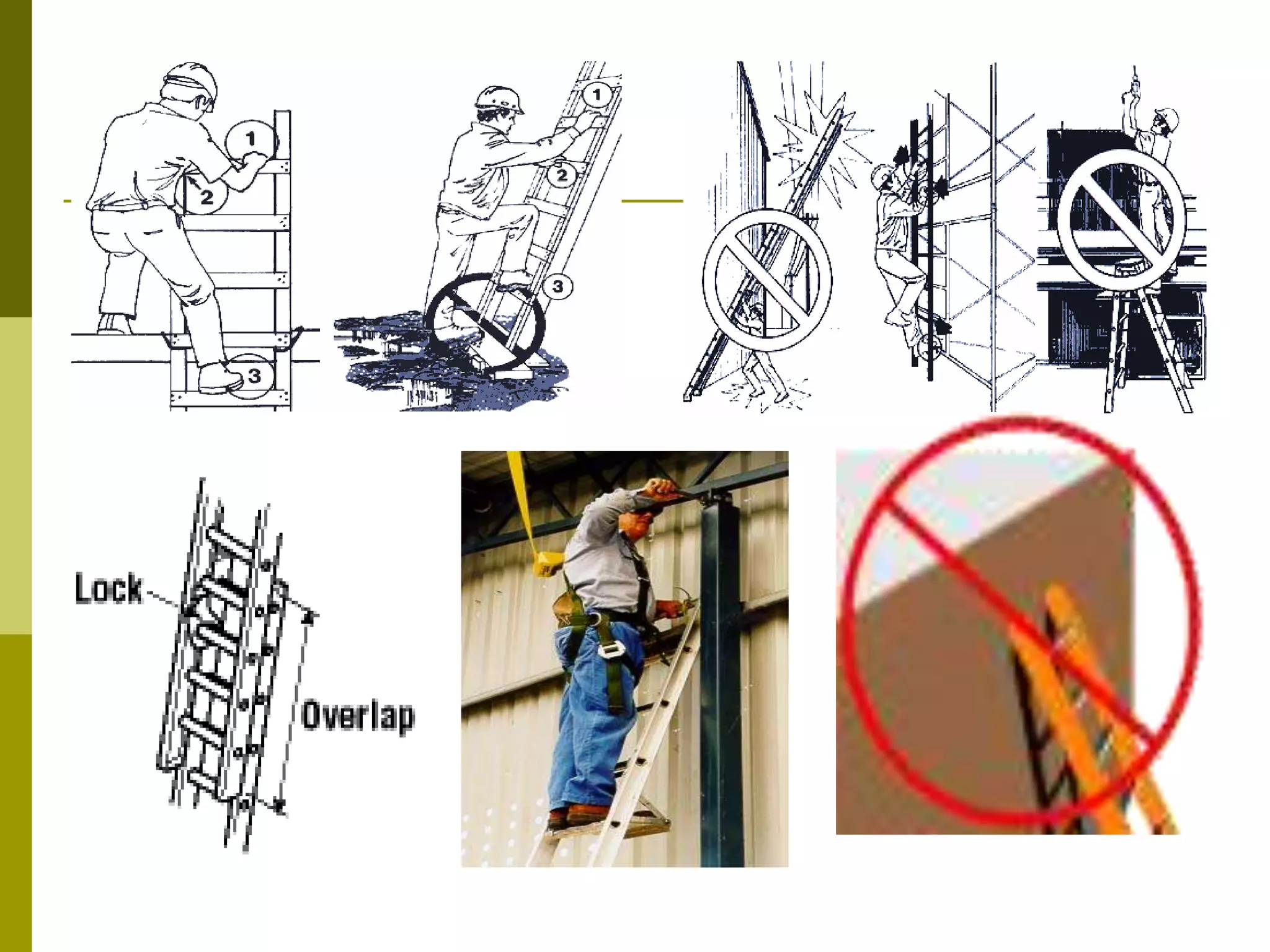
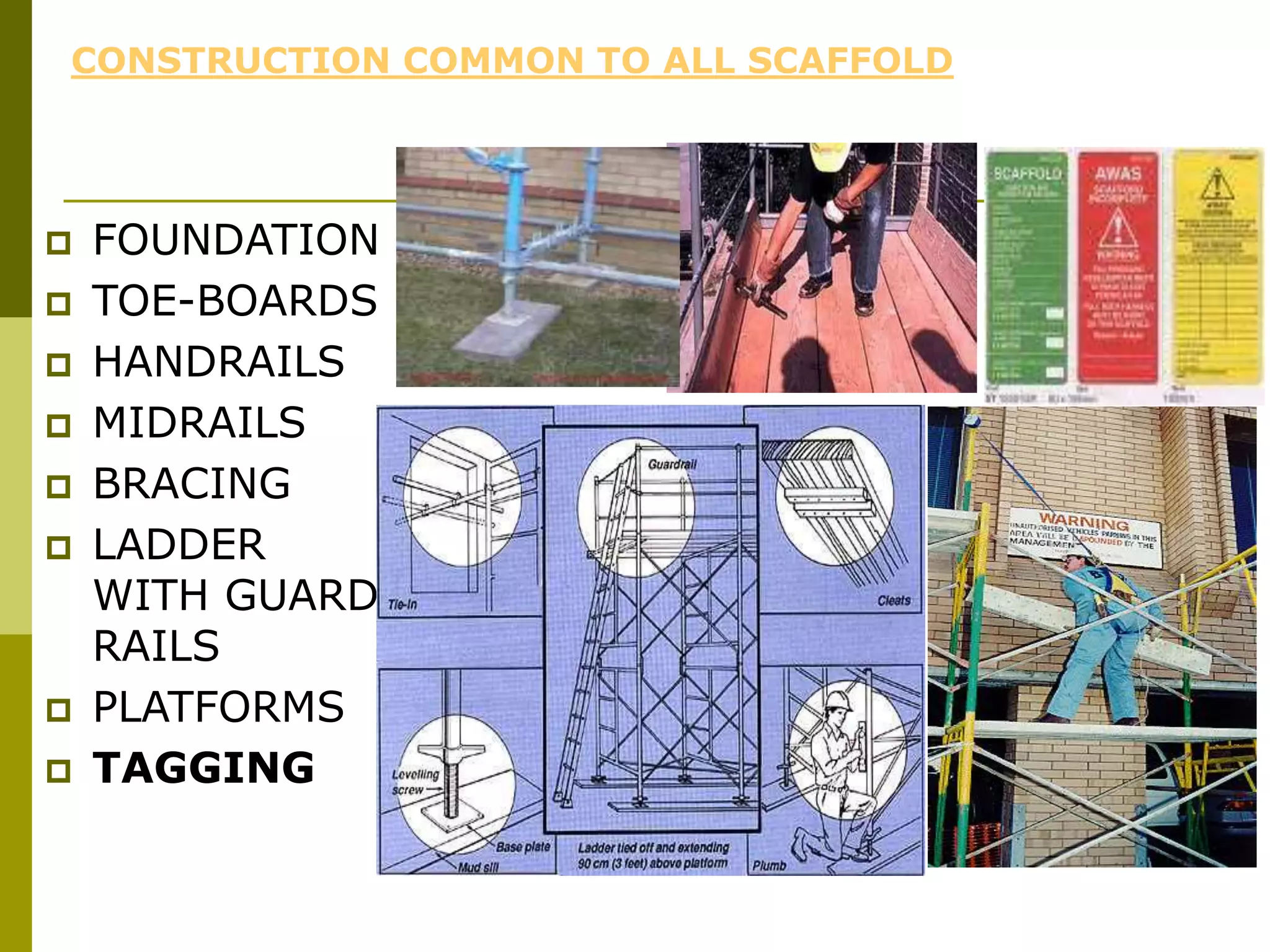
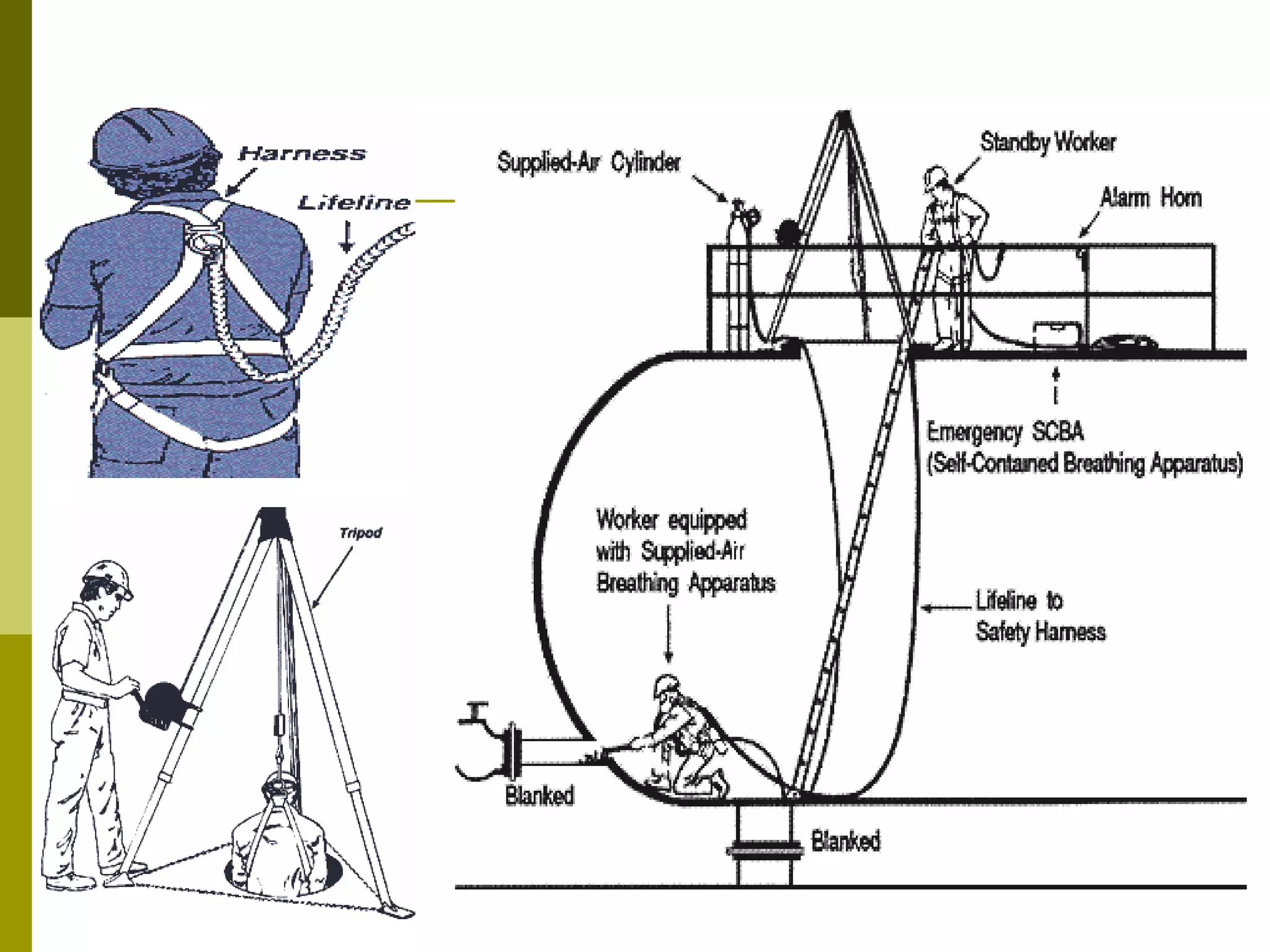
