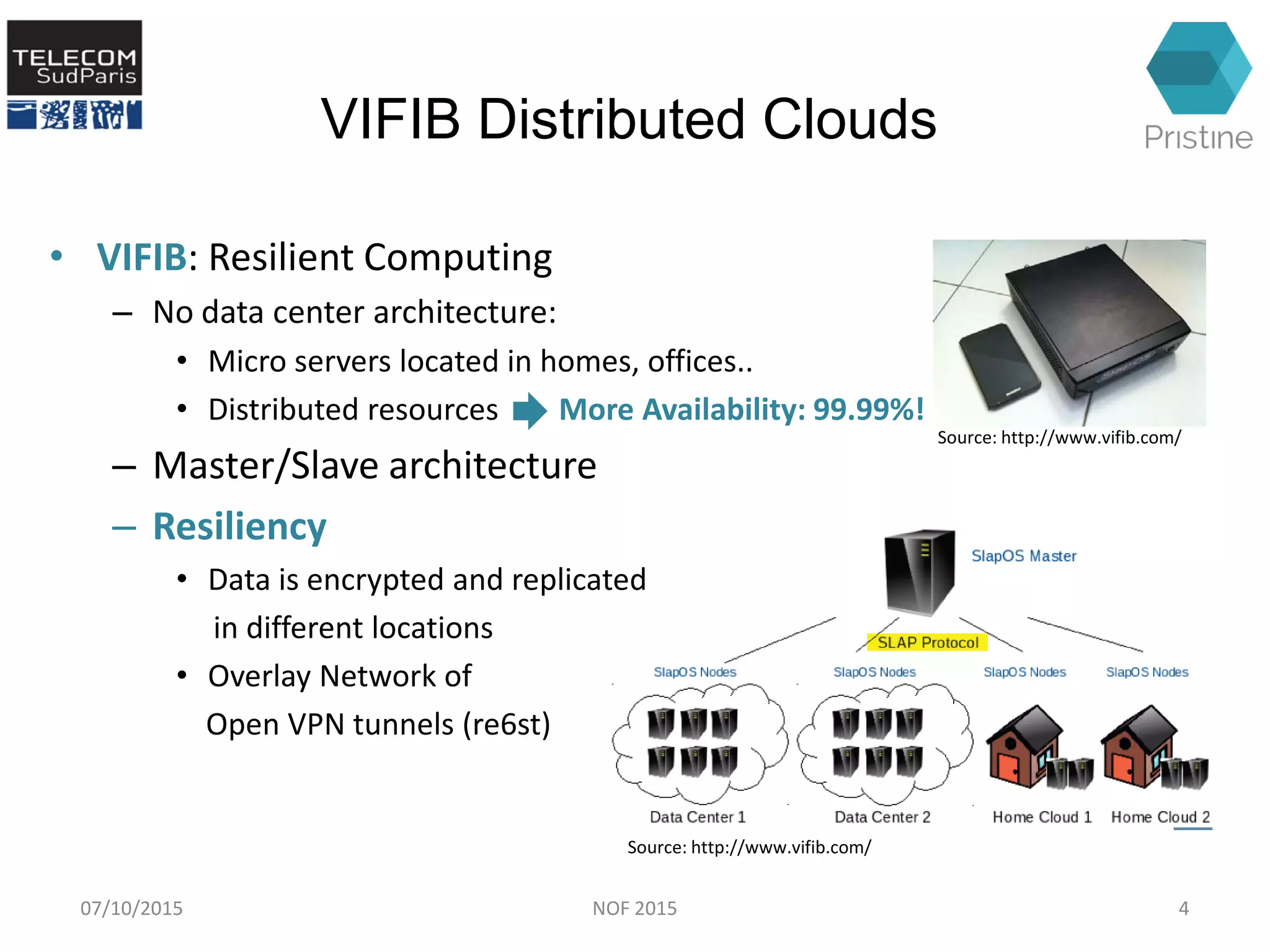
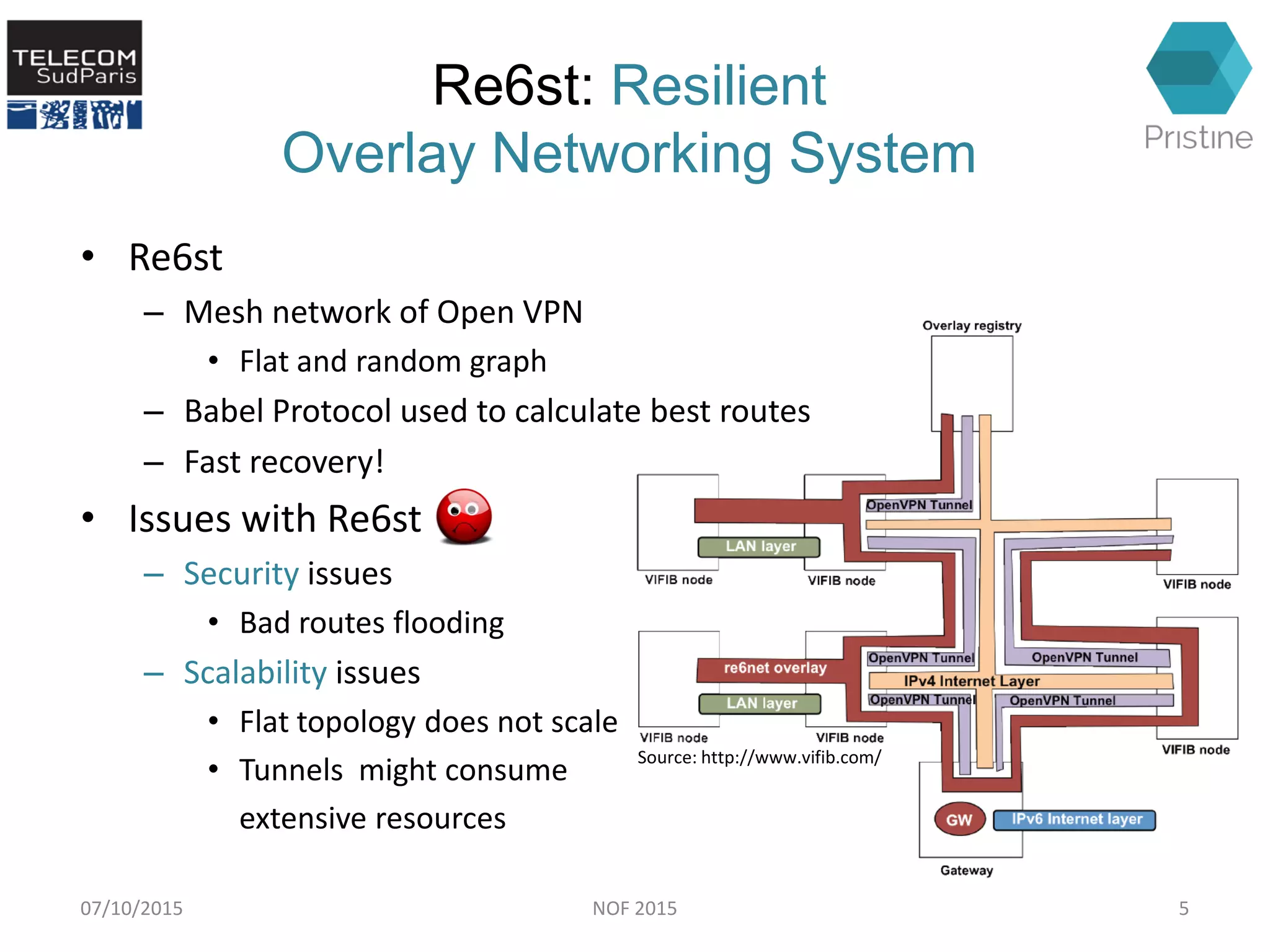
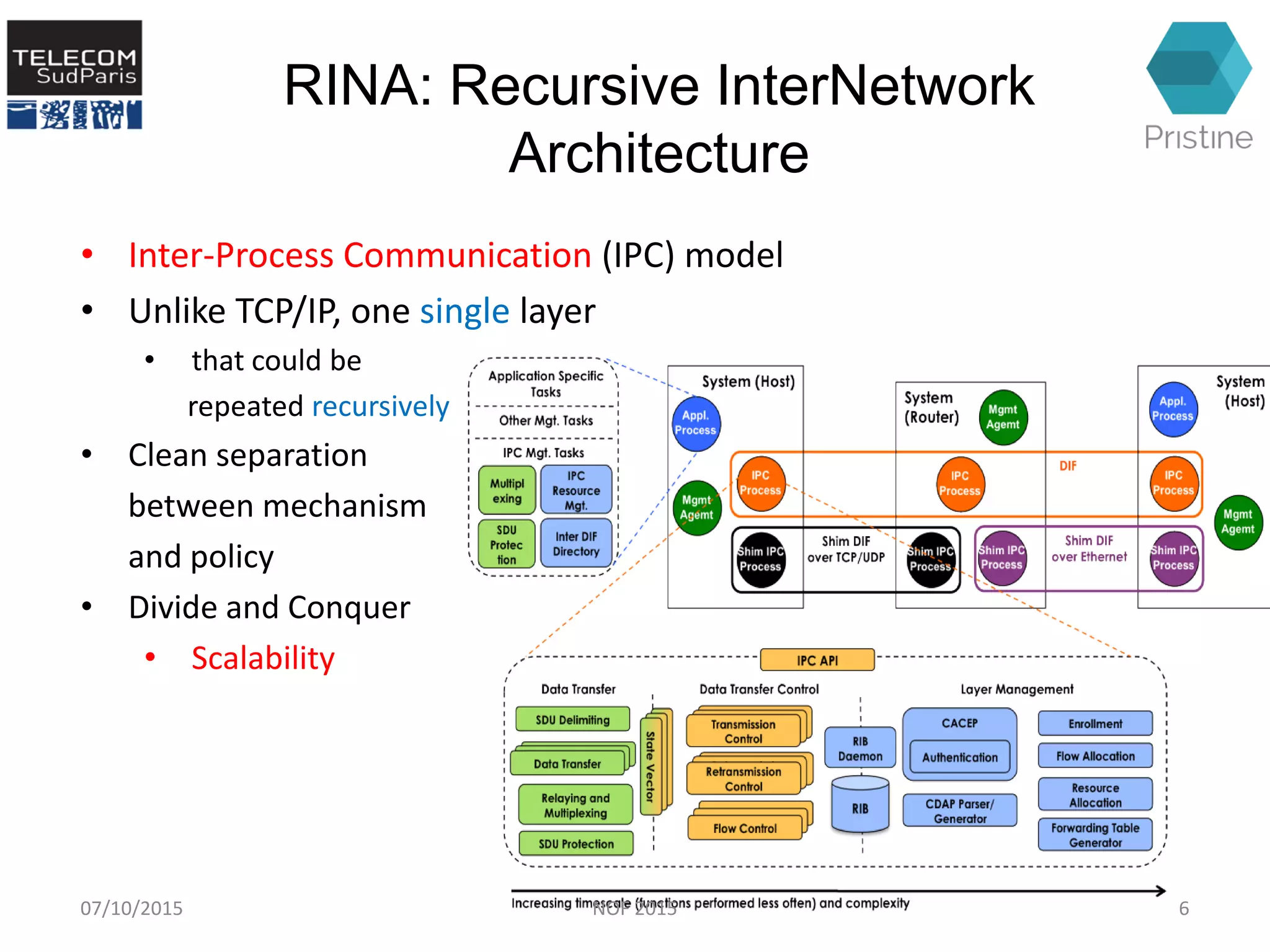
