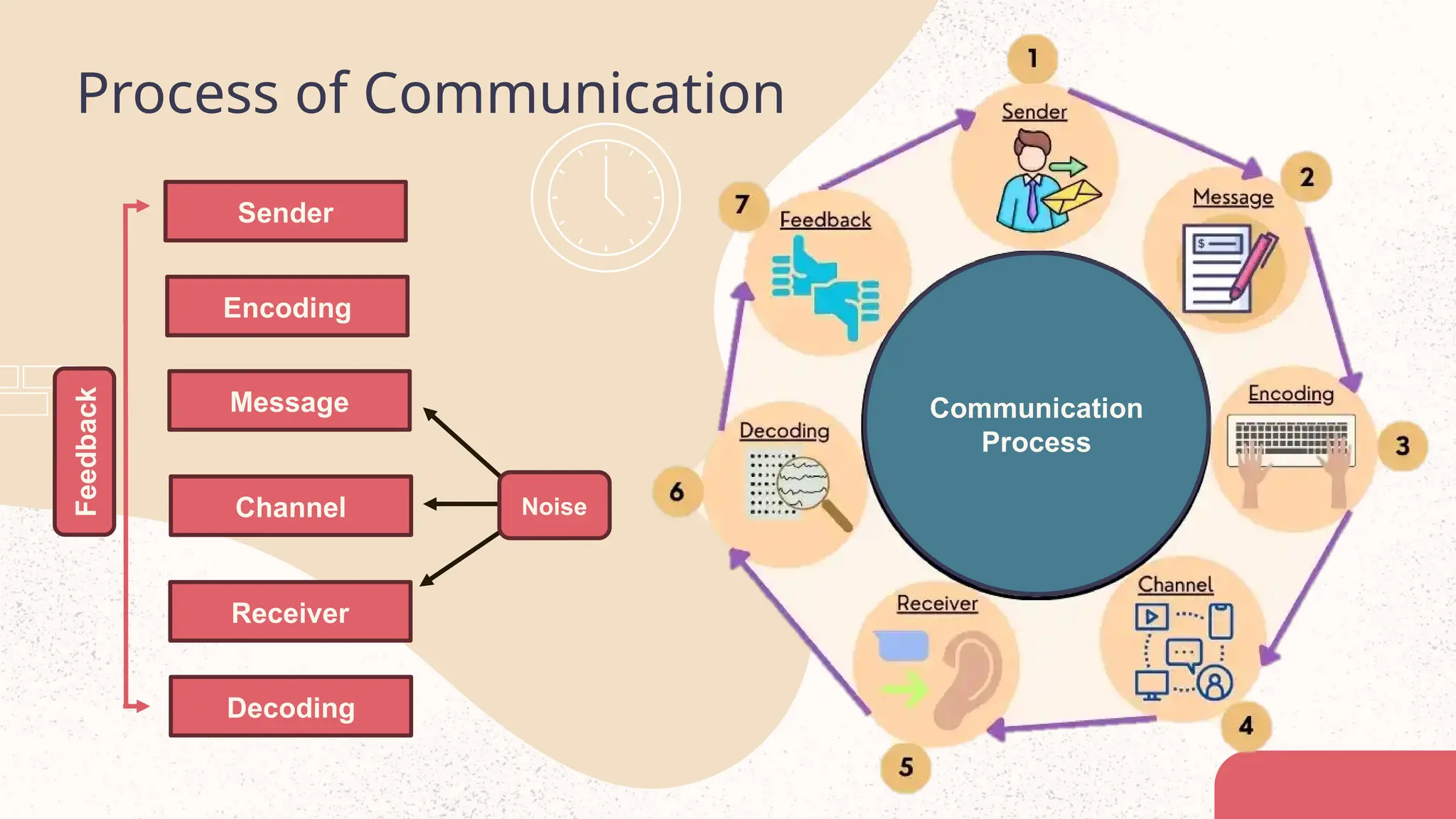
The document discusses the concept of communication, highlighting its definitions, types (verbal and non-verbal), and the communication process involving sender, message, encoding, medium, receiver, decoding, noise, and feedback. It emphasizes the importance of effective communication, barriers that hinder it, and methods to overcome these obstacles. Notable communication methods mentioned include face-to-face conversations, written communication, and non-verbal cues such as gestures and facial expressions.