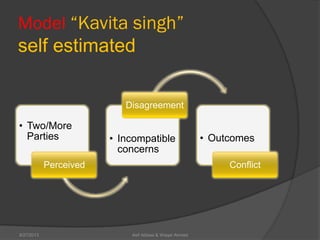
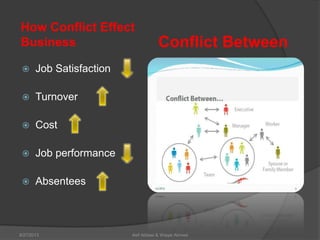
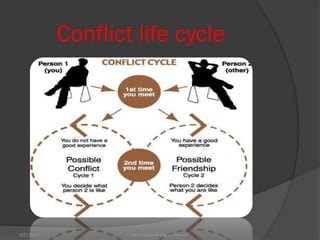
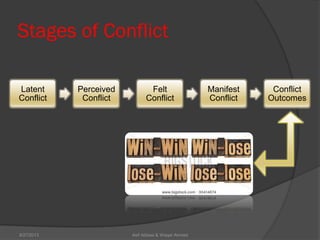
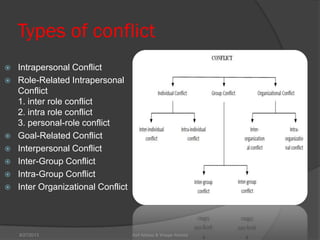
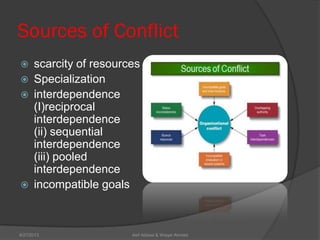
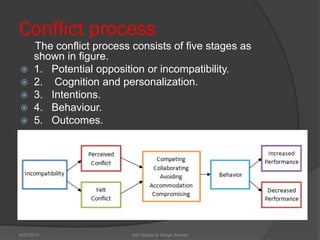
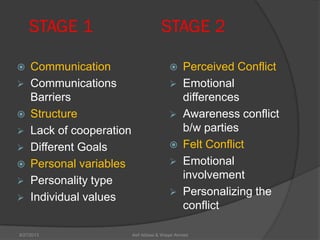
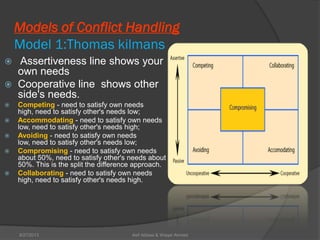
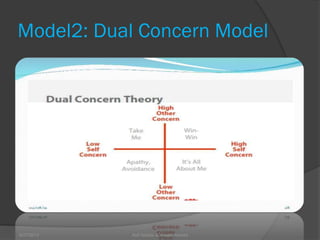
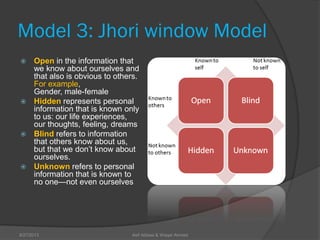
This document discusses conflict management and resolution. It defines conflict as occurring when one party perceives their values, needs or identity are challenged or threatened. Conflict arises from situations, expectations, fear and misunderstandings. The document outlines various views and types of conflict, as well as conflict's stages and processes. It discusses constructive versus destructive conflict and models for conflict handling. Finally, the document provides techniques for conflict resolution, including communication, collaboration and compromise, as illustrated through the example of two girls resolving a dispute over an orange.