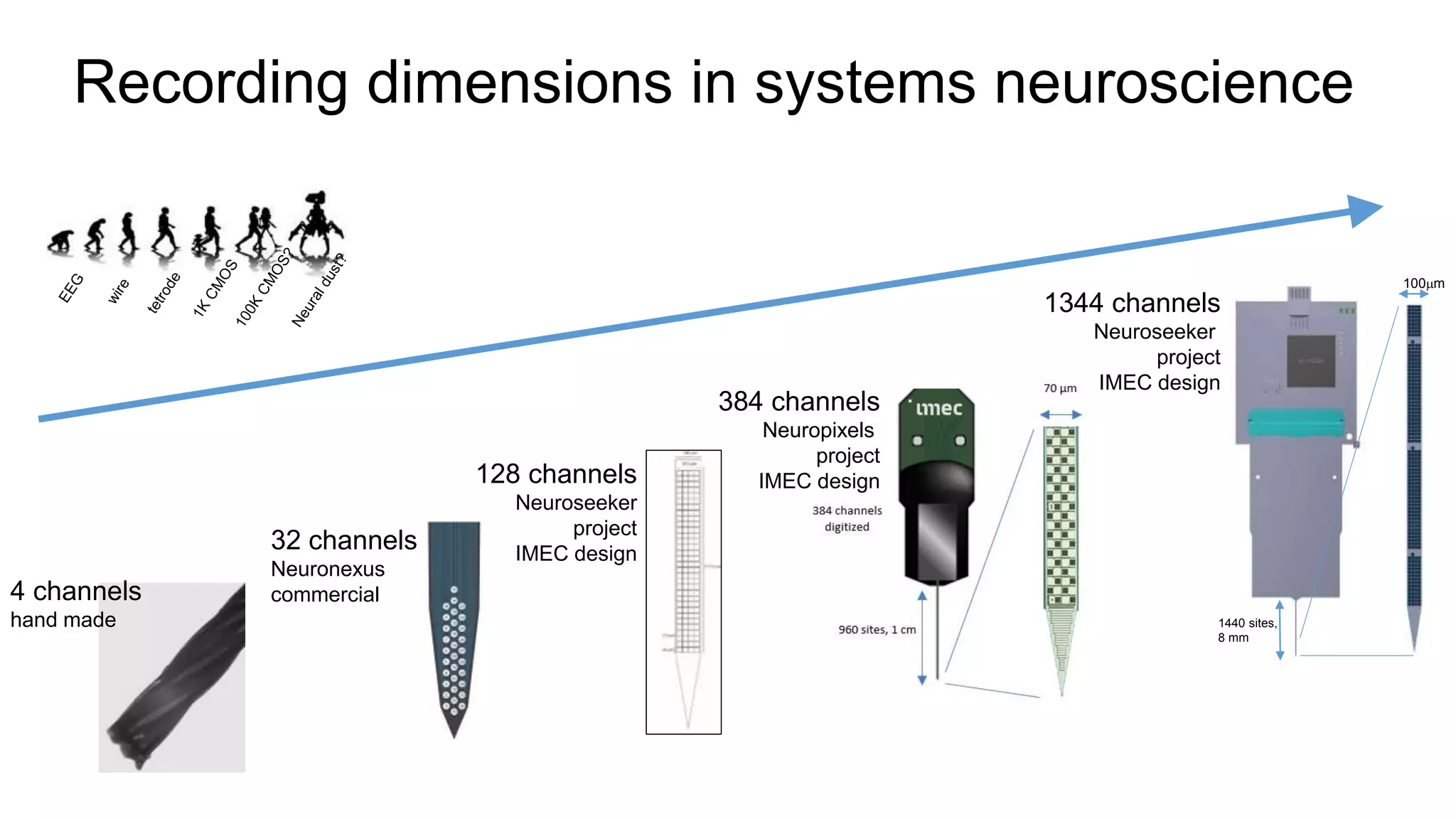
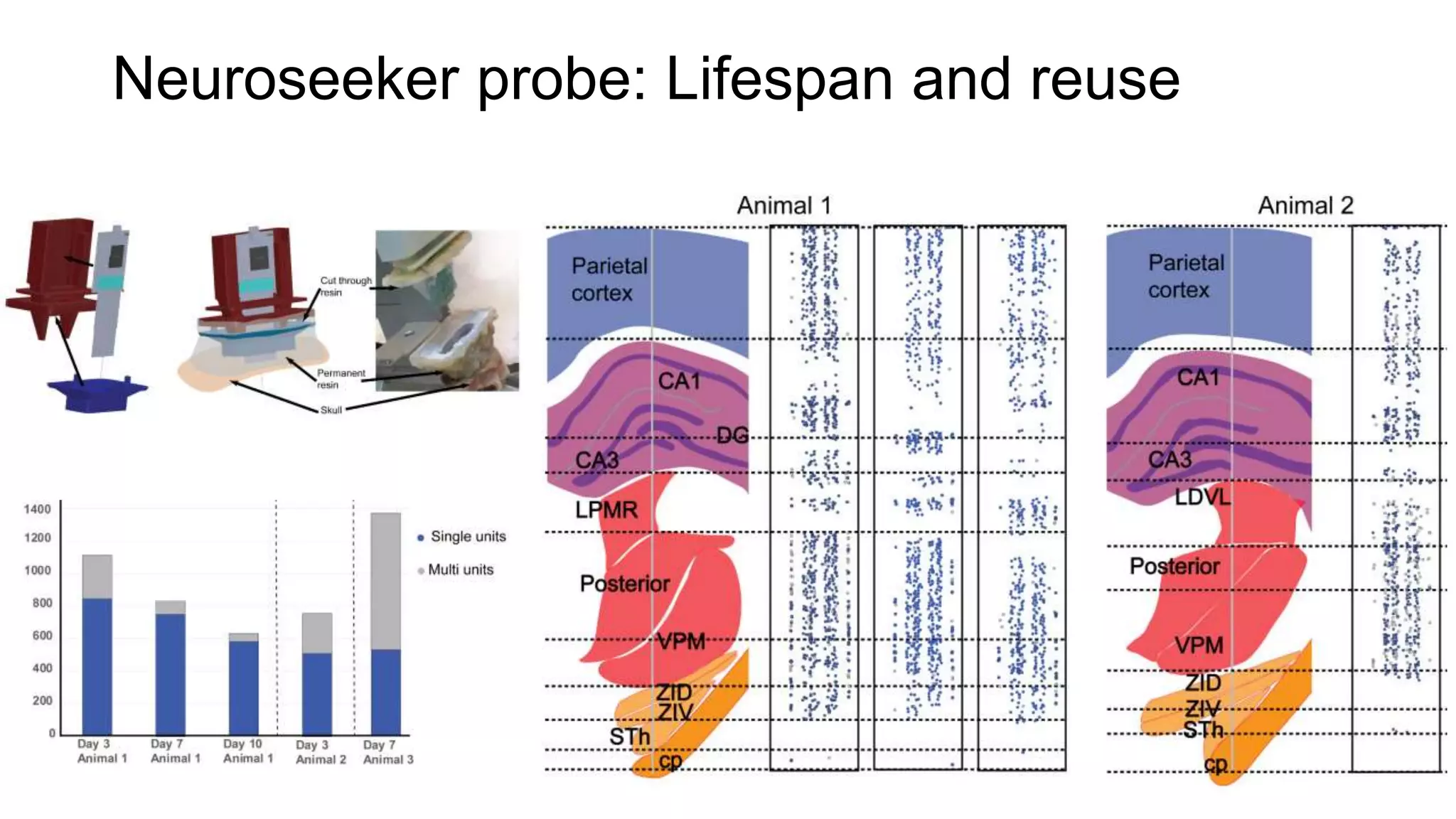
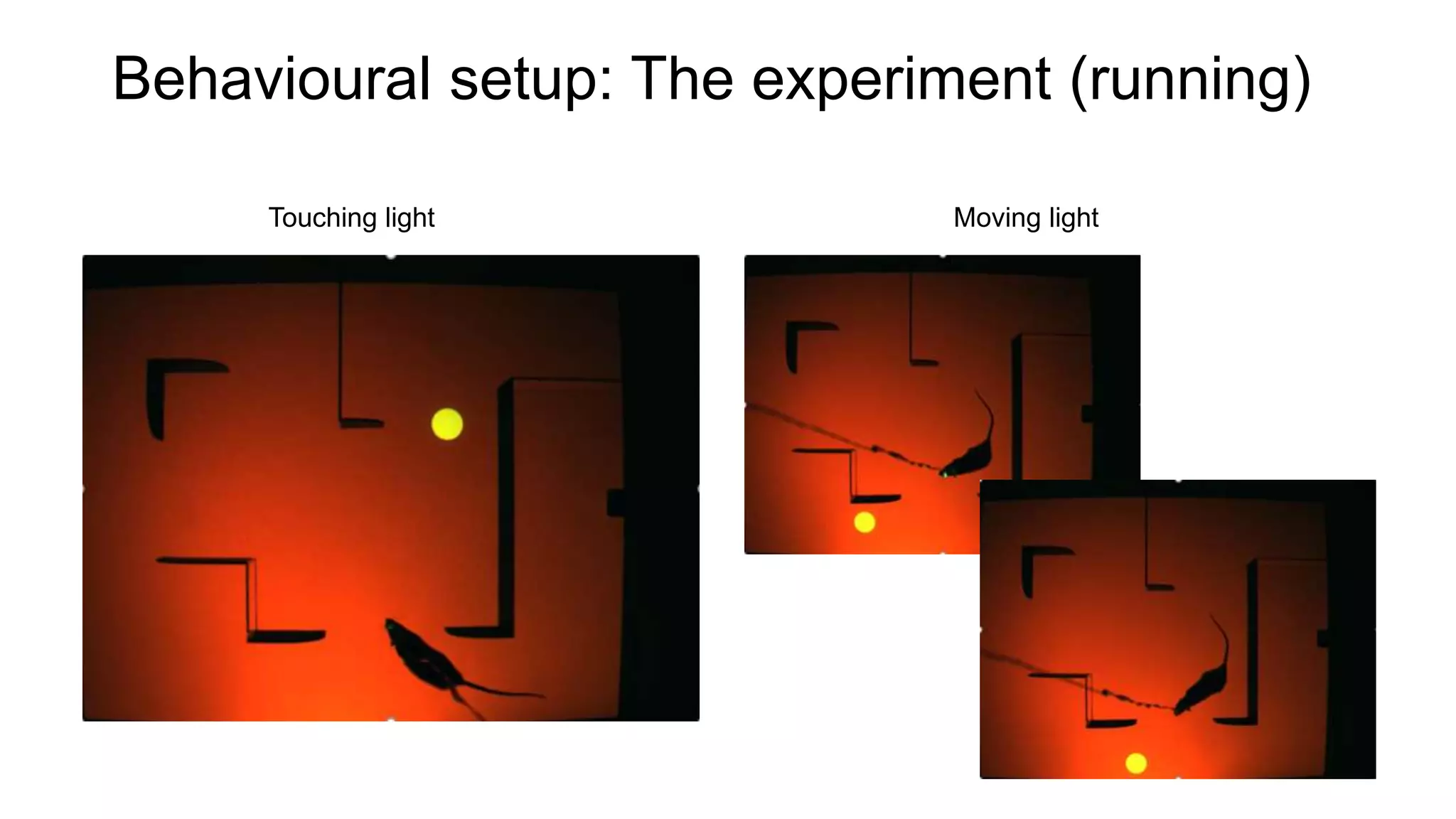
