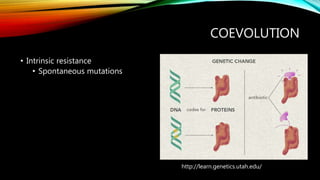
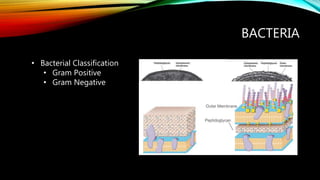
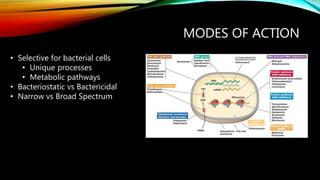
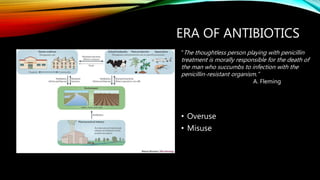
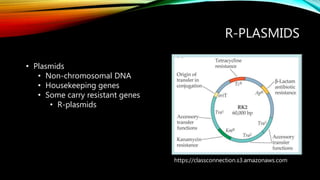
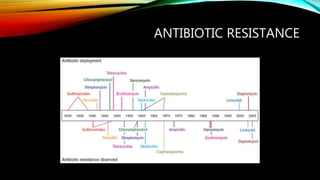
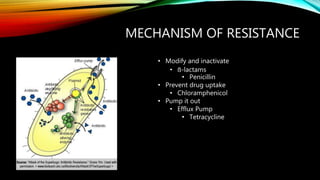
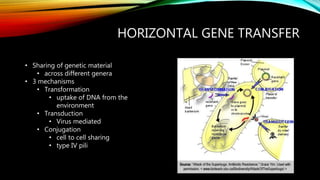
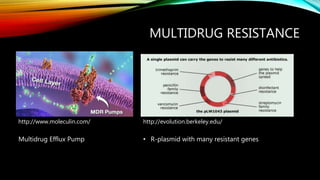
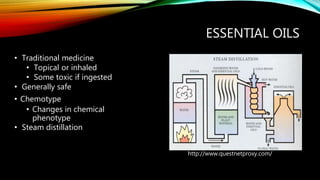
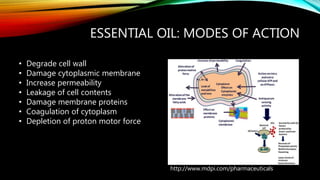
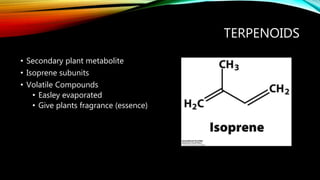
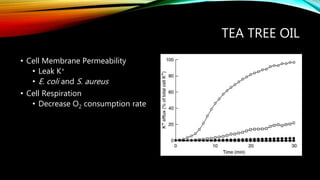
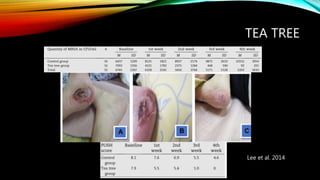
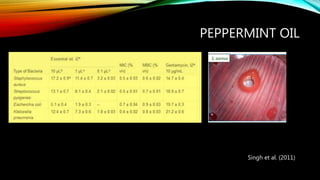
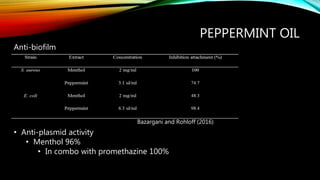
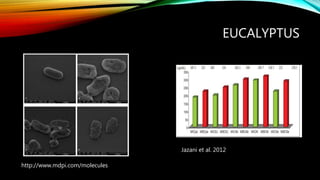
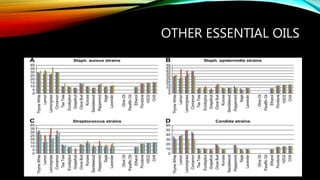
Essential oils from plants such as tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia), peppermint (Mentha piperita), and eucalyptus (Eucalyptus camaldulensis) have demonstrated antibacterial properties against multidrug-resistant bacteria through their ability to damage bacterial cell membranes and disrupt cellular functions. These essential oils represent promising alternatives or adjuncts to conventional antibiotics for treating infections caused by multidrug-resistant pathogens like MRSA and ESBL-producing E. coli and Klebsiella. Further research is needed to better understand their synergistic effects when combined with antibiotics to potentially enhance antibacterial activity.