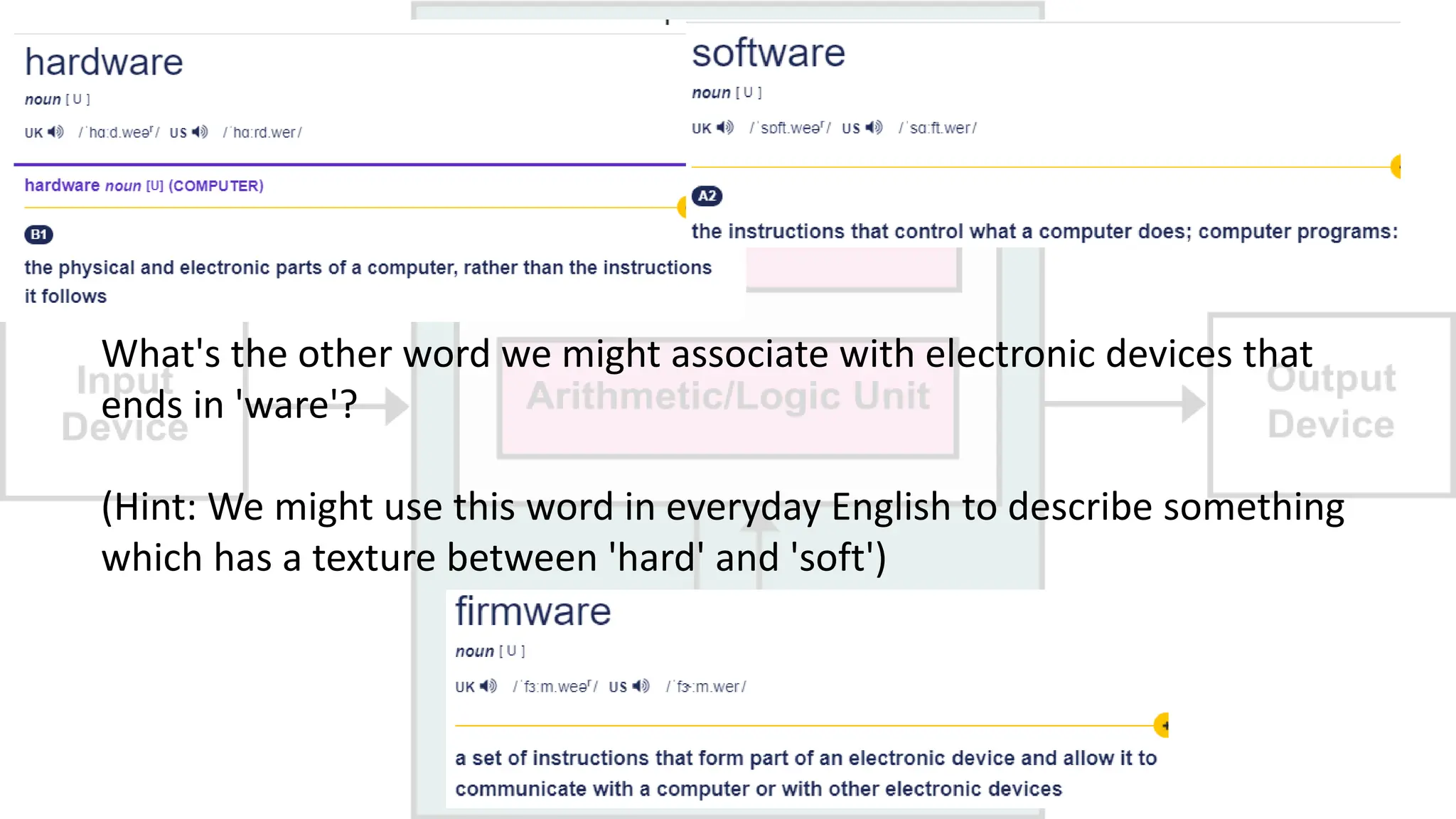
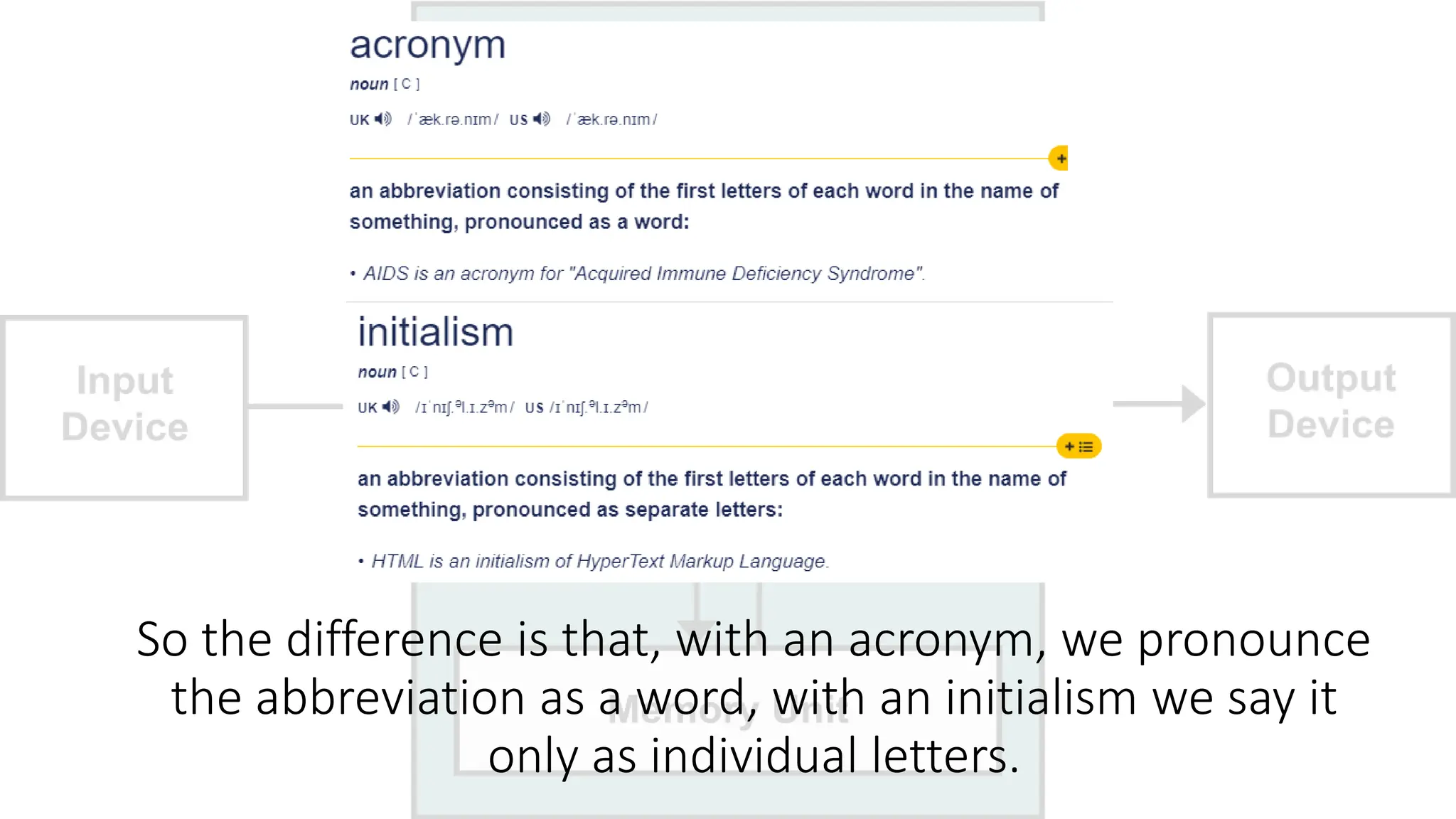
