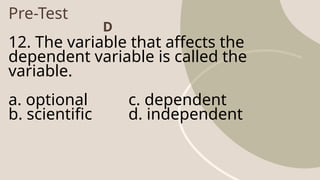
The document discusses data gathering methods such as surveys, experiments, and observations, outlining their definitions, purposes, processes, and advantages and disadvantages. It includes detailed pre-test questions assessing knowledge about these methods, as well as their key characteristics and challenges. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of representative samples, unbiased responses, and systematic approaches in research methodology.