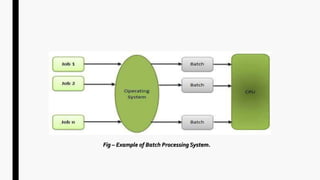
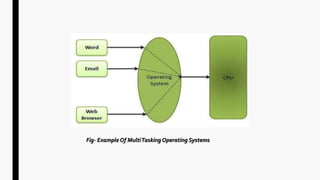
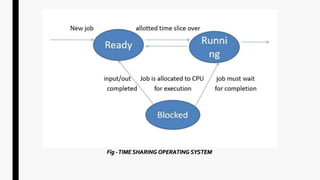
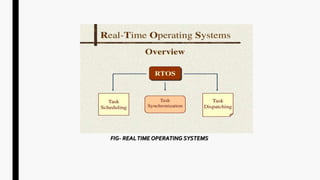
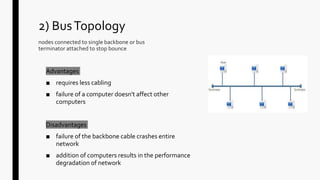
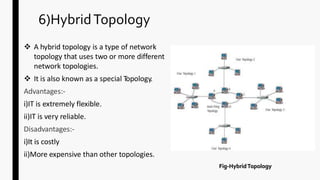
This document provides an overview of operating systems and network topologies. It discusses the history and evolution of operating systems from the 1940s to present. Key developments include the introduction of batch processing systems in the 1950s, multi-tasking systems in the 1960s, and graphical user interfaces in the 1980s. The document also defines different types of operating systems such as single-user, multi-user, real-time, and time-sharing systems. Additionally, it describes various network topologies like bus, star, ring, mesh and hybrid along with their advantages and disadvantages.