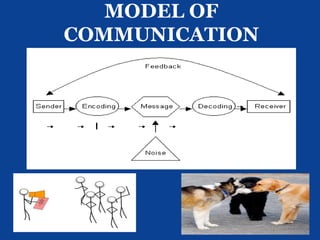
This document discusses various aspects of communication. It defines communication and provides a model of communication that includes a sender, encoding, message, channel, decoding, receiver, and feedback. It discusses verbal and nonverbal communication. It outlines five types of communication: intrapersonal, interpersonal, small group, public, and mass communication. It also discusses what communication can include, the differences between truth and validity, and the concept of threshold in decision making.