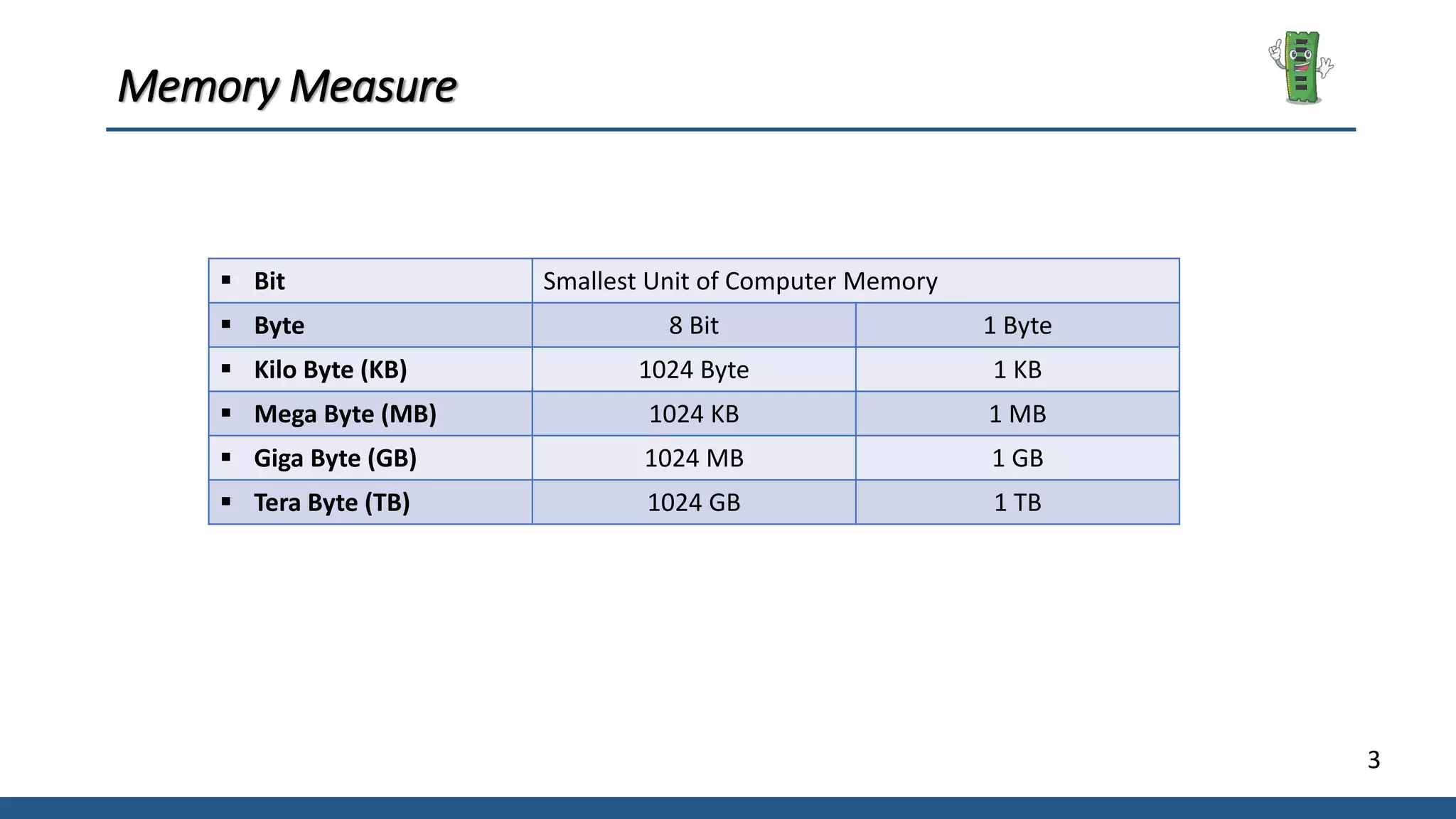
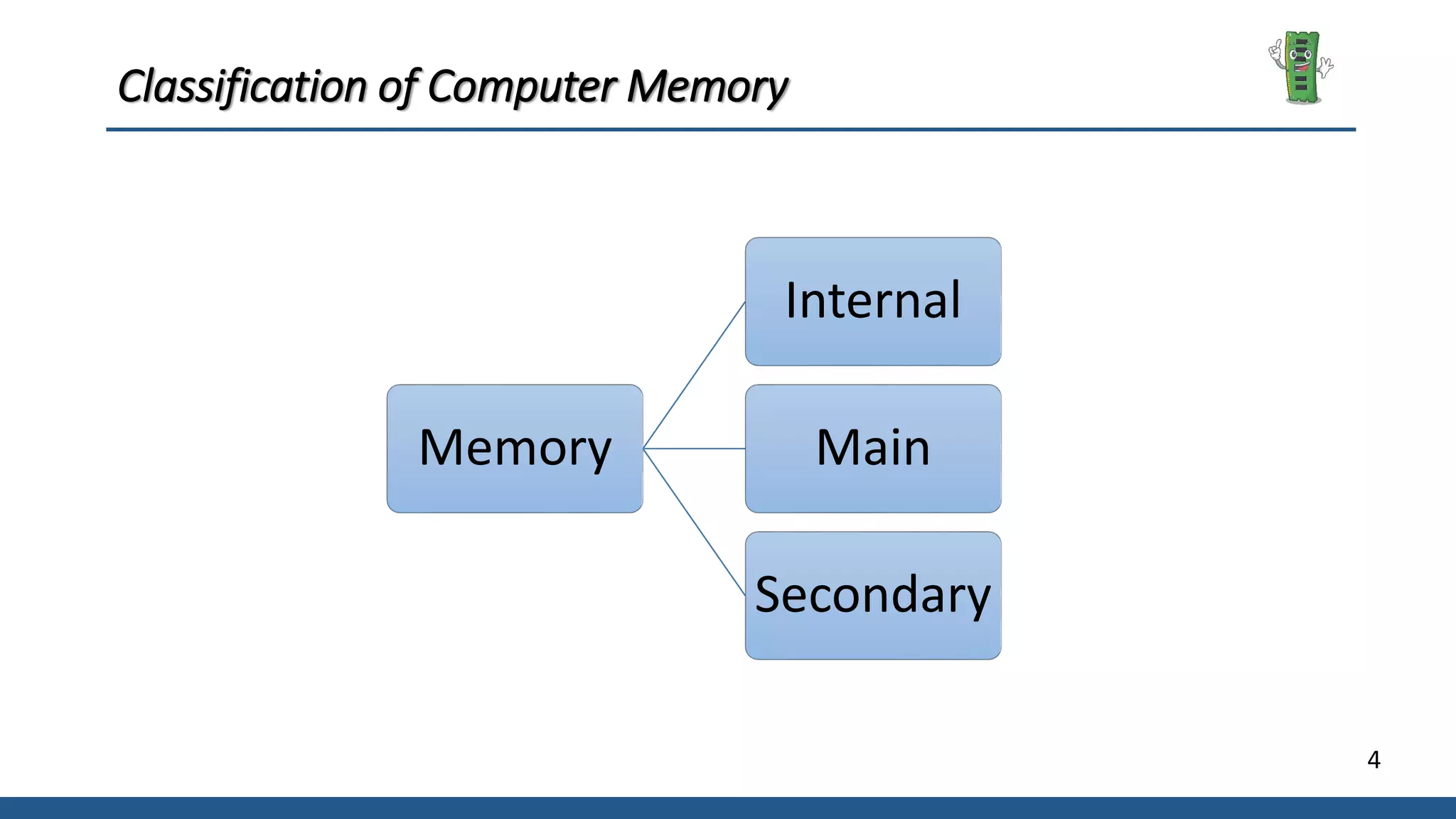
The document provides an overview of computer memory, detailing its definitions, classifications, and types. It explains internal memory, main memory (including RAM and ROM), and secondary memory, along with their characteristics and roles in a computer system. It also includes a breakdown of memory measurements from bits to terabytes.






![15
Reference
[1] www.tutorialspoint.com
[2] www.geeksforgeeks.org
[3] www.arrow.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationse-222191-35-2656-200815115125/75/Computer-Memory-15-2048.jpg)
