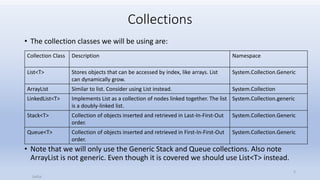
The document discusses collections in programming and introduces some common collection classes. It explains that a collection gathers objects together and allows methods to manage the objects. Arrays have fixed sizes and require manual management, while collection classes are more flexible and remove disadvantages of arrays. Generic collection classes like List, Stack, and Queue provide type safety by only allowing objects of a specified type.

![Collections
• An Array can be used to group a bunch of objects together
• Disadvantages of using an Array
• Array is fixed size. It cannot grow or shrink
• int[] numbers = new int[100]; // size of the numbers array is fixed to 100
• Programmer has to manage the collection, such as, adding, removing,
searching and moving items within the array etc.
• Collection classes removes the above disadvantages
• To work with Collection classes in C# the following namespaces have
to be included in your project:
• Systems.Collections
• Systems.Collections.Generic
Saifut
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/collections1-190701214026/85/Collections-1-2-320.jpg)