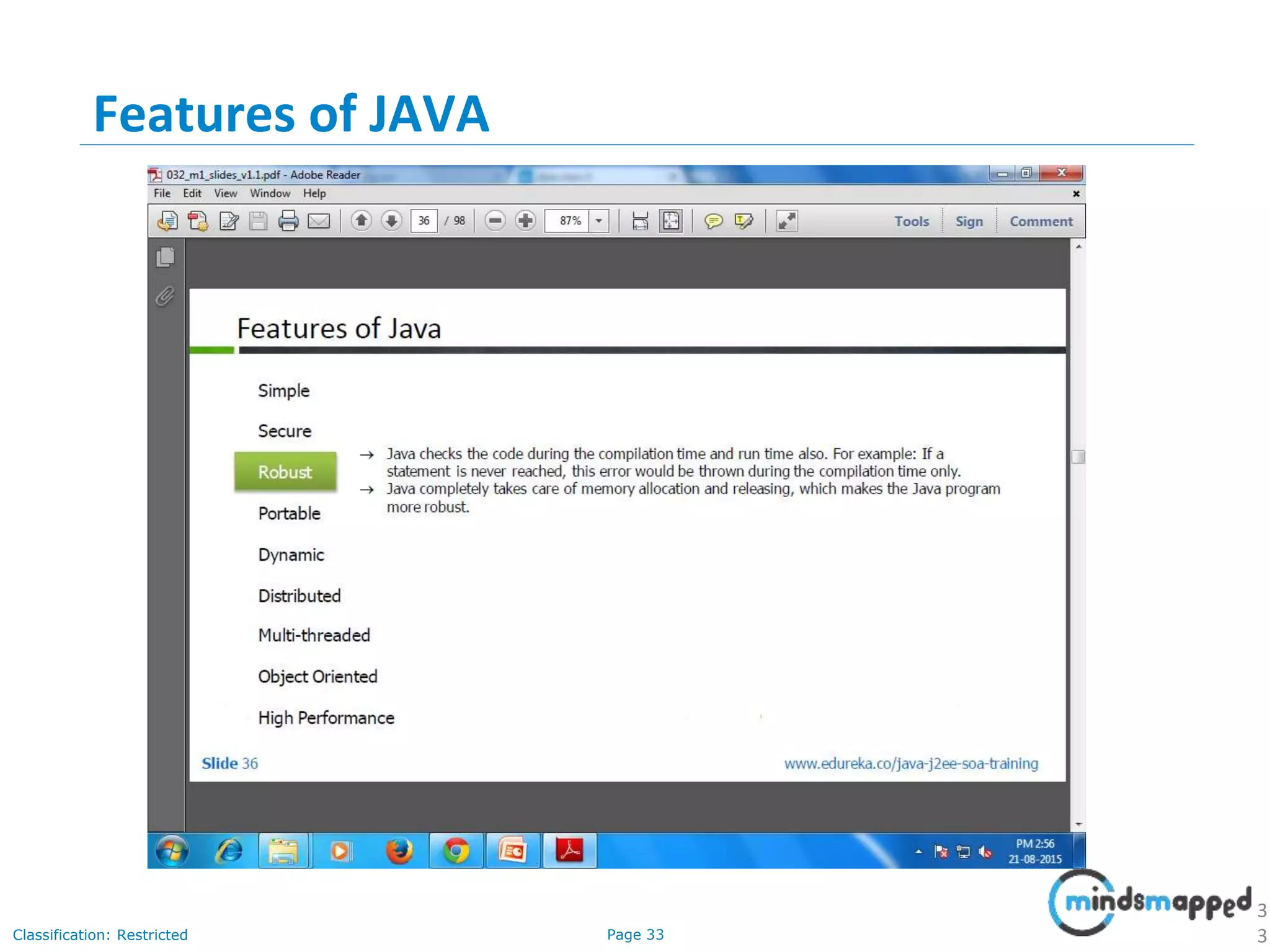
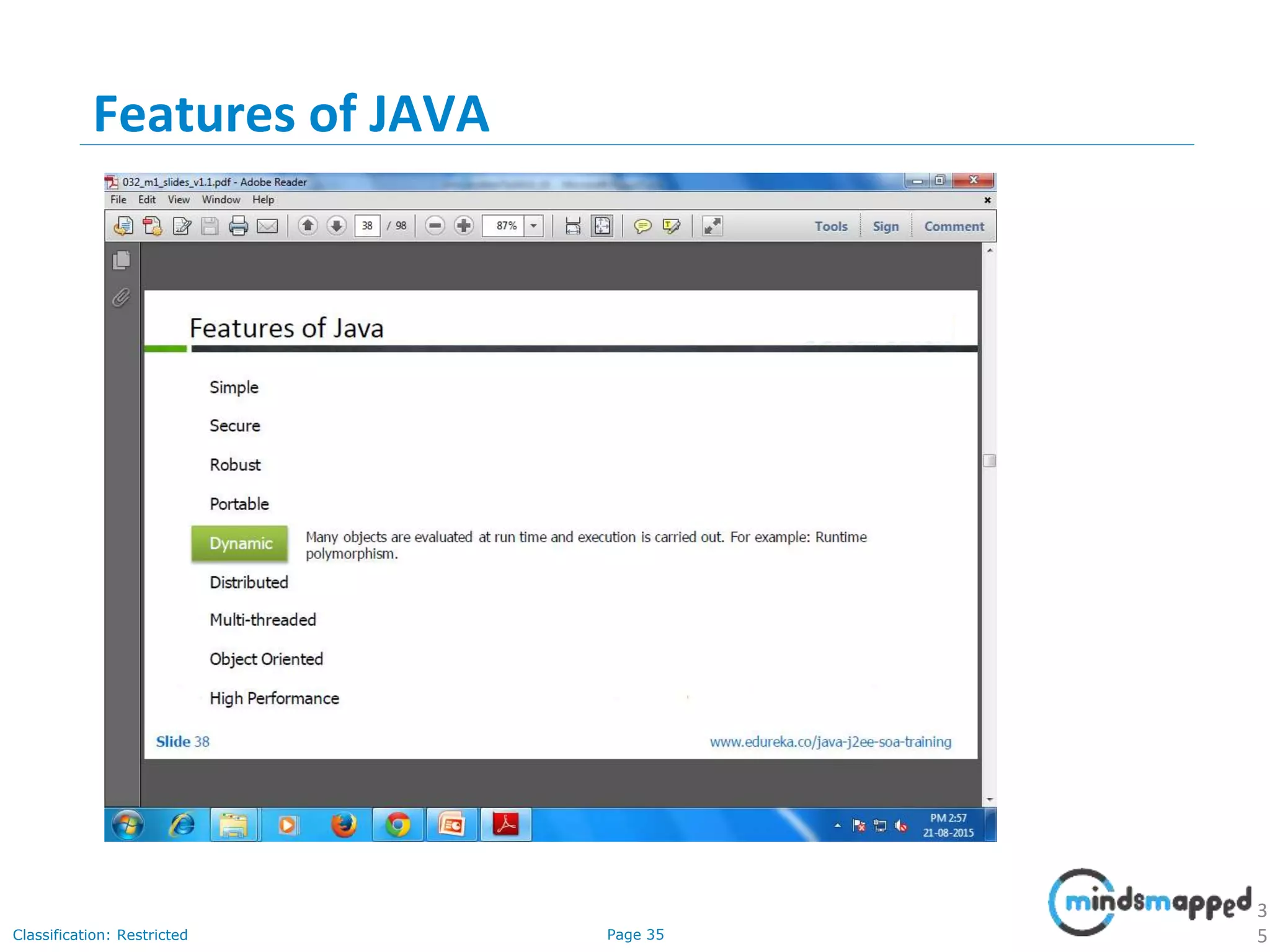
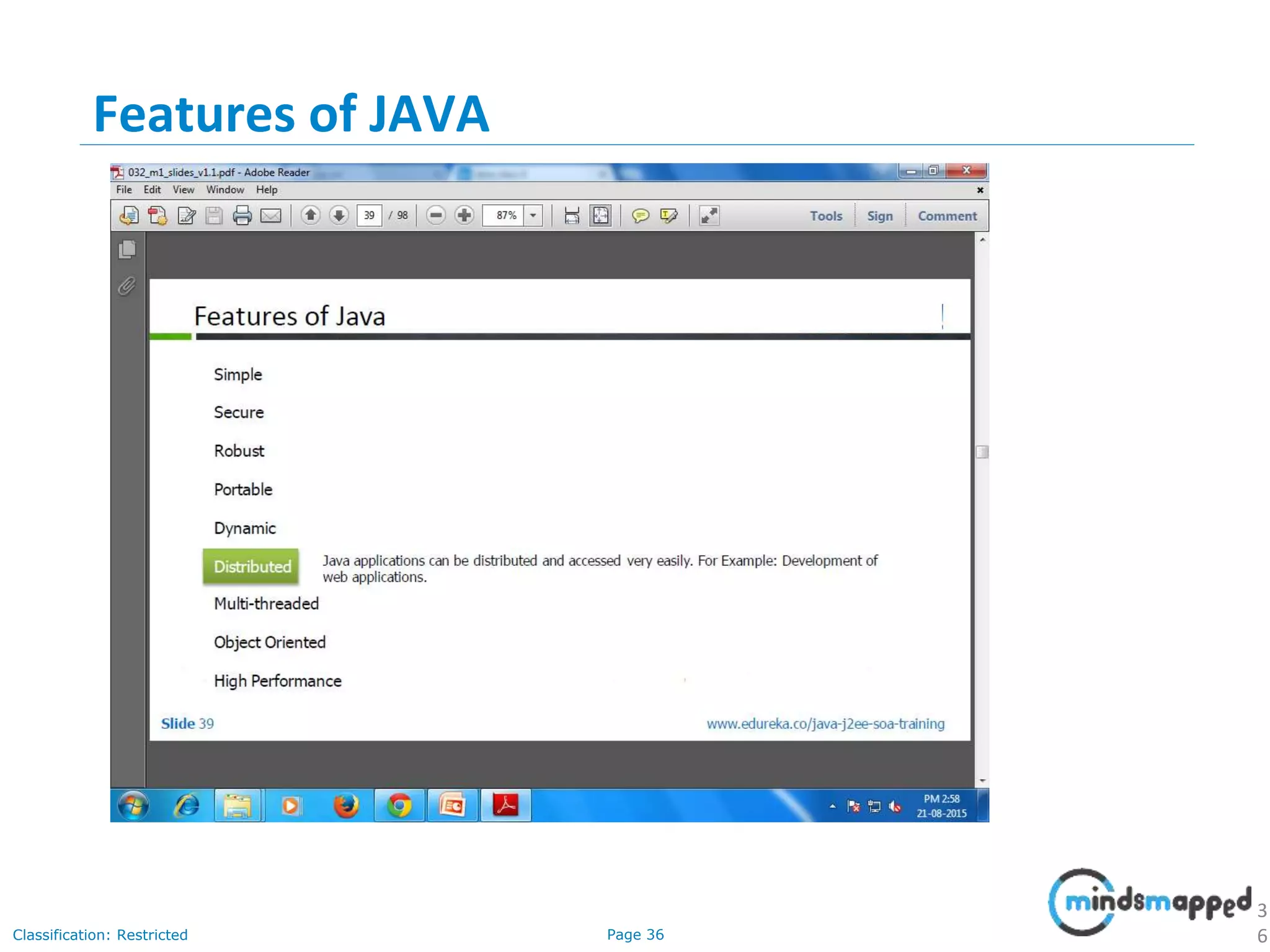
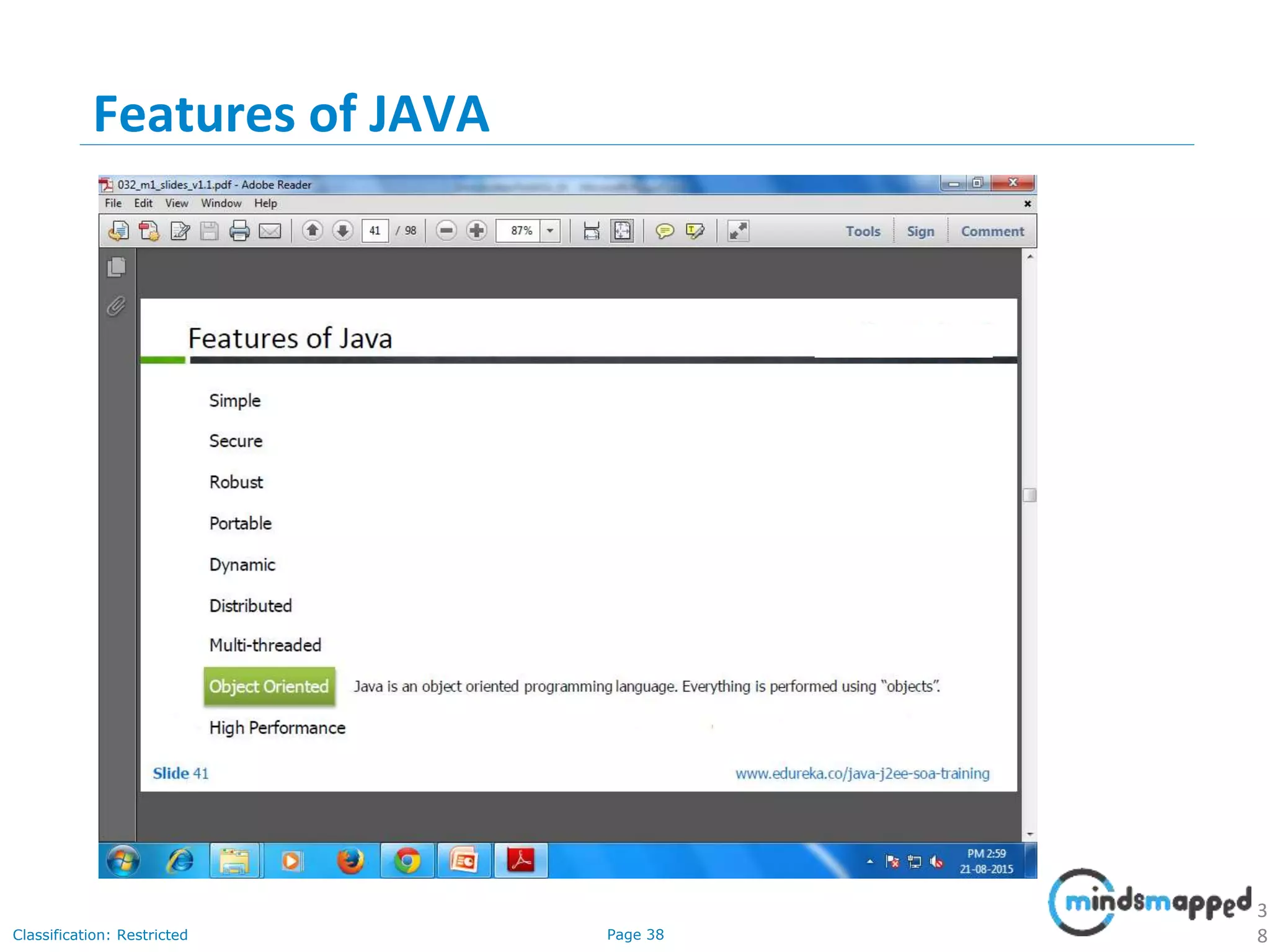
