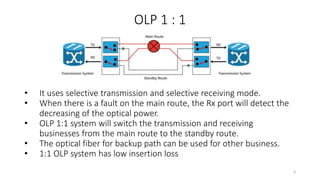
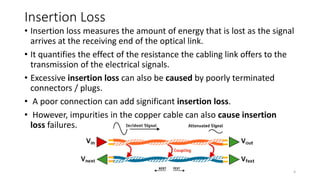
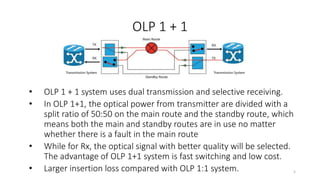
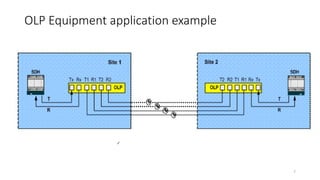
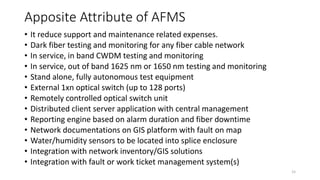
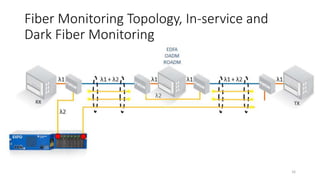
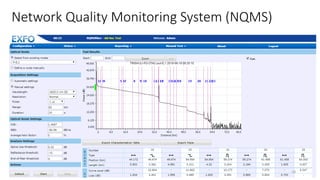
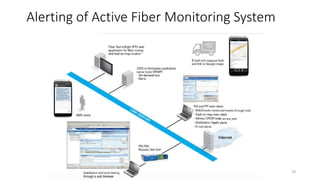
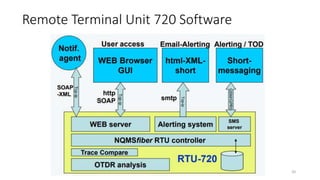
The document presents an in-depth overview of Optical Line Protection (OLP) switches and Active Fiber Monitoring Systems (AFMS) used by Nepal Telecom. It details the two types of OLP systems (1:1 and 1+1) highlighting their functionalities, advantages, and specifications, as well as the benefits of AFMS for fiber monitoring and maintenance. The document also covers insertion loss, equipment applications, and additional features of fiber monitoring technologies.