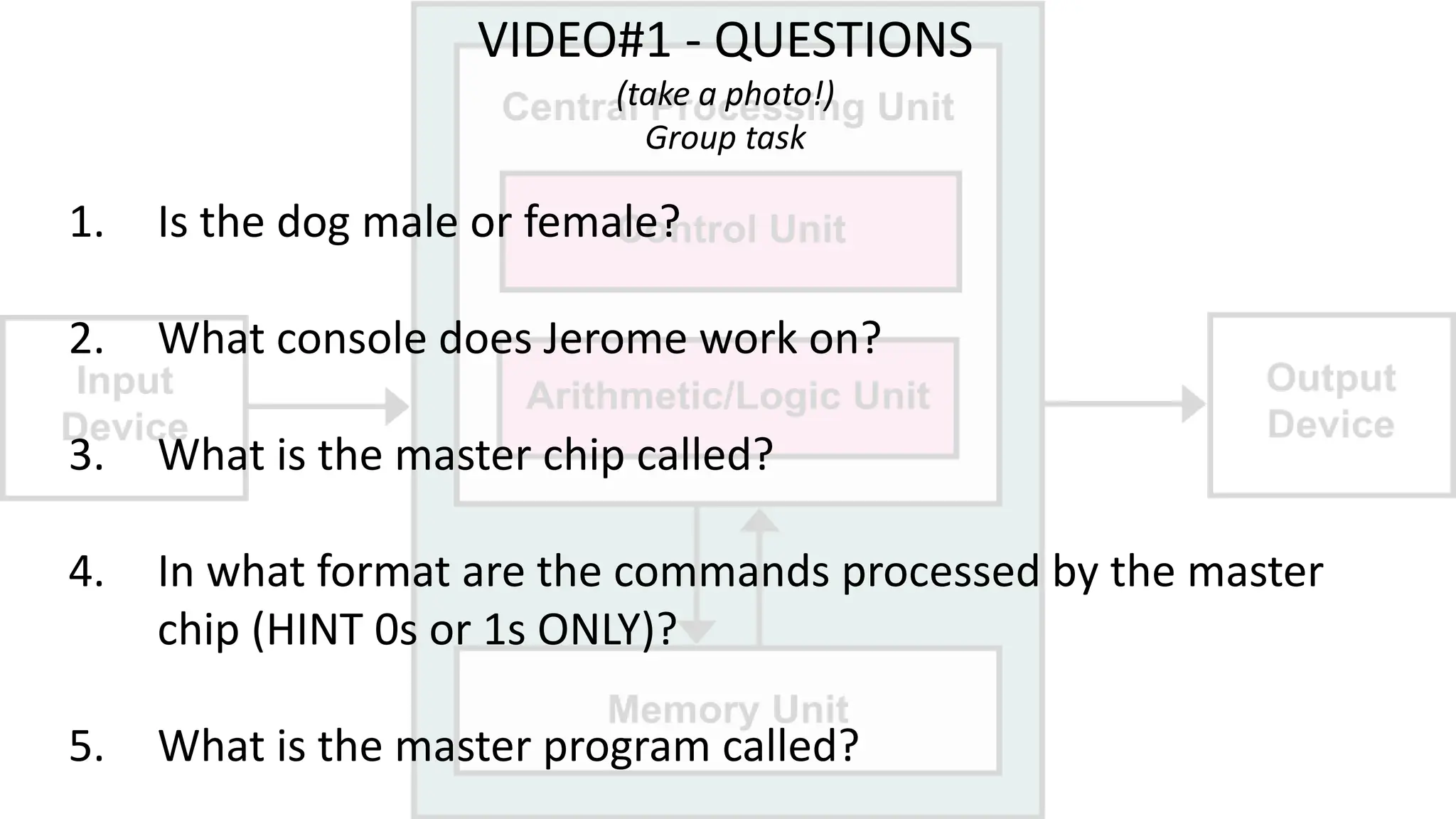
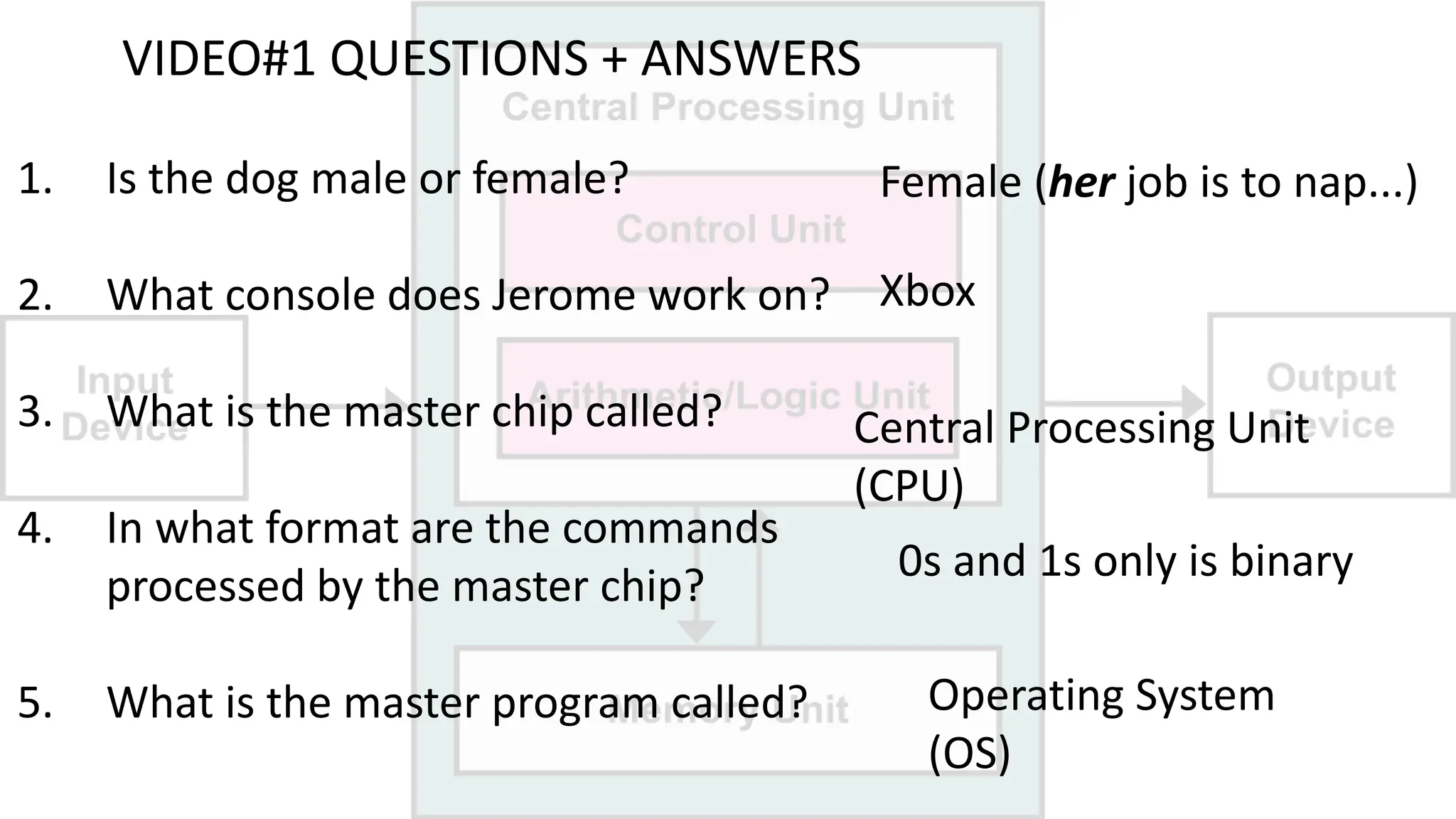
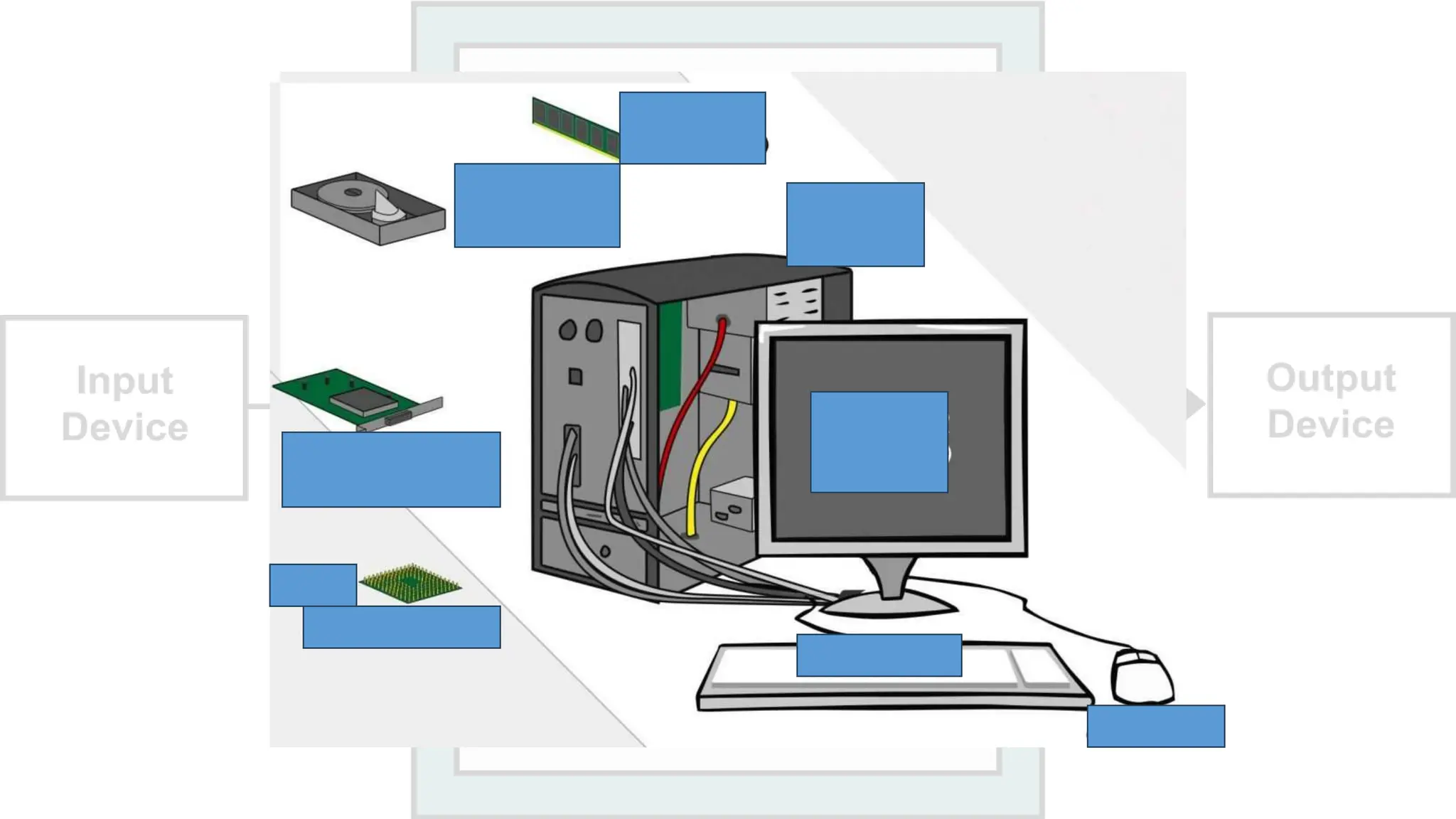
