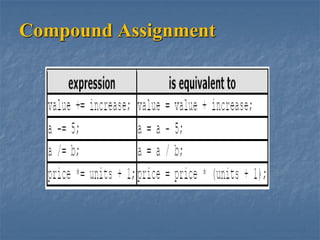
This document discusses various types of operators in C++, including arithmetic, relational, logical, unary, assignment, compound assignment, conditional, and comma operators. It provides examples of how these operators function, particularly focusing on increment and decrement operations, as well as the usage of the conditional operator. Additionally, it introduces the sizeof operator and concludes with an invitation for questions.