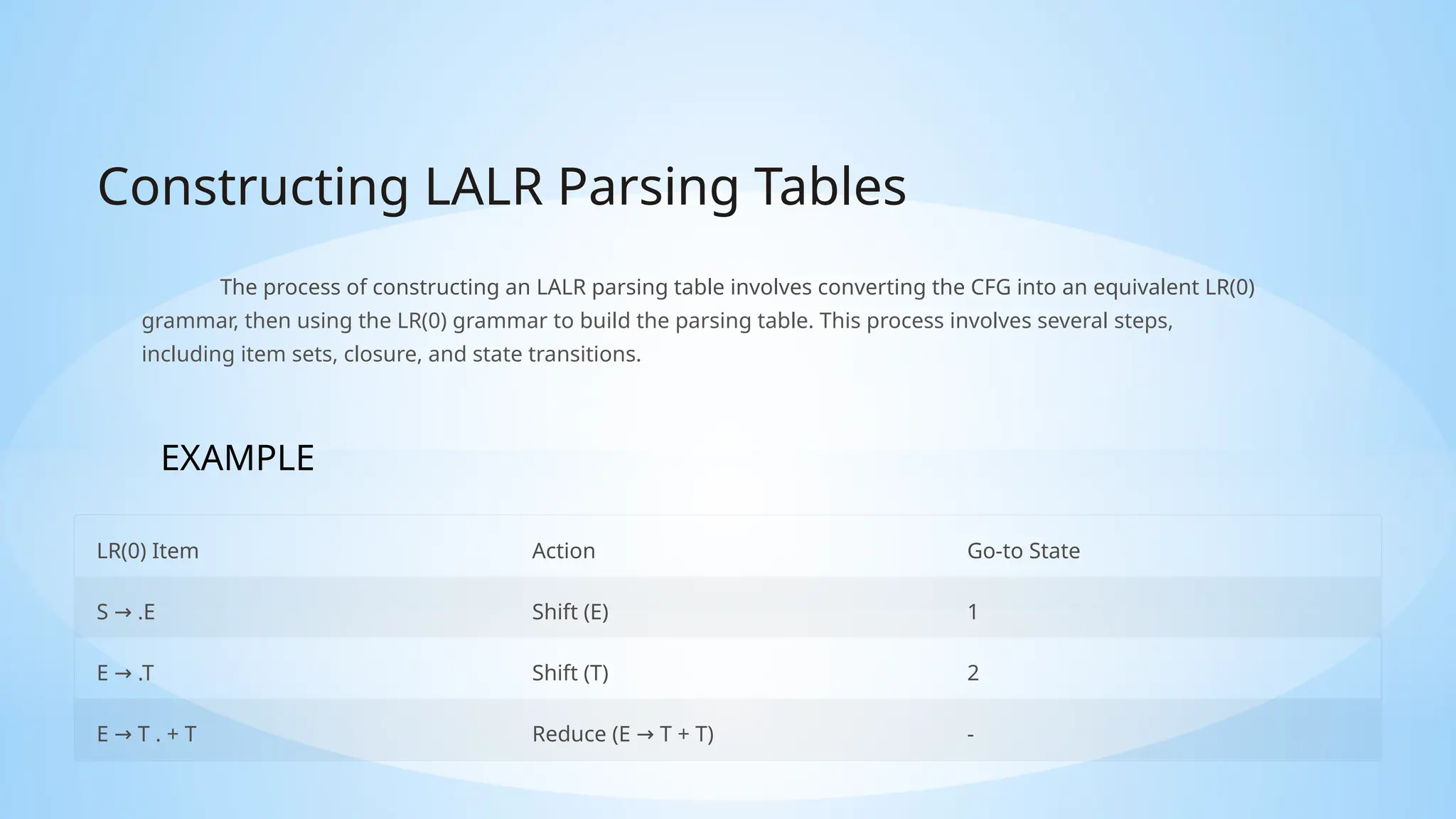
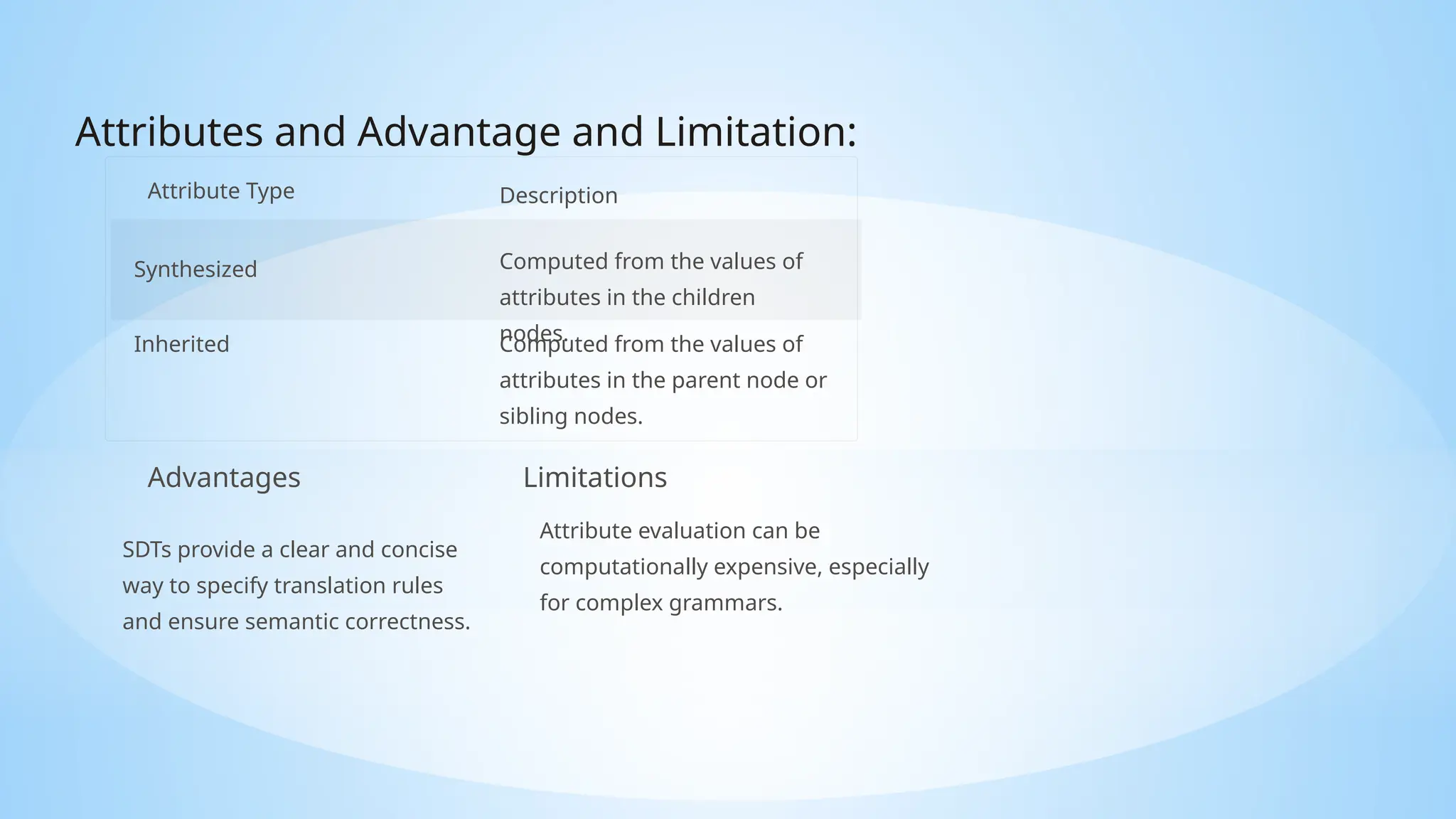
This document introduces LALR parsing, a method for parsing context-free grammars that utilizes a single lookahead symbol for efficient parsing, along with the construction of LALR parsing tables. It covers essential concepts such as context-free grammars, parsing techniques, and syntax-directed translation schemes, detailing their applications in compilers and code generation. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and limitations of LALR parsing and syntax-directed translations, highlighting their importance in programming language processing.