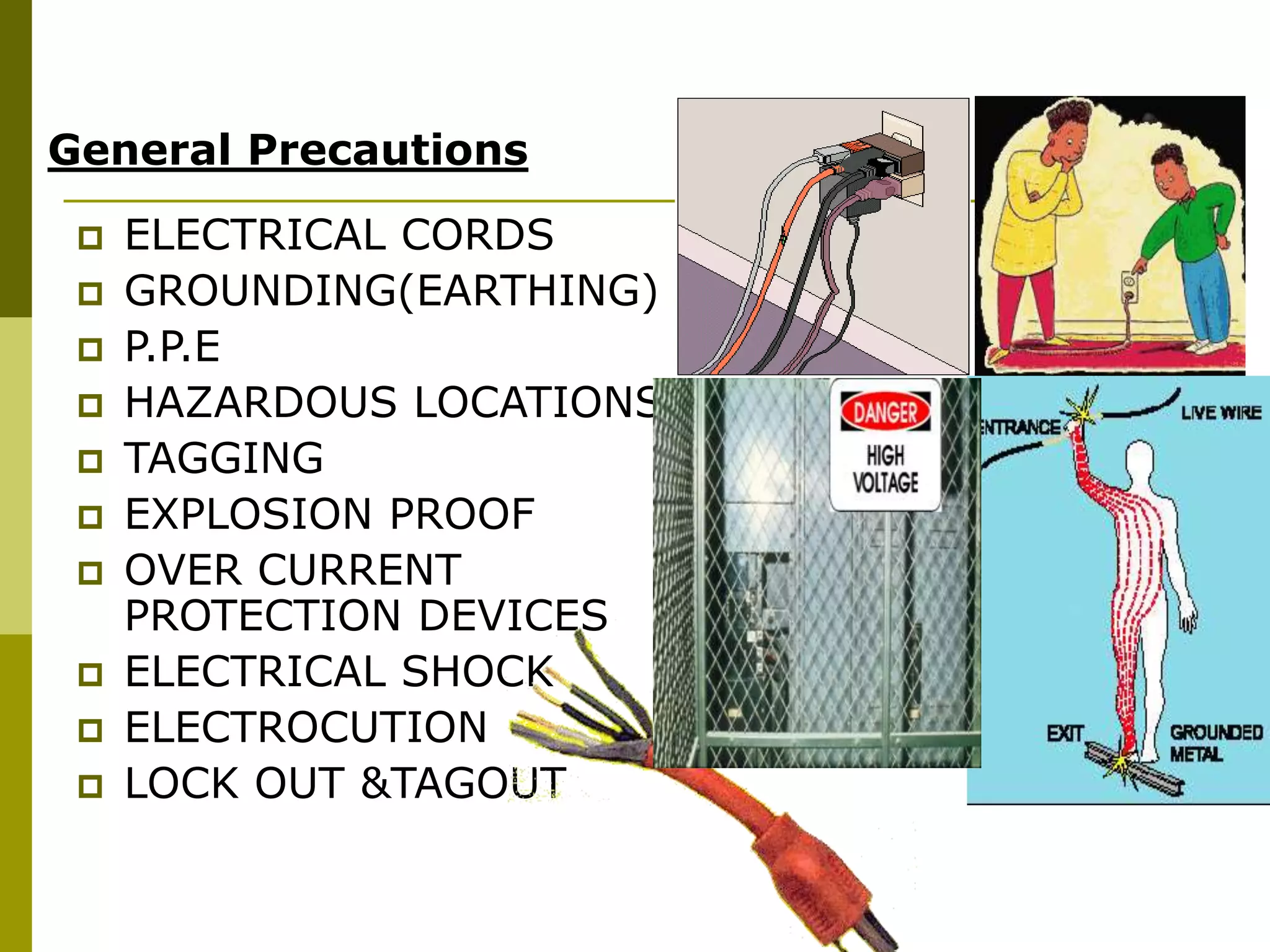
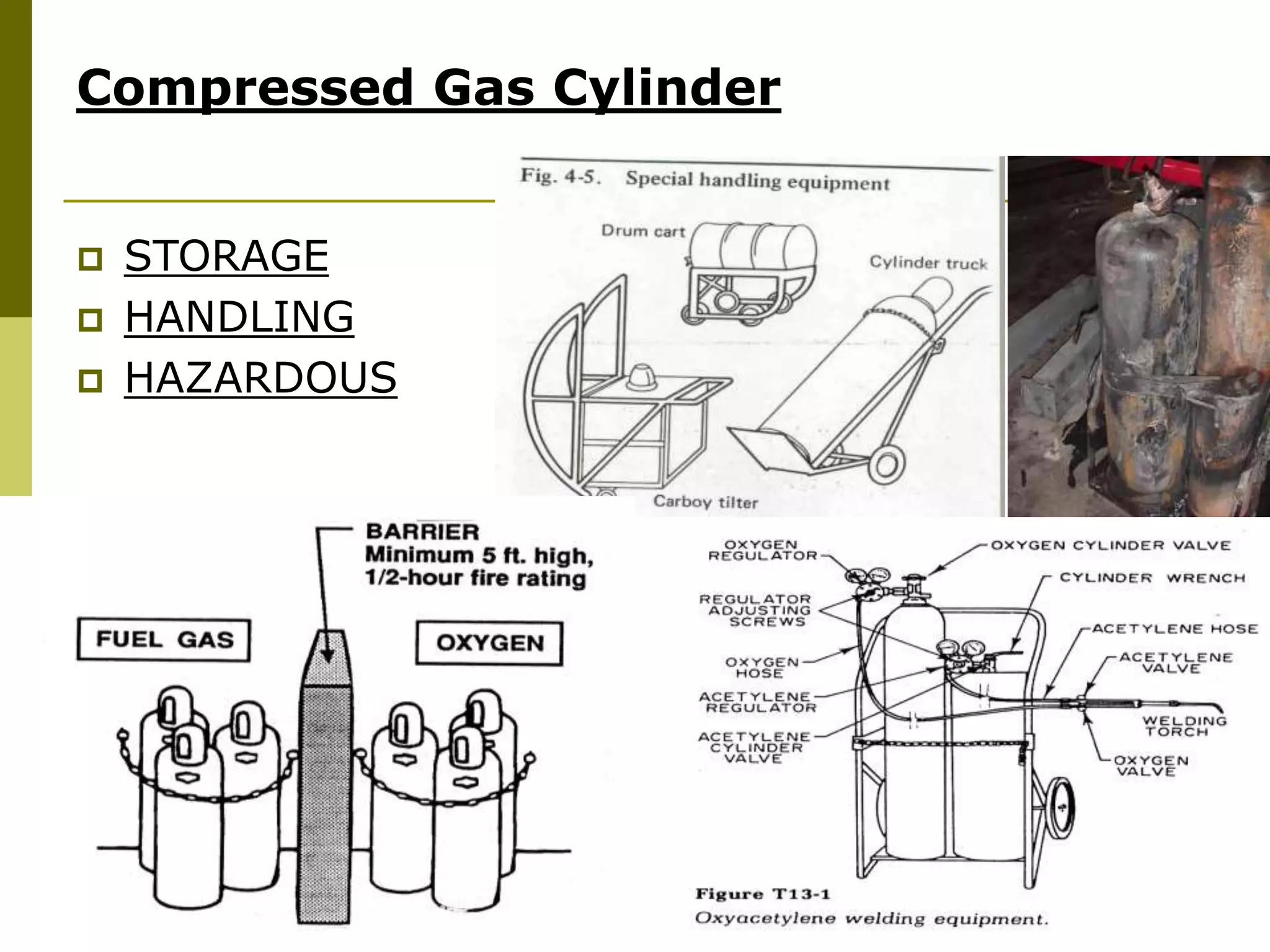
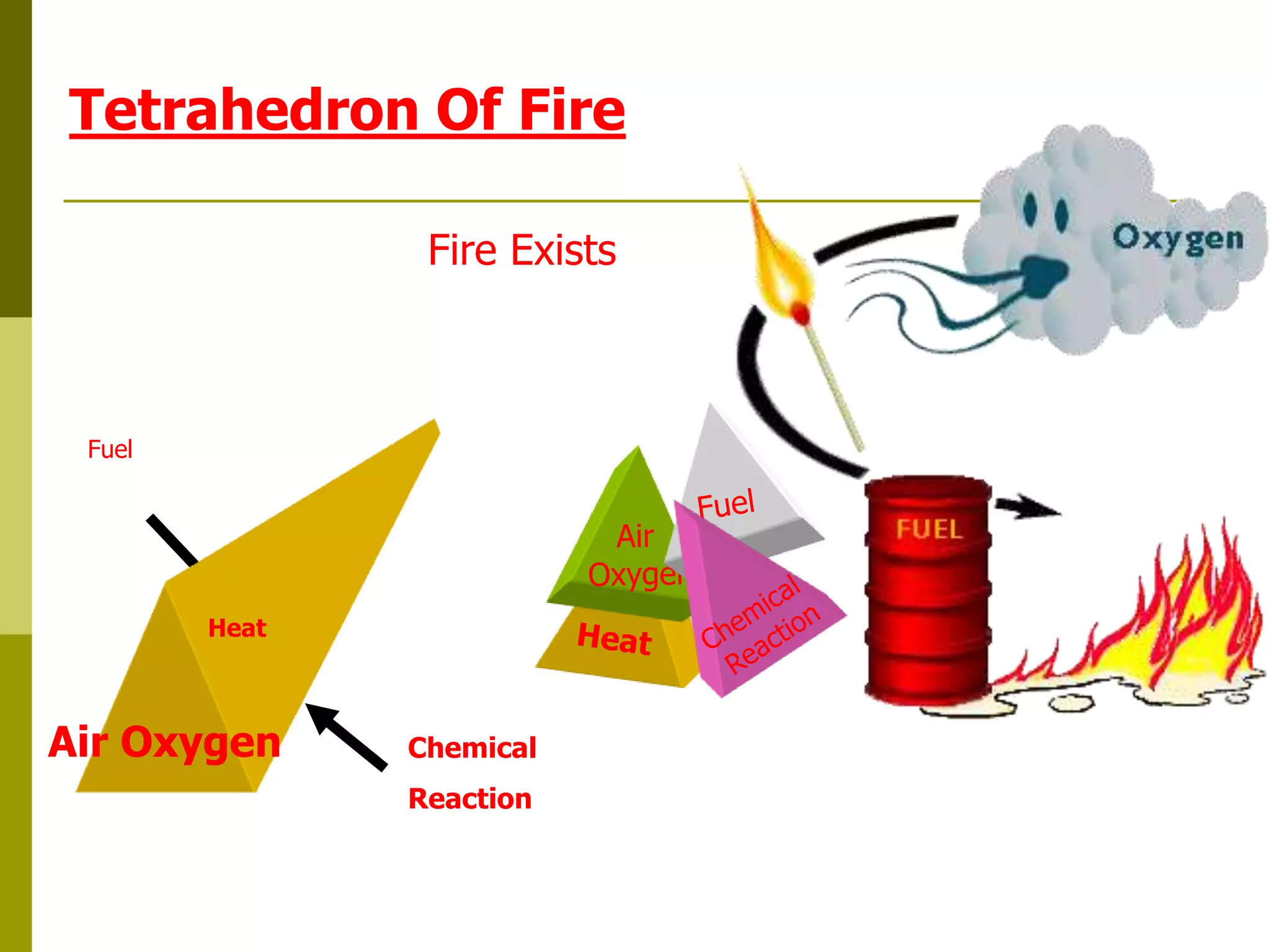
