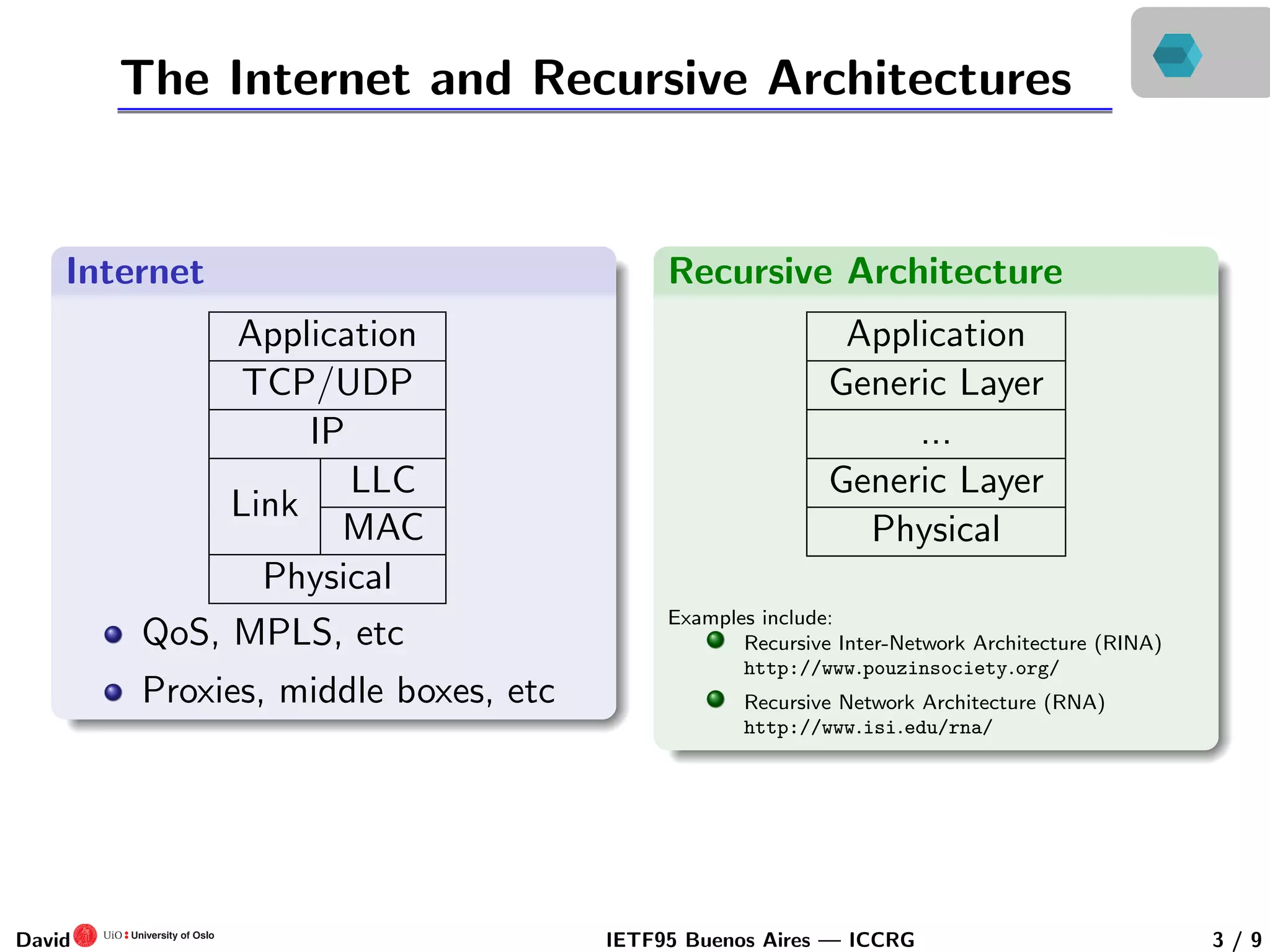
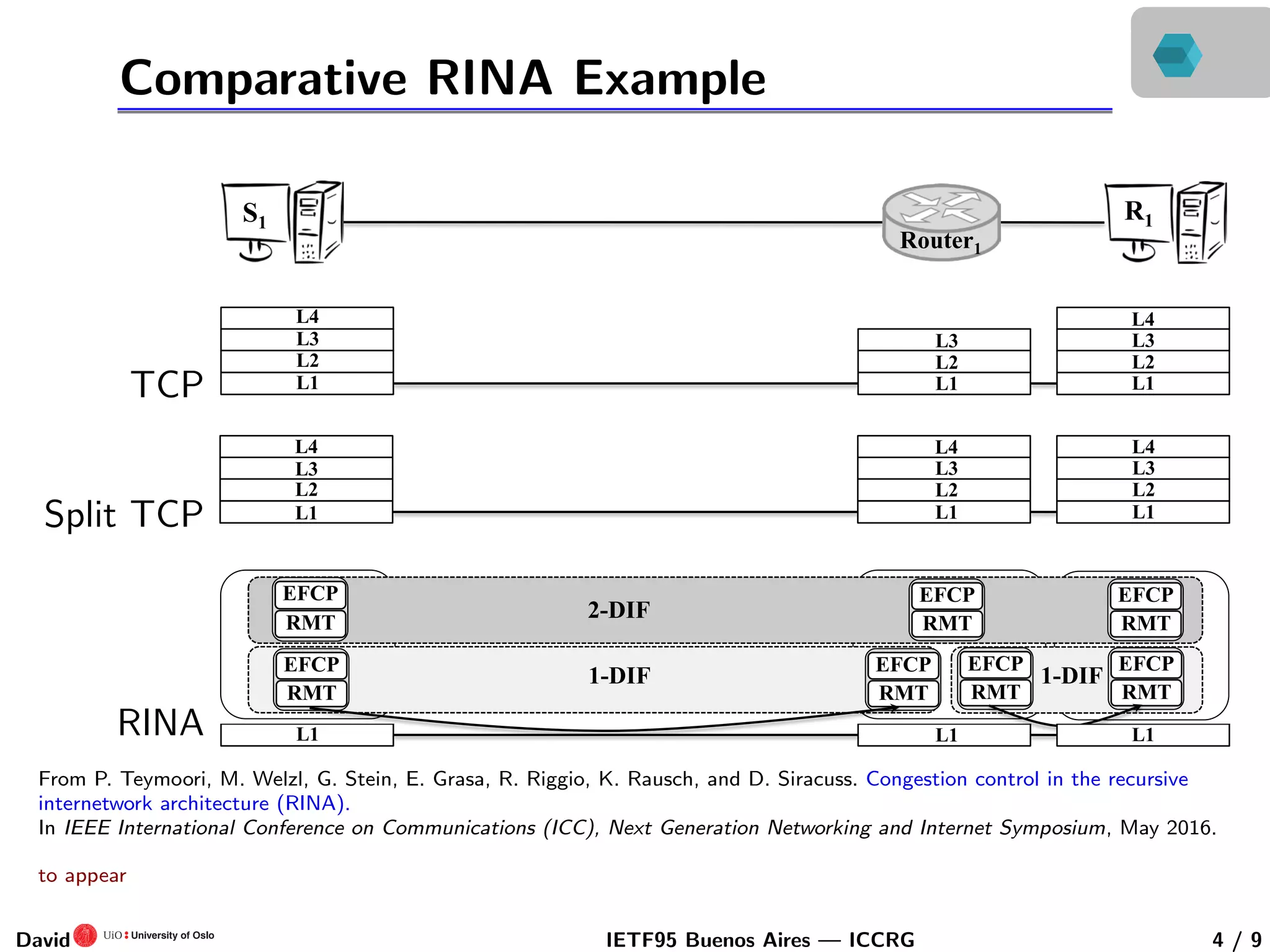
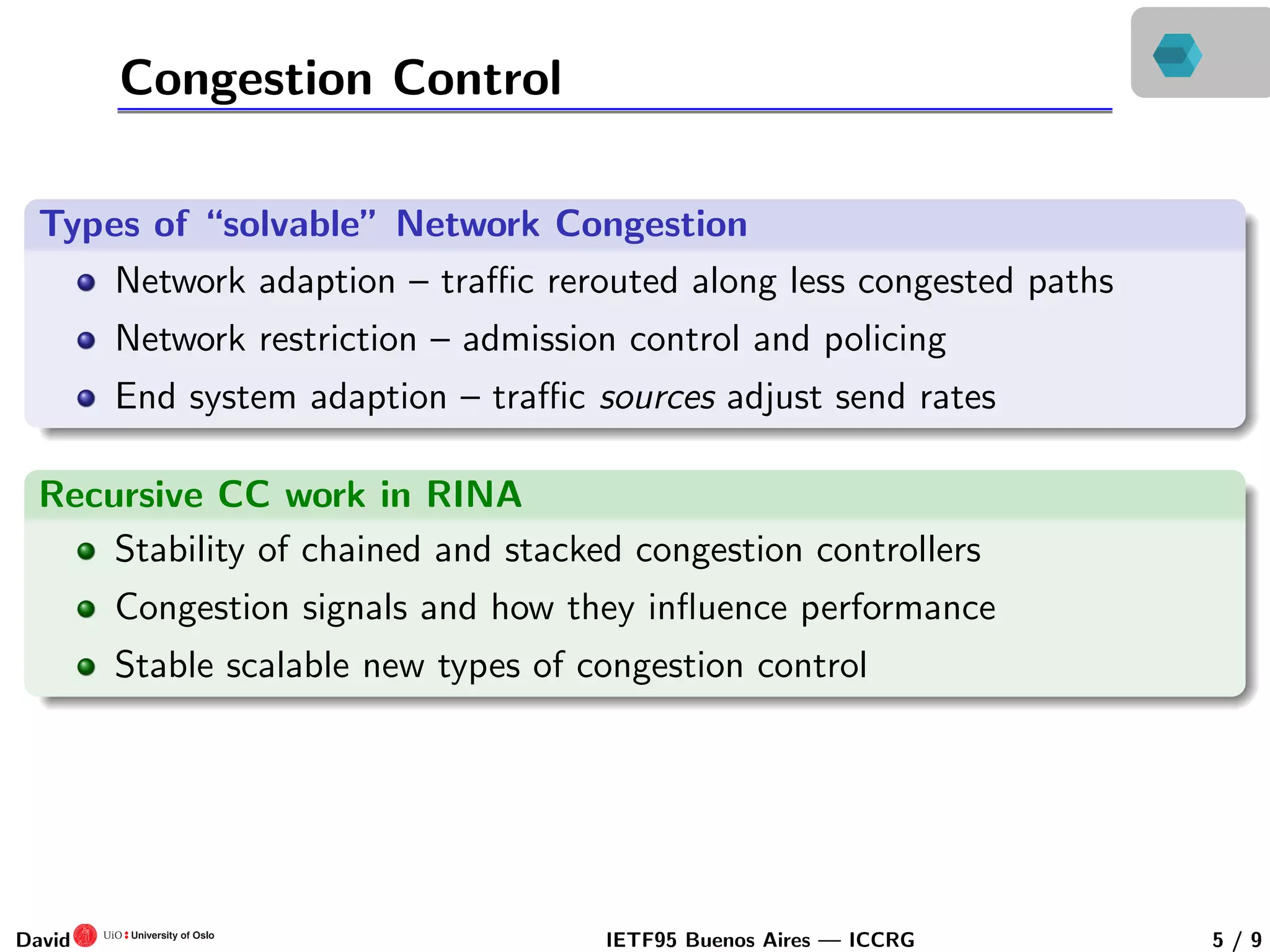
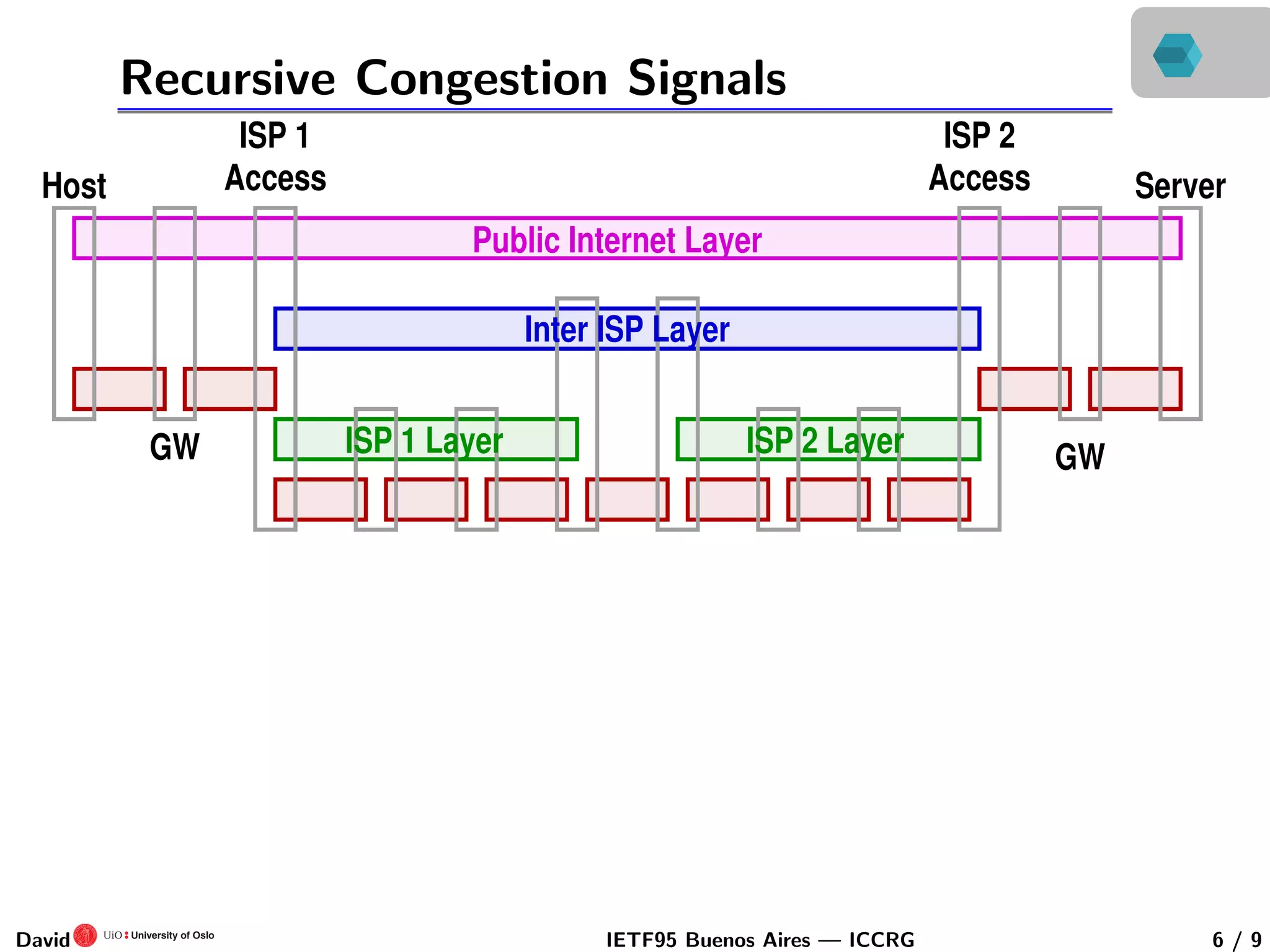
