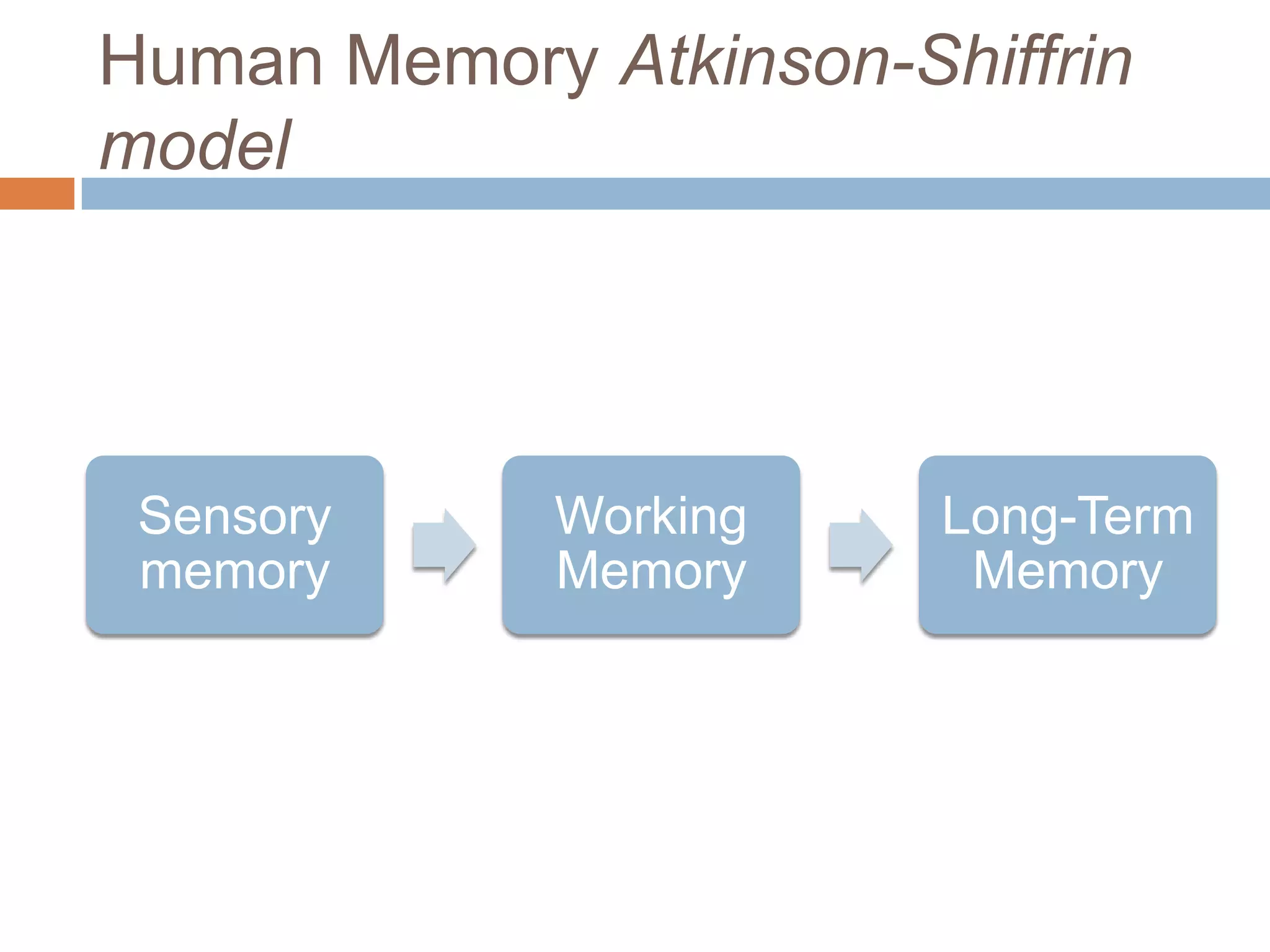
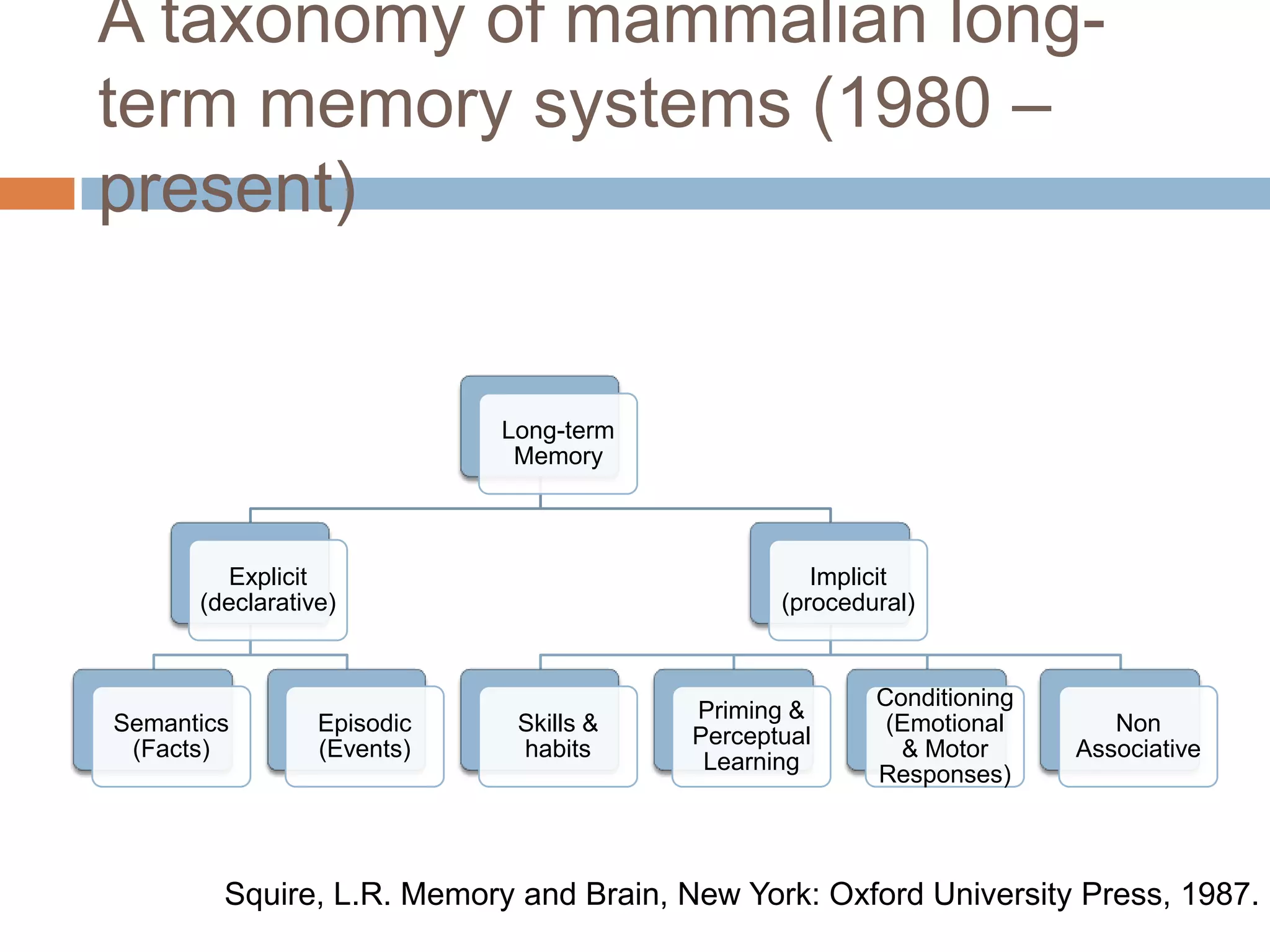
