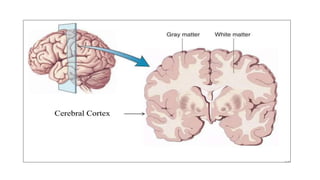
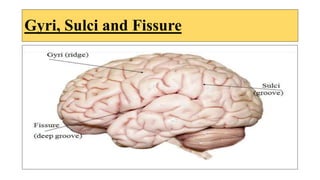
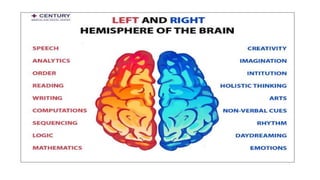
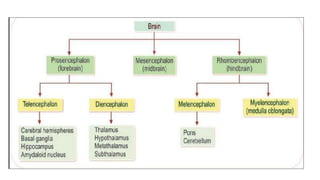
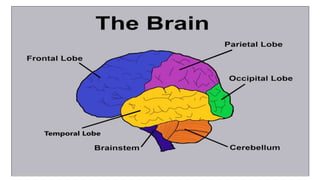
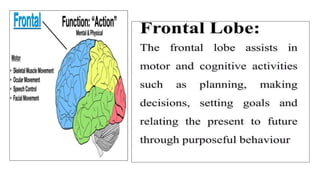
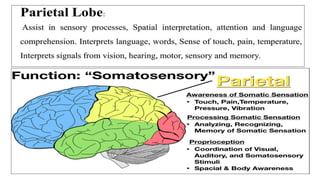
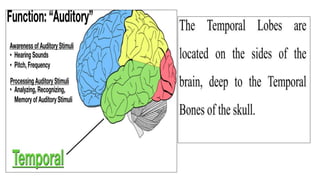
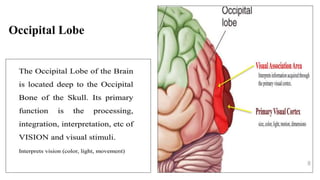
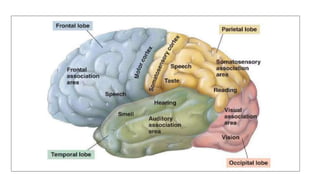
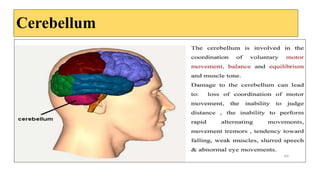
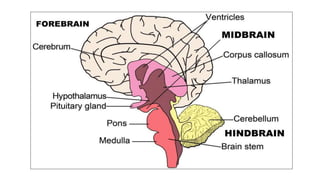
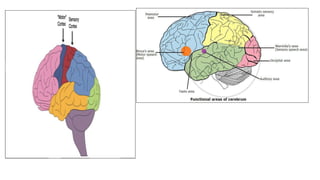
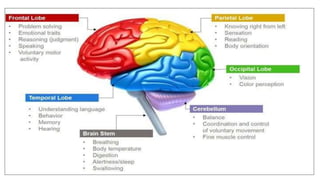
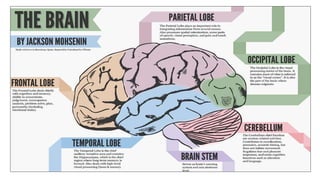
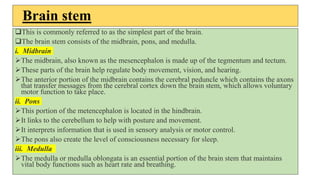
The document provides an overview of the central nervous system, detailing various brain regions including the cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem, and spinal cord, along with their functions. It describes the roles of different lobes of the cerebrum such as the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes in controlling cognition, sensory processing, and motor functions. Additionally, it highlights the structure of the spinal cord and its pathways for sensory and motor information.