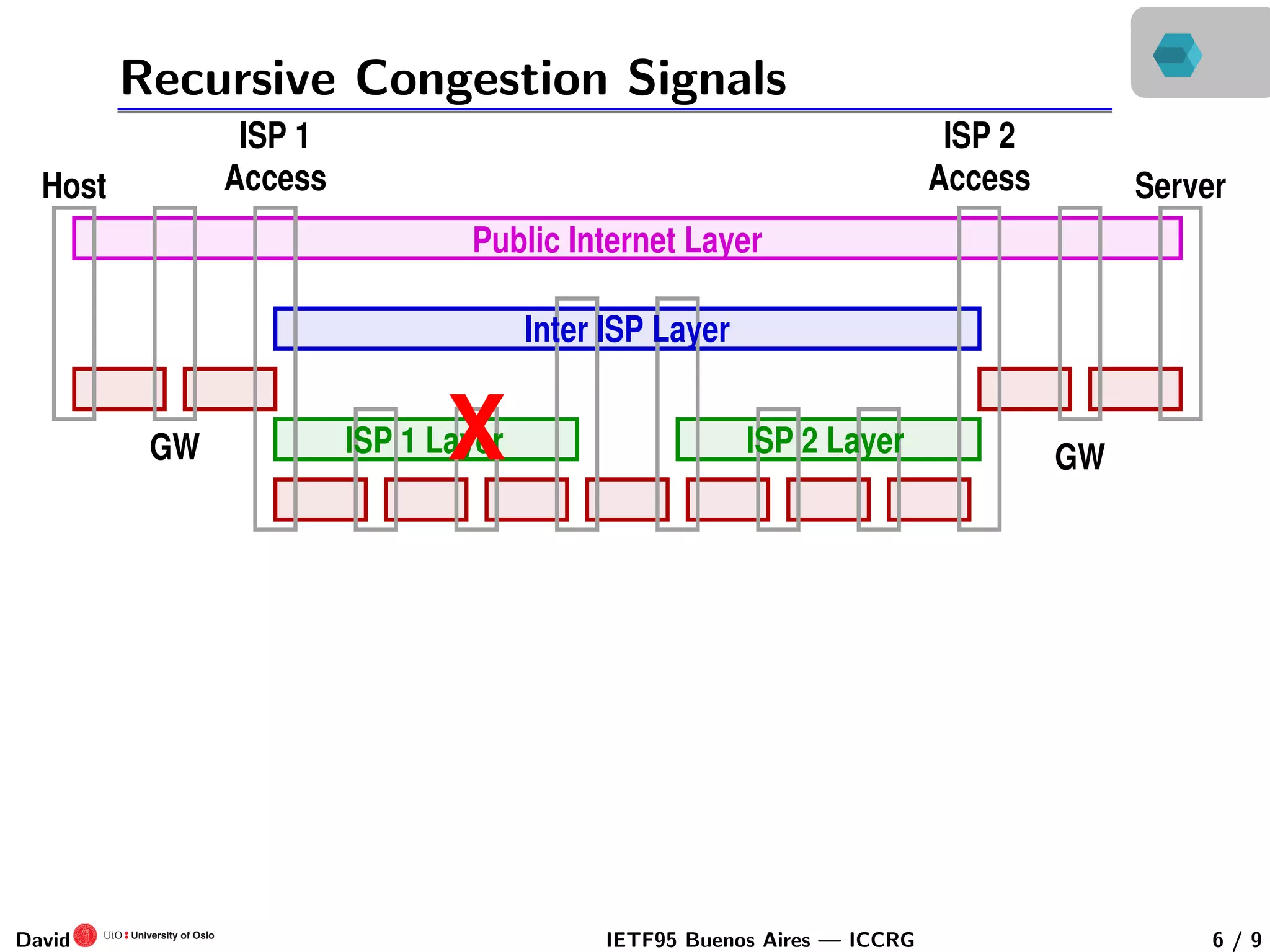
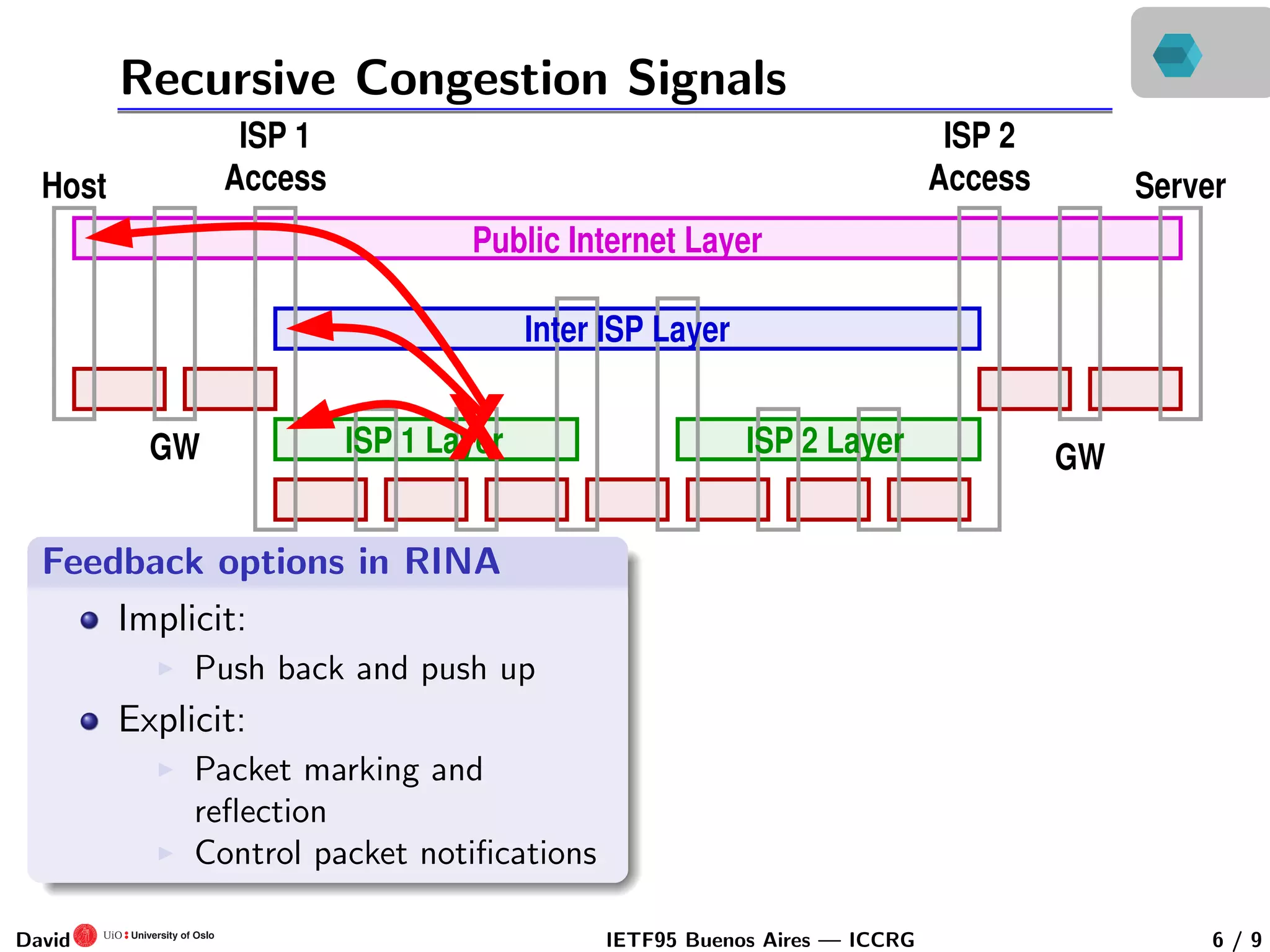
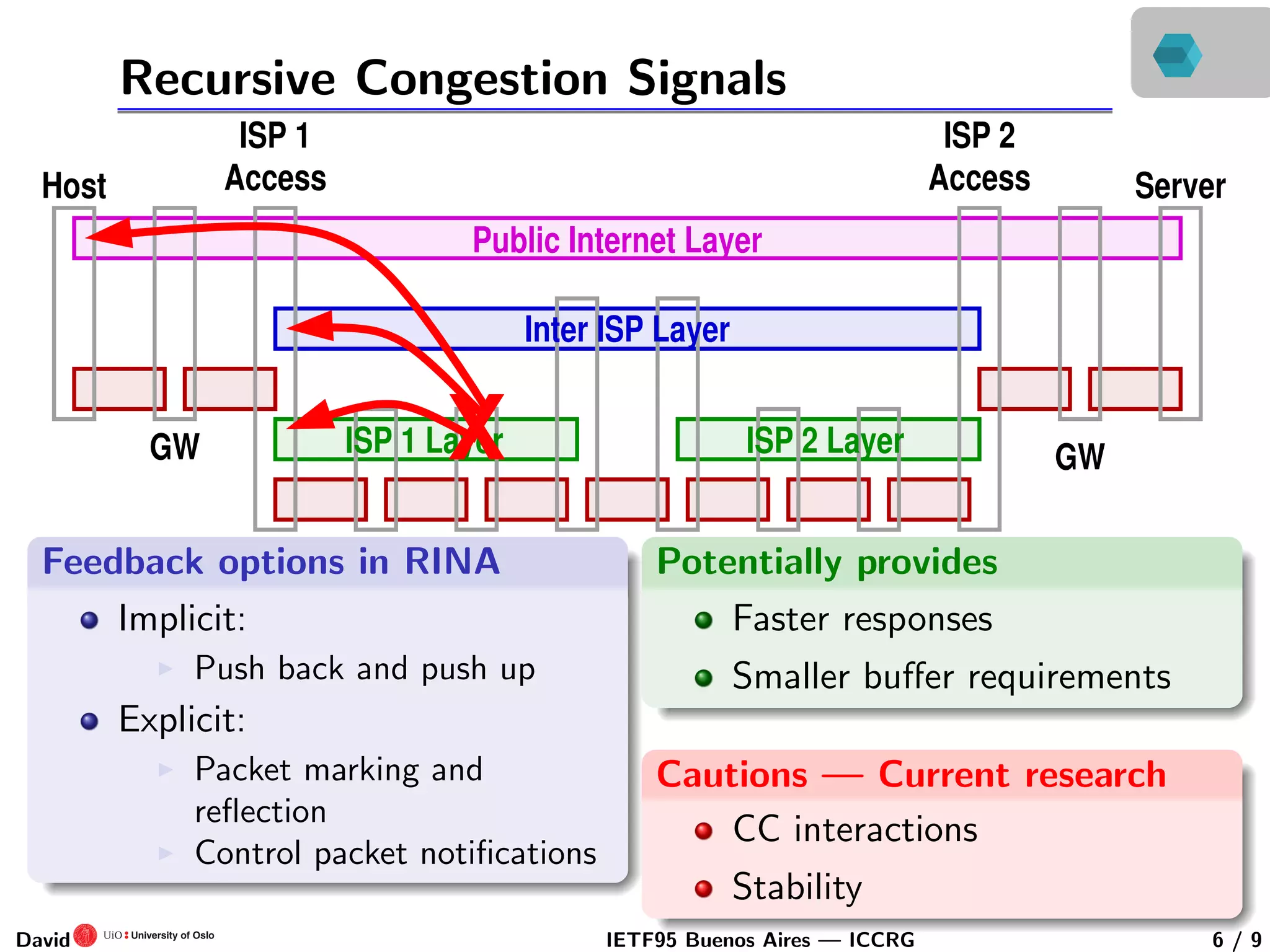
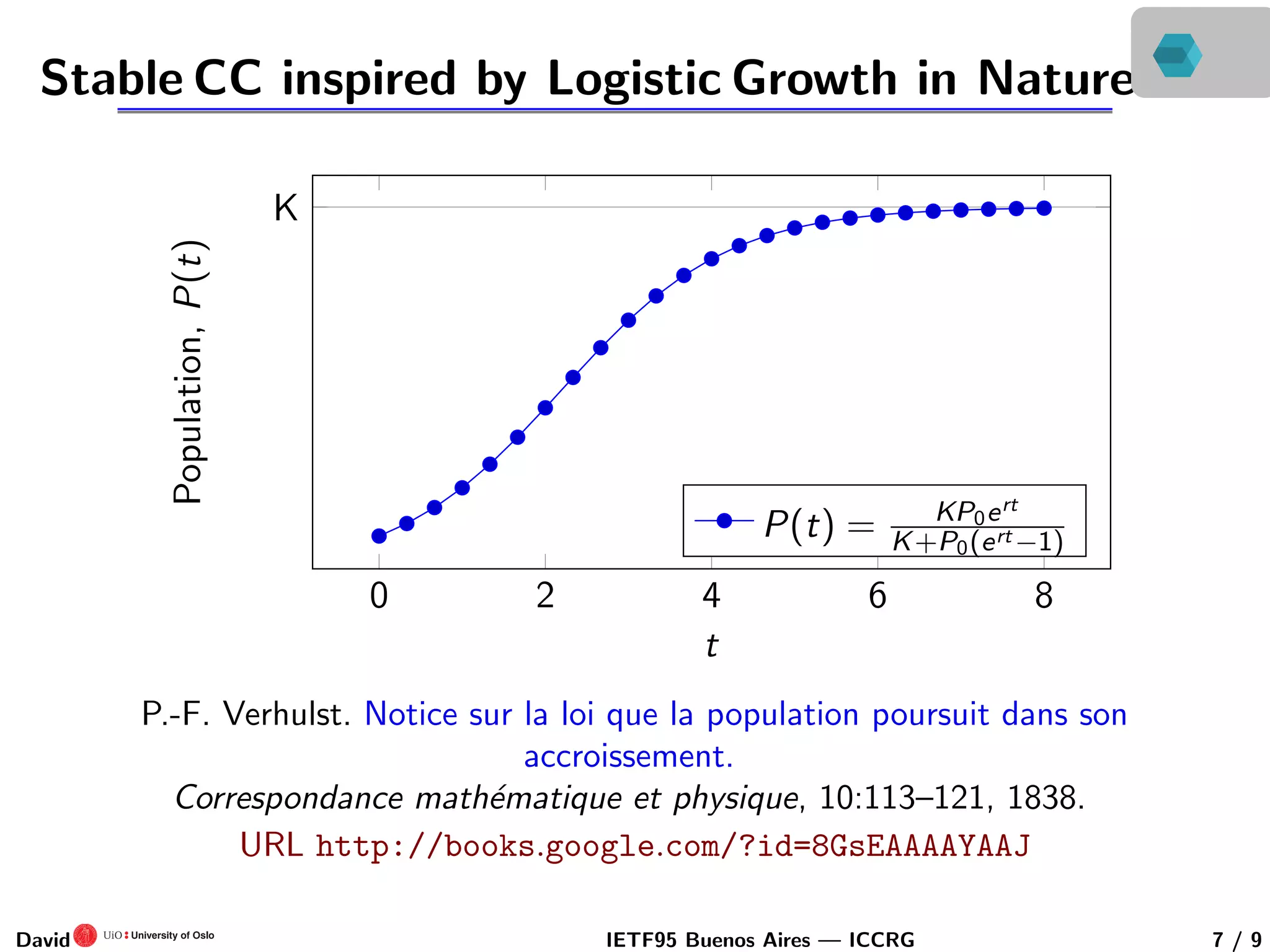
