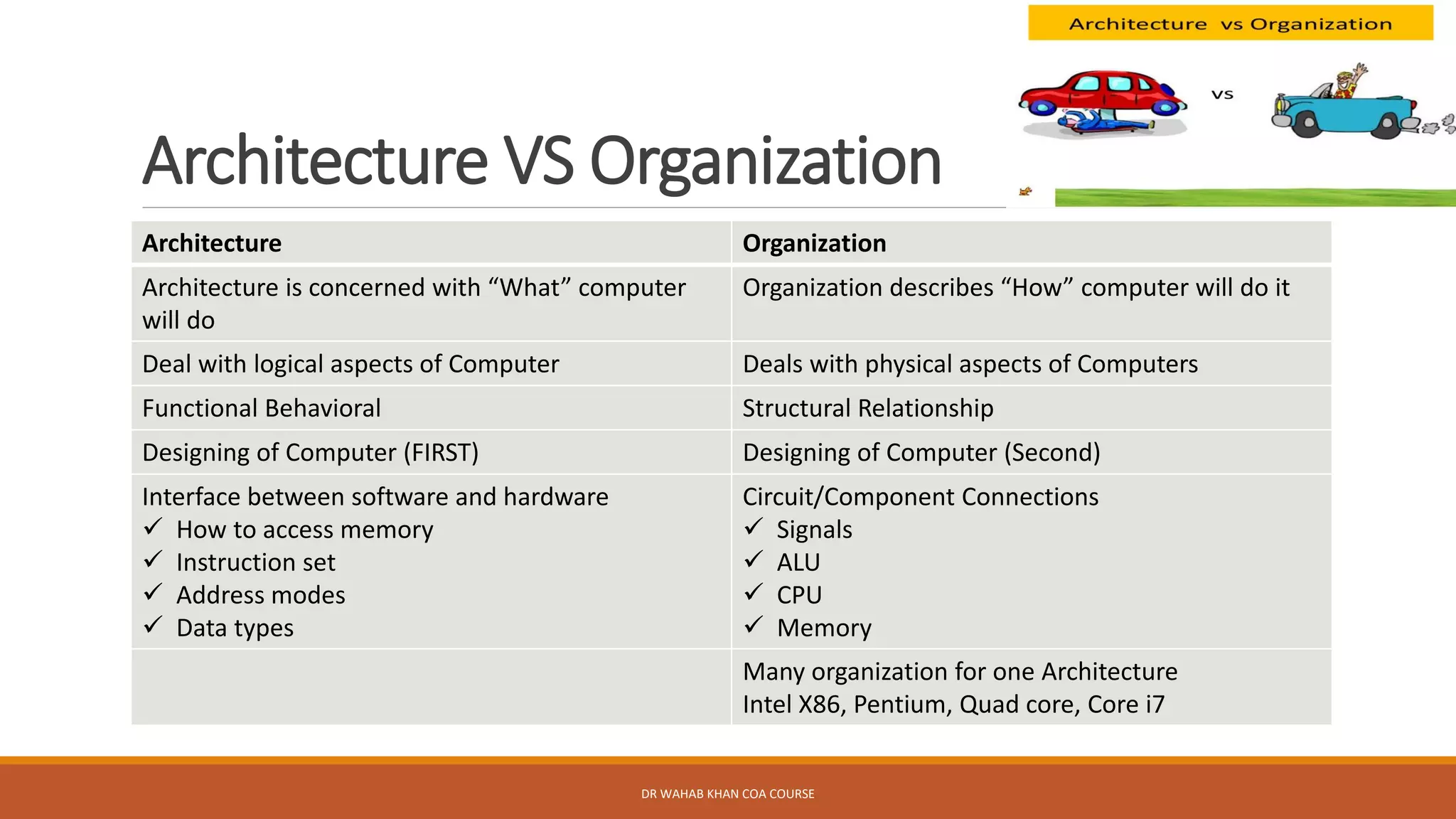
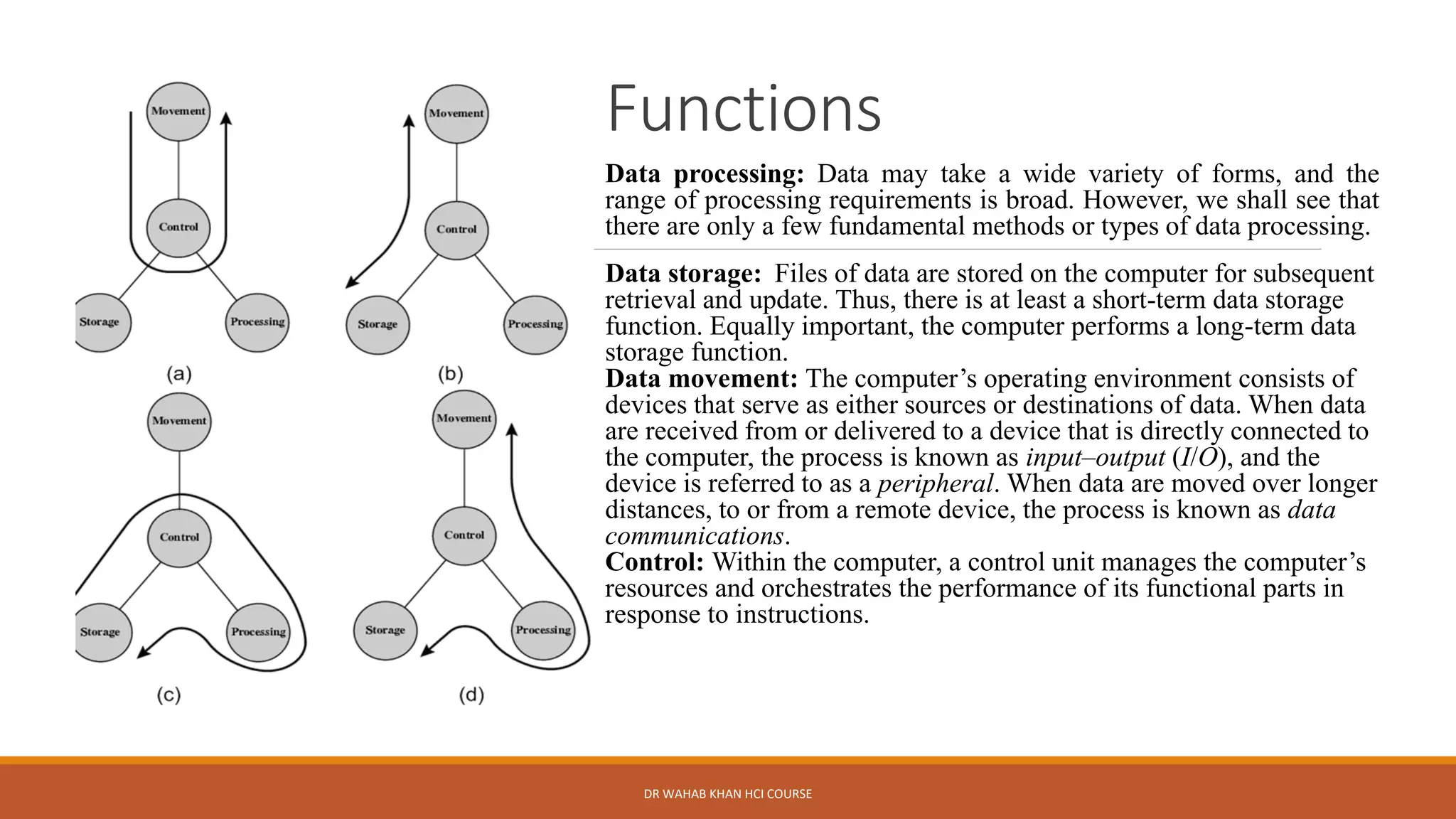
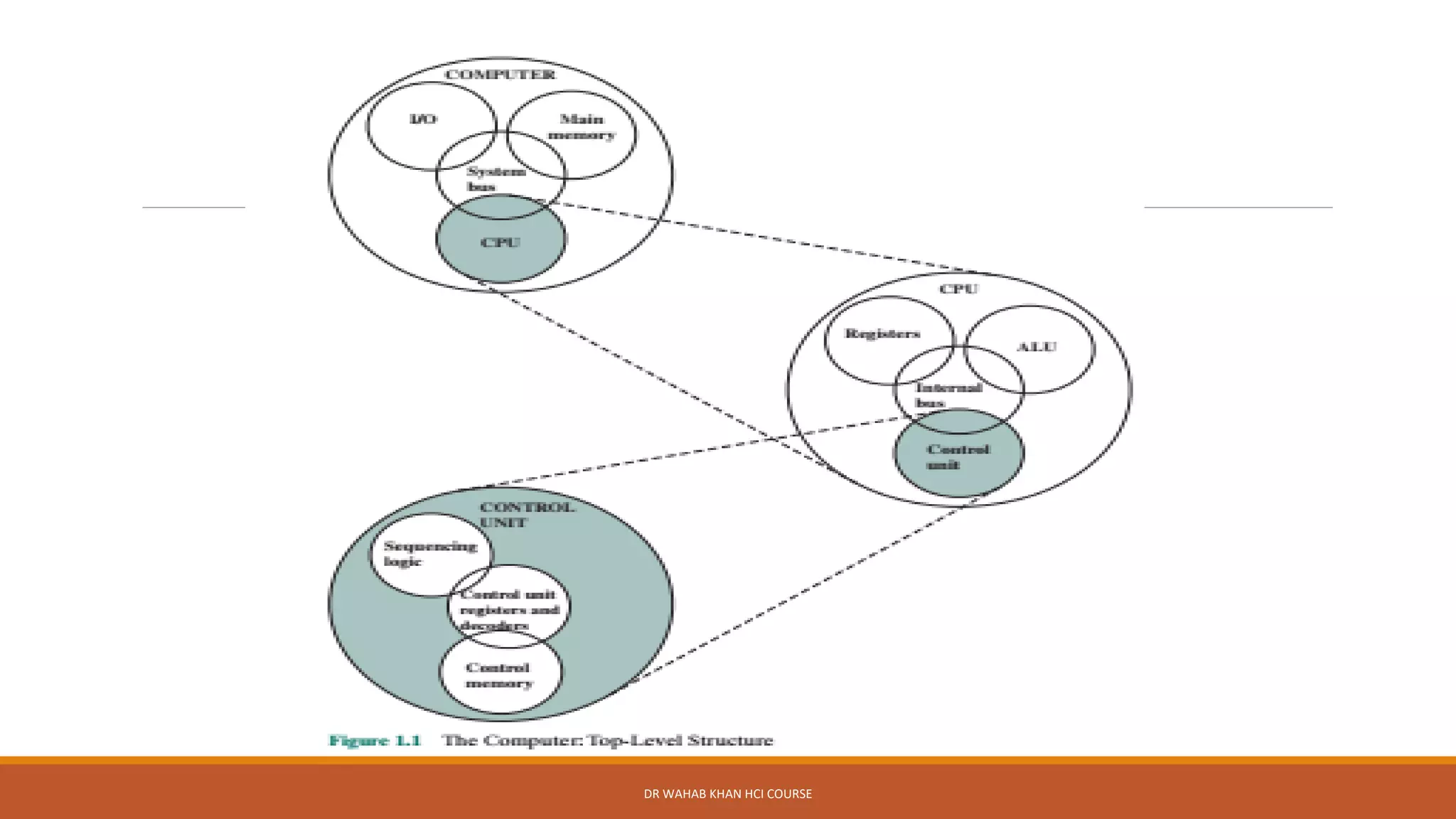