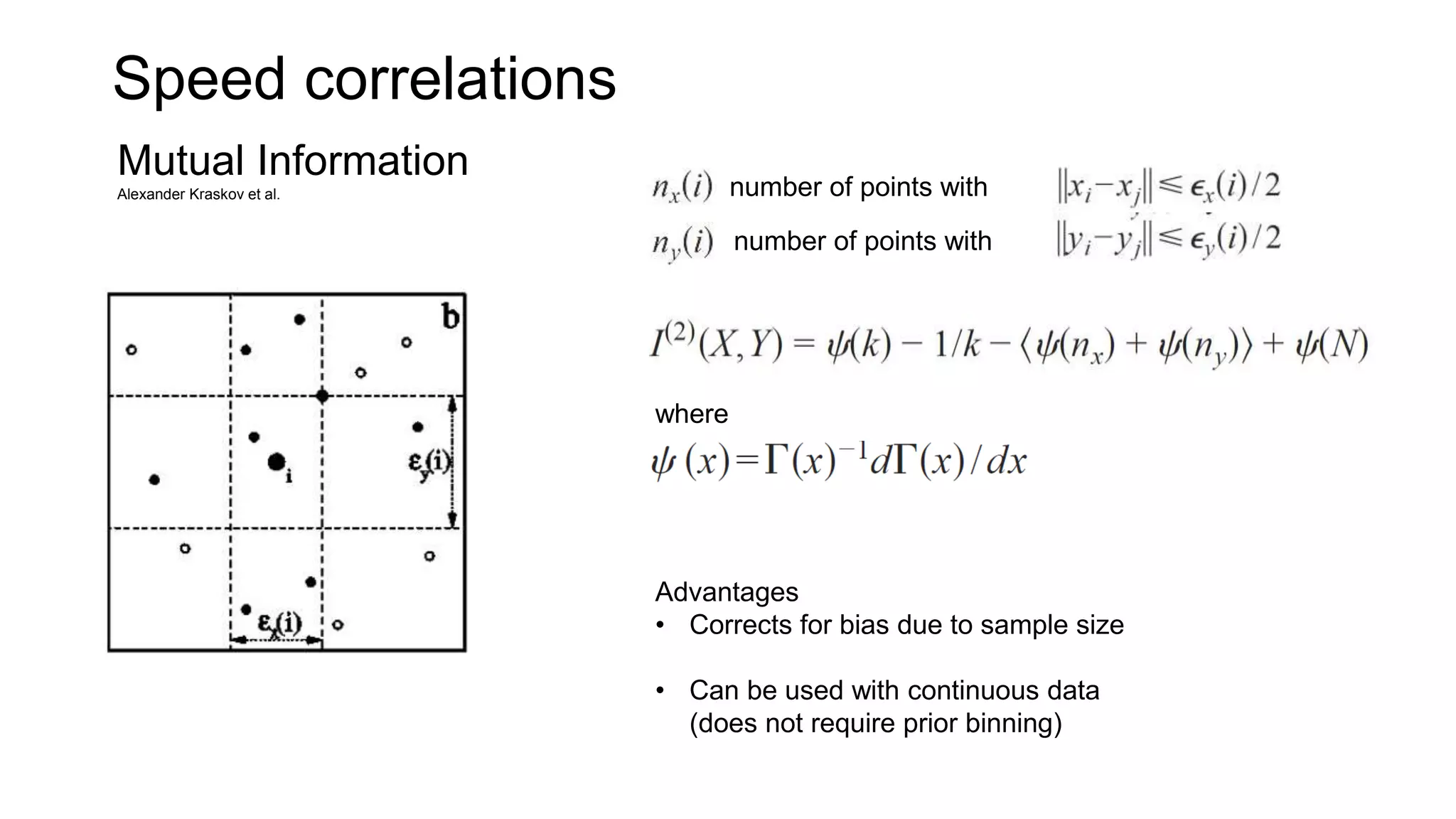
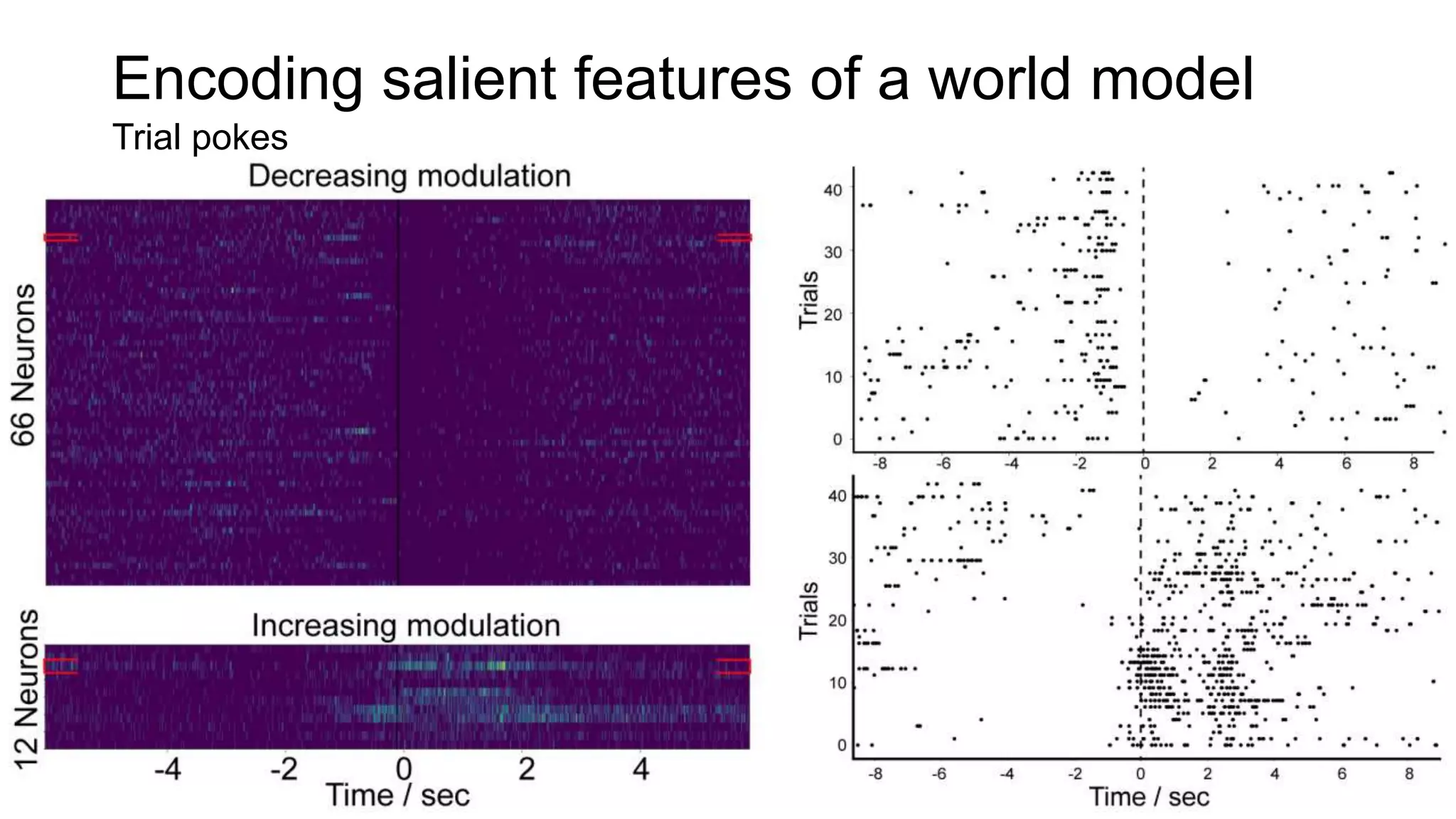
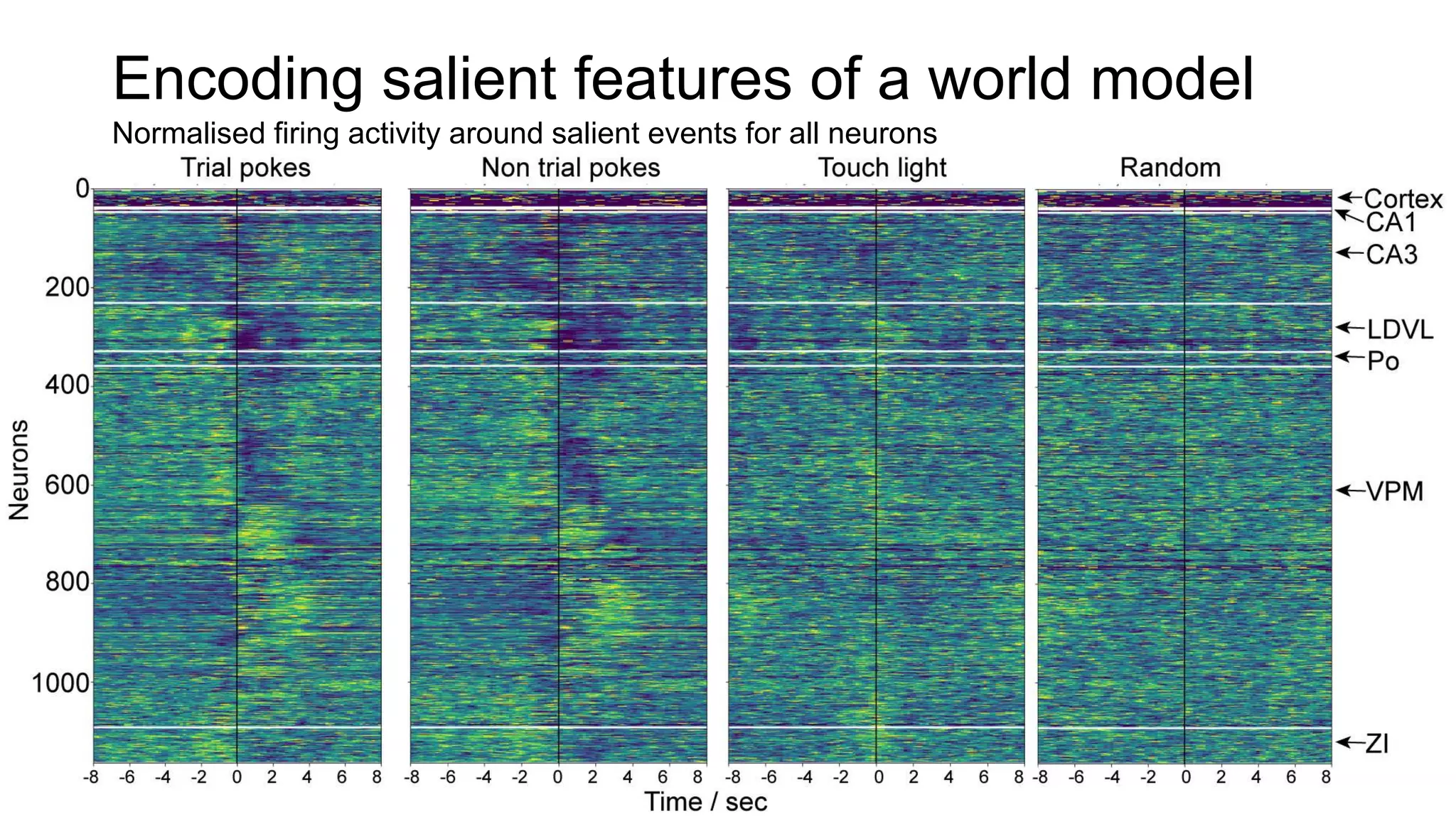