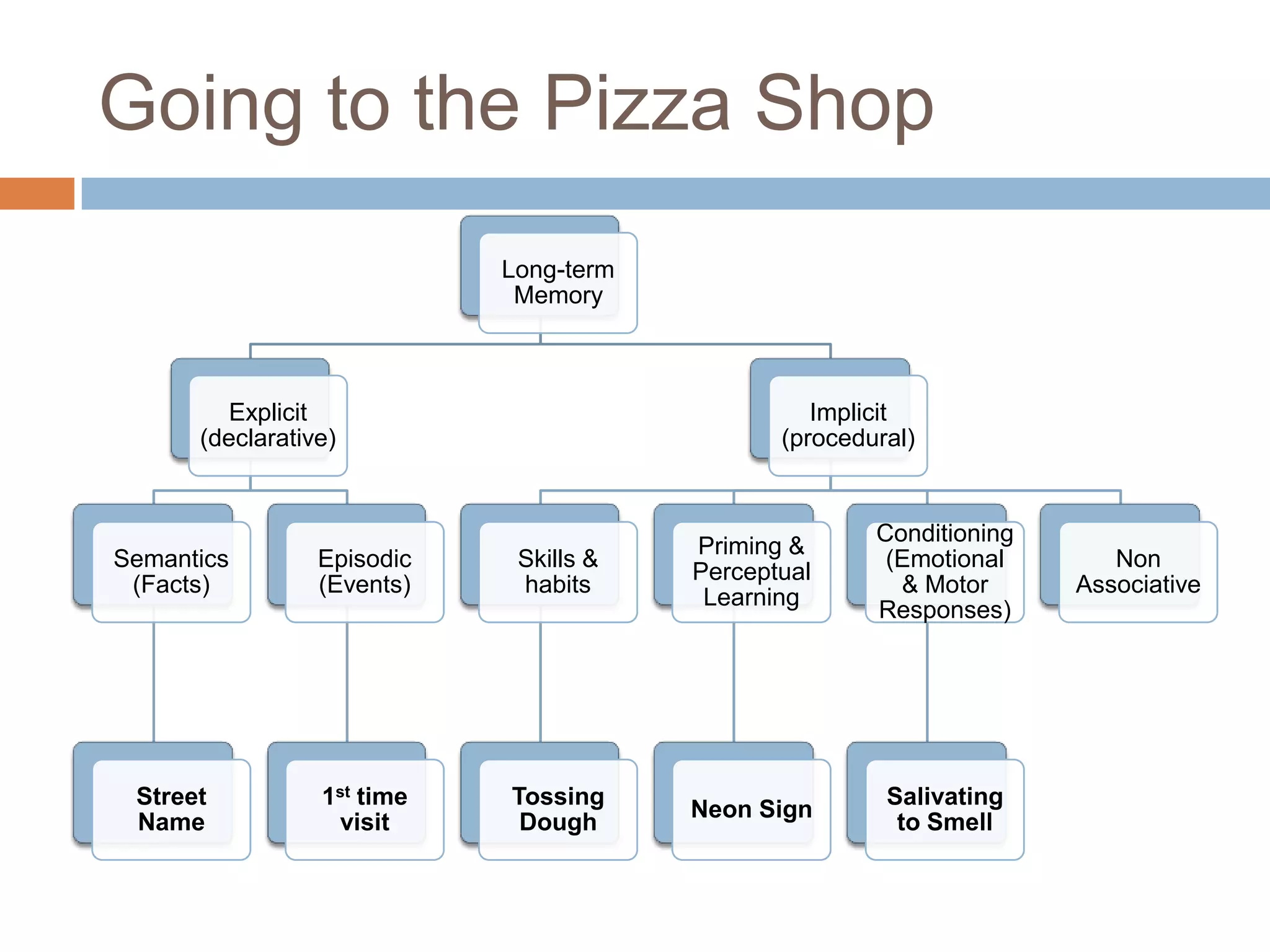
