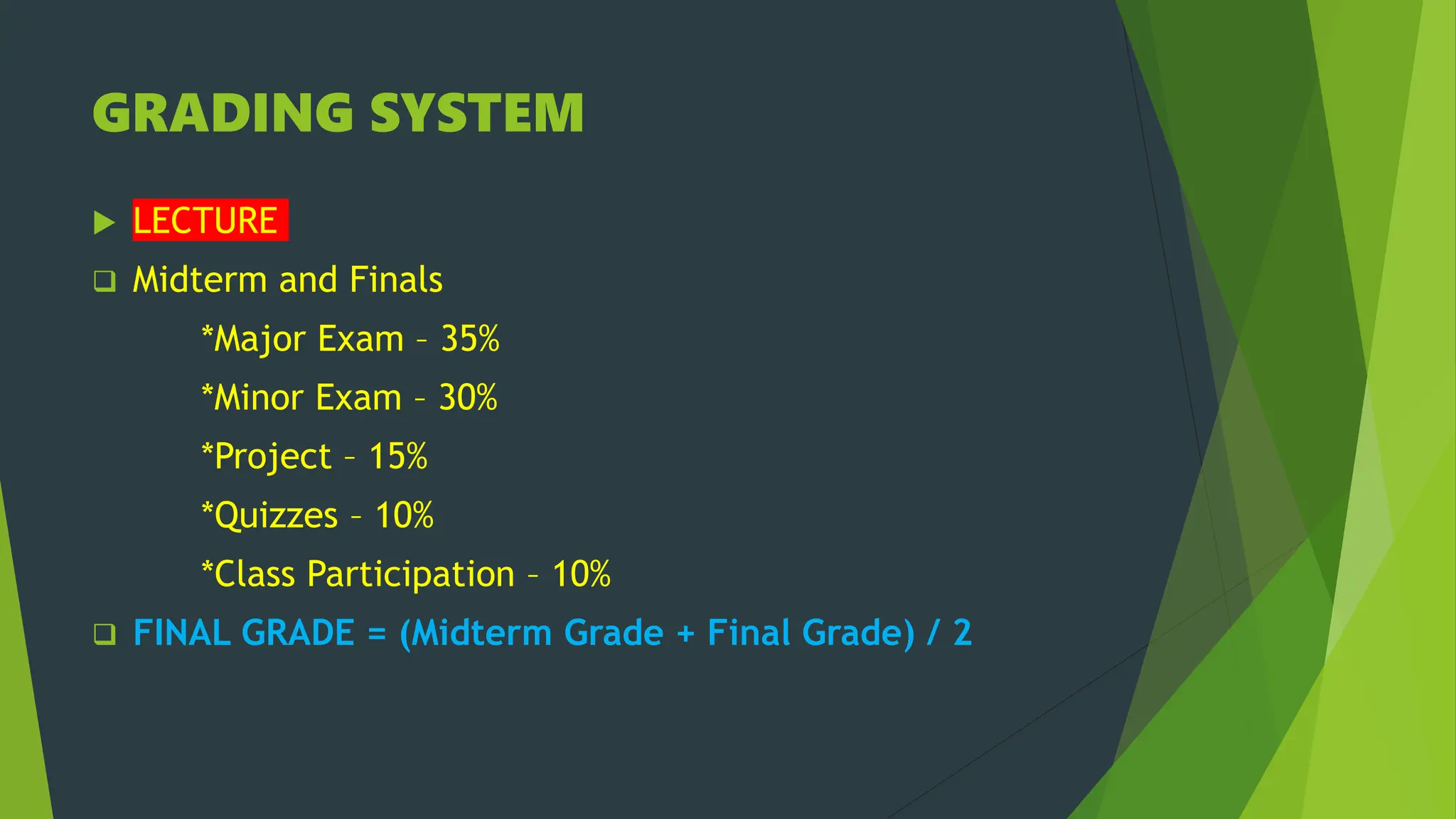
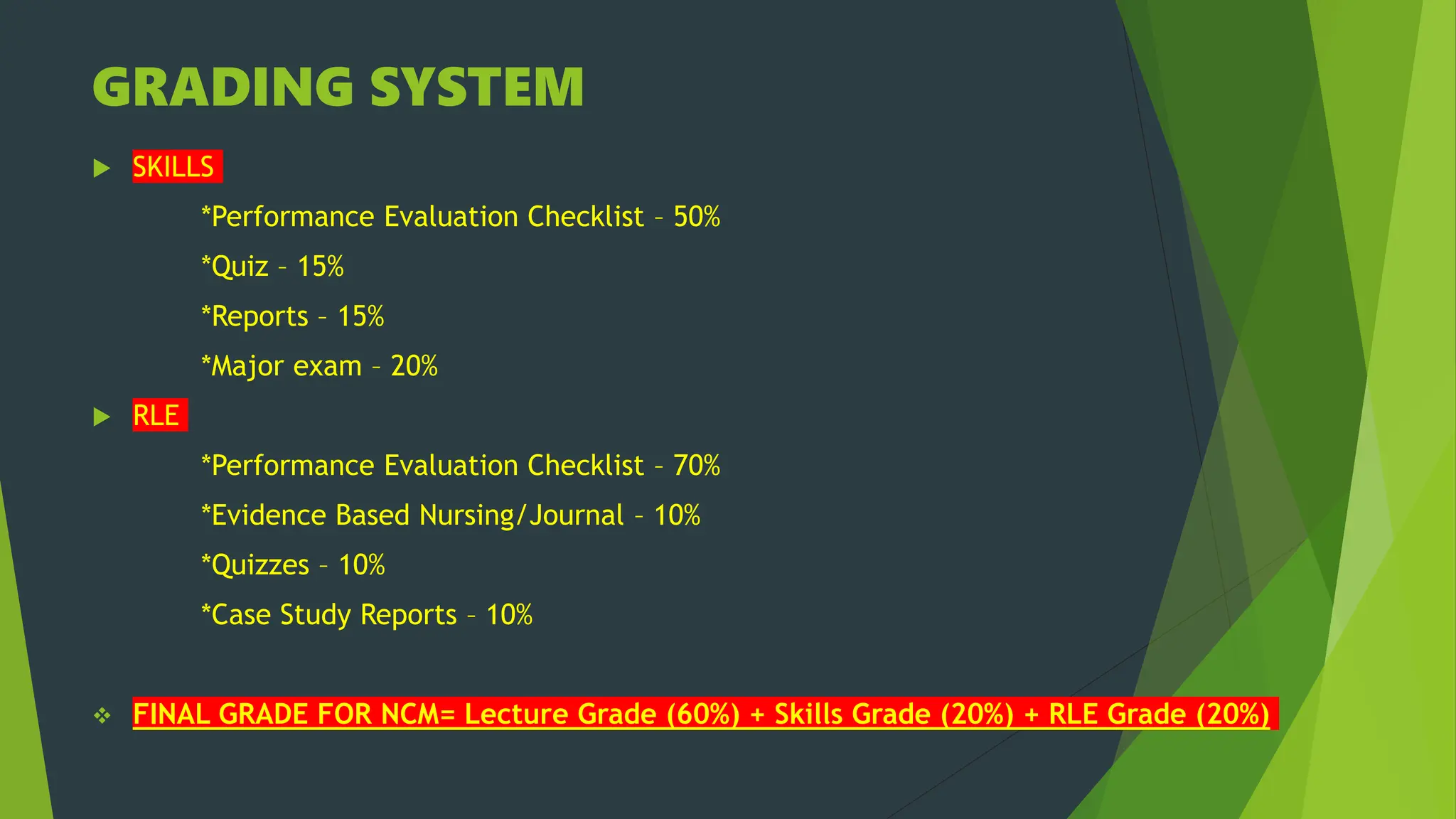
This document provides an overview of the Community Health Nursing 2 course. It outlines the course outcomes, which involve defining key health concepts and applying the nursing process to community health situations. The document details the topics that will be covered in each of the 6 weeks, including community organizing, the nursing process, laws related to public health, and epidemiology. It also provides the grading criteria for lectures, skills, and reflective learning experiences. The overall goal is for students to demonstrate safe and holistic nursing care for populations and communities.