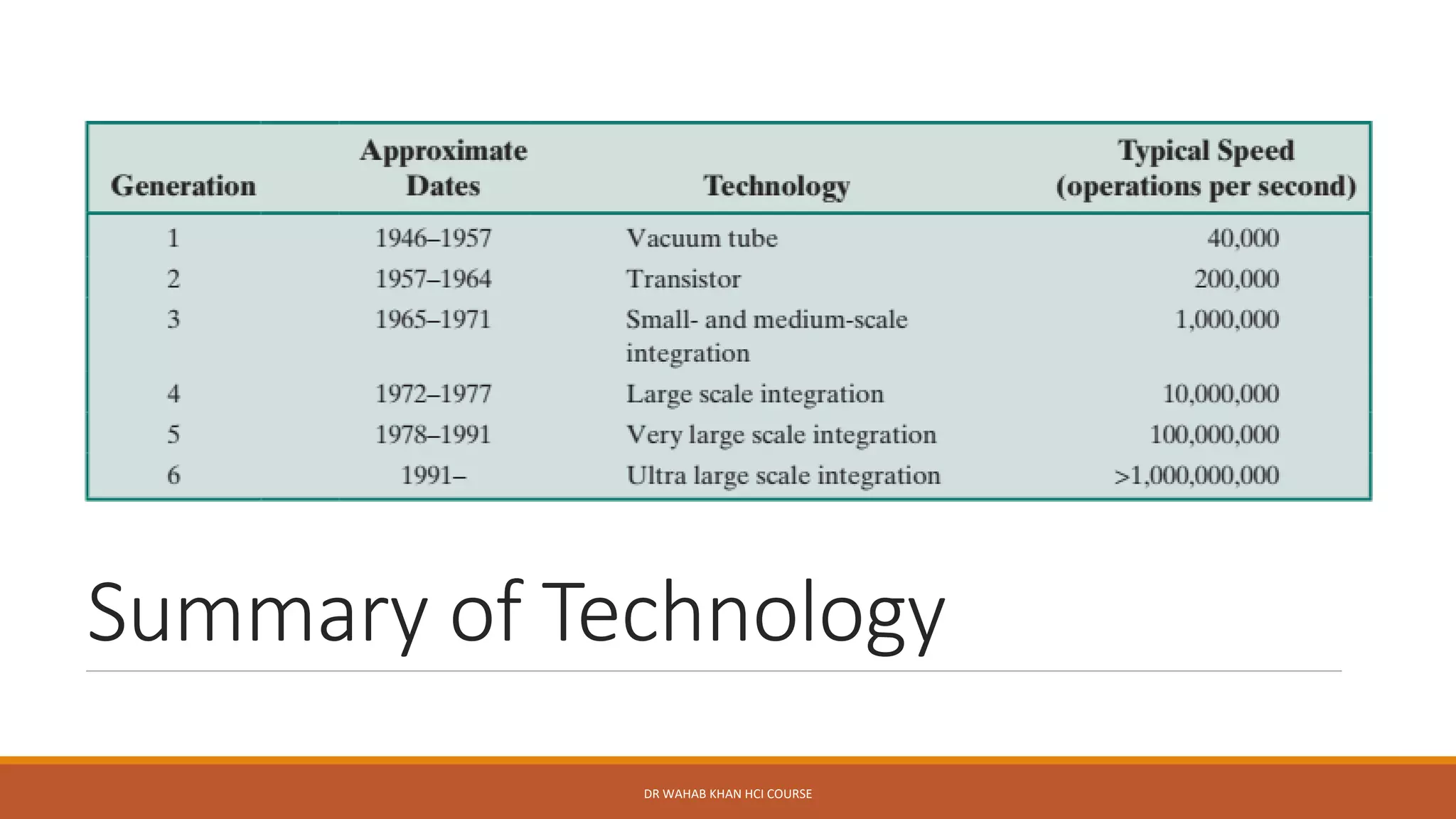
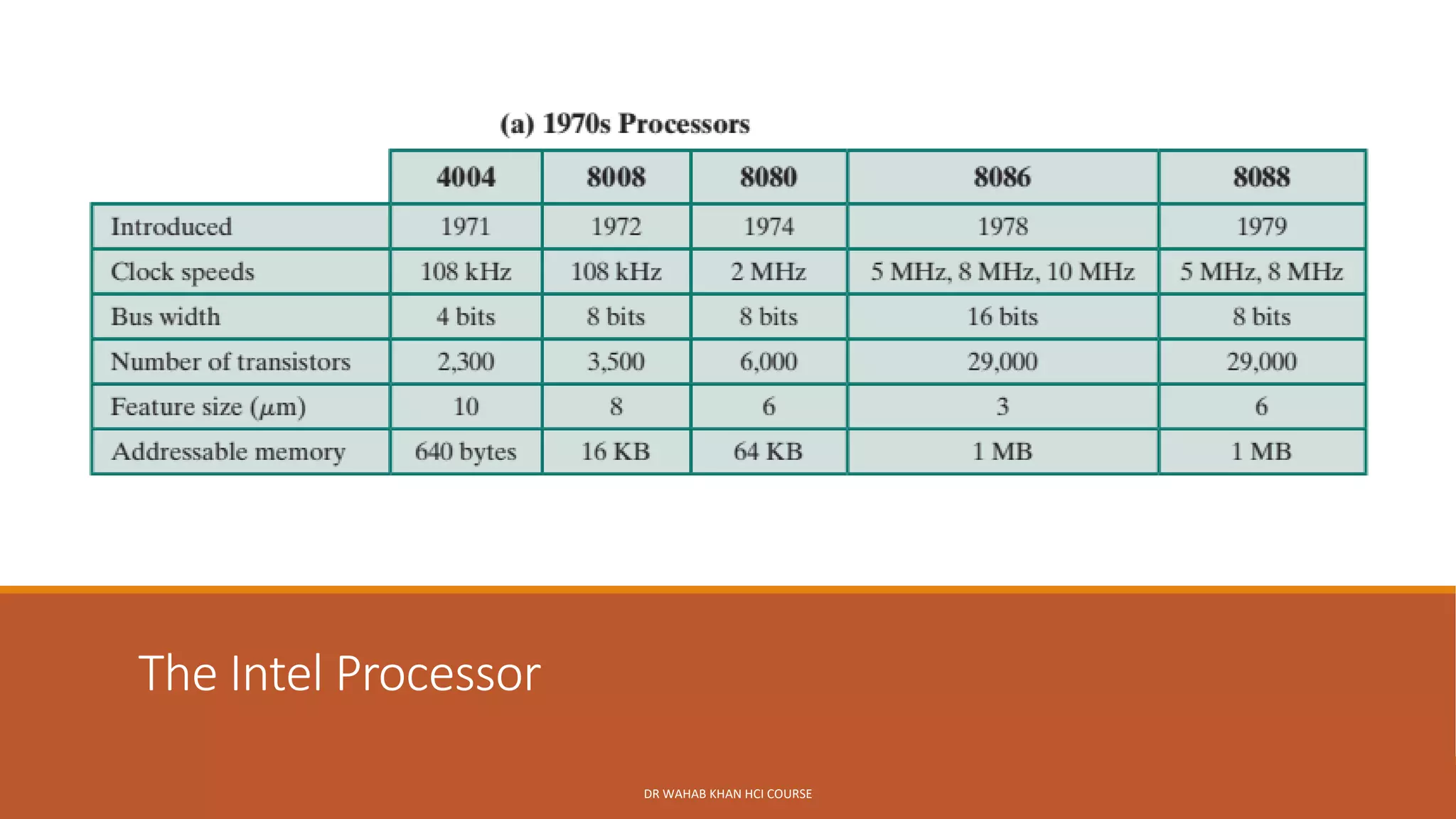