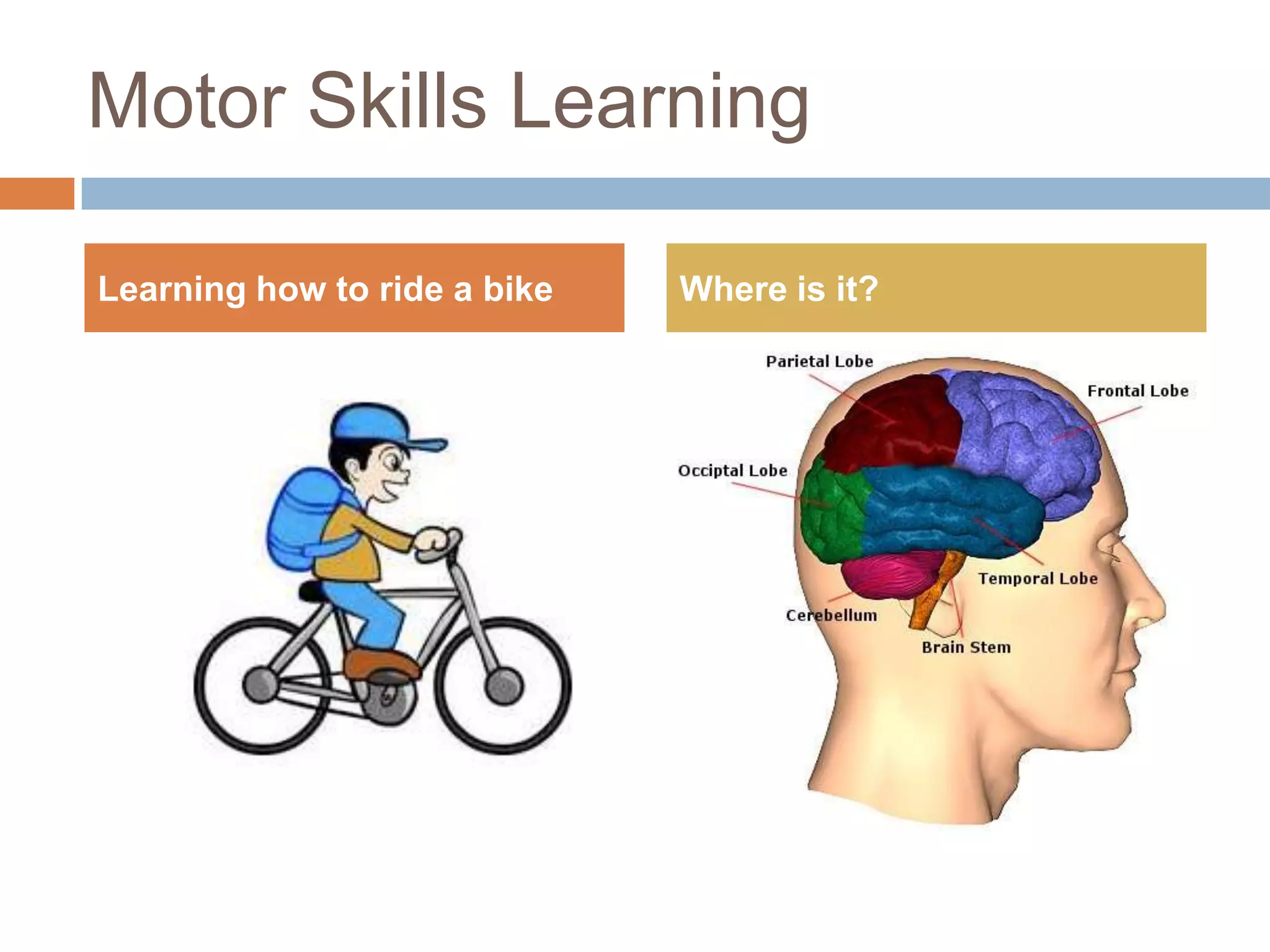
