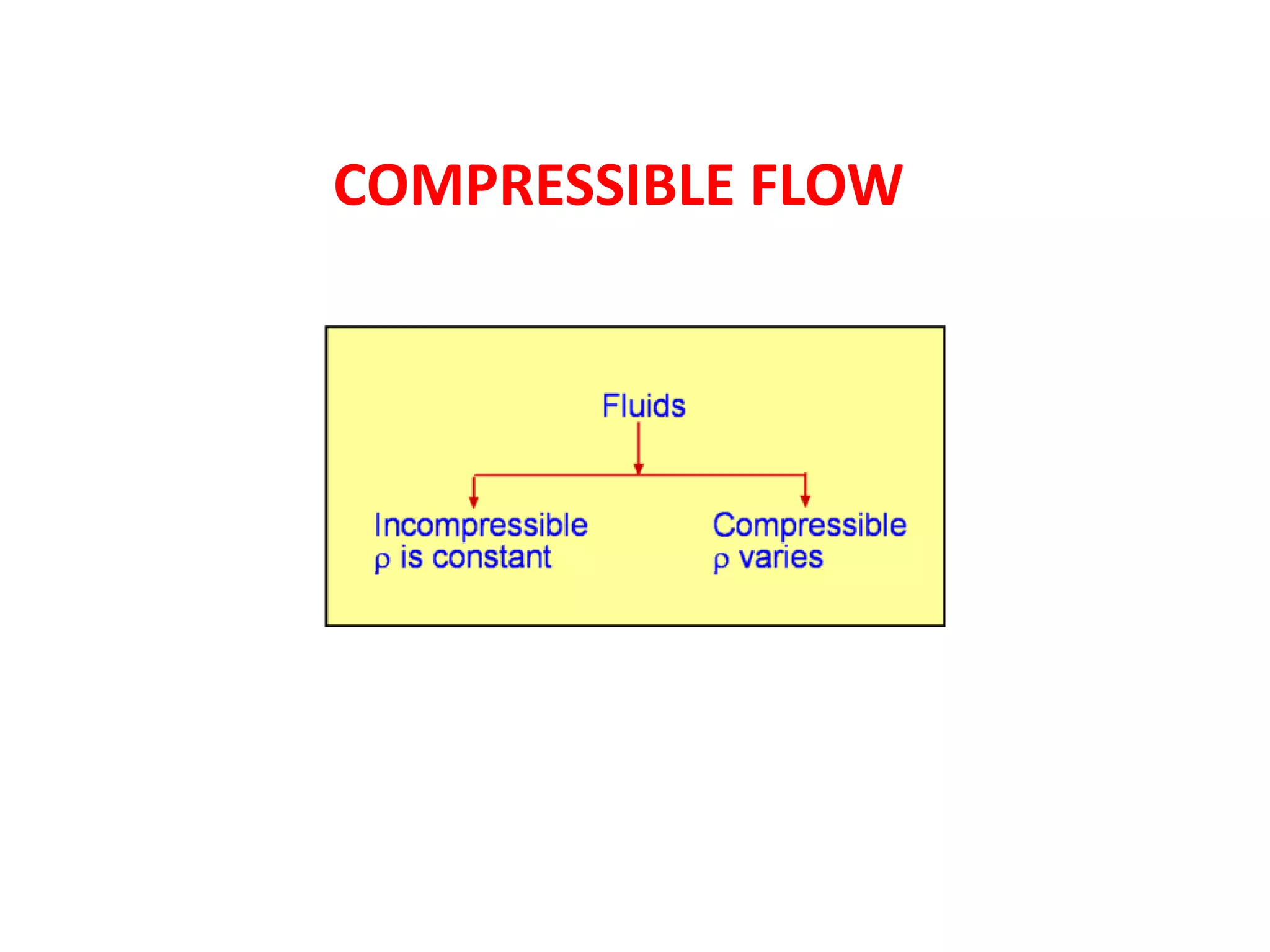
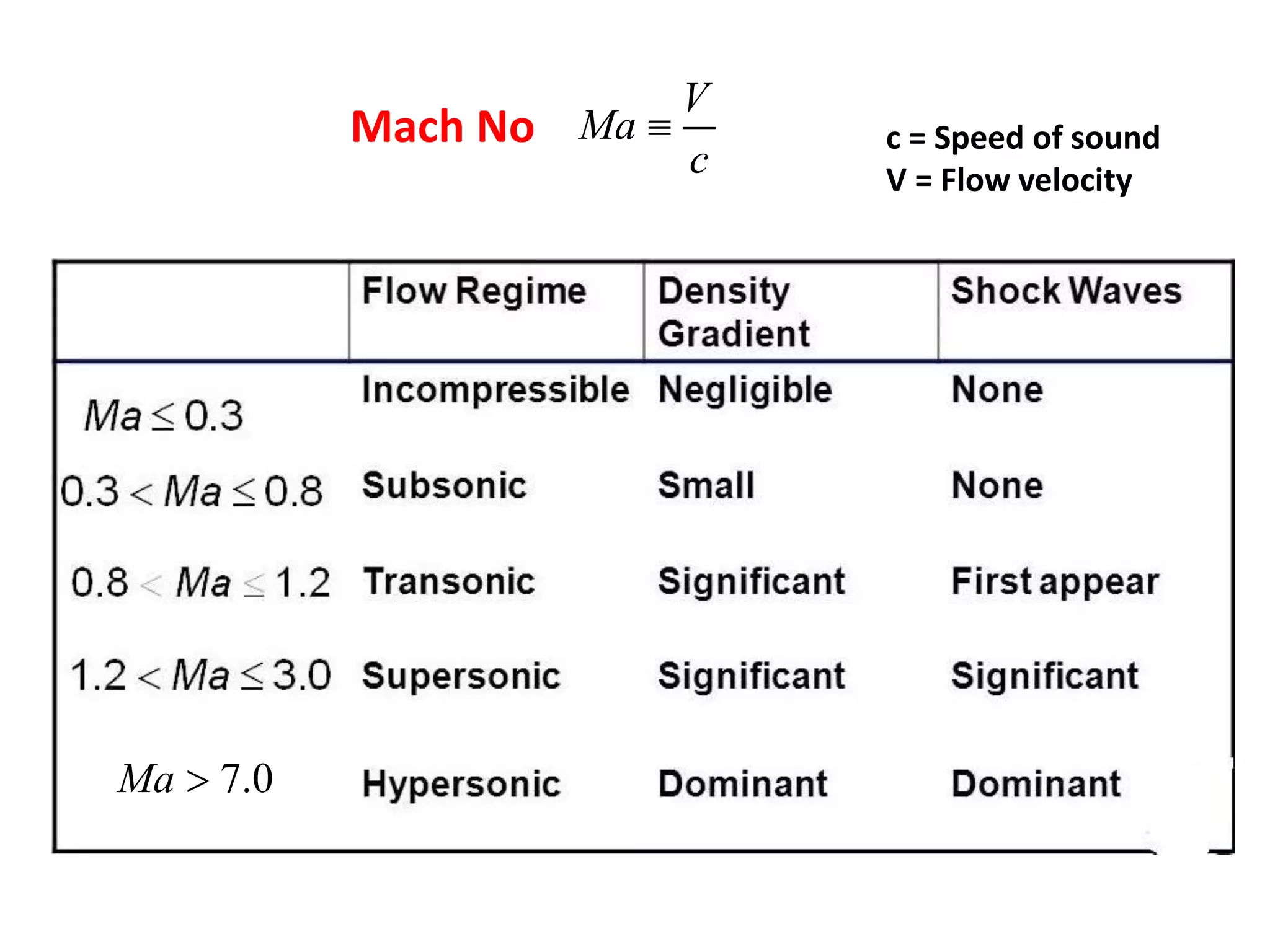
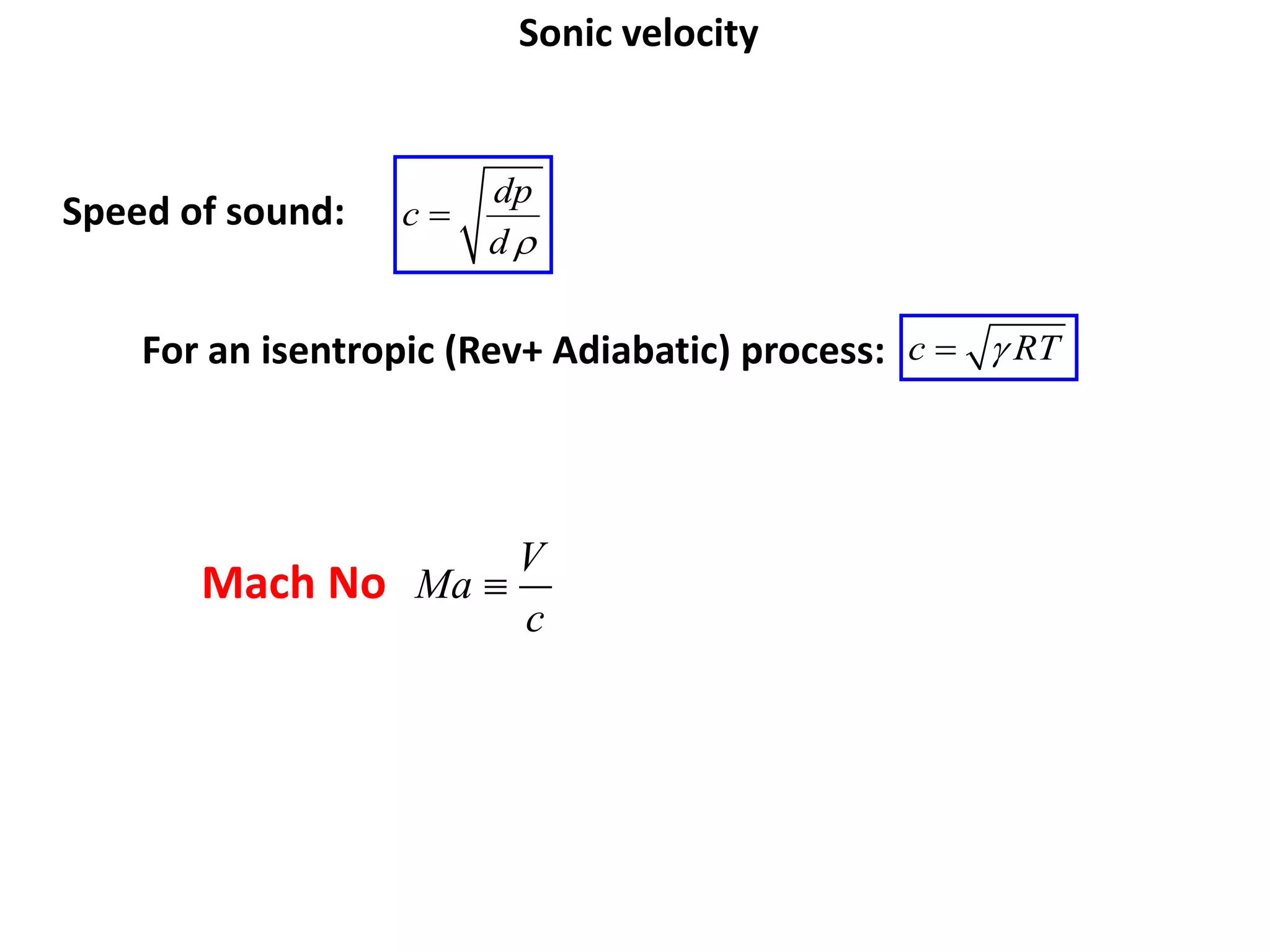
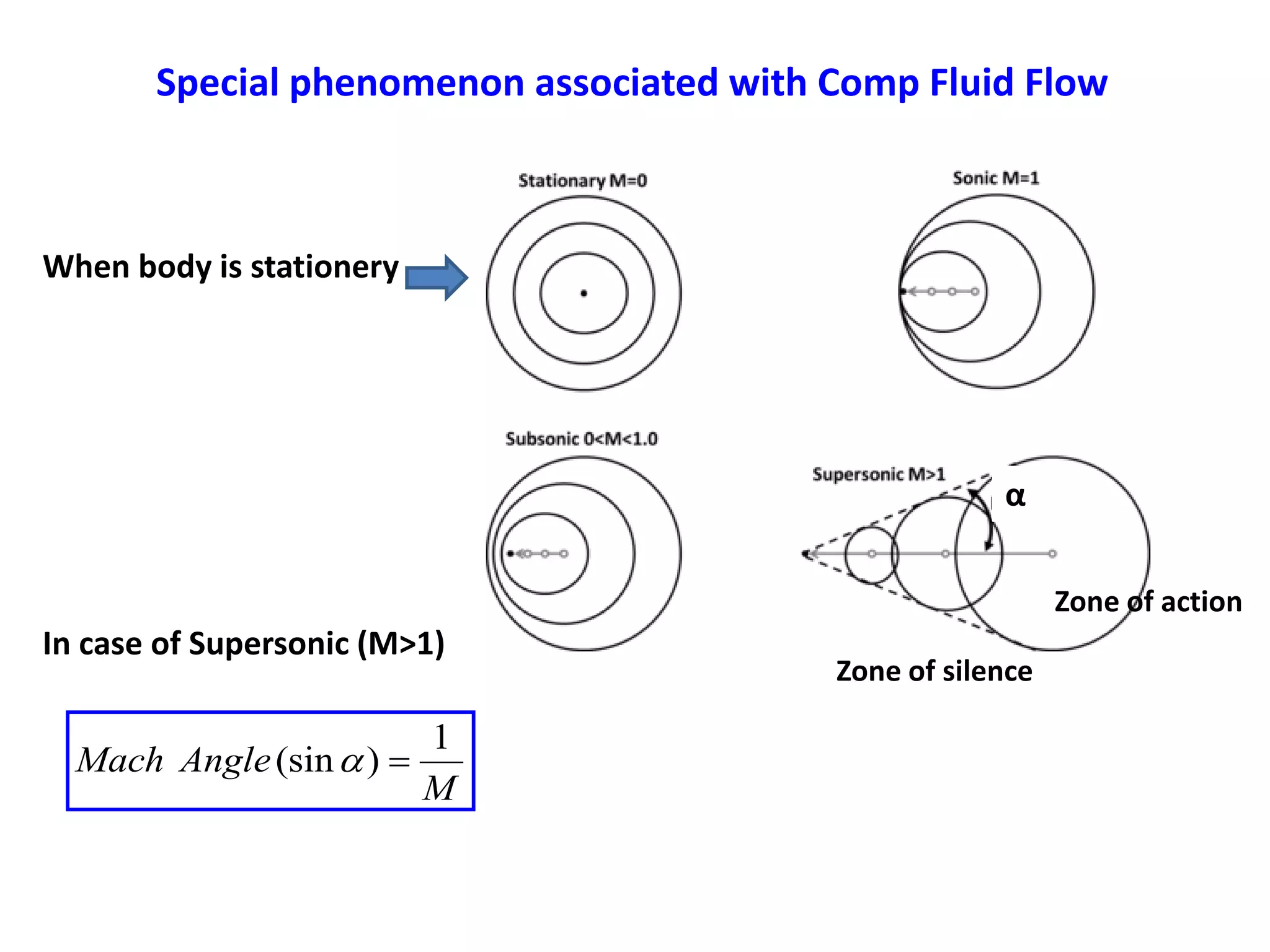
