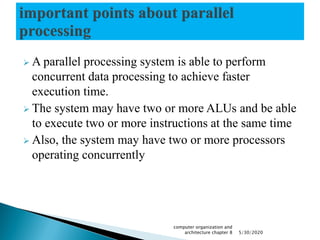
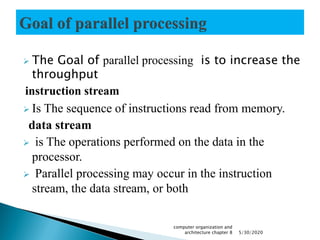
Parallel processing involves performing multiple calculations simultaneously by dividing large problems into smaller subproblems that can be solved concurrently. This allows parallel systems to achieve faster execution times using multiple processing elements that perform concurrent data processing. Parallel processing can occur at the instruction level, data level, or both. Common parallel processing architectures include single instruction single data (SISD), single instruction multiple data (SIMD), multiple instruction single data (MISD), and multiple instruction multiple data (MIMD). Pipelining is a technique used in parallel processing where multiple instructions are overlapped in their execution across different functional units of a processor.








![ The difference between the two is that scalar
processors operate on only one data point at a time,
while vector processors operate on an array of data.
Many scientific problems require arithmetic
operations on large arrays of numbers.
These numbers are usually formulated as vectors and
matrices of floating point numbers.
A vector is an ordered set of a one dimensional array
of data items.
A vector V of length n is represented as a row vector
by V= [V1, V2, V3,...,Vn].
5/30/2020
computer organization and
architecture chapter 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-231216100902-83d08c07/85/Computer-organization-and-architectures-chapter8-14-320.jpg)