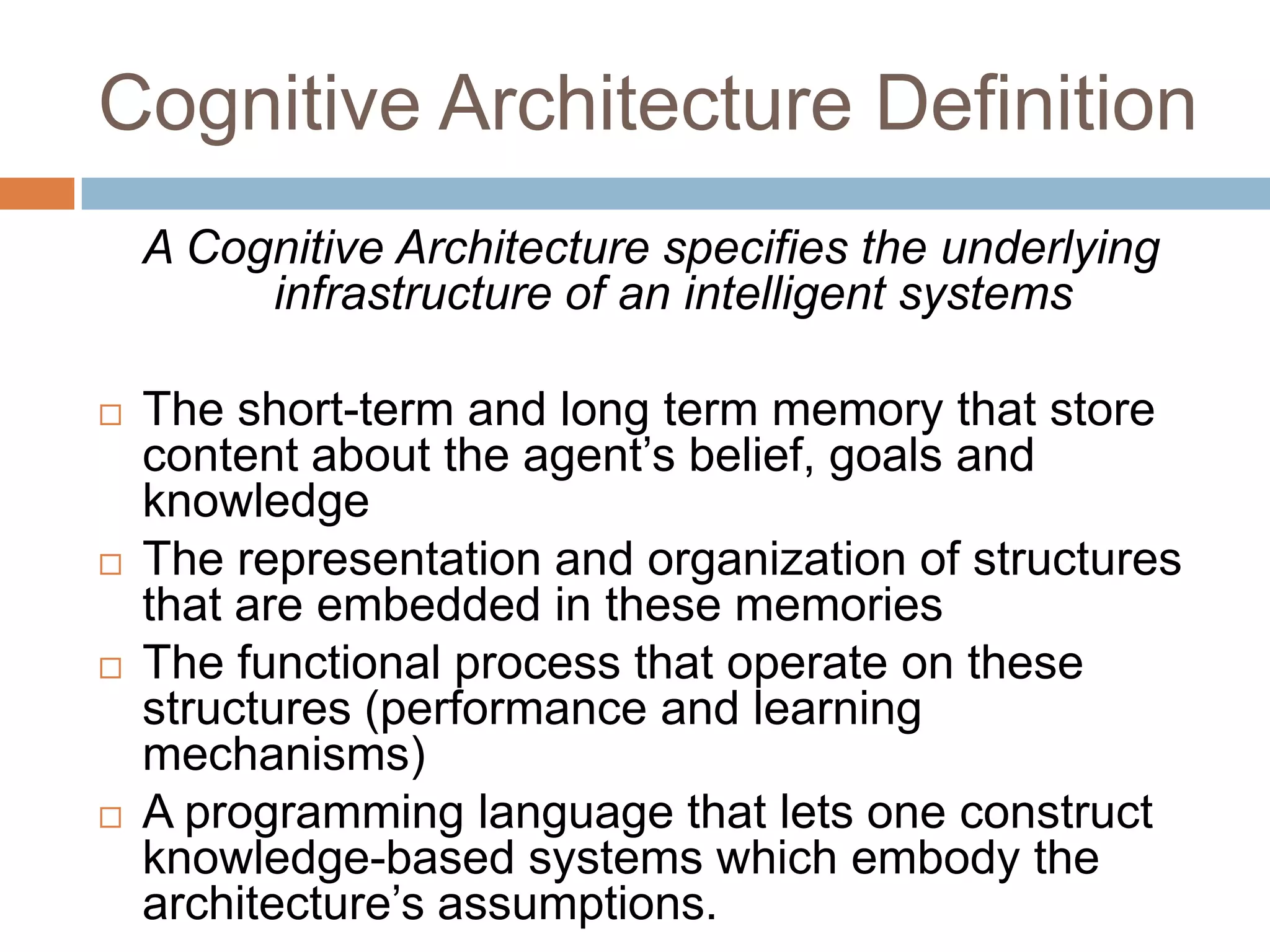
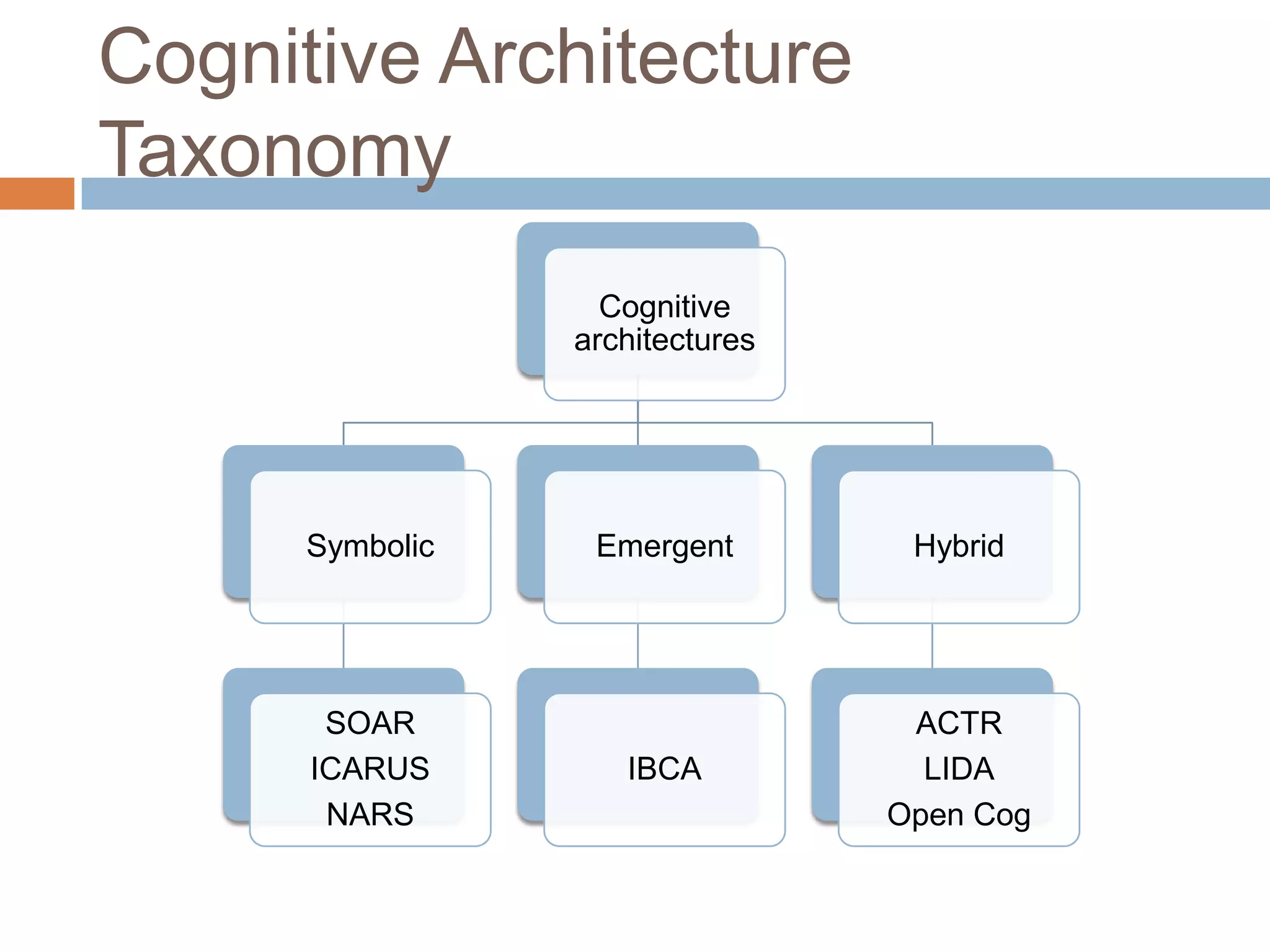