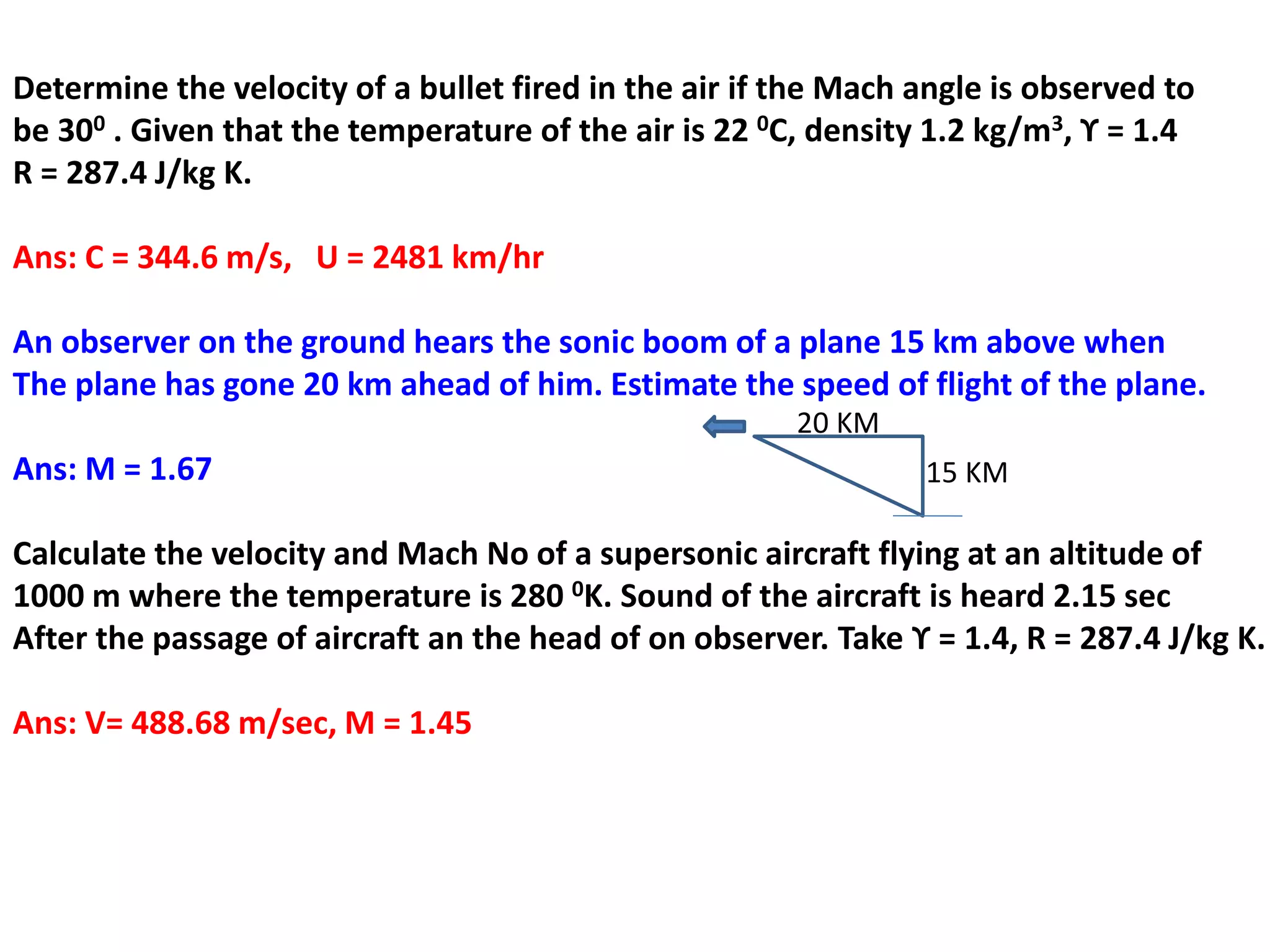
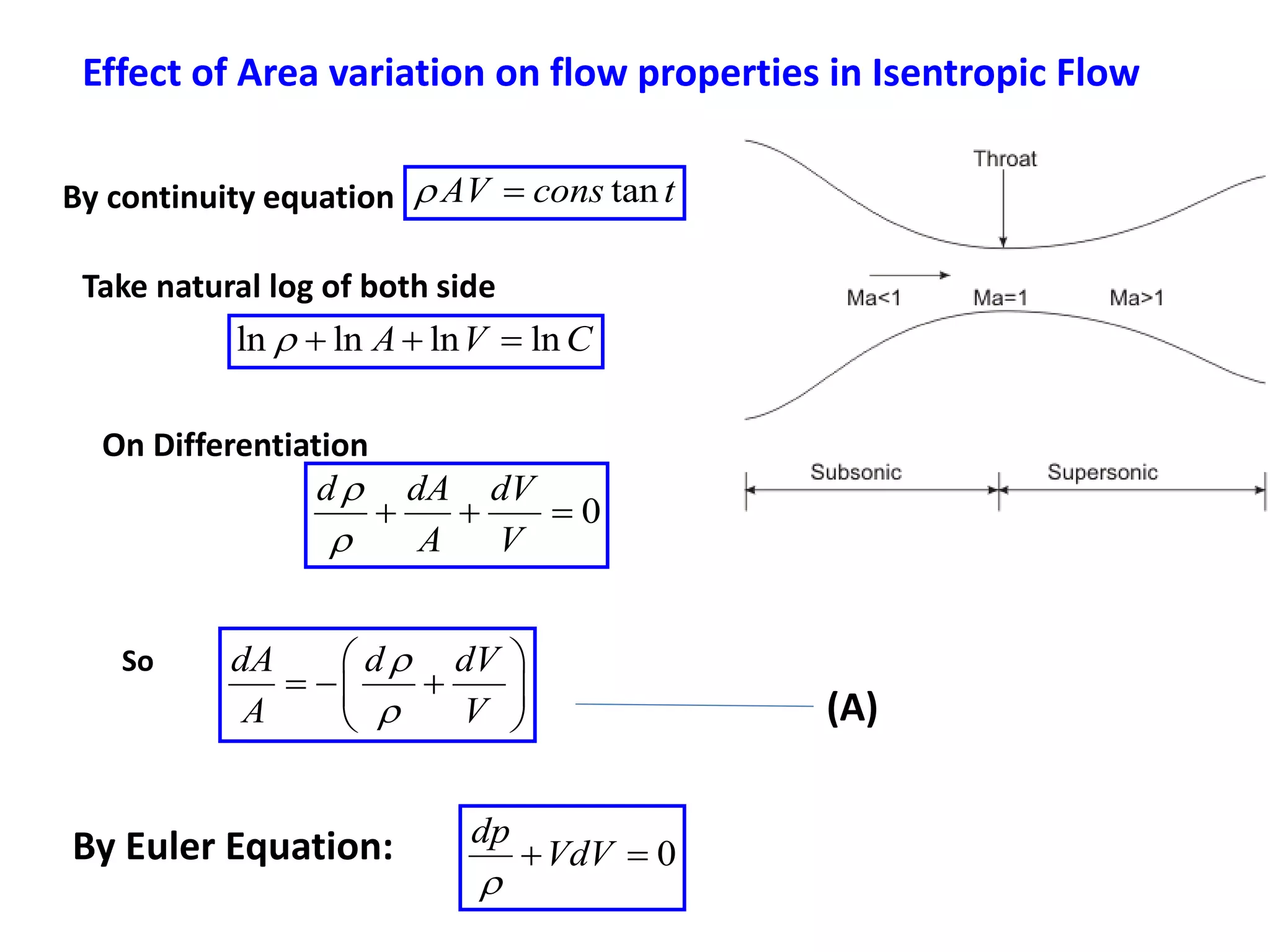
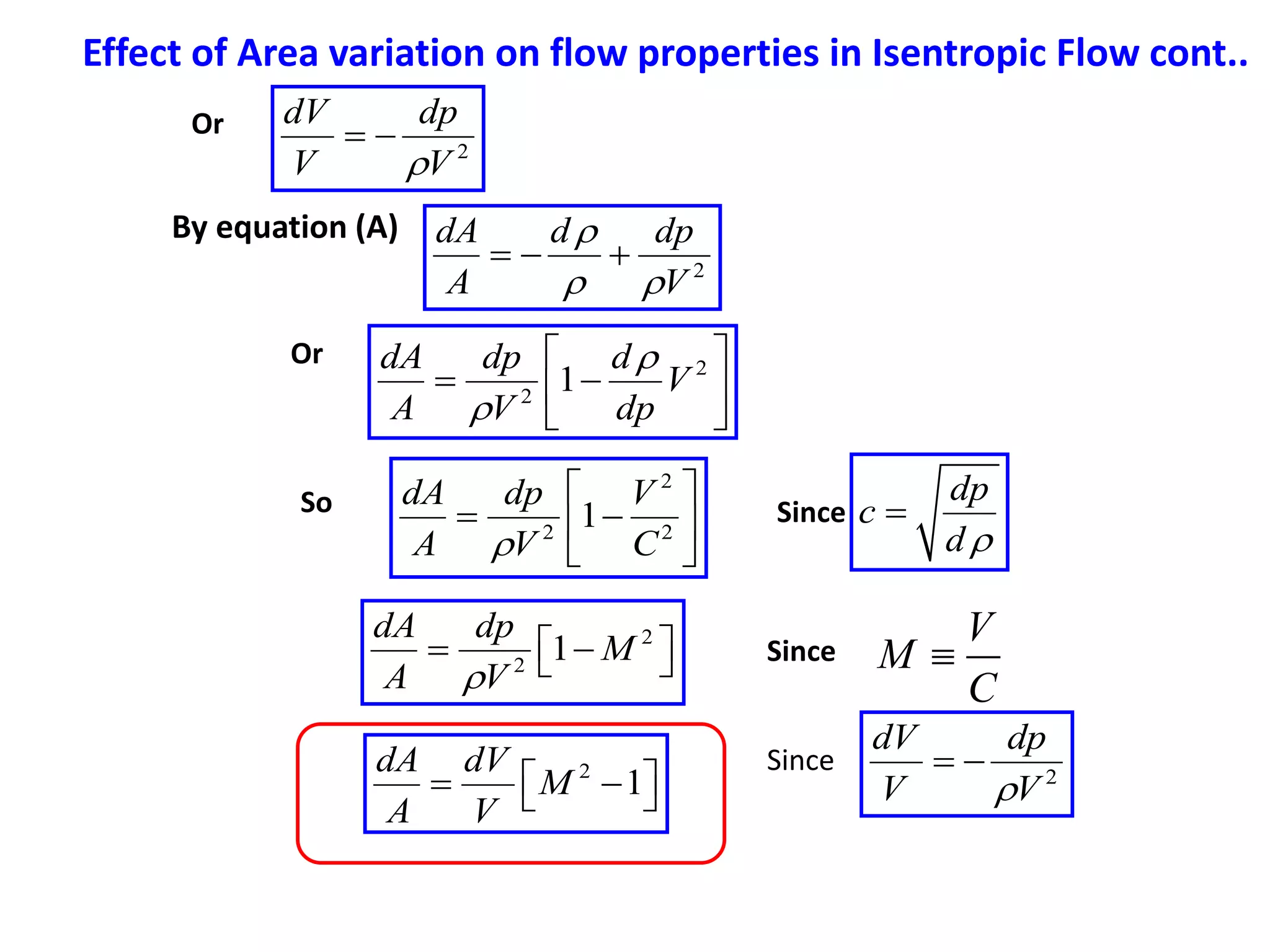
