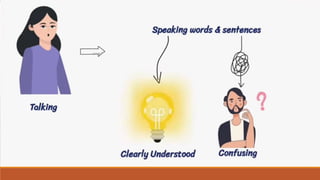
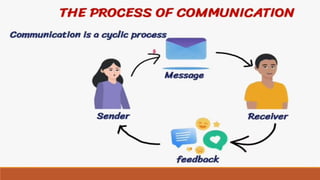
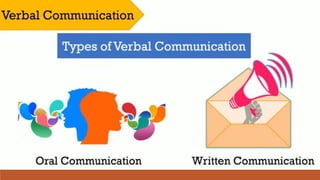
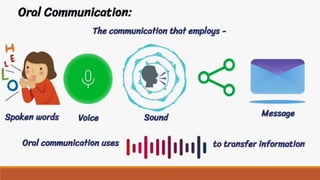
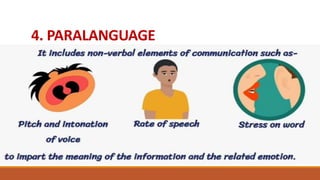
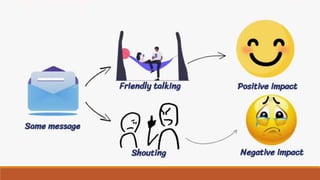
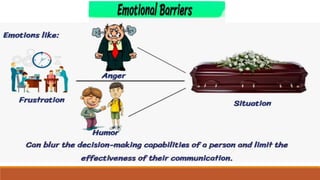
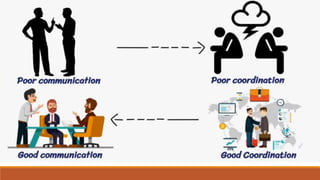
The document provides an overview of various communication skills, emphasizing the importance of non-verbal communication types such as body language, proxemics, chronemics, and paralanguage. It also highlights the significance of operational communication within organizations, detailing internal, external, and personal communication types, along with effective ways to improve organizational communication. Different communication styles—submissive, assertive, and aggressive—are discussed, with tips for enhancing communication skills.