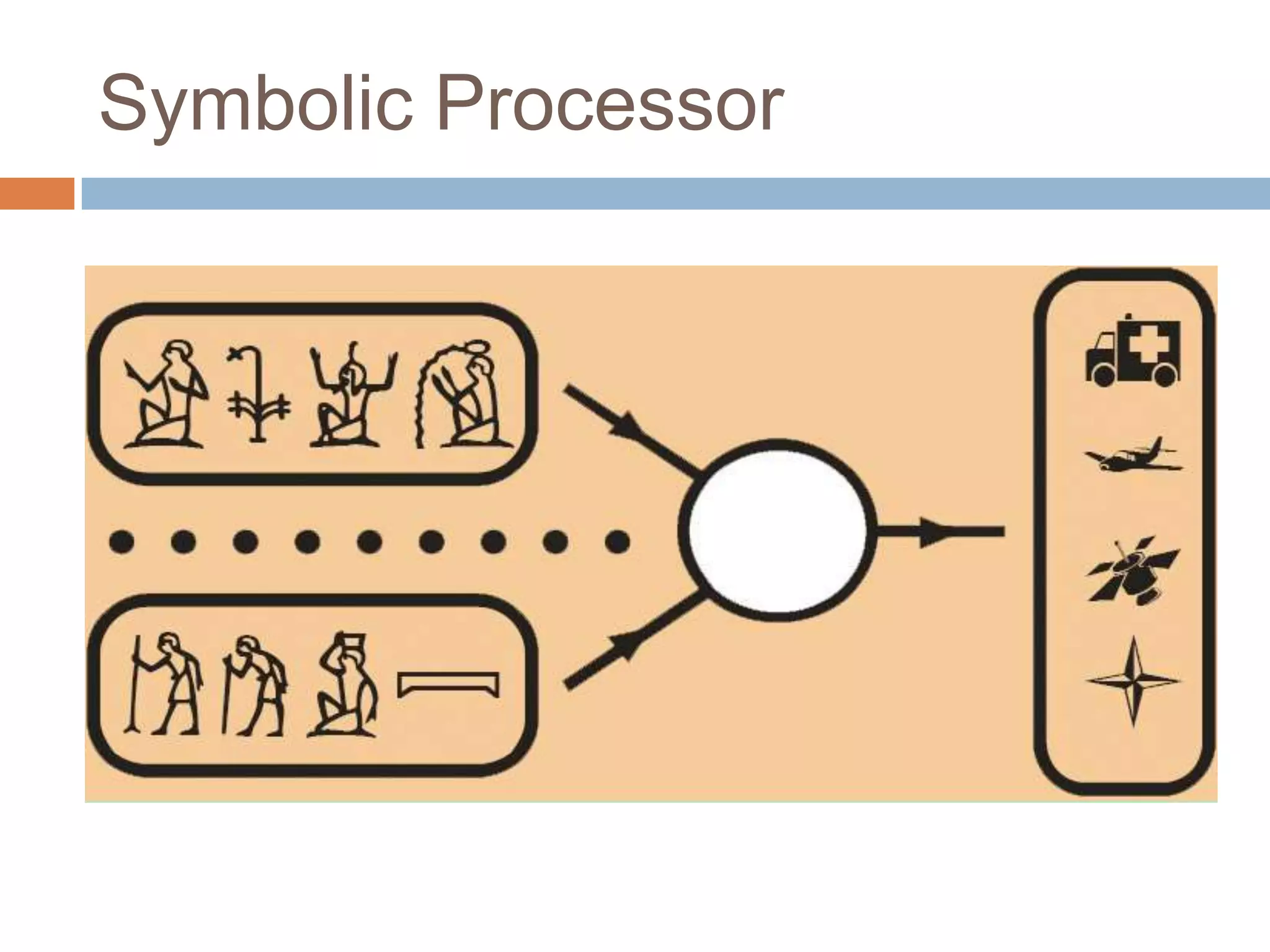
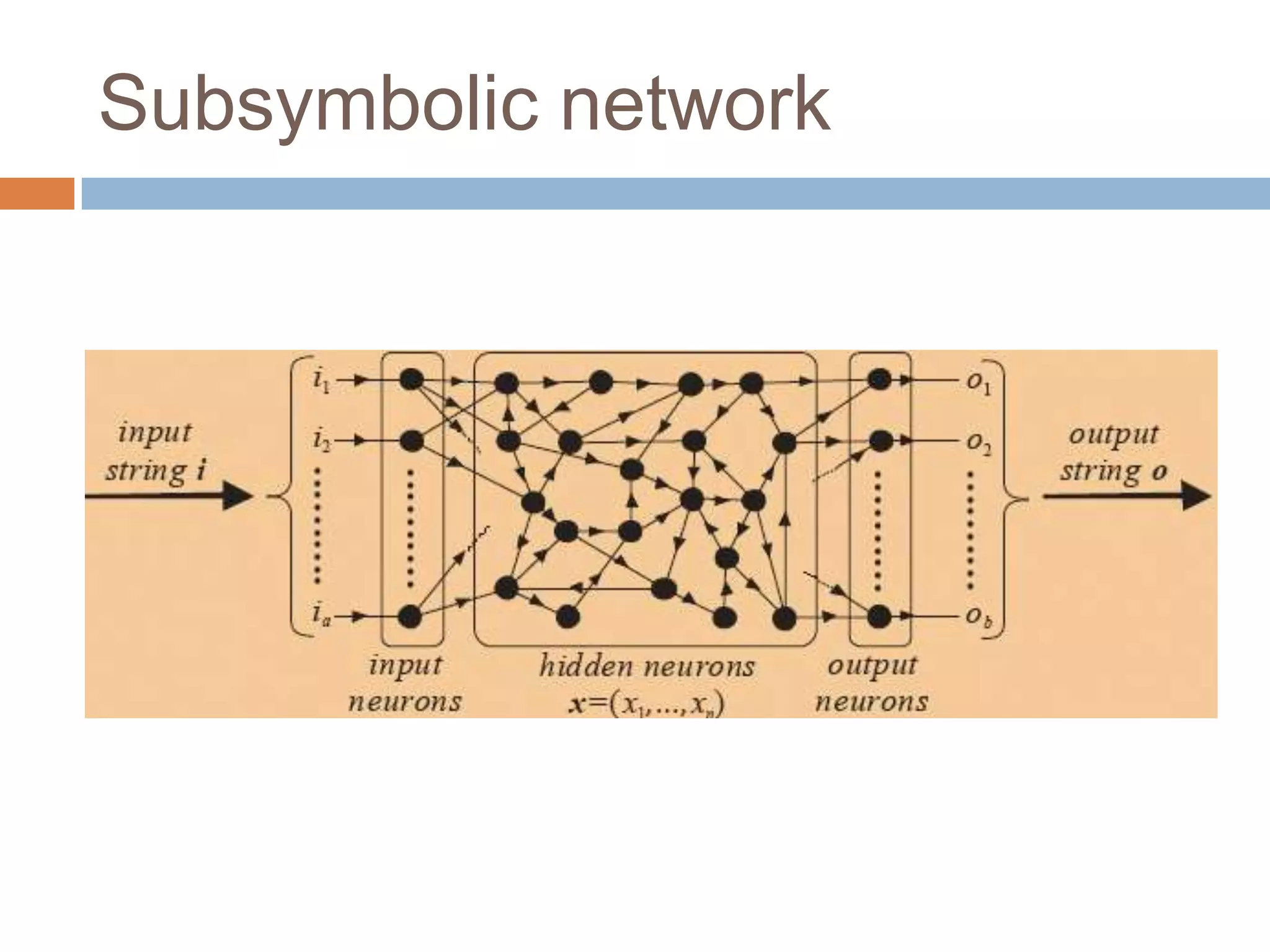