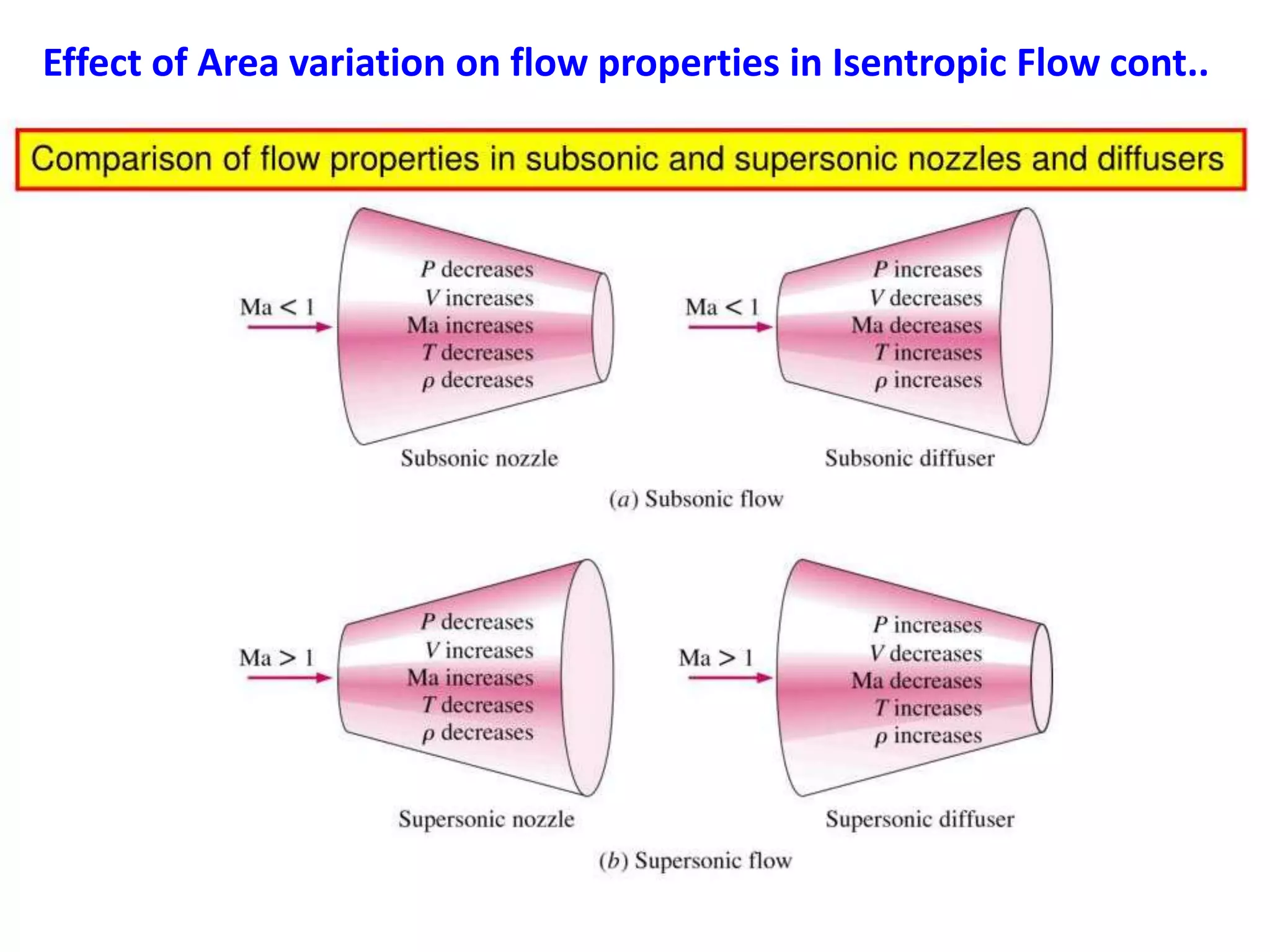
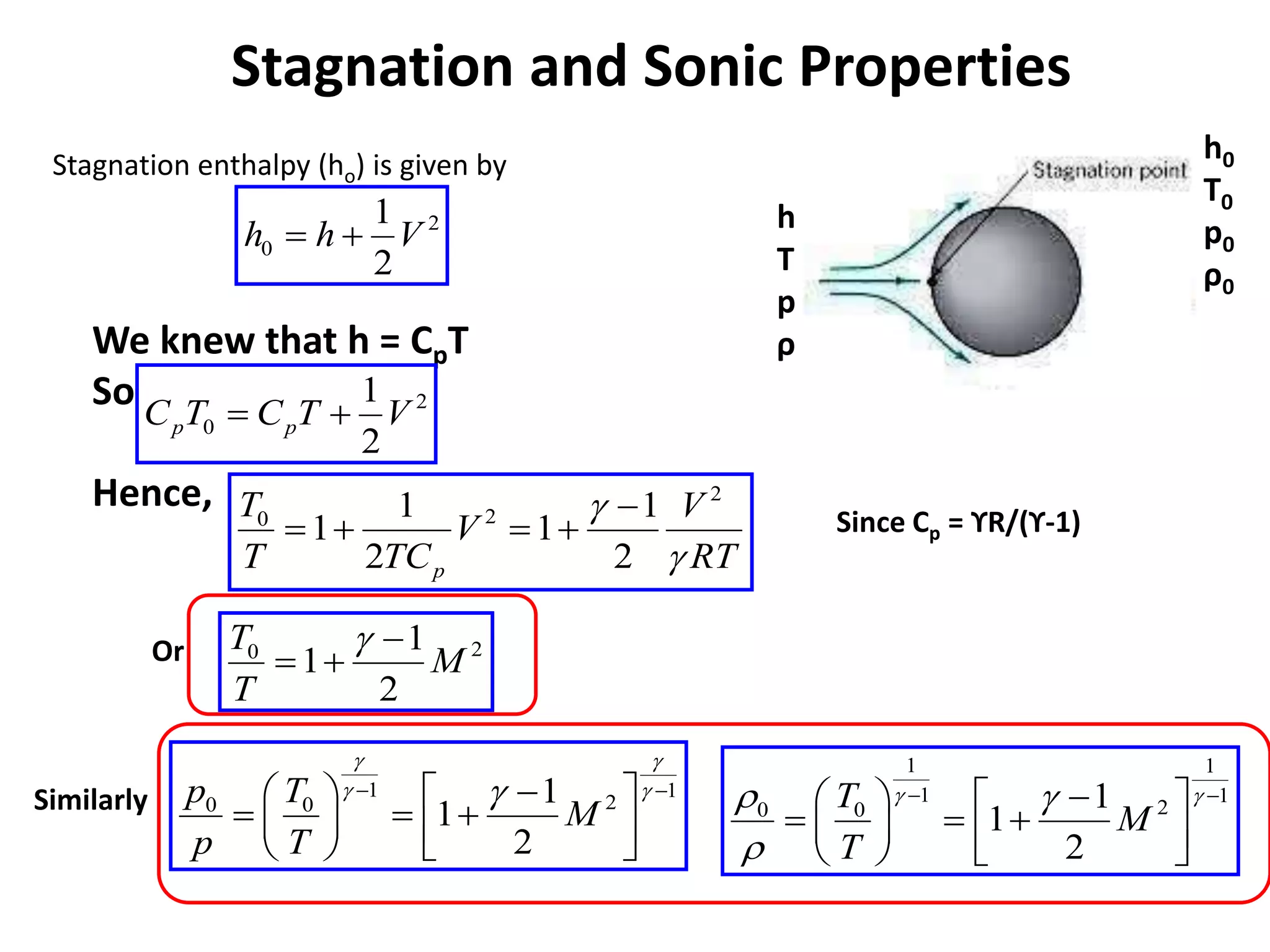
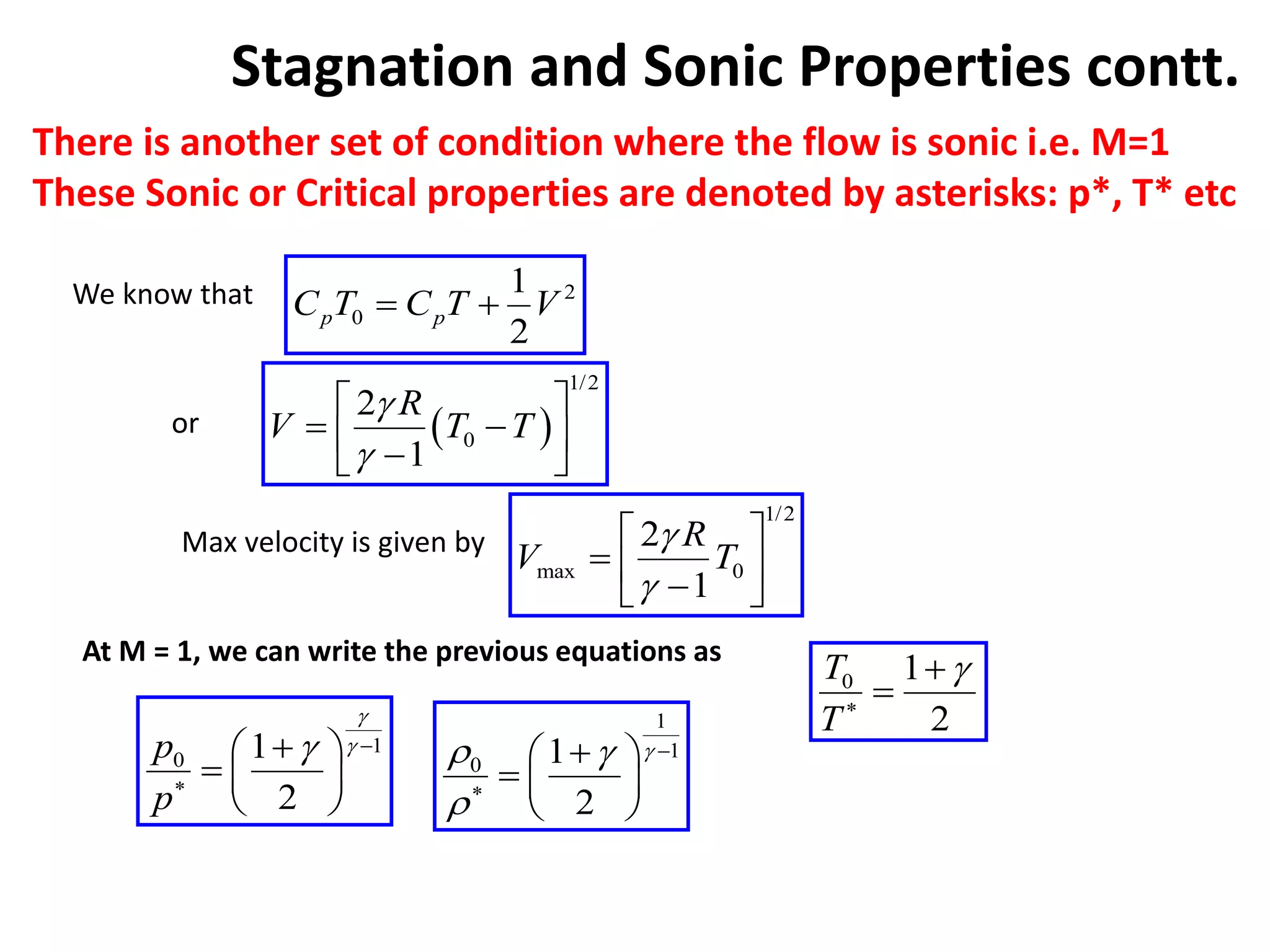
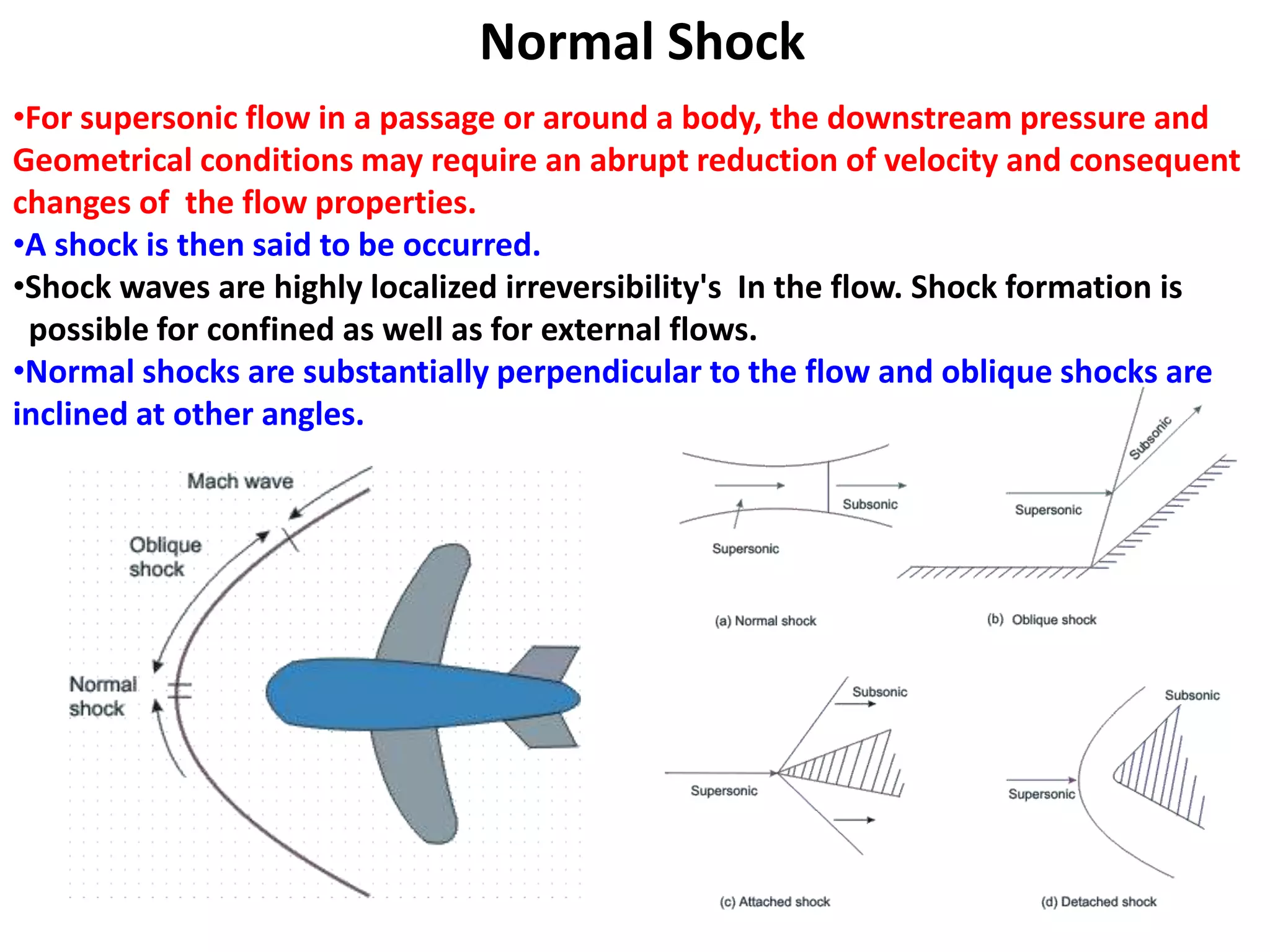