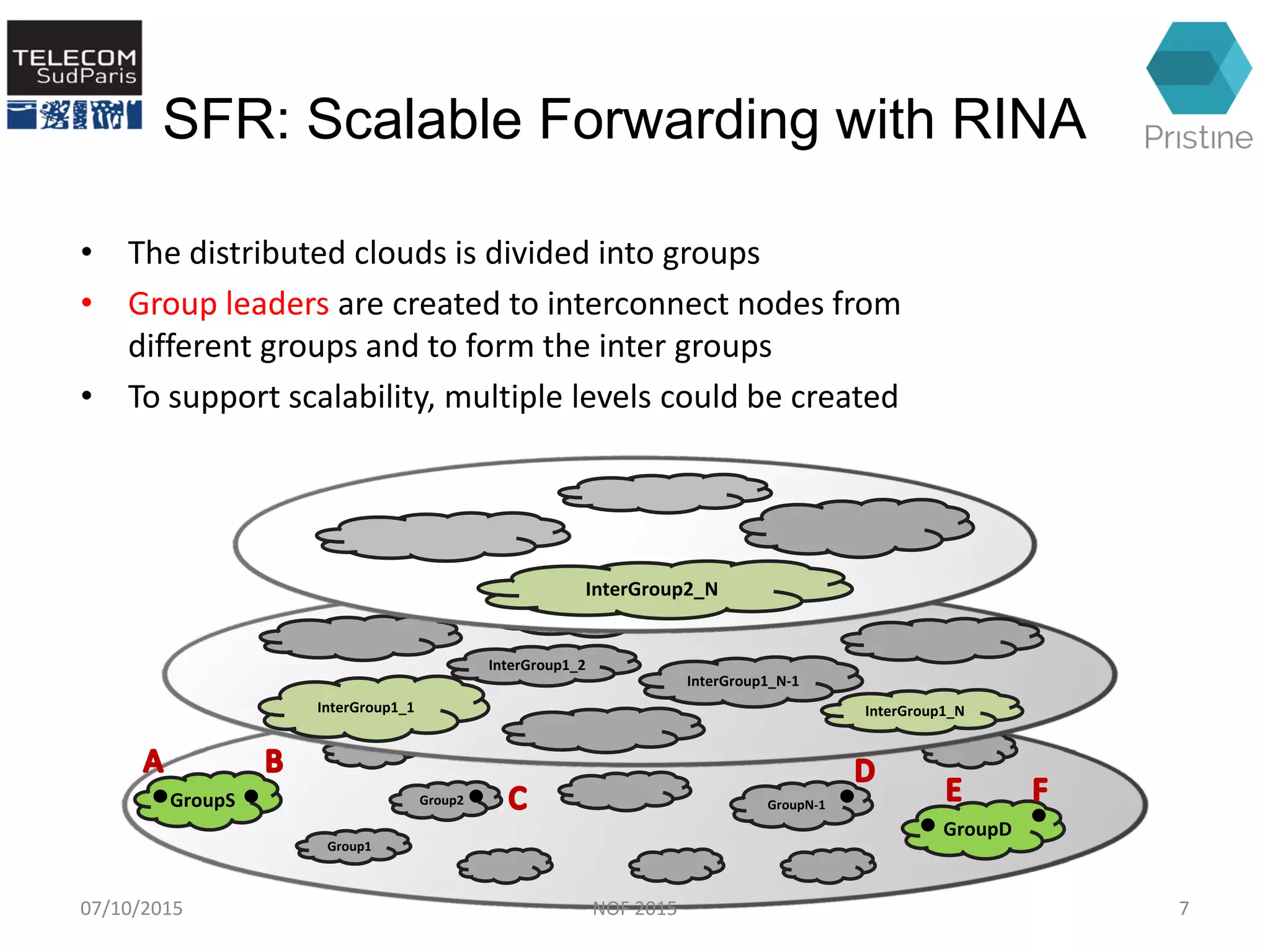
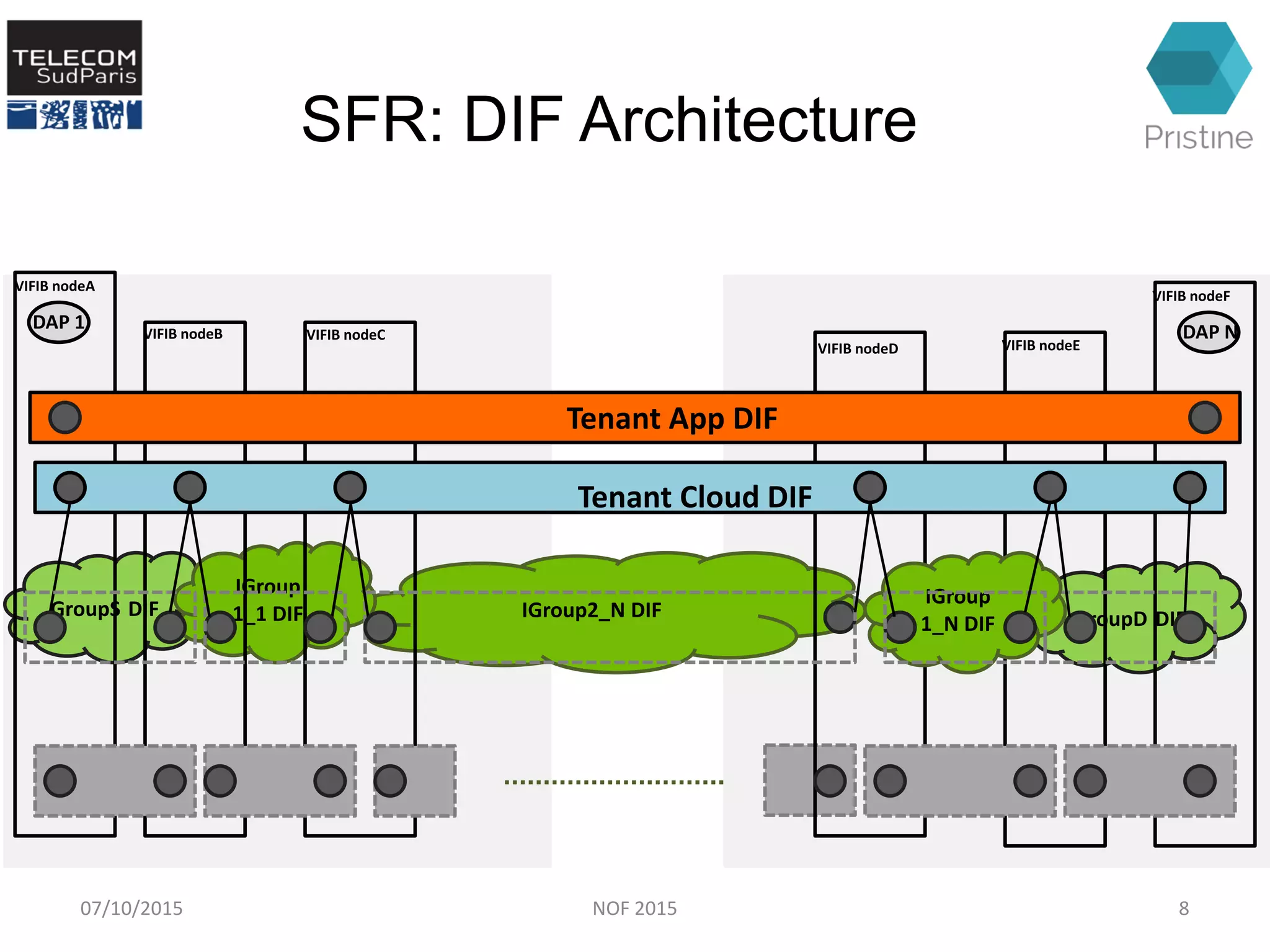
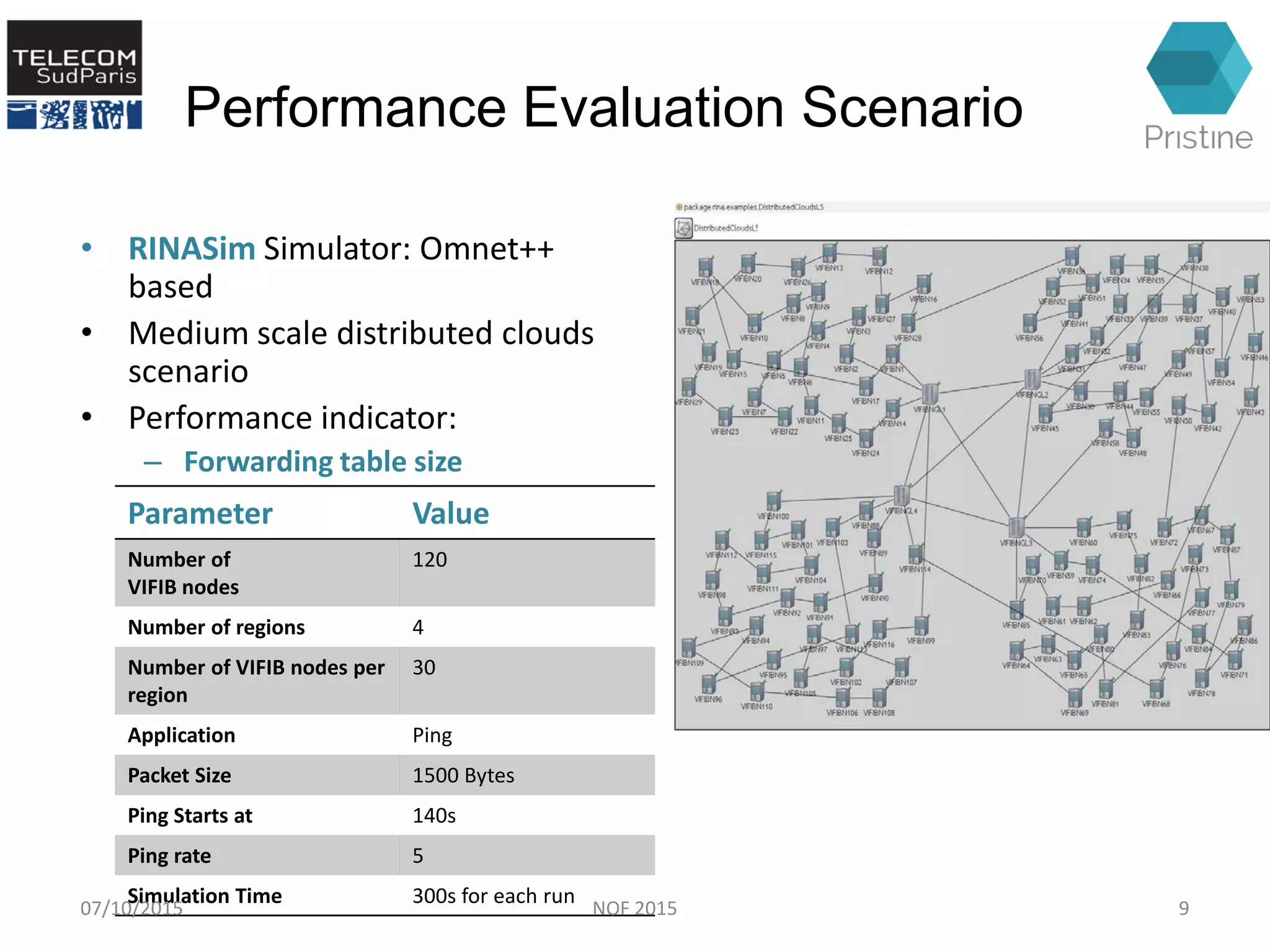
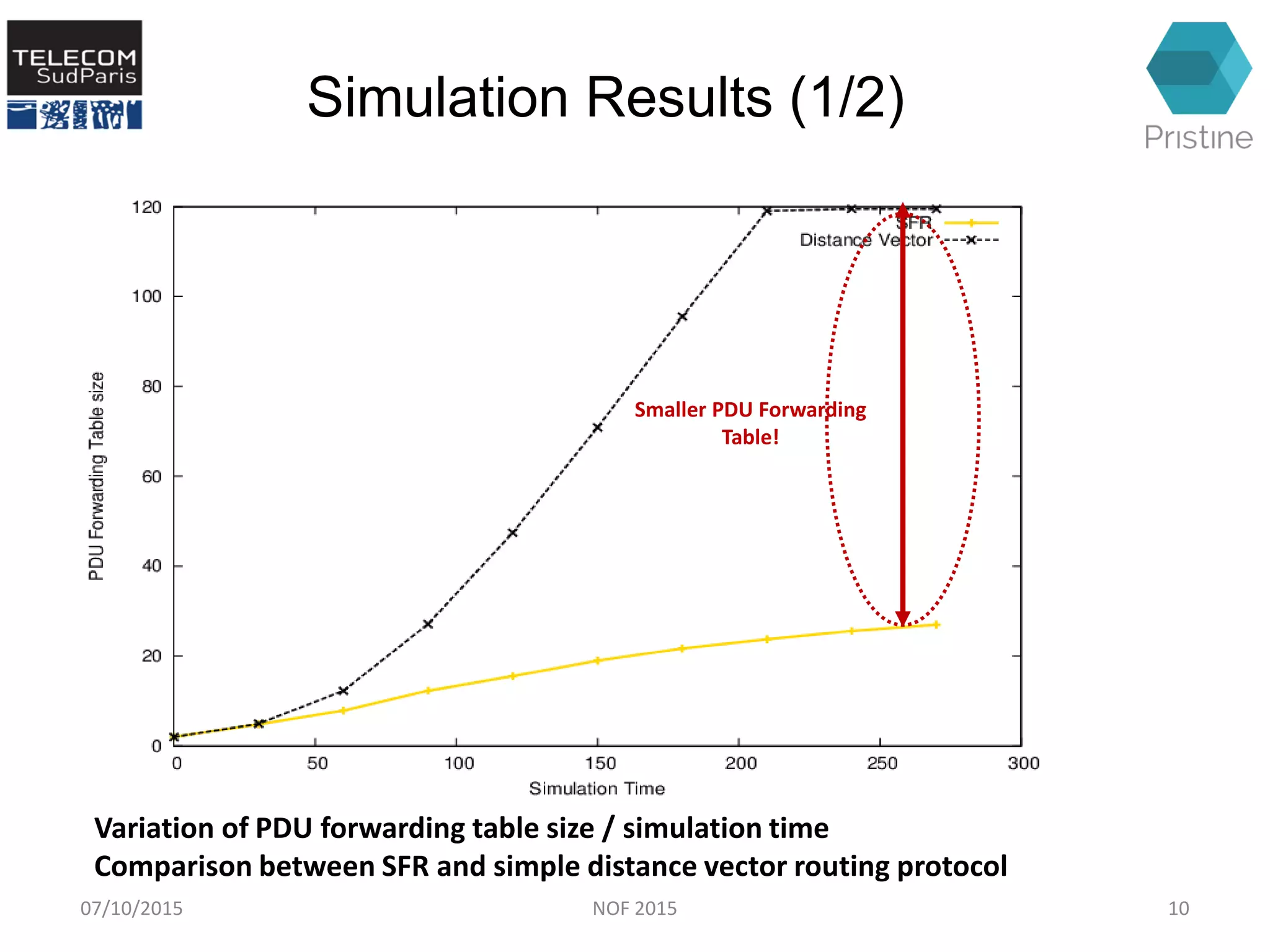