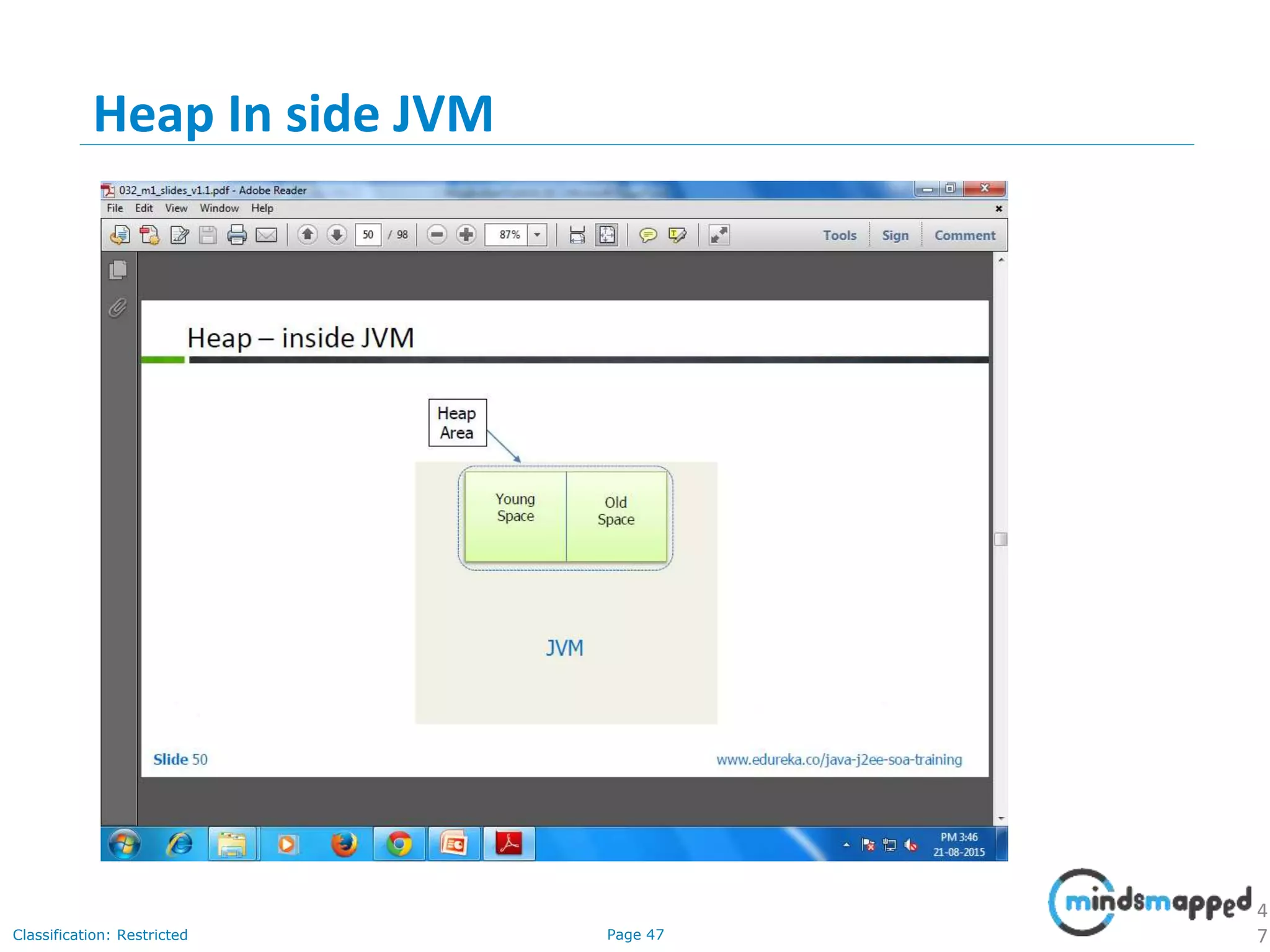
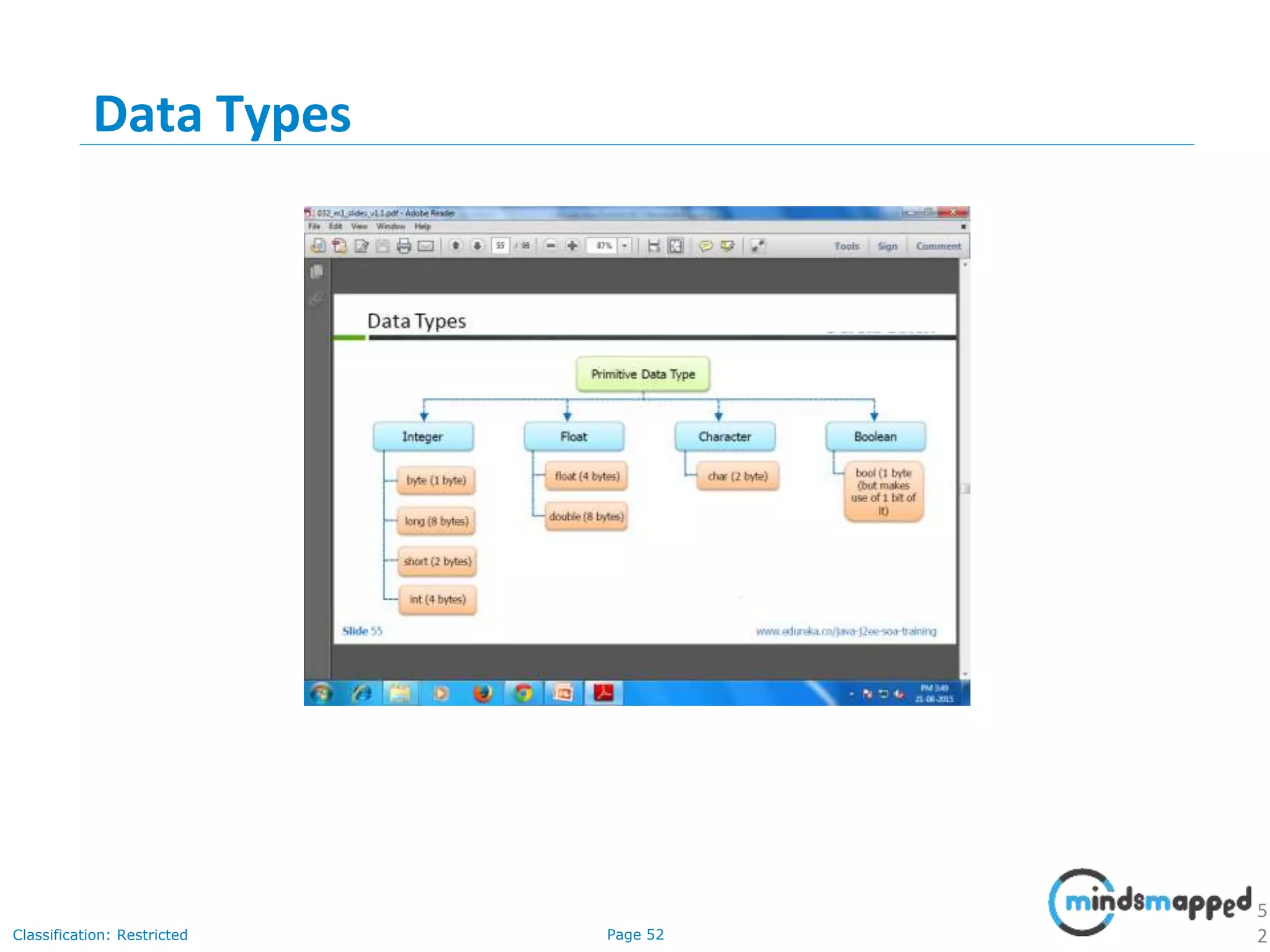
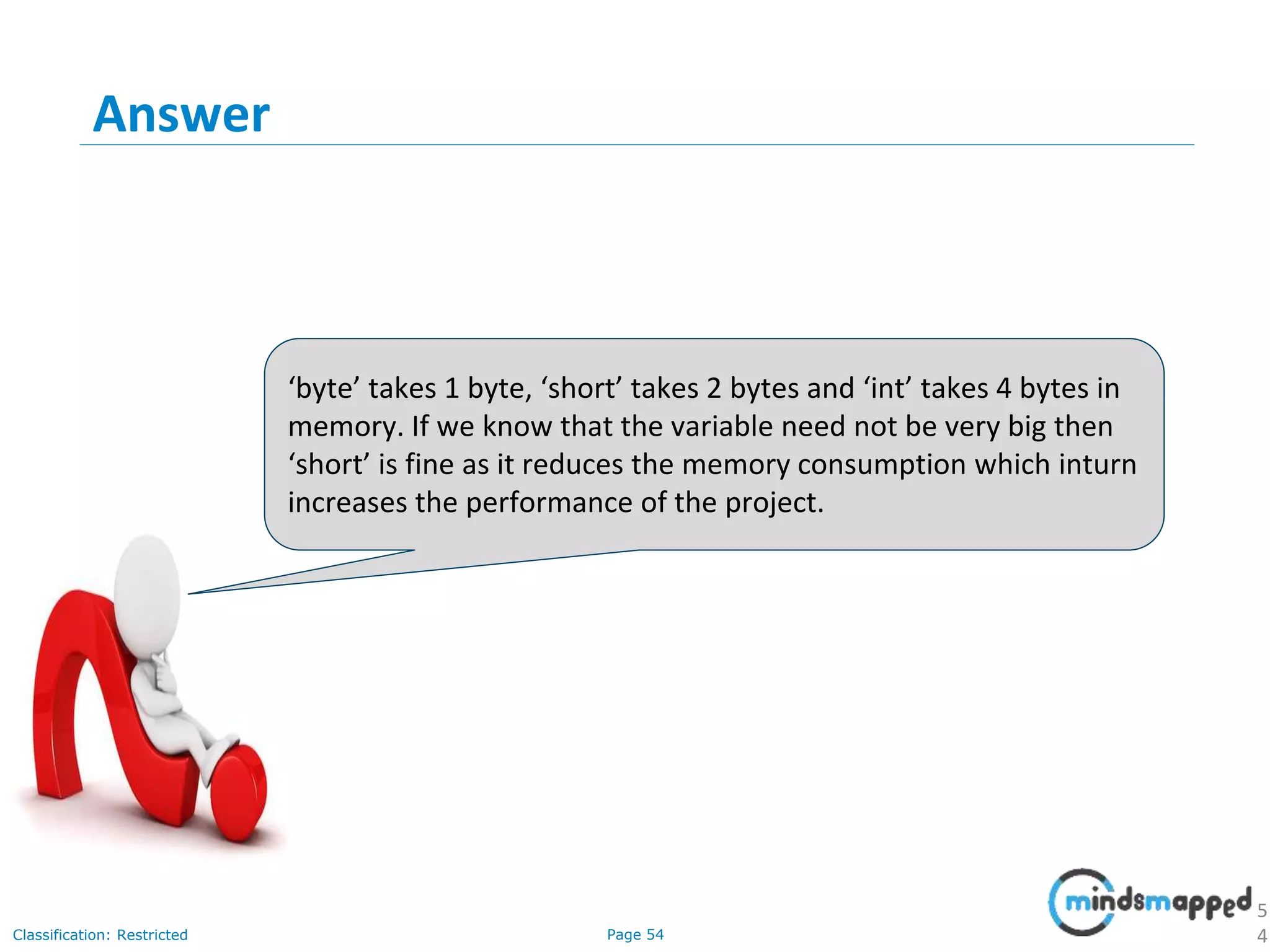
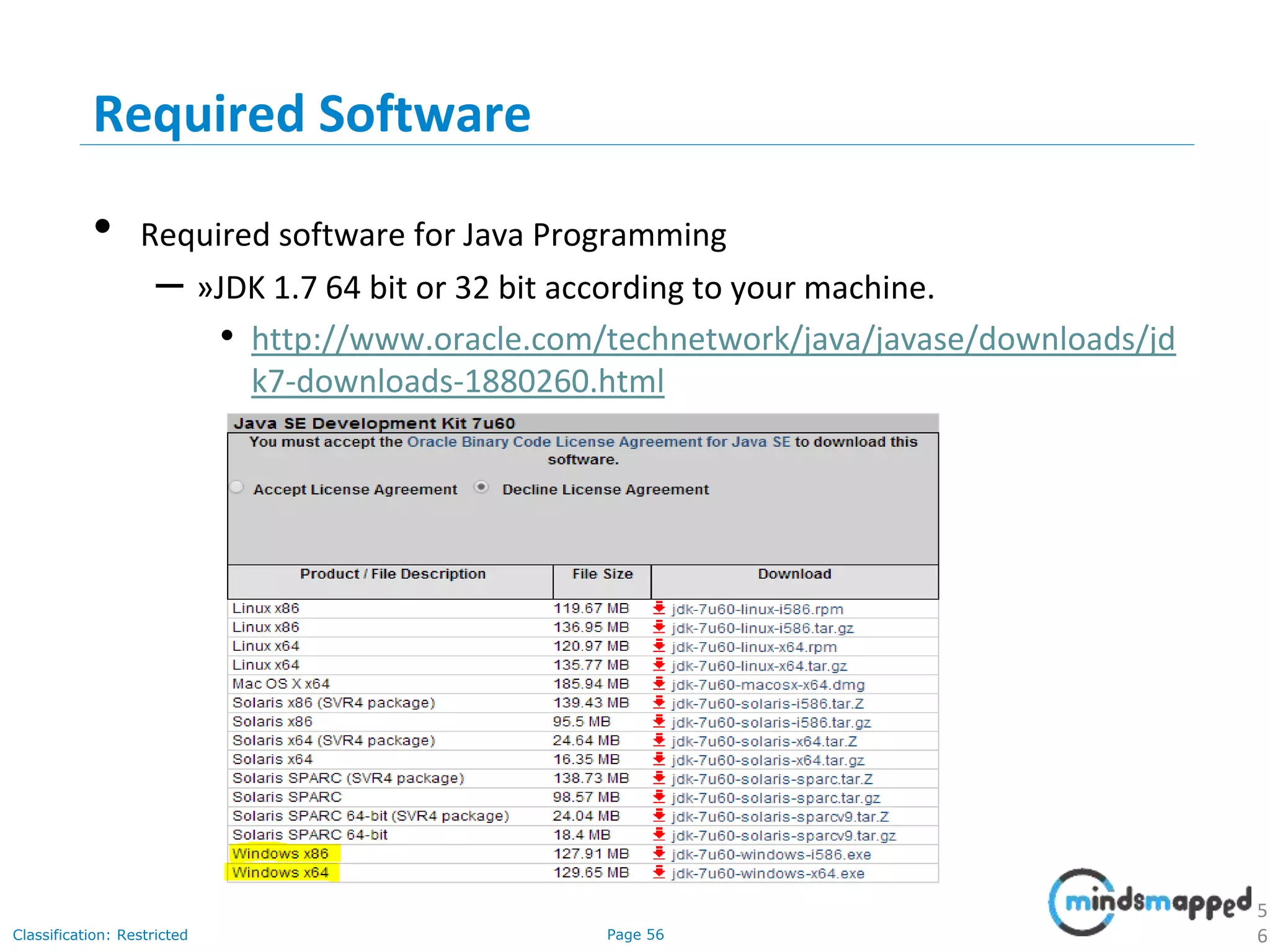