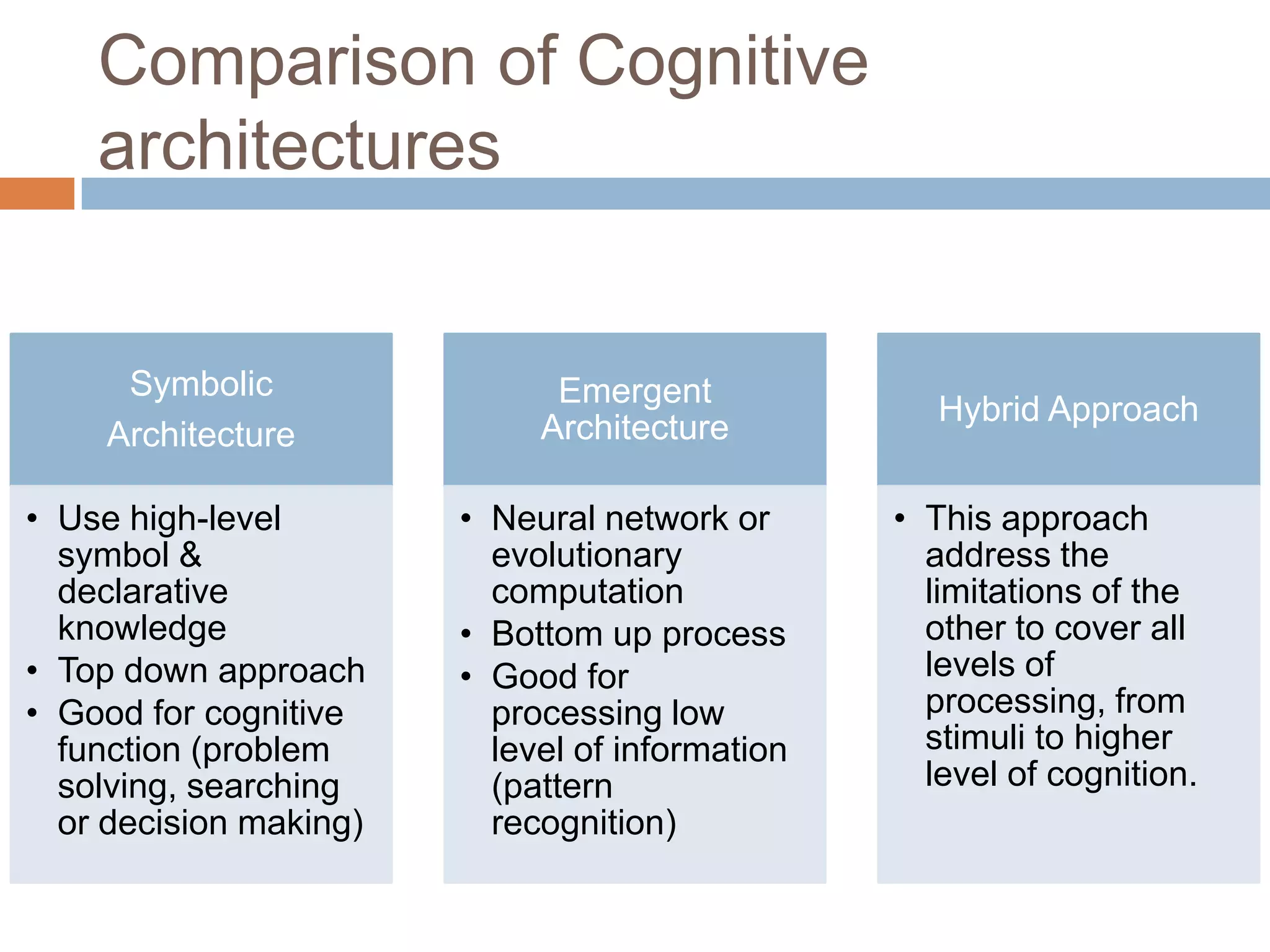
