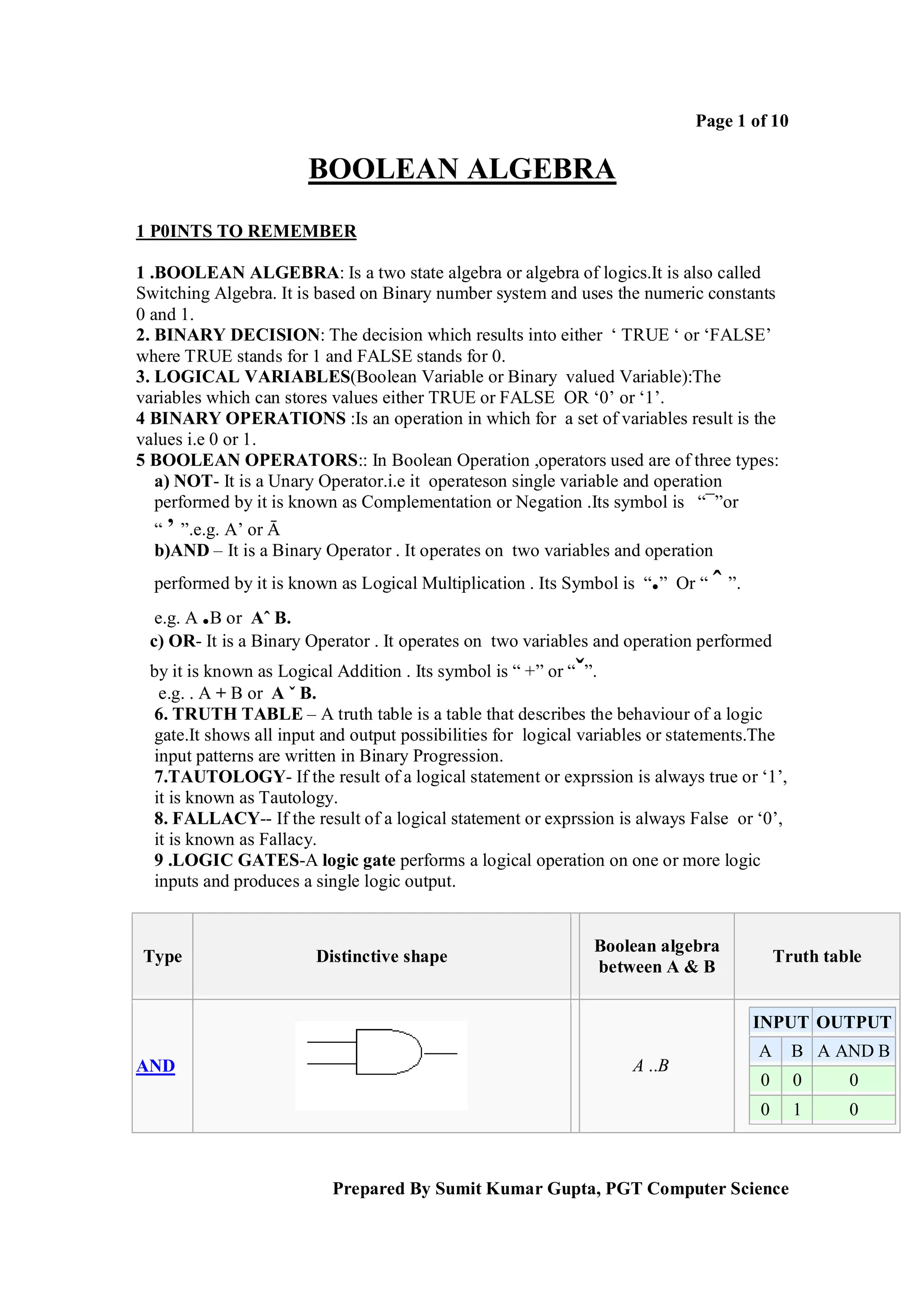
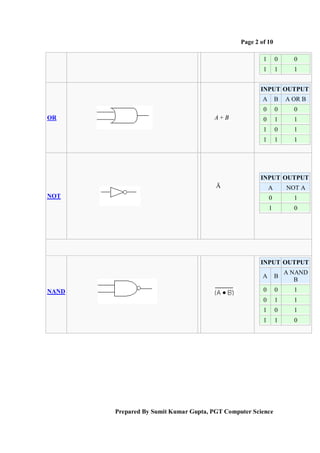
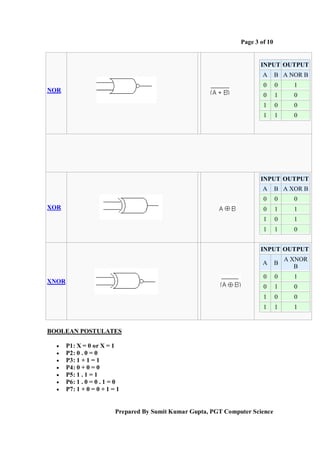
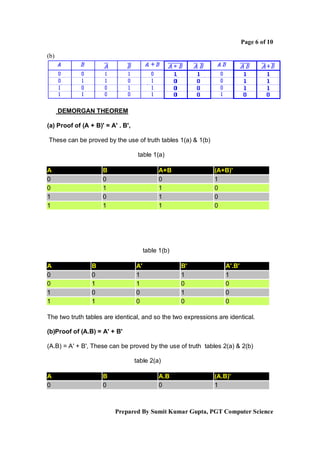
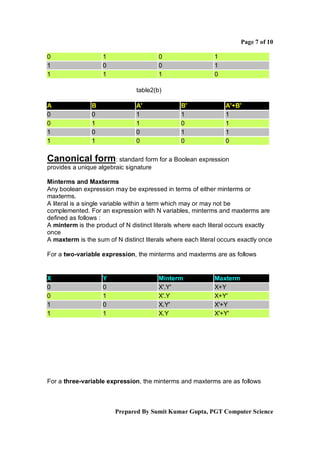
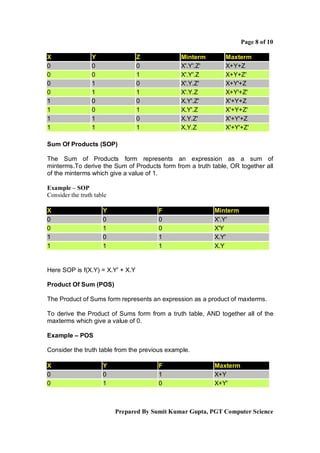
Boolean algebra is a logical system used to simplify binary expressions. It uses binary variables that can have a value of 1 or 0, and logical operators like AND, OR and NOT. Boolean expressions can be represented in truth tables and minimized using Karnaugh maps or algebraic manipulation. Key concepts include minterms, maxterms, sum of products form, and product of sums form. Boolean algebra provides a standard way to simplify logical statements and circuits into their essential components.