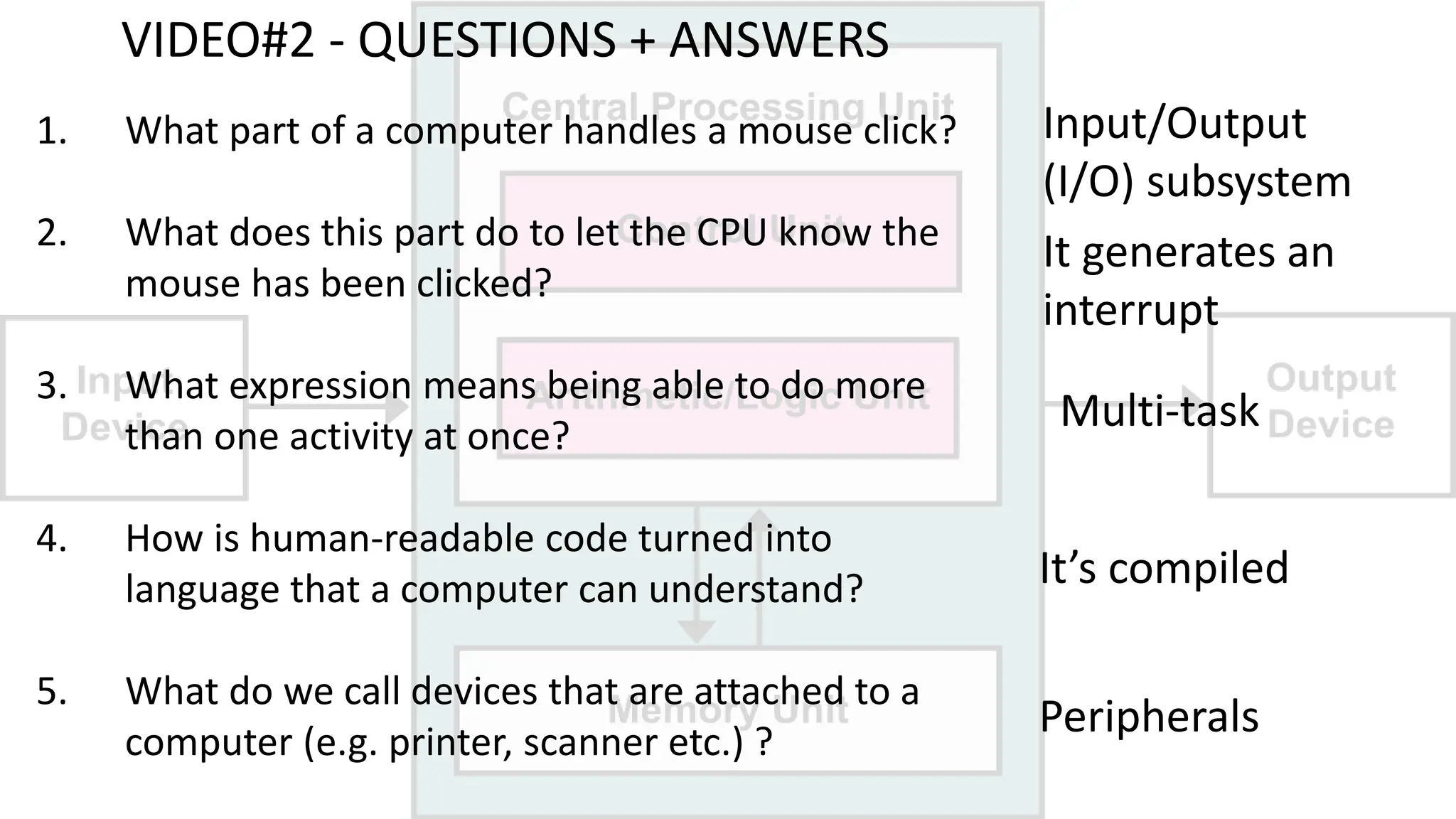
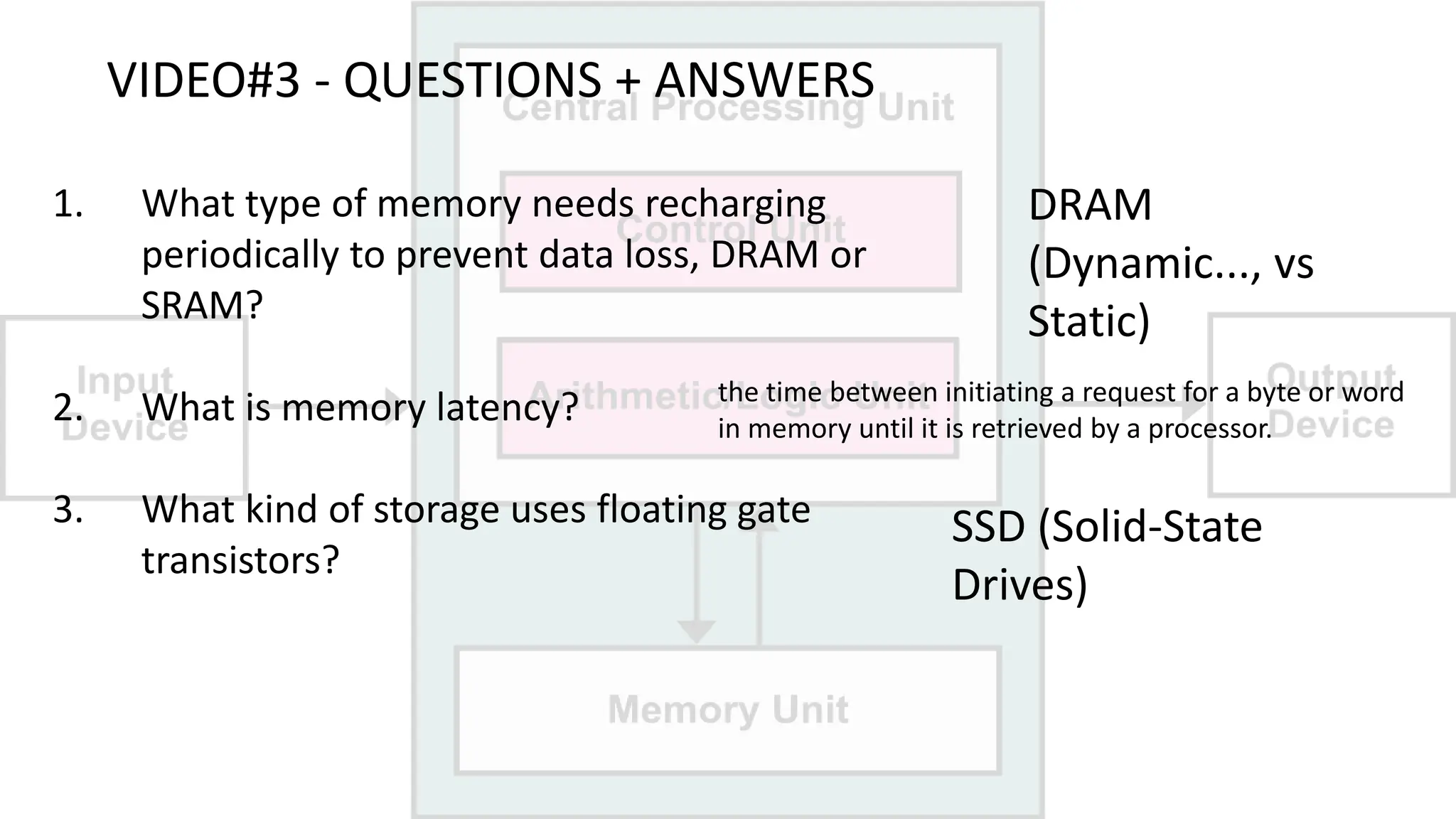
