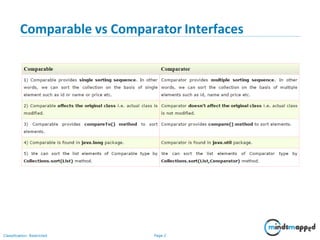
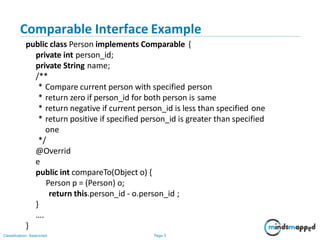
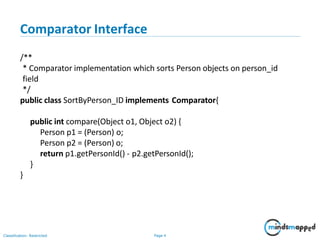
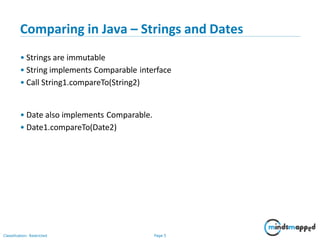
The document outlines a training agenda on Java/J2EE programming, focusing on sorting and comparing collections such as arrays and ArrayLists. It explains the use of Comparable and Comparator interfaces for implementing sorting logic. Additionally, it includes an exercise to create an Employee class and apply various sorting criteria using both interfaces.