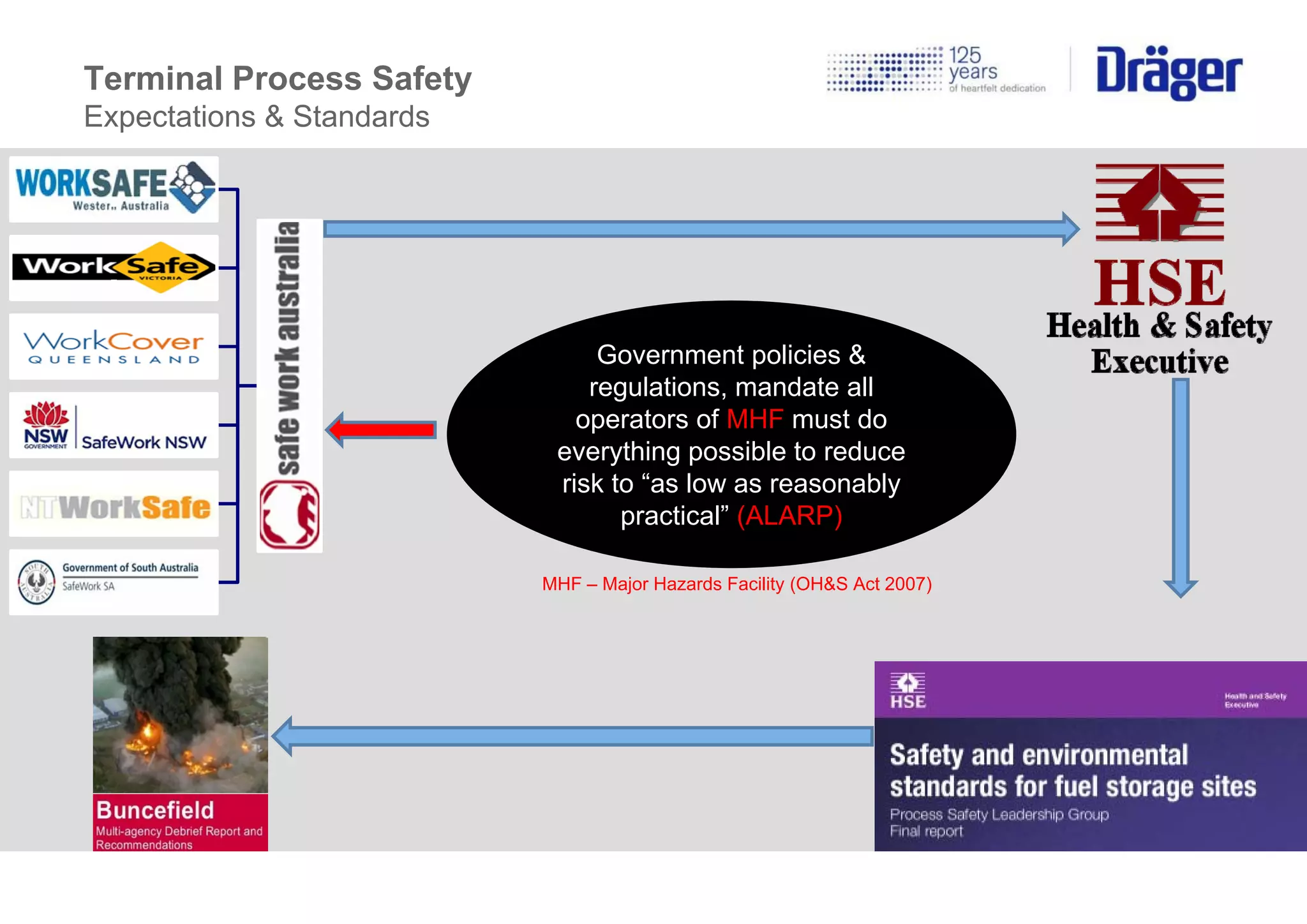
The document details the importance of adhering to terminal process safety standards, particularly in the context of major hazard facilities (MHF) to reduce risks to as low as reasonably practical (ALARP). It discusses the Buncefield disaster, highlighting its causes, consequences, and the necessity for robust safety systems like overfill prevention and hazardous condition detection. Additionally, it emphasizes necessary safety measures and solutions for various operational scenarios to mitigate risks associated with toxic substances and flammable materials.