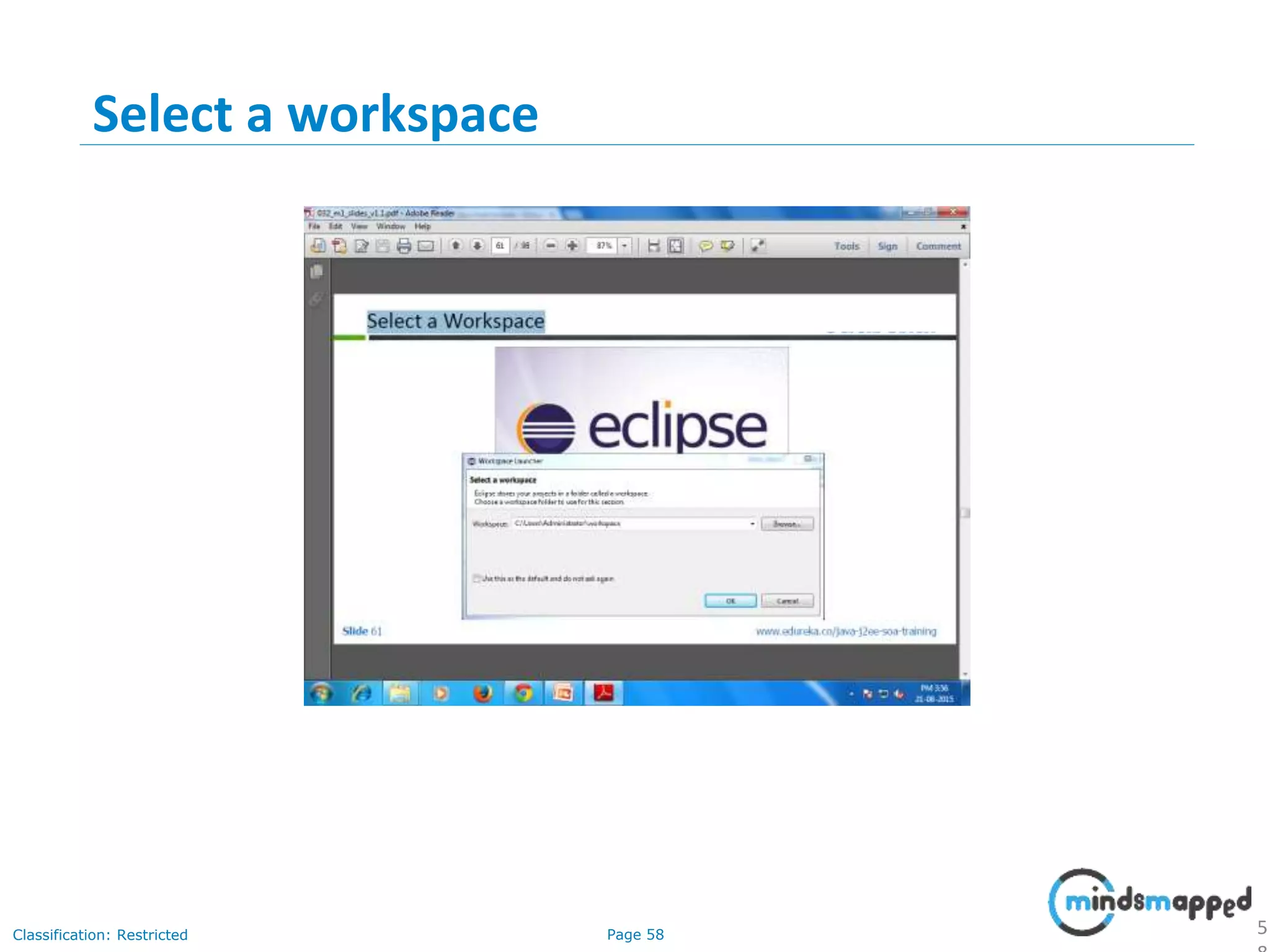
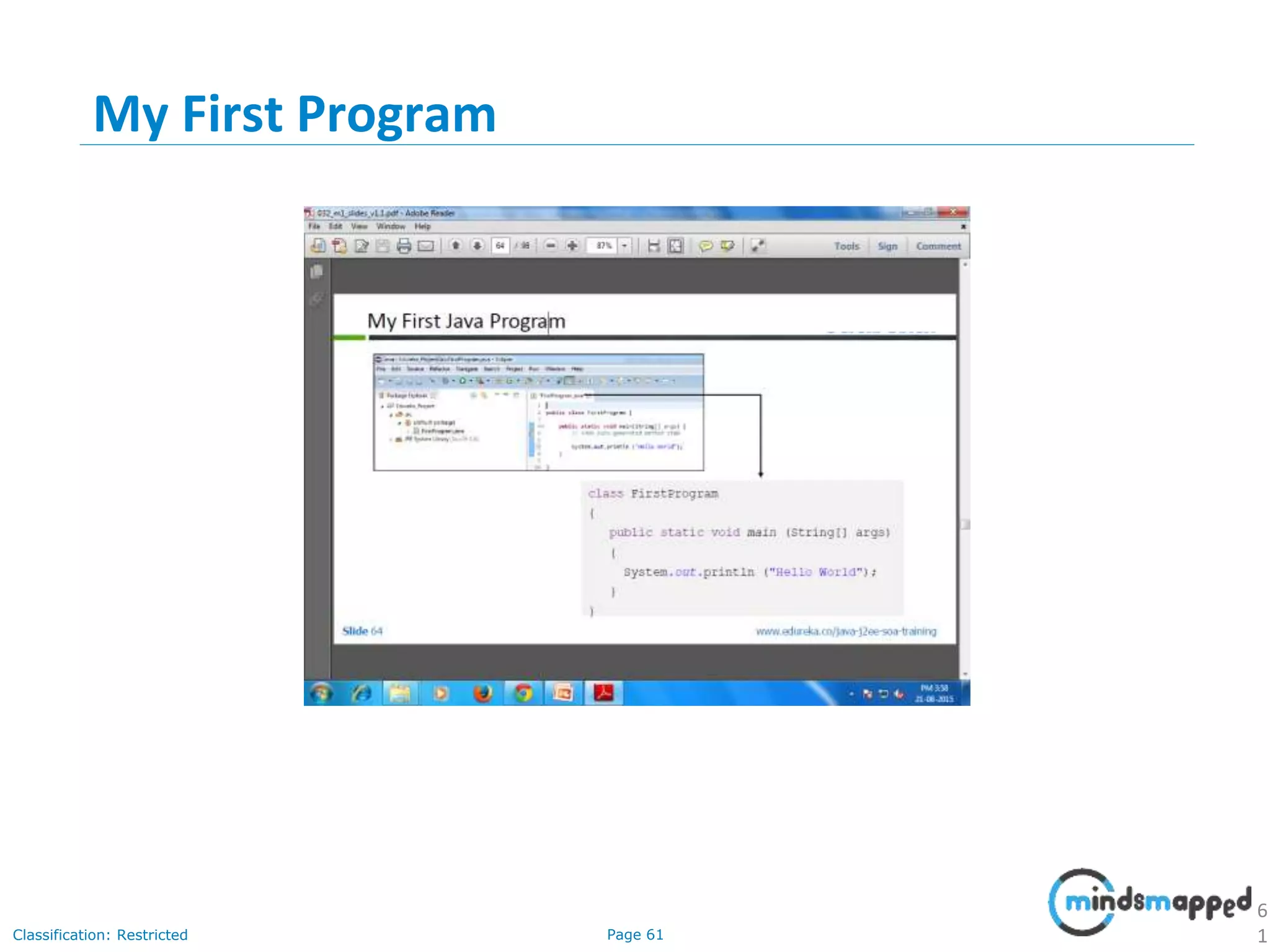
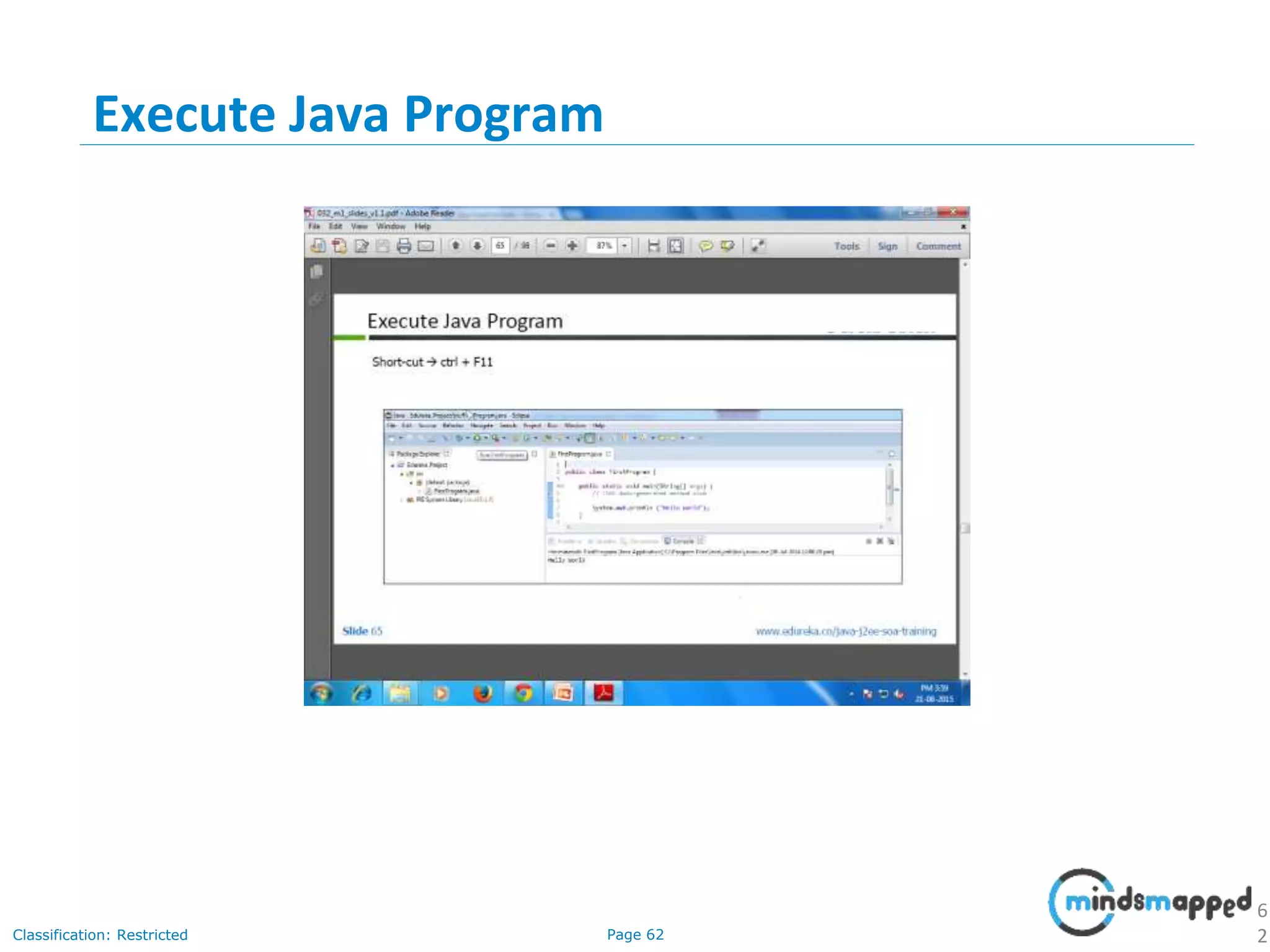
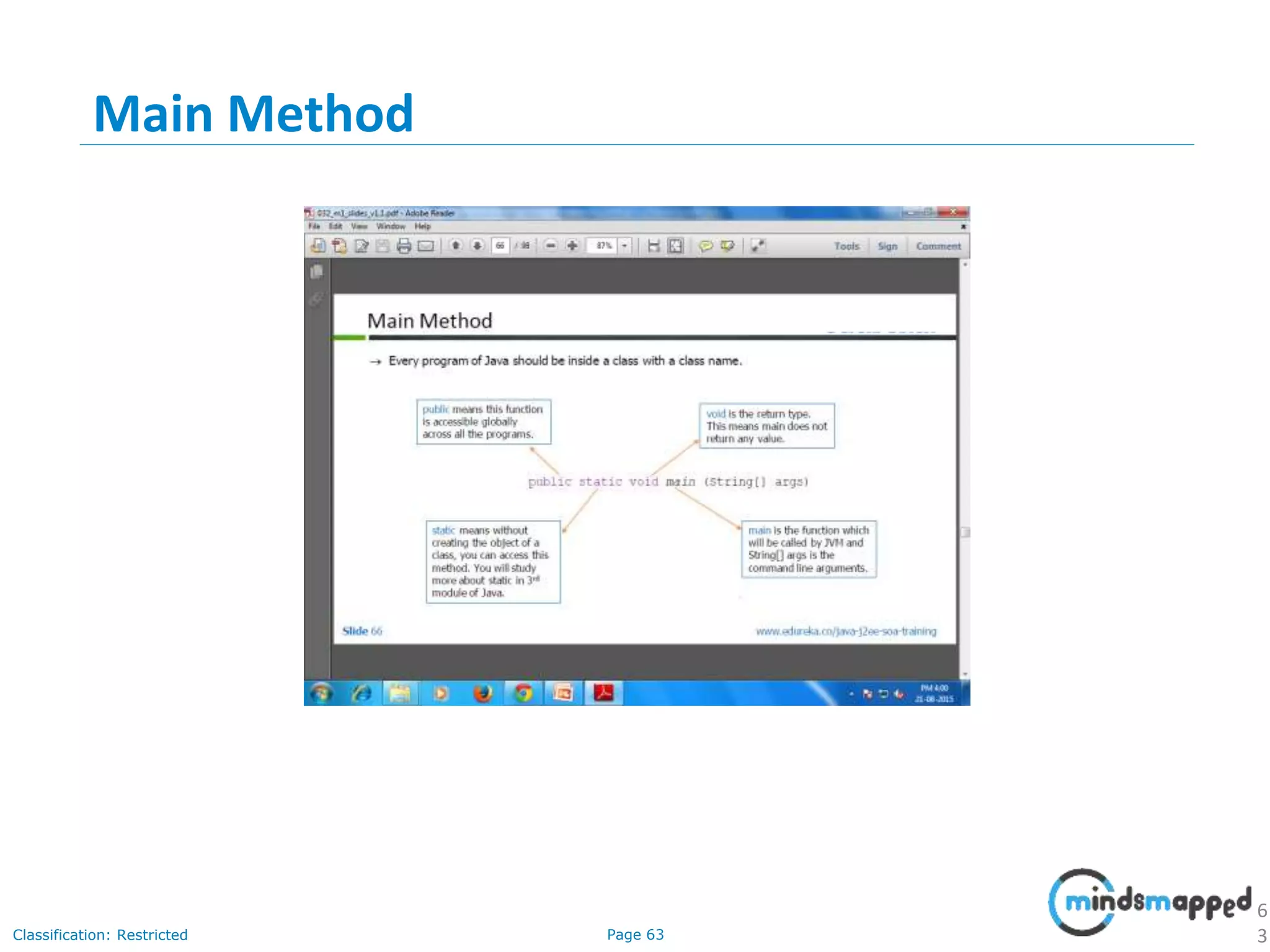