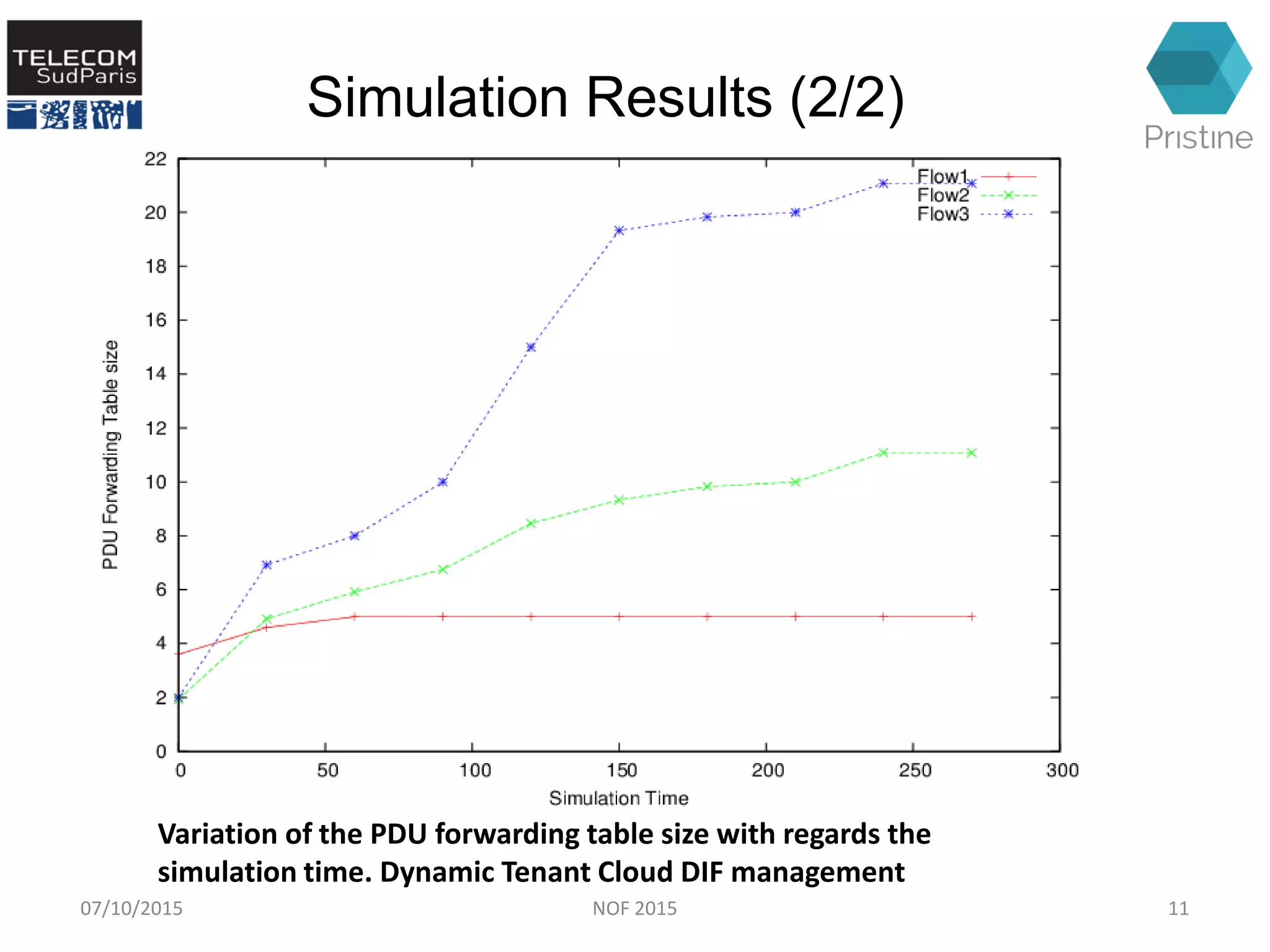
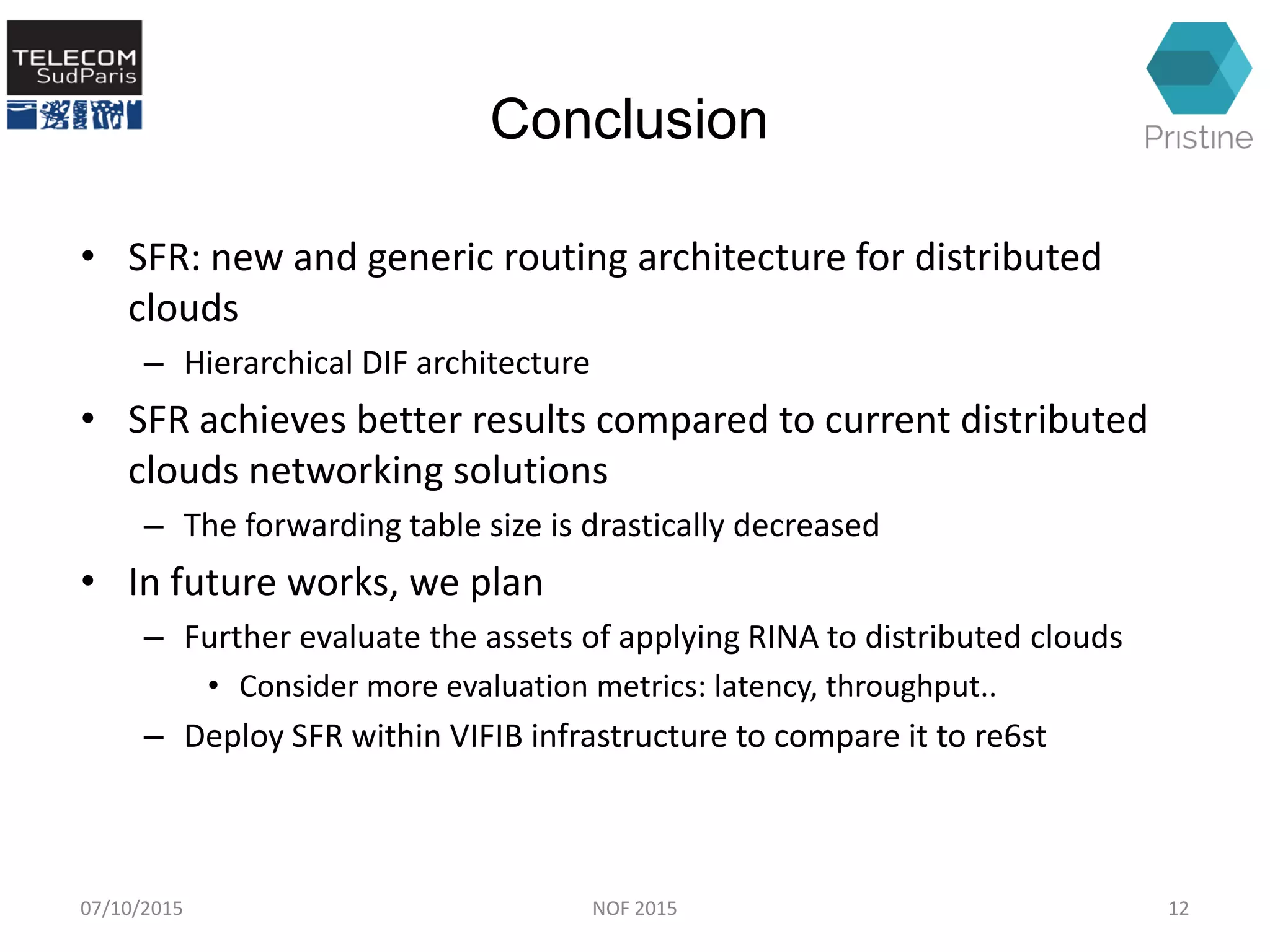
This document summarizes a research paper presented at the 6th International Conference NOF 2015 in Montreal, Canada on September 30, 2015. The paper proposes a new routing architecture called Scalable Forwarding with RINA (SFR) for distributed cloud computing networks. SFR uses a hierarchical Distributed Interprocess Communication Facility (DIF) architecture based on the Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) model. Simulation results show that SFR achieves better scalability than traditional distance vector routing, with drastically smaller forwarding tables. Future work will further evaluate SFR's performance for distributed clouds and deploy it within the VIFIB volunteer cloud infrastructure.