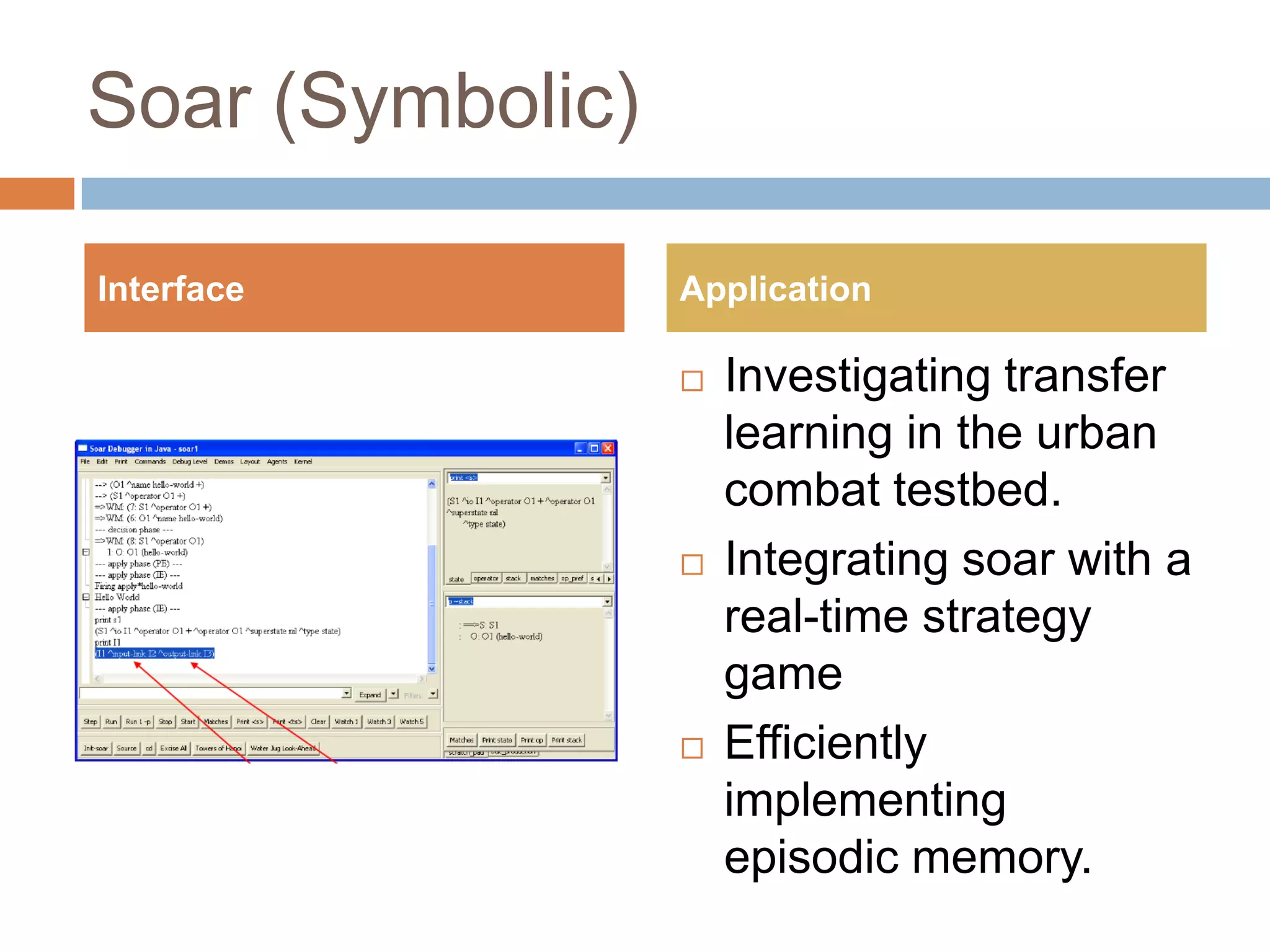