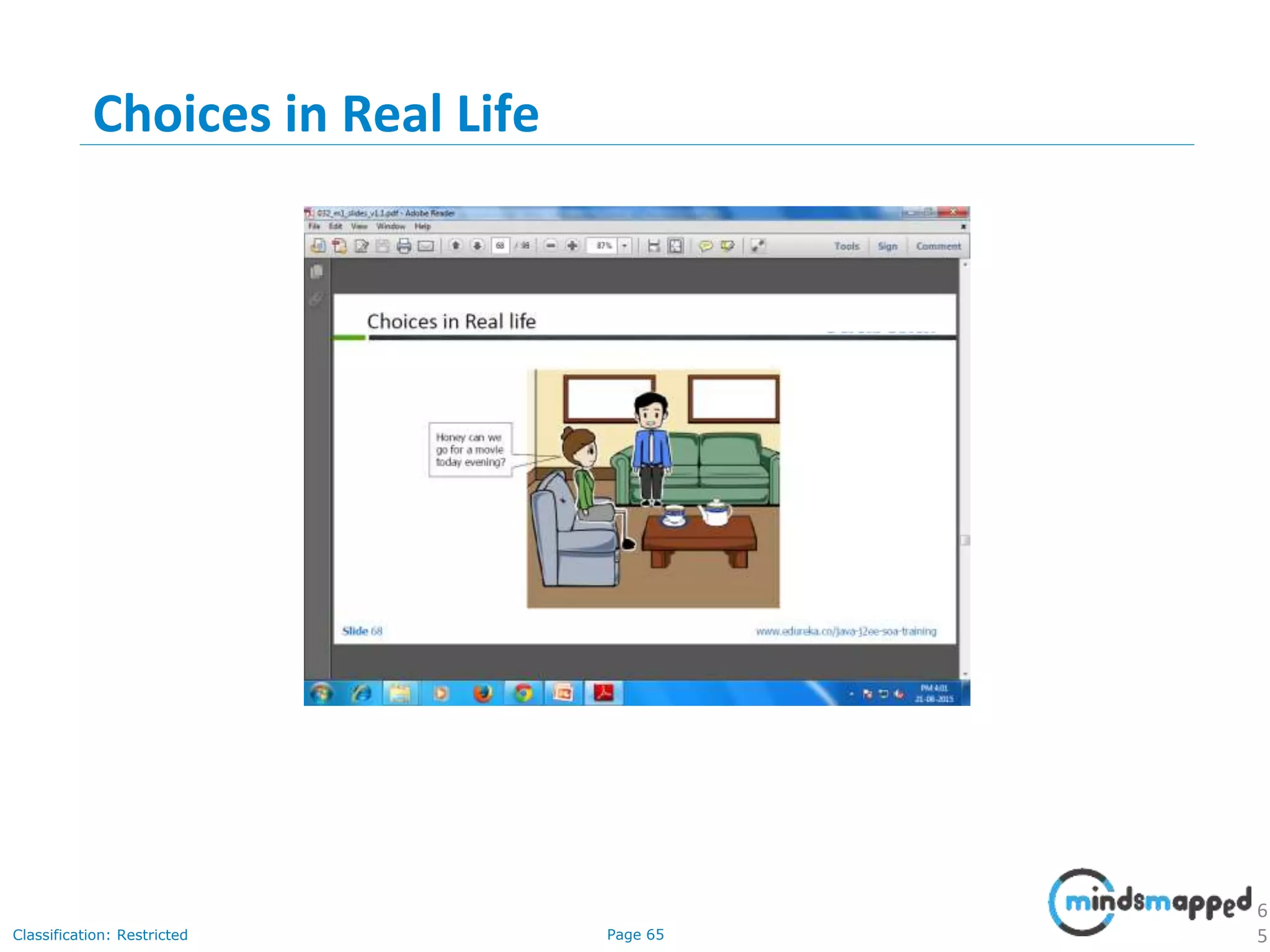
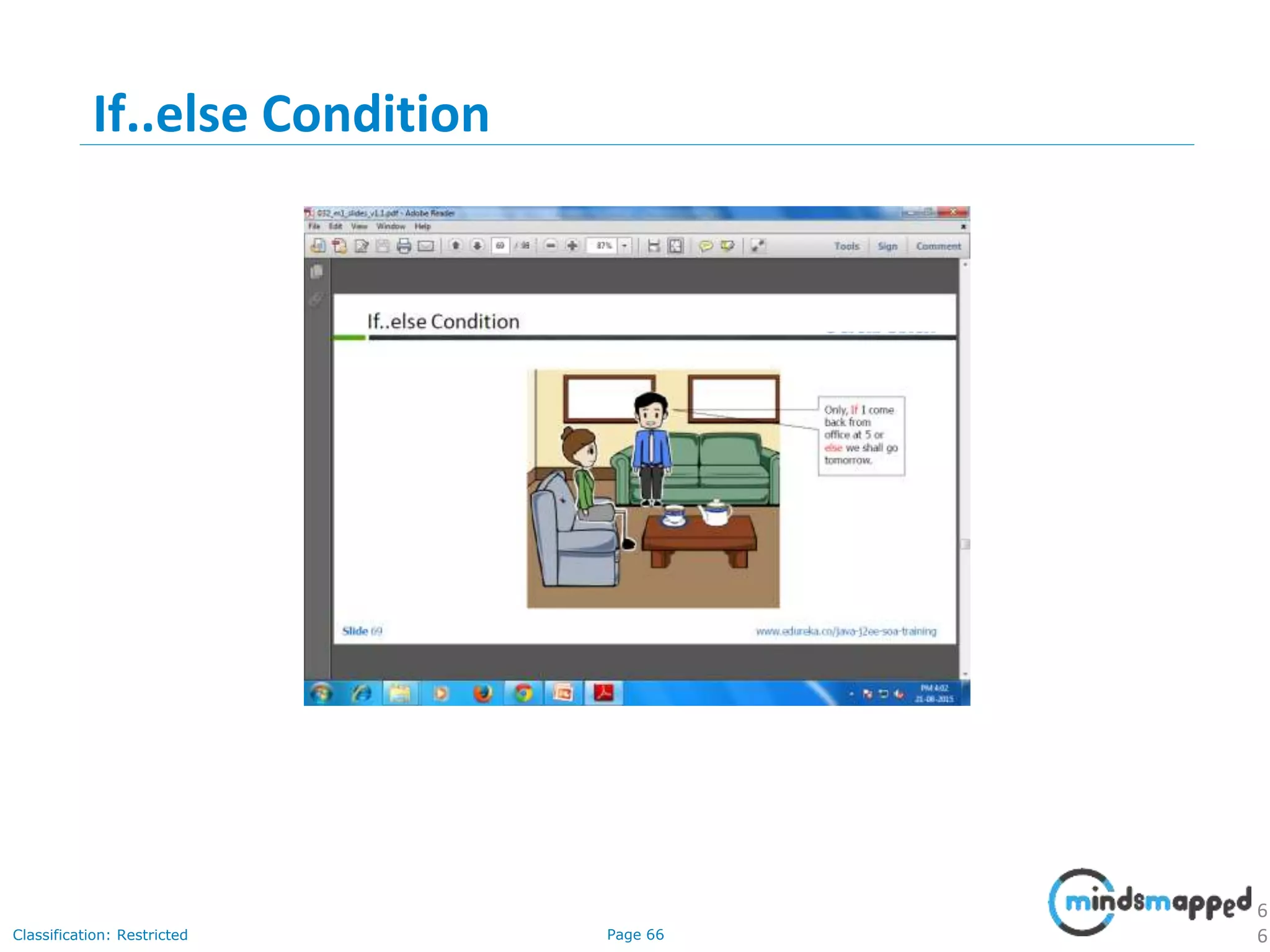
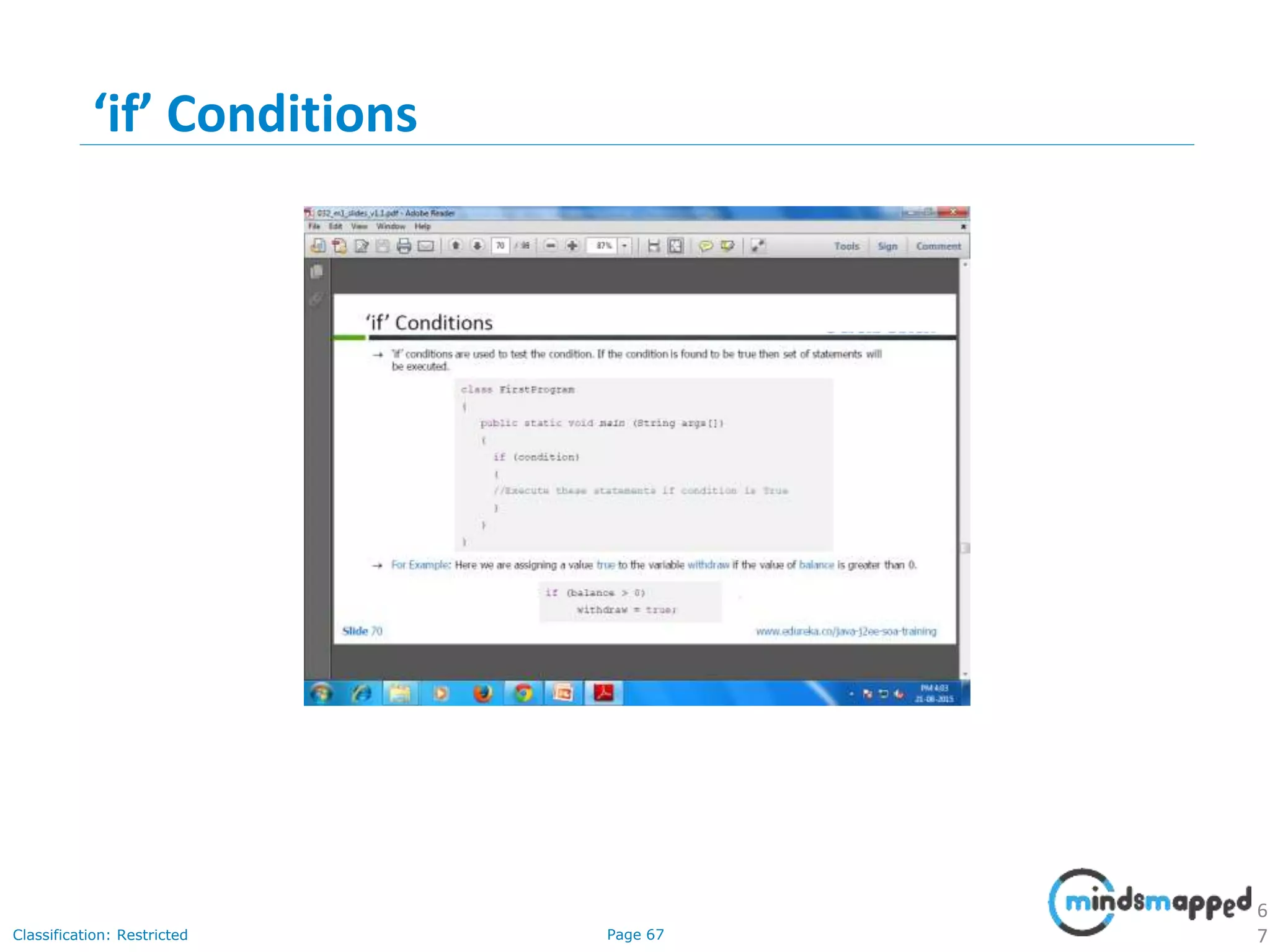
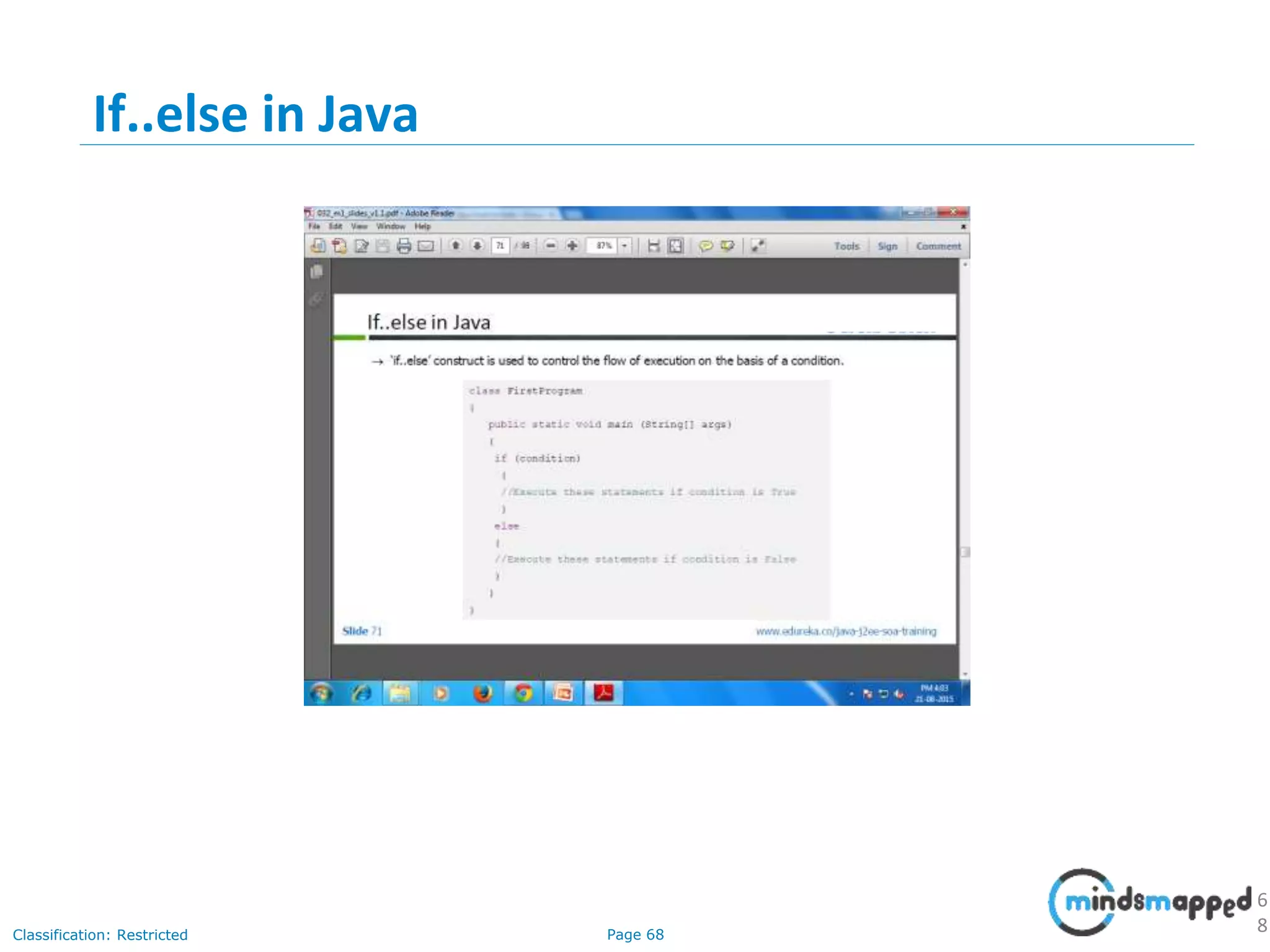
