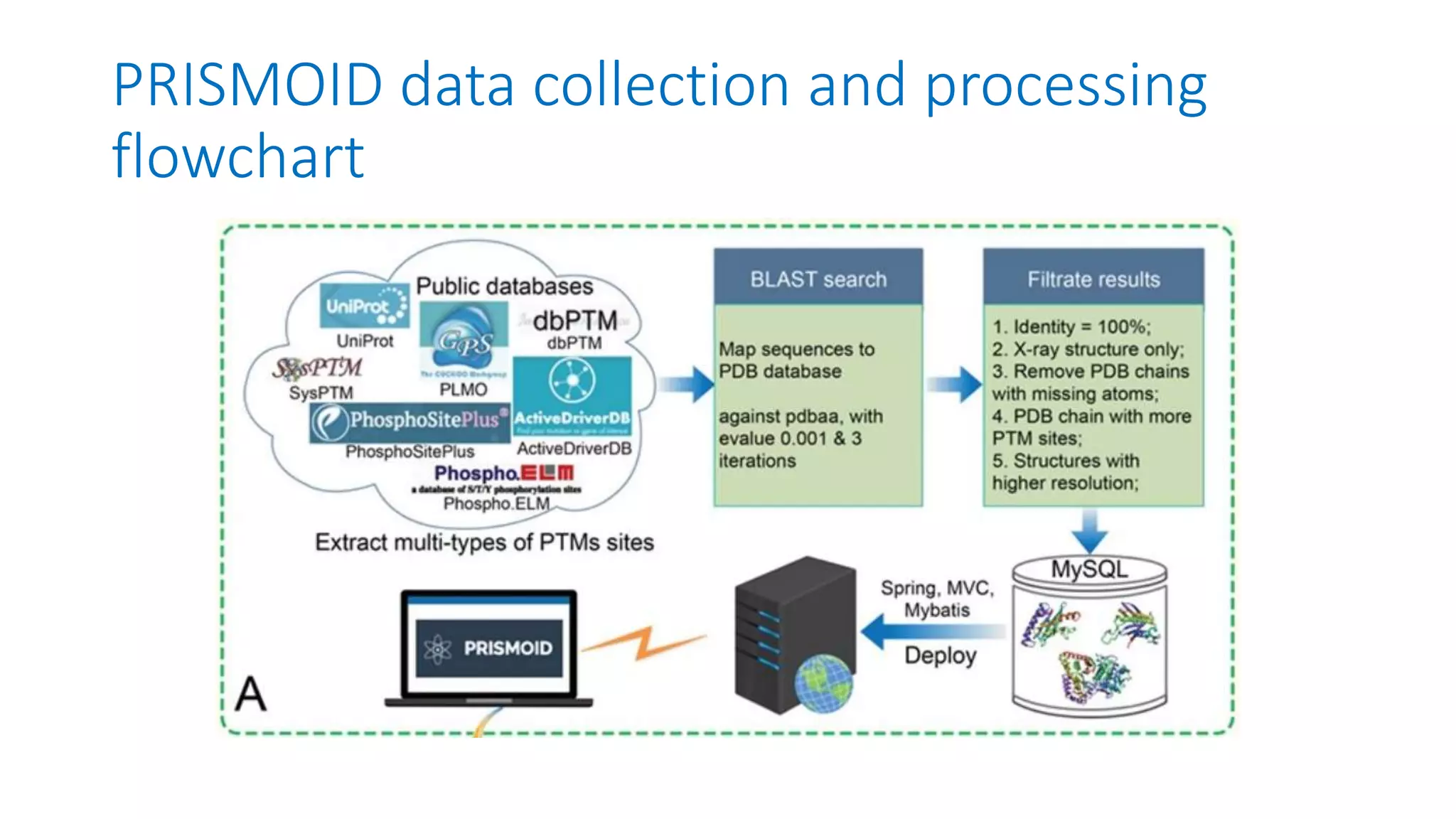
PRISMOID is a comprehensive 3D structure database for post-translational modifications and mutations with functional impact. It contains over 17,000 PTM sites from nearly 4,000 proteins annotated with 37 different types of PTMs. PRISMOID also annotates disease mutations affecting PTM sites. It collects protein structural features like secondary structure, solvent accessibility, and disorder regions. PRISMOID maps PTM sites from sequence databases to 3D protein structures from the PDB. It aims to provide an interactive resource for visualizing protein structures with PTMs and their associations with disease mutations.







![References
[1] Li, F, Fan, C, Marquez-Lago, TT, Leier, A, Revote, J, Jia, C, Zhu, Y, Smith, AI, Webb, GI, Liu, Q, Wei, L,
Li, J & Song, J 2020, 'PRISMOID: a comprehensive 3D structure database for post-translational
modifications and mutations with functional impact', Briefings in Bioinformatics, vol. 21, no. 3, pp.
1069-1079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbz050
[2] Pierrick Craveur, Joseph Rebehmed, and Alexandre G. de Brevern PTM-SD: a database of
structurally resolved and annotated posttranslational modifications in proteins Database 2014:
bau041 doi:10.1093/database/bau041 published online May 24, 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prismoid-200816003209/75/Prismoid-11-2048.jpg)