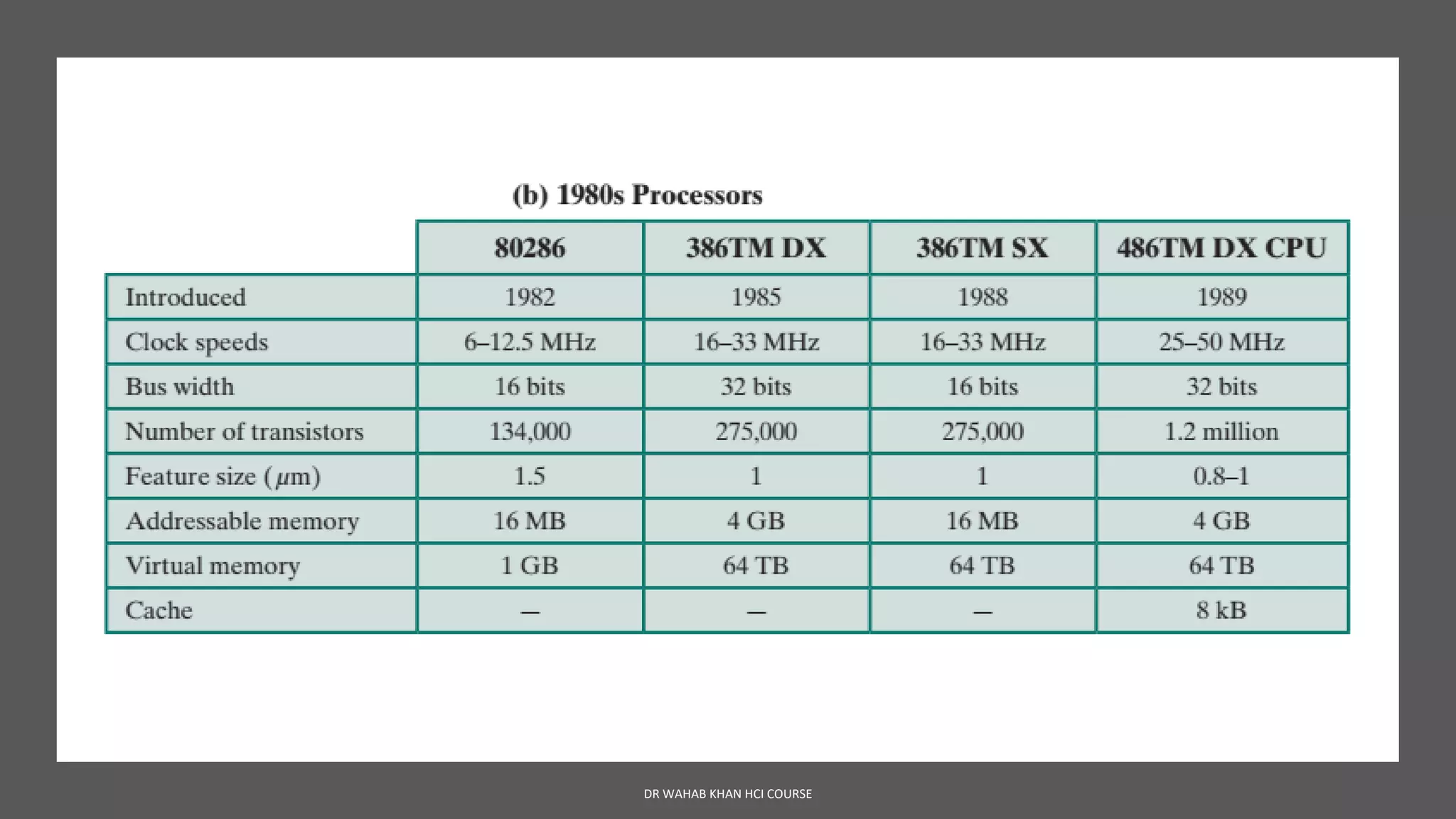
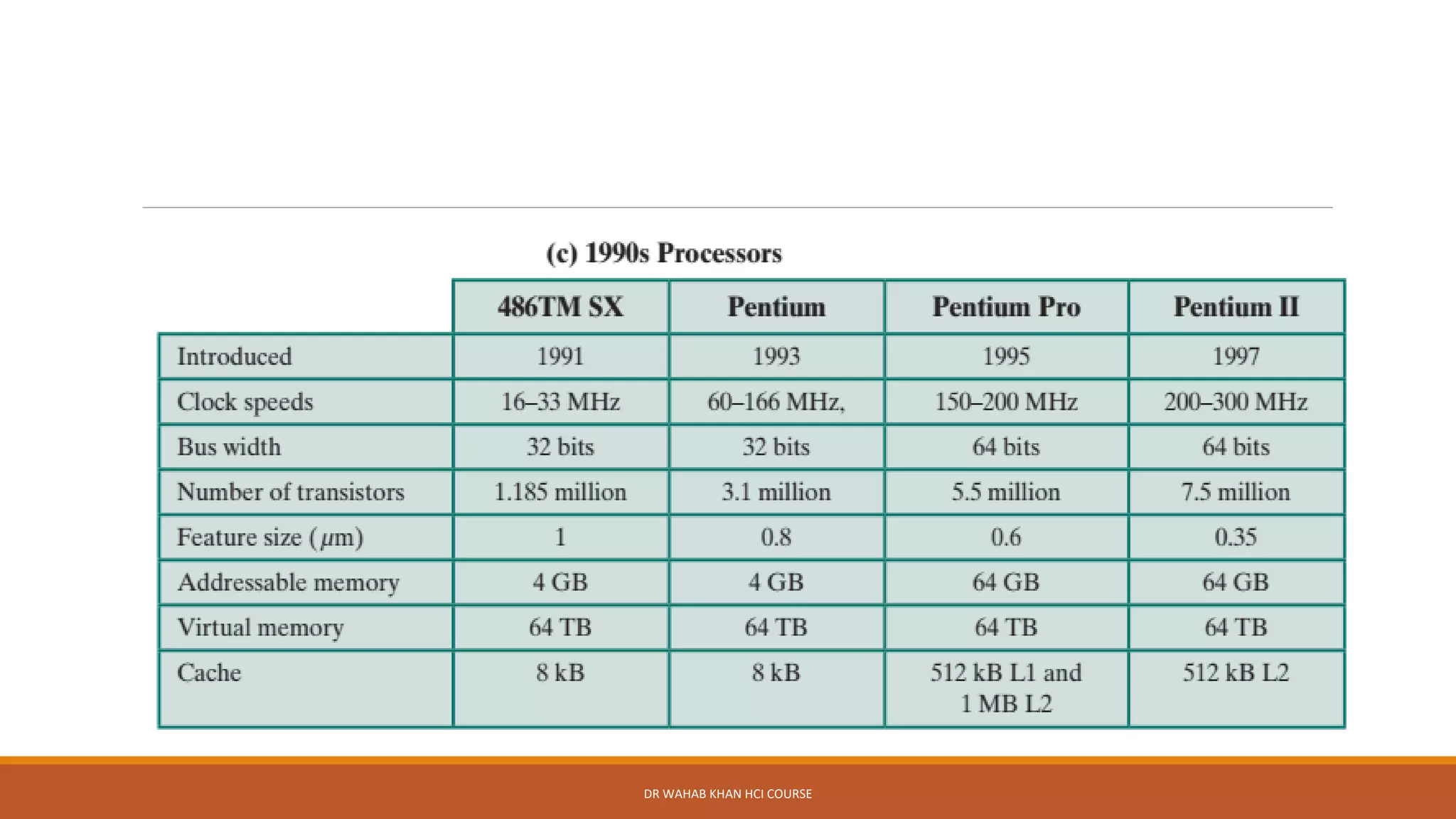
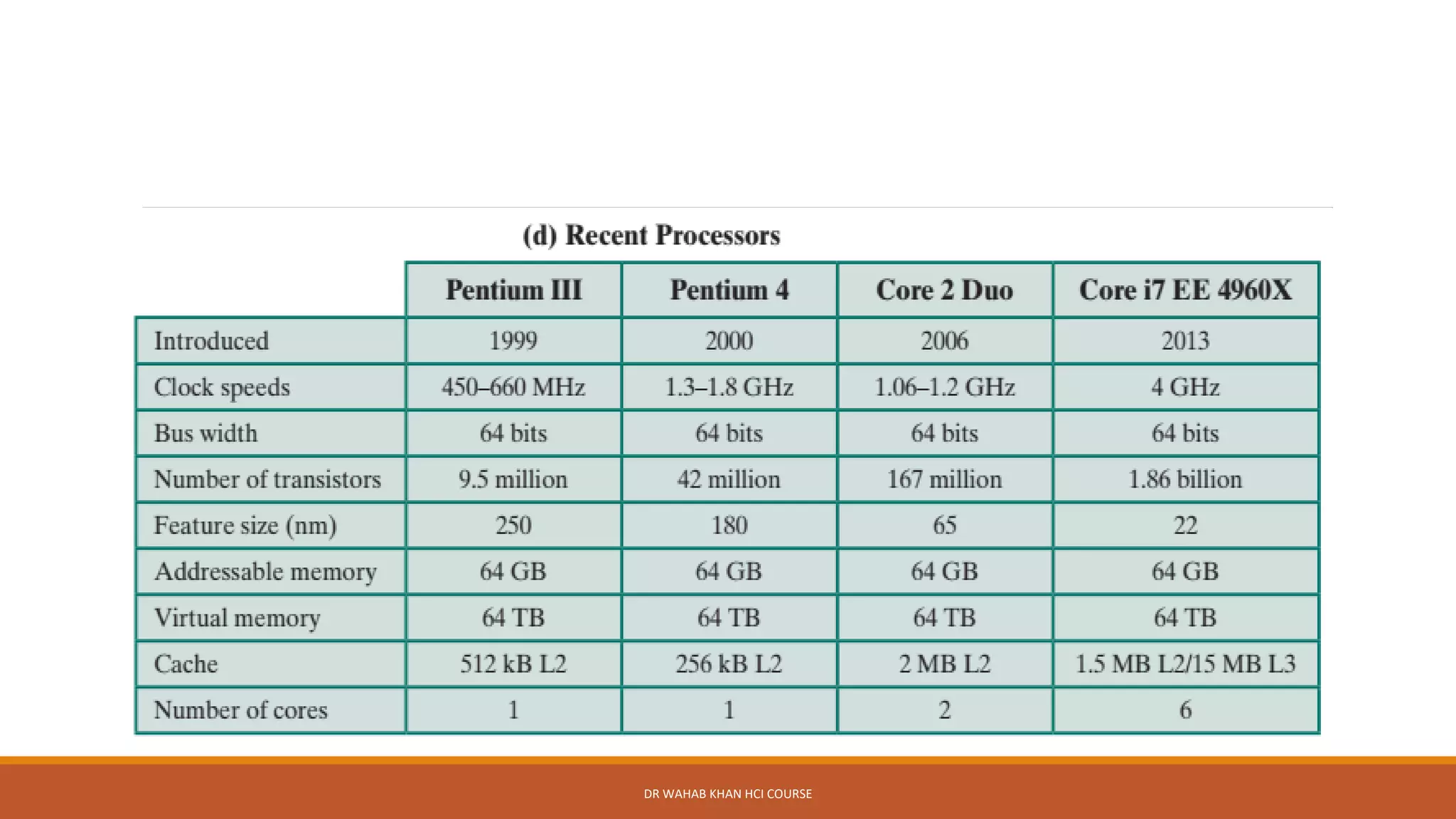
The document outlines various concepts in computer architecture and organization, detailing the differences between architecture (what a computer does) and organization (how it does it), along with the basic functions of a computer. It also discusses the evolution of computer generations, from vacuum tubes in first-generation computers to advancements such as microprocessors in subsequent generations. Additionally, a summary of the Intel processor evolution highlights key innovations and developments in CPU architecture over the years.