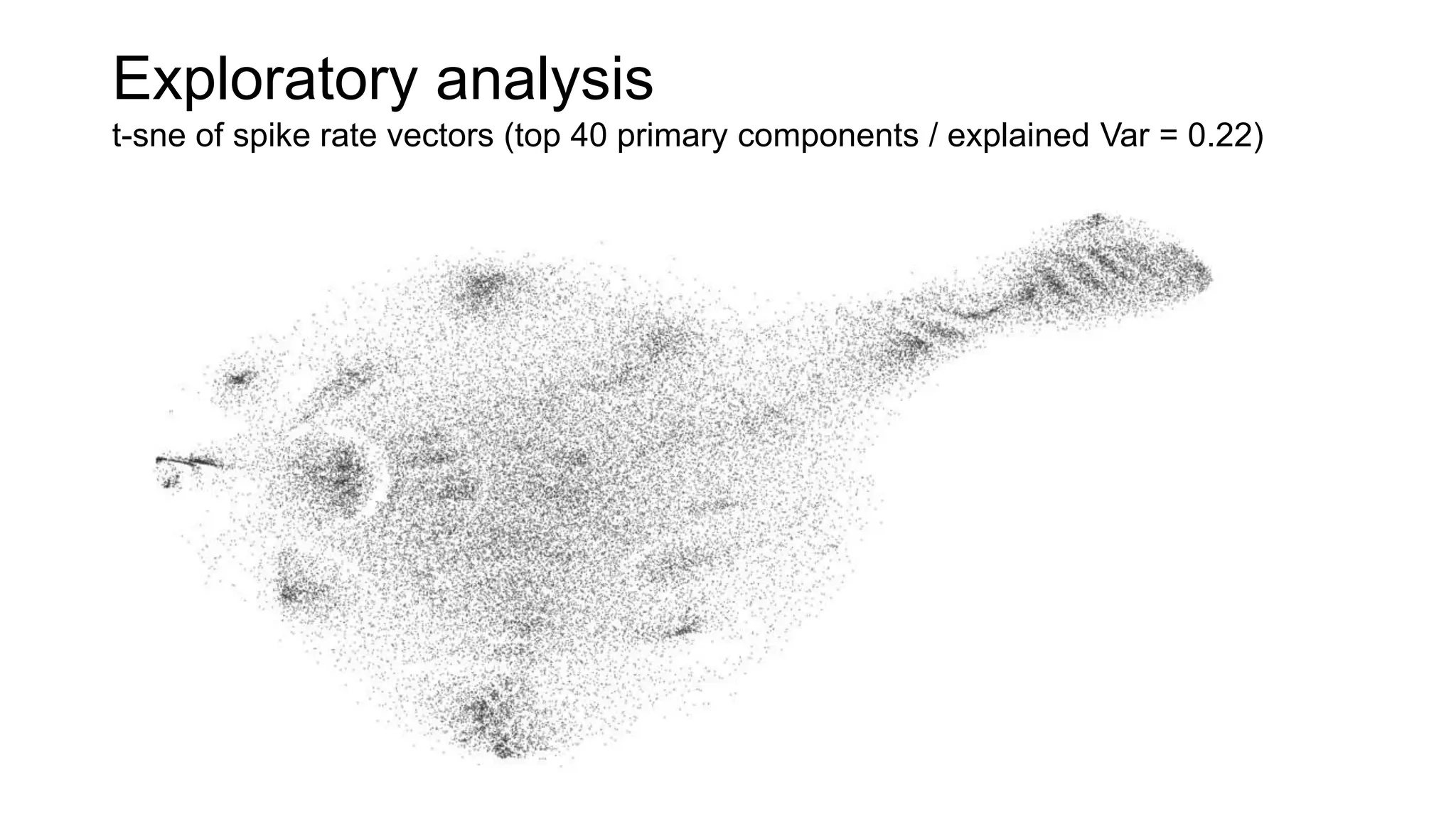
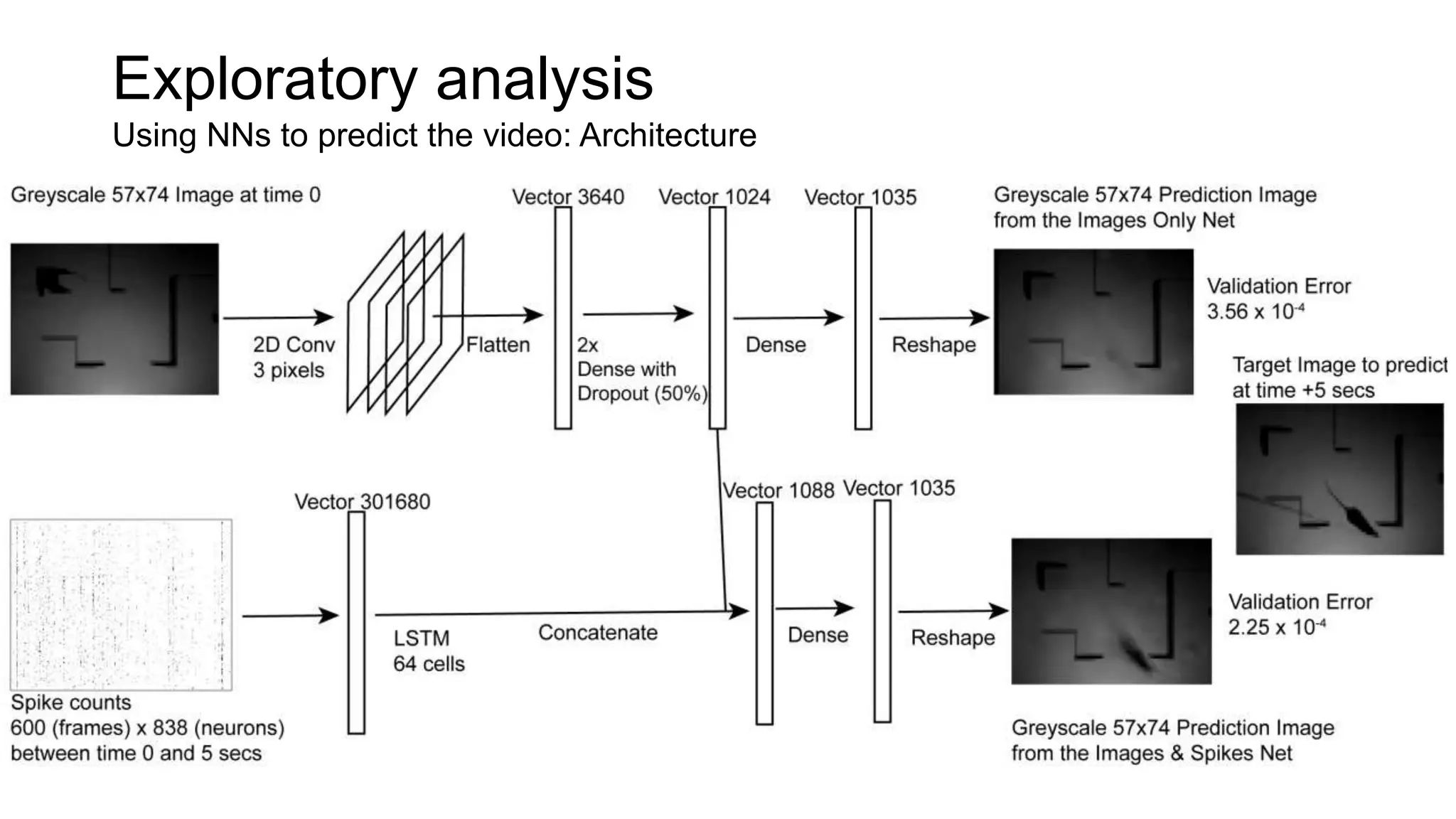
The document discusses advancements in complex systems neuroscience, focusing on high-dimensional recordings and behavioral setups utilizing various designs like Neuroseeker probes and their applications in understanding neuronal activity and behavior correlations. It highlights experimental methodologies, analyses such as t-SNE, and the integration of machine learning for predictive tasks in understanding how neurons interact within their environments. The acknowledgments section lists numerous contributors and emphasizes a philosophy of inquiry and the pursuit of knowledge.