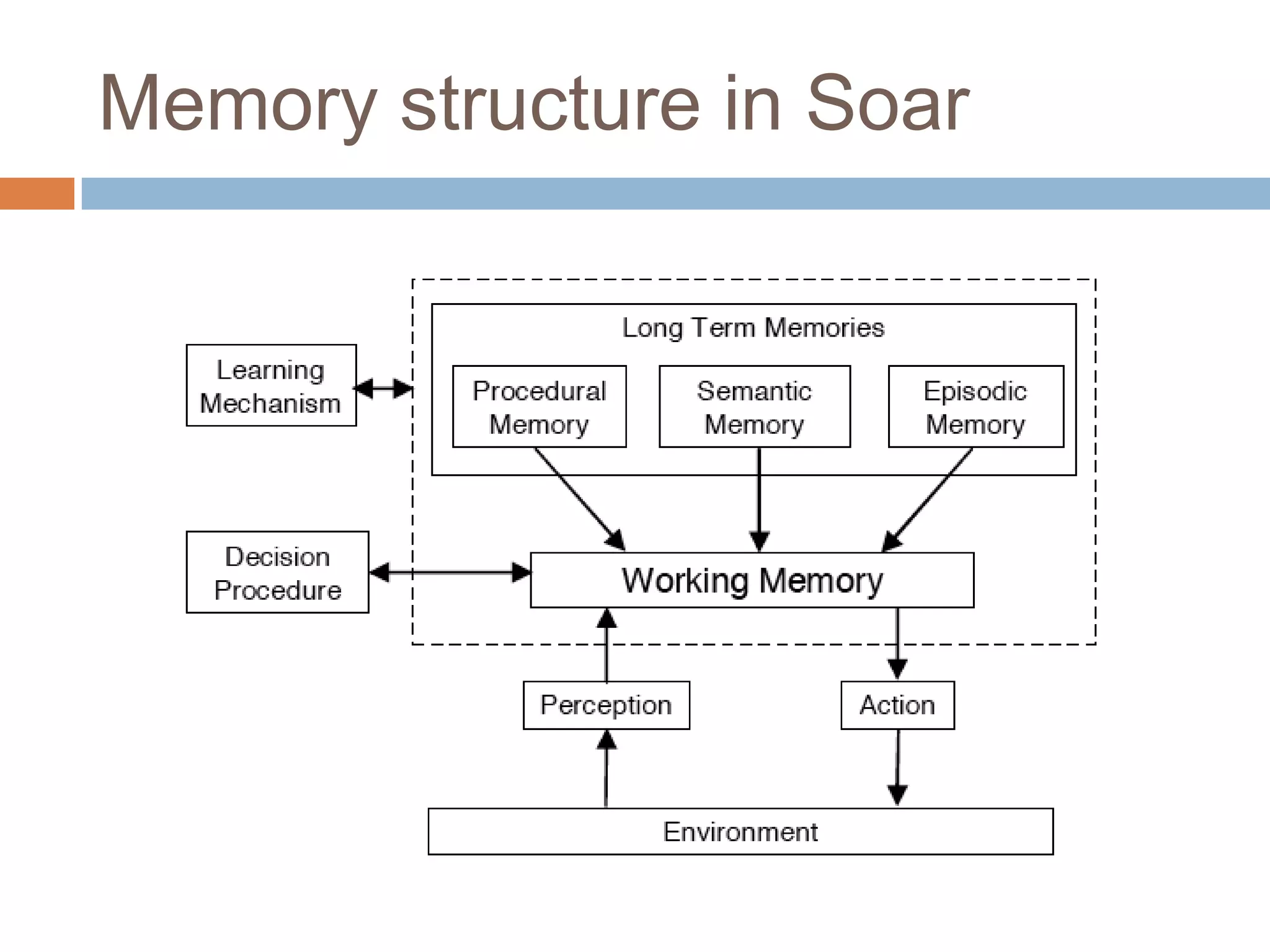
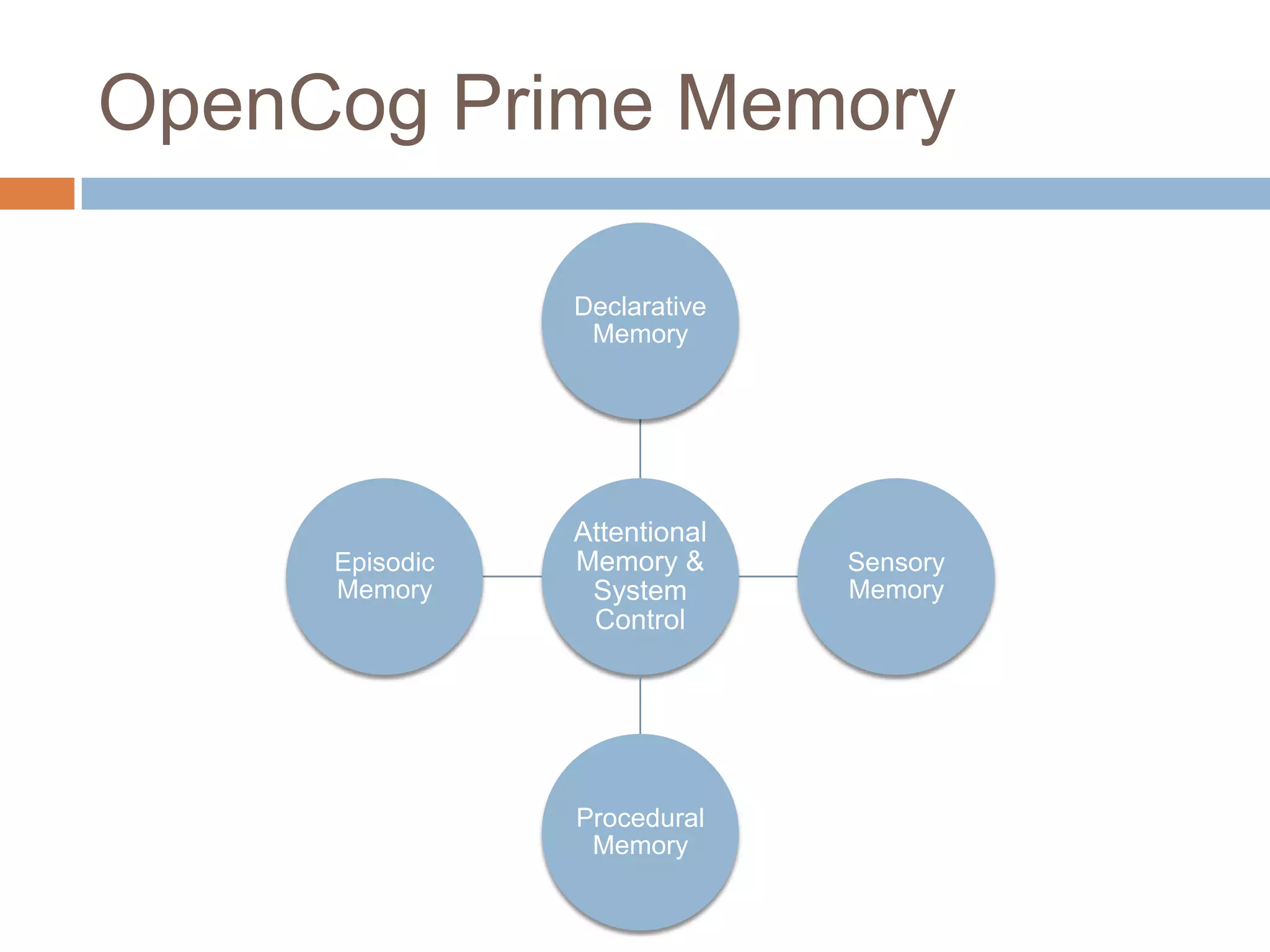