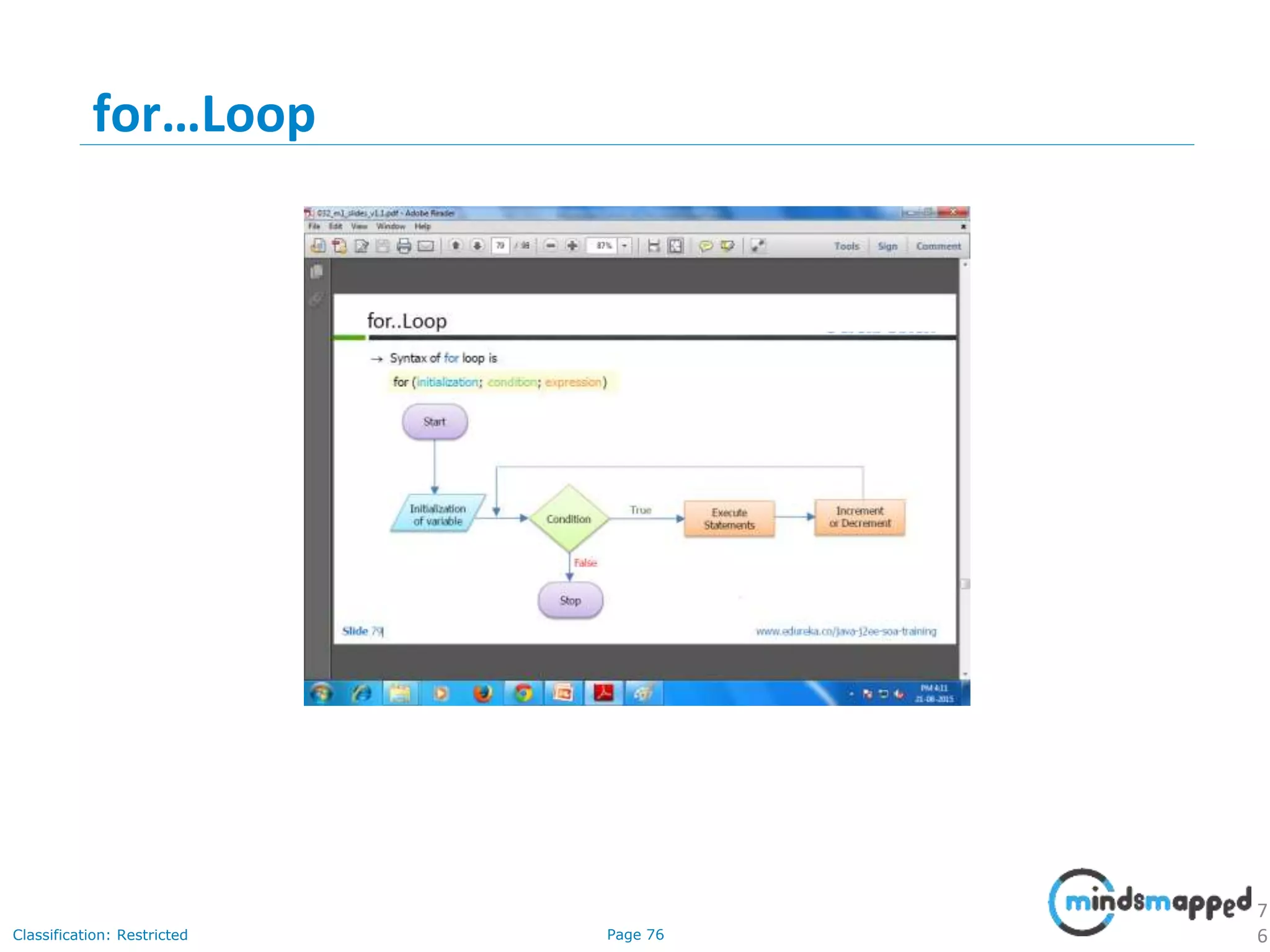
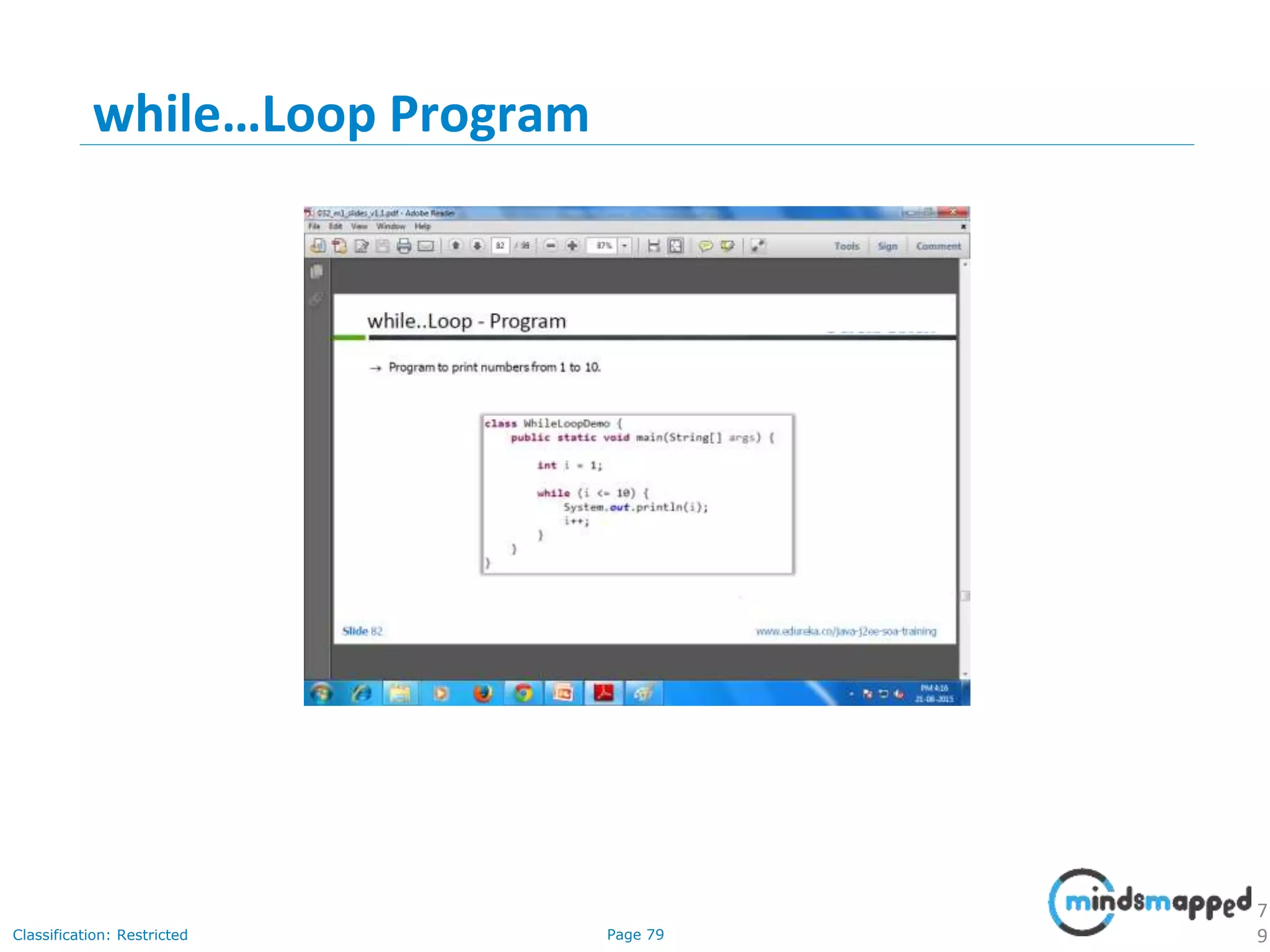
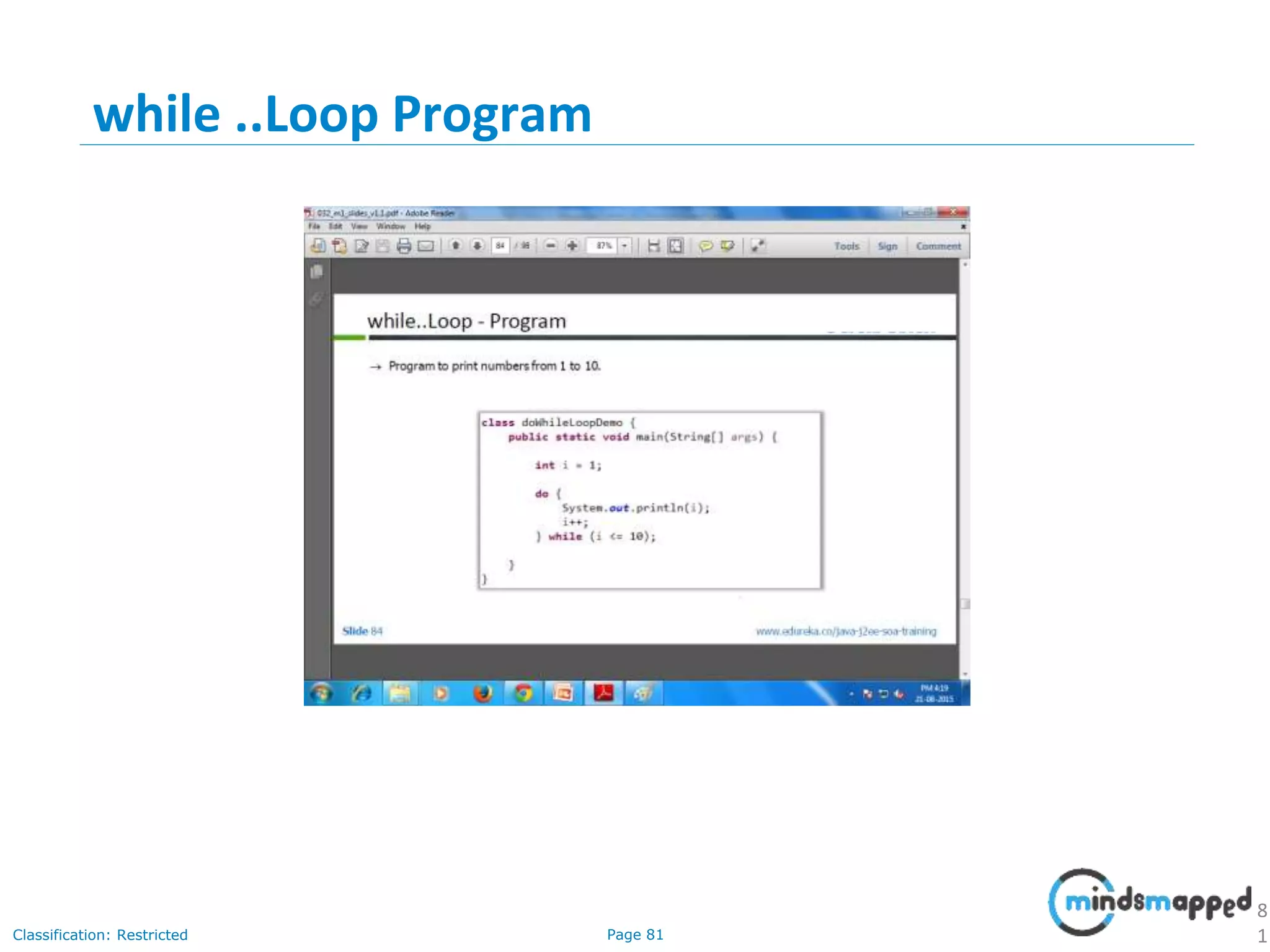
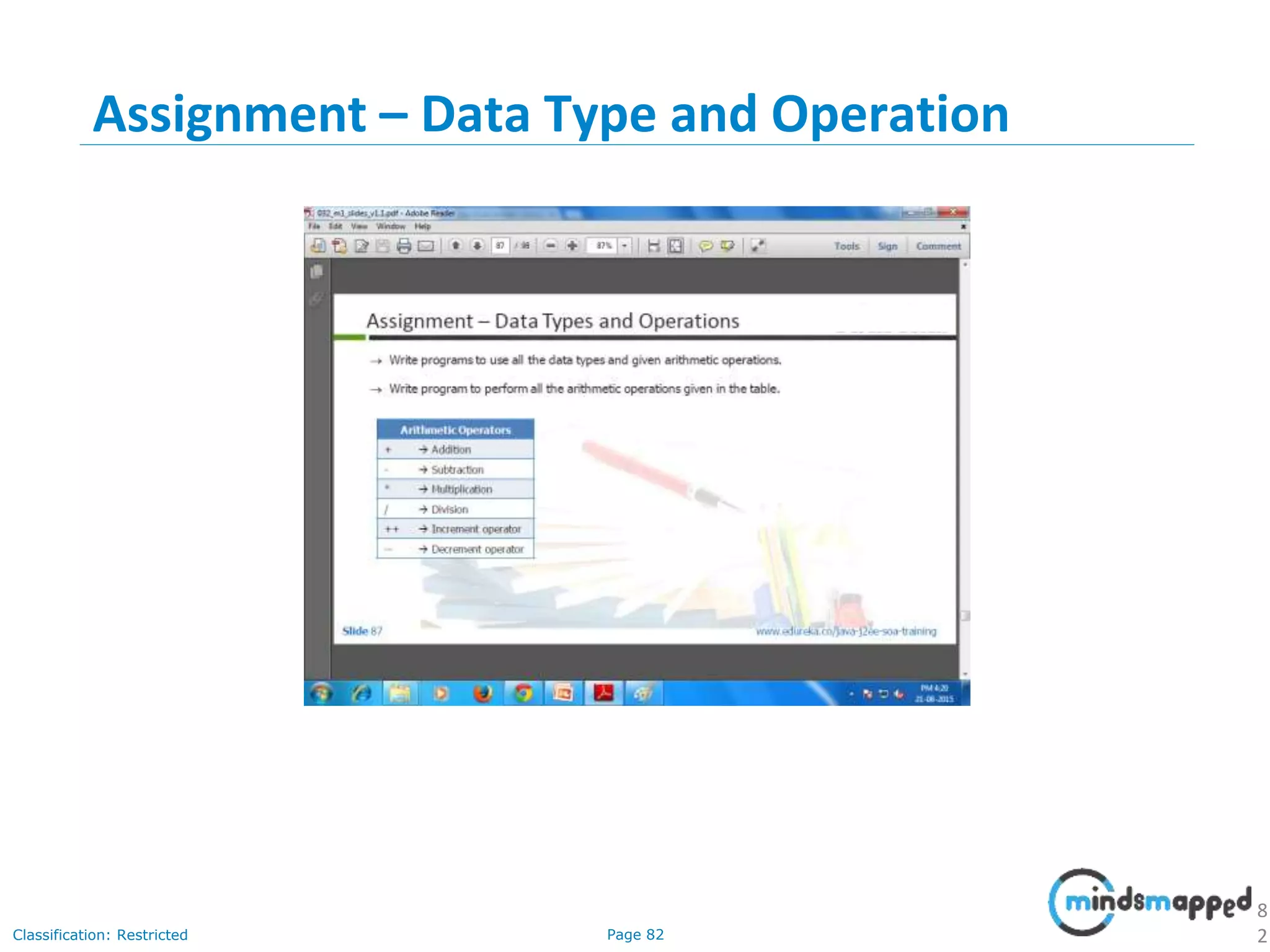
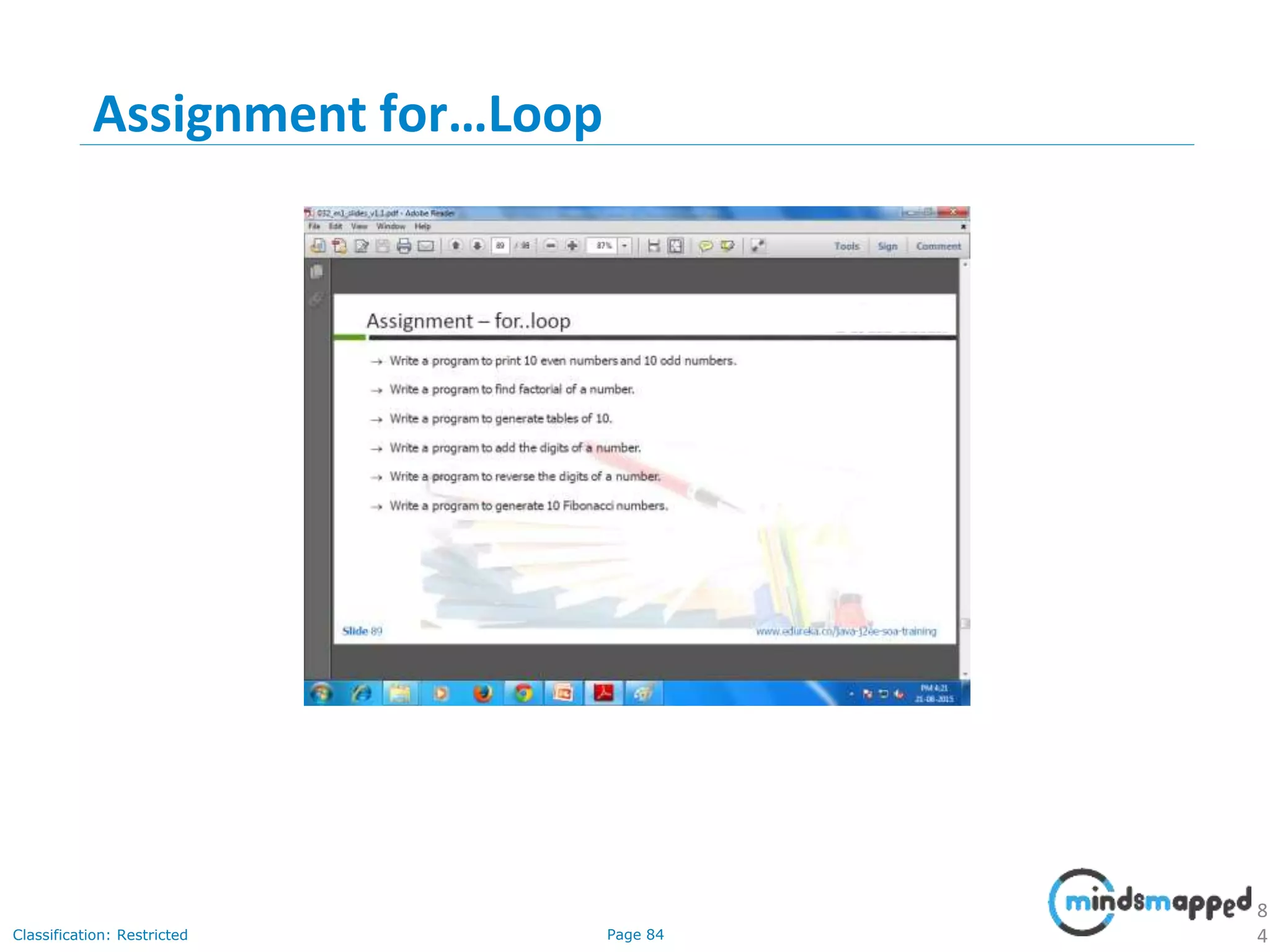
The document provides an introduction to Java programming, covering its advantages, applications, memory management, and basic coding concepts such as loops and data types. It features a narrative about a student named John who learns about Java, emphasizing its platform independence and the significance of garbage collection in memory management. Additionally, it outlines required software for Java development, including JDK and Eclipse, and offers practical programming exercises.