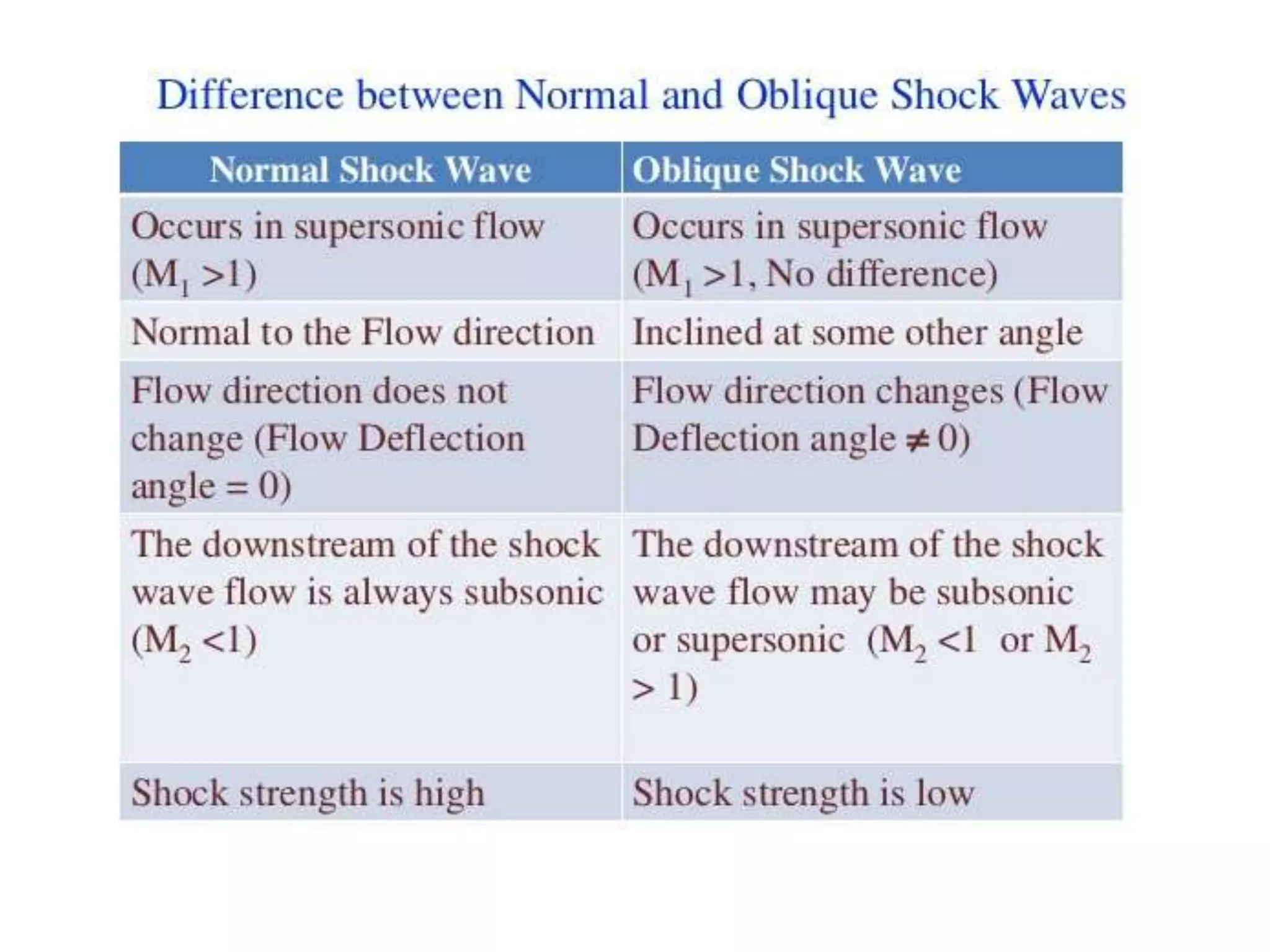
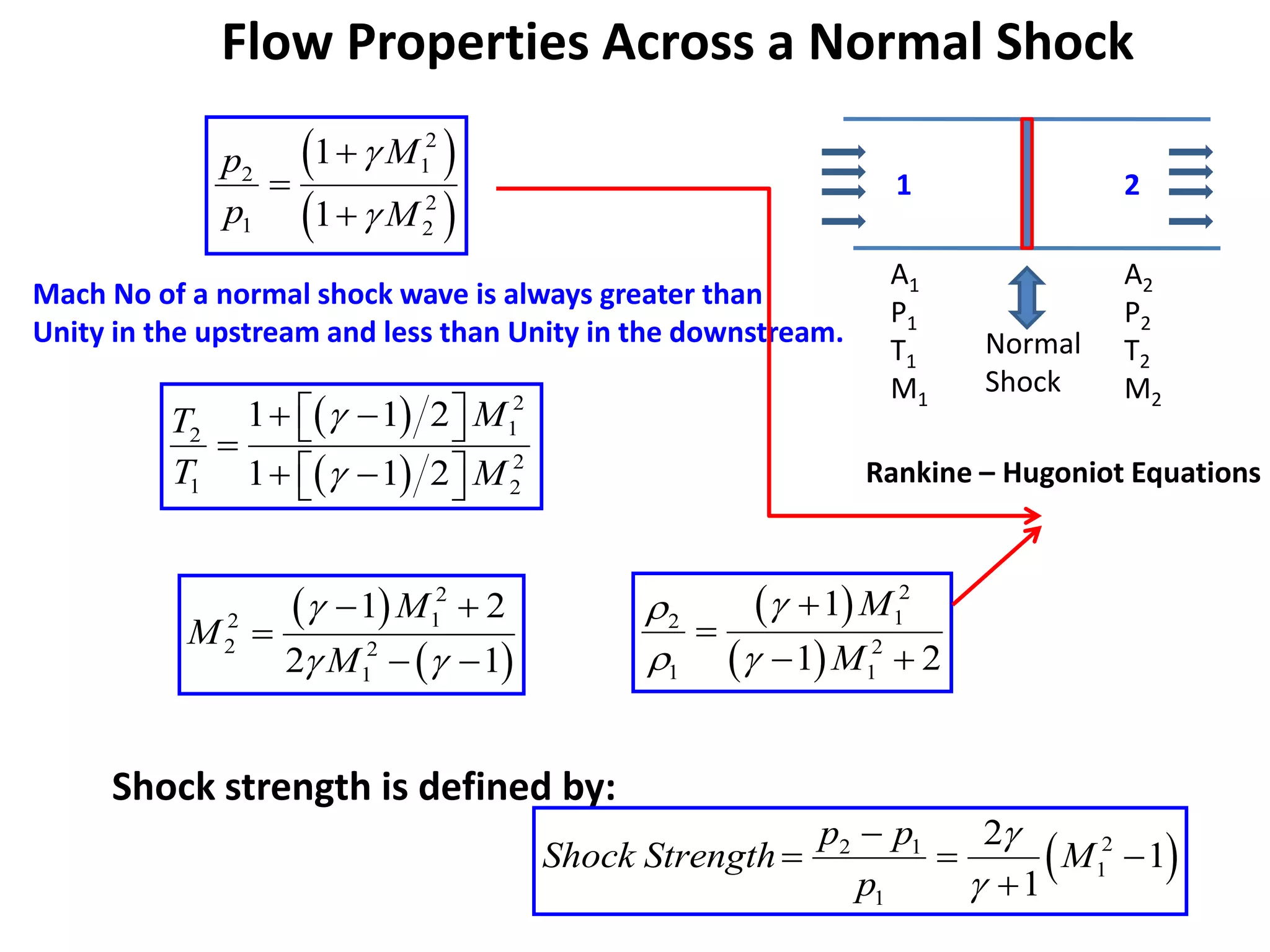
1) A normal shock wave occurs when the flow velocity decreases abruptly from supersonic to subsonic speeds. Flow properties like pressure, temperature, and density change discontinuously across the shock.
2) The flow Mach number decreases from a value greater than 1 upstream to less than 1 downstream. Pressure and temperature increase across the normal shock.
3) Normal shock waves are analyzed using the Rankine-Hugoniot equations which relate flow properties on both sides of the shock based on conservation of mass, momentum, and energy. Examples show how to calculate post-shock properties given pre-shock conditions.