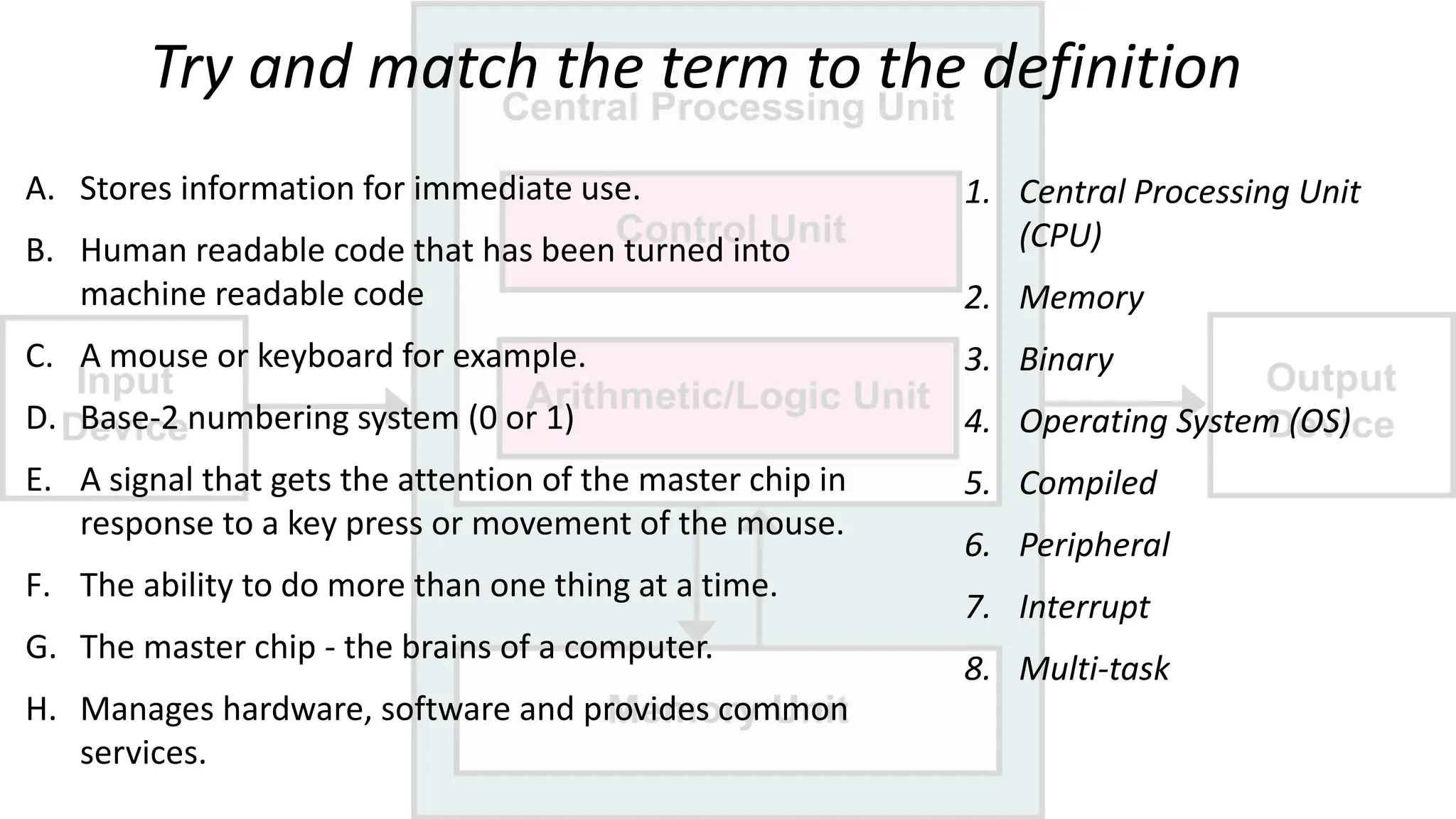
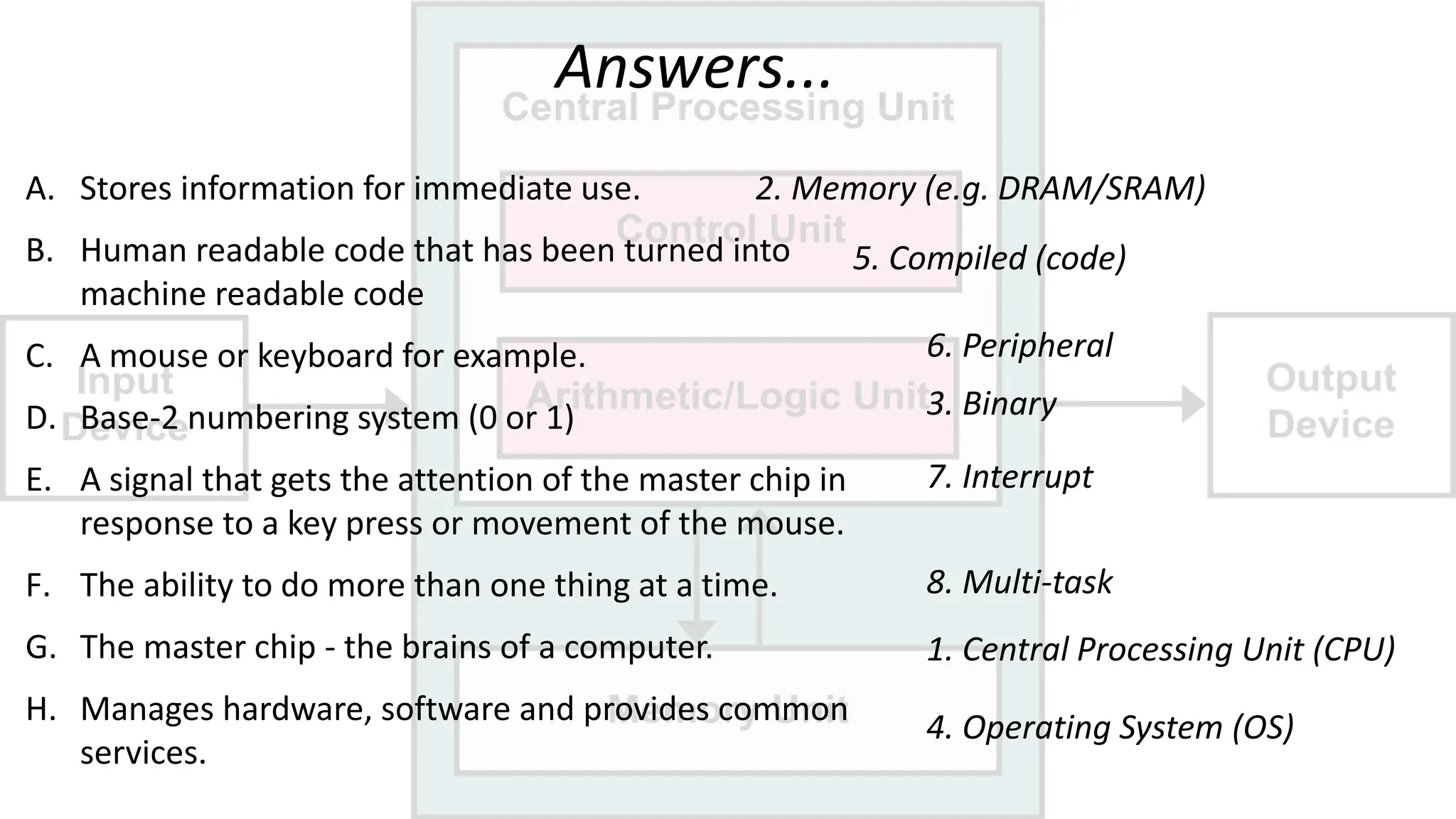
The document outlines a curriculum for an academic content workshop focused on computer science and computer architecture basics. It covers vocabulary related to computer components, programming concepts, and methods of processing commands, including discussions, videos, and quizzes. Key learning objectives include understanding hardware and software distinctions, as well as memory types and their functions.