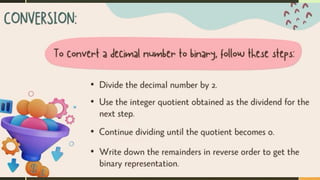
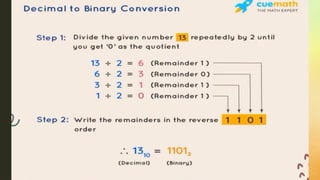
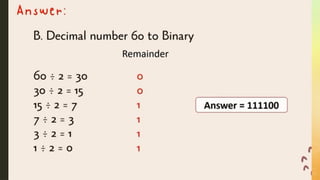
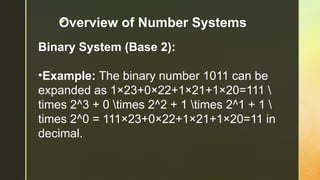
COMPUTER NUMBER SYSTEM( ACTIVITIES)INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY GRADE 7 LEARNING AREA..........................................................................................................................................................................