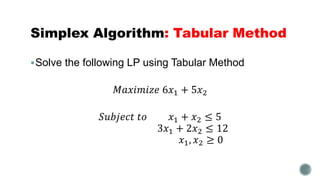
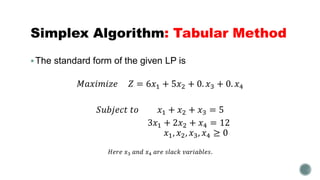
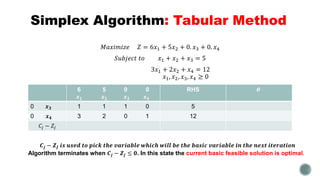
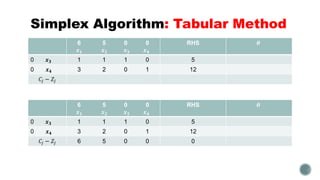
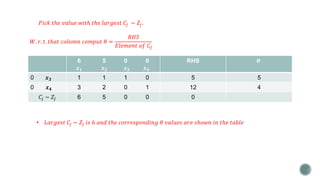
The document summarizes the simplex algorithm for solving linear programs. It discusses how the simplex algorithm works by generating a sequence of basic feasible solutions until it finds an optimal solution. It provides the standard form for a linear program and describes how the simplex algorithm sets up a tableau to solve the problem using an iterative method. Finally, it provides an example linear program and begins setting up the tableau to solve it using the simplex algorithm's tabular method.

![Simplex Algorithm
[1947]. George B. Dantzig developed a technique to solve linear
programs----known as Simplex Algorithm
The simplex method is an iterative method that generates a sequence
of basic feasible solutions (corresponding to different bases) and
eventually stops when it has found an optimal basic feasible solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/co-lec-7-210526055638/85/Combinatorial-optimization-CO-7-2-320.jpg)