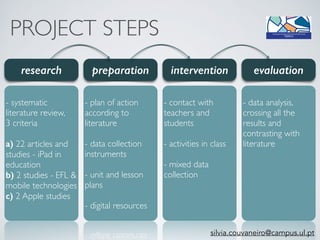
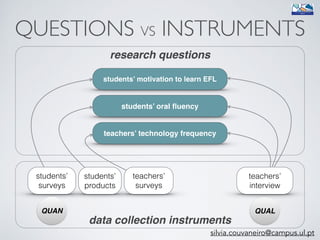
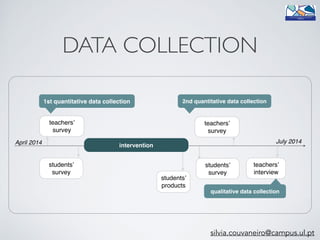
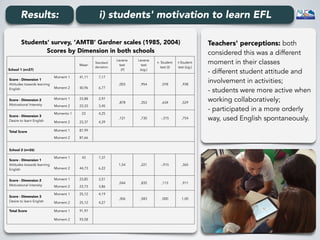
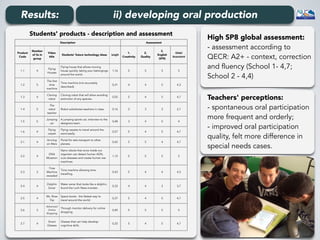
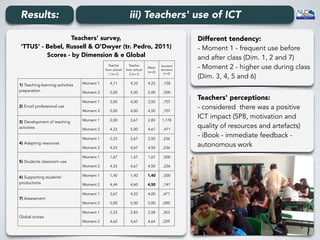
The document outlines a project conducted by Sívia Roda Couvaneiro and Neuza Pedro on the use of tablets for collaborative learning in English as a foreign language (EFL) to enhance oral communication. It details the project’s objectives, data collection methods, and findings, indicating that iPads positively impacted student motivation, oral fluency, and teacher engagement with ICT. The study highlights improvements in student participation and quality of oral production, while suggesting the need for longer-term evaluations and teacher training to maximize the potential of mobile technologies in education.