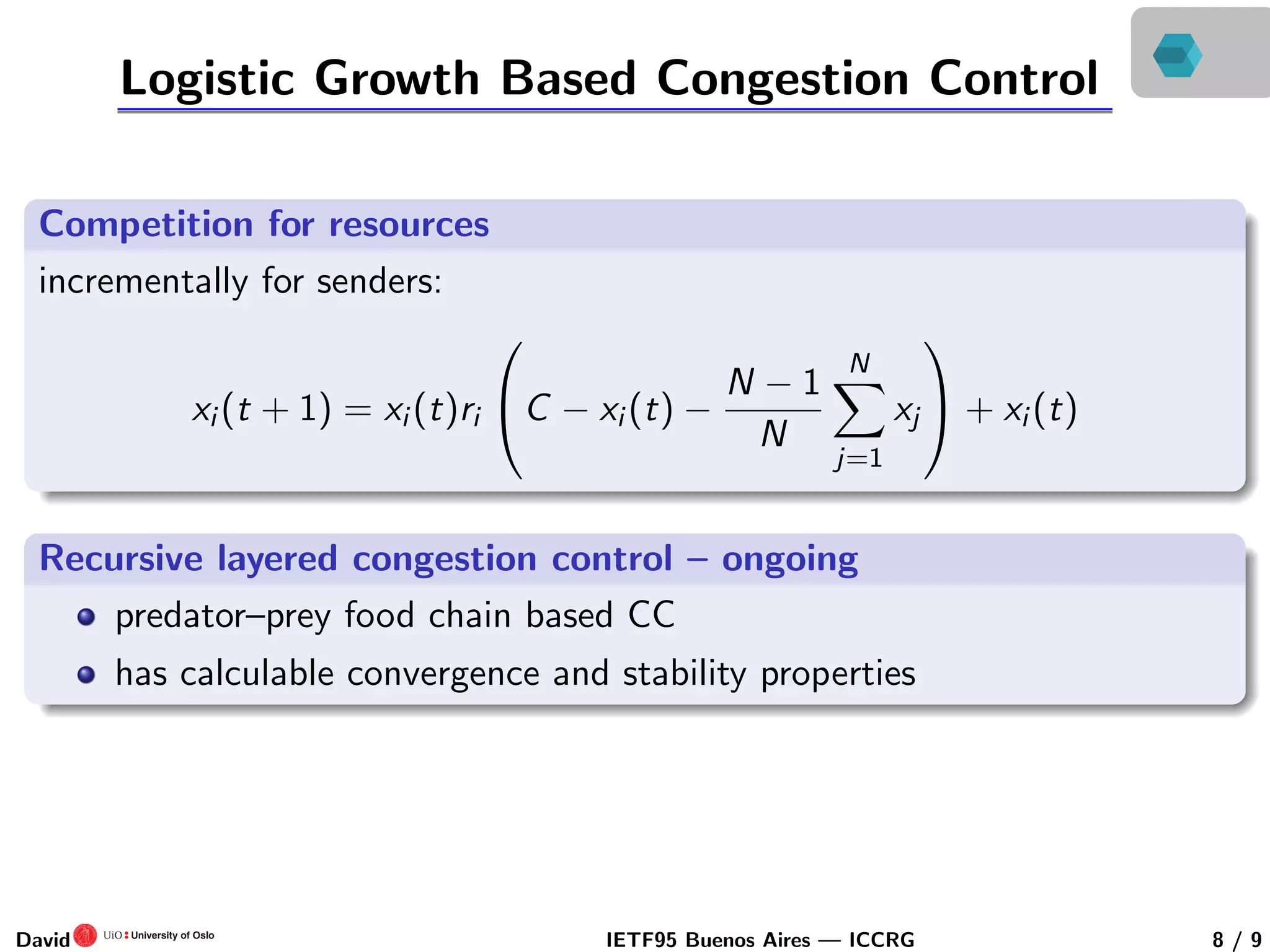
This document discusses congestion control in recursive network architectures like the Recursive Inter-Network Architecture (RINA). It describes how RINA uses a layered, recursive stack approach compared to the layered Internet architecture. It also discusses types of network congestion that can be addressed, including through end system adaptation of traffic sources adjusting their send rates. The document outlines ongoing research into developing stable, scalable new types of congestion control for recursive networks, including approaches inspired by logistic growth models in nature.
![Congestion Control in Recursive Network
Architectures
David Hayes, Peyman Teymoori, and Michael Welzl
University of Oslo
[davihay,peymant,michawe]@ifi.uio.no
IETF95 Buenos Aires — ICCRG
David IETF95 Buenos Aires — ICCRG 1 / 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-95-iccrg-1-160429110325/75/Congestion-Control-in-Recursive-Network-Architectures-1-2048.jpg)