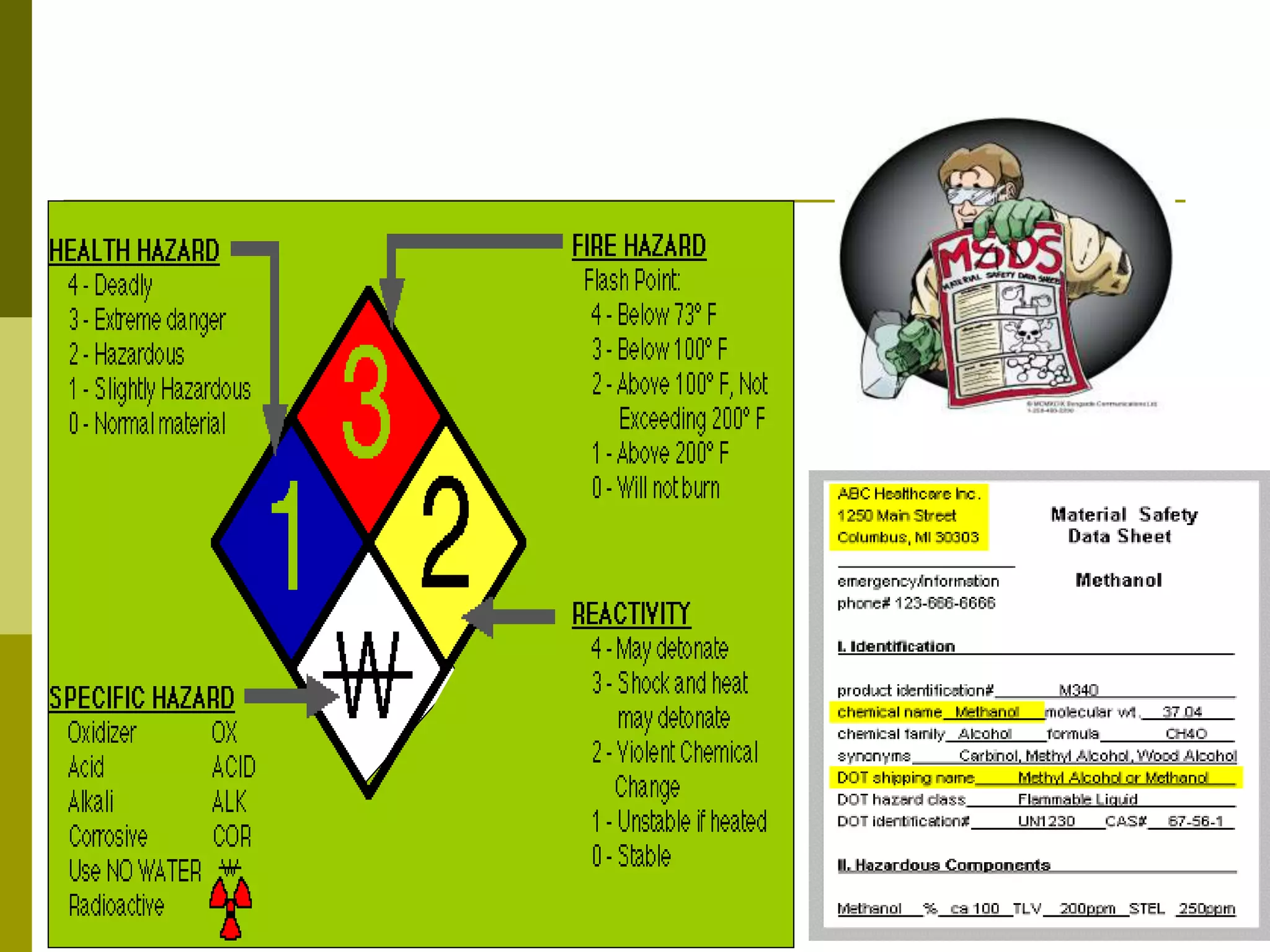
This document discusses construction safety. It identifies the main causes of accidents as unsafe work practices, physical conditions, or a lack of knowledge or skill. It outlines various preventative techniques including administrative policies and engineering controls. Specific safety issues covered include working at heights, ladder safety, excavation work, crane safety, traffic safety, and proper use of personal protective equipment. The document emphasizes that all accidents are preventable by prioritizing safety over expediency and making it a shared responsibility of all workers.