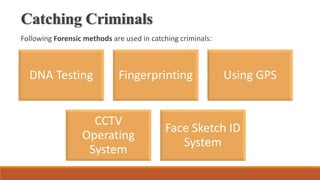
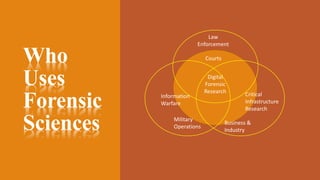
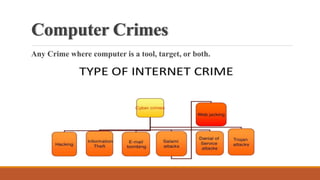
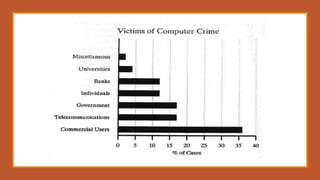
The document provides an overview of computer forensics, detailing its definition, history, objectives, and the various entities involved in its application, including law enforcement and investigative agencies. It covers the process of evidence identification, preservation, extraction, and interpretation, along with the necessary skills and equipment required. Additionally, the document highlights the challenges and disadvantages of computer forensics as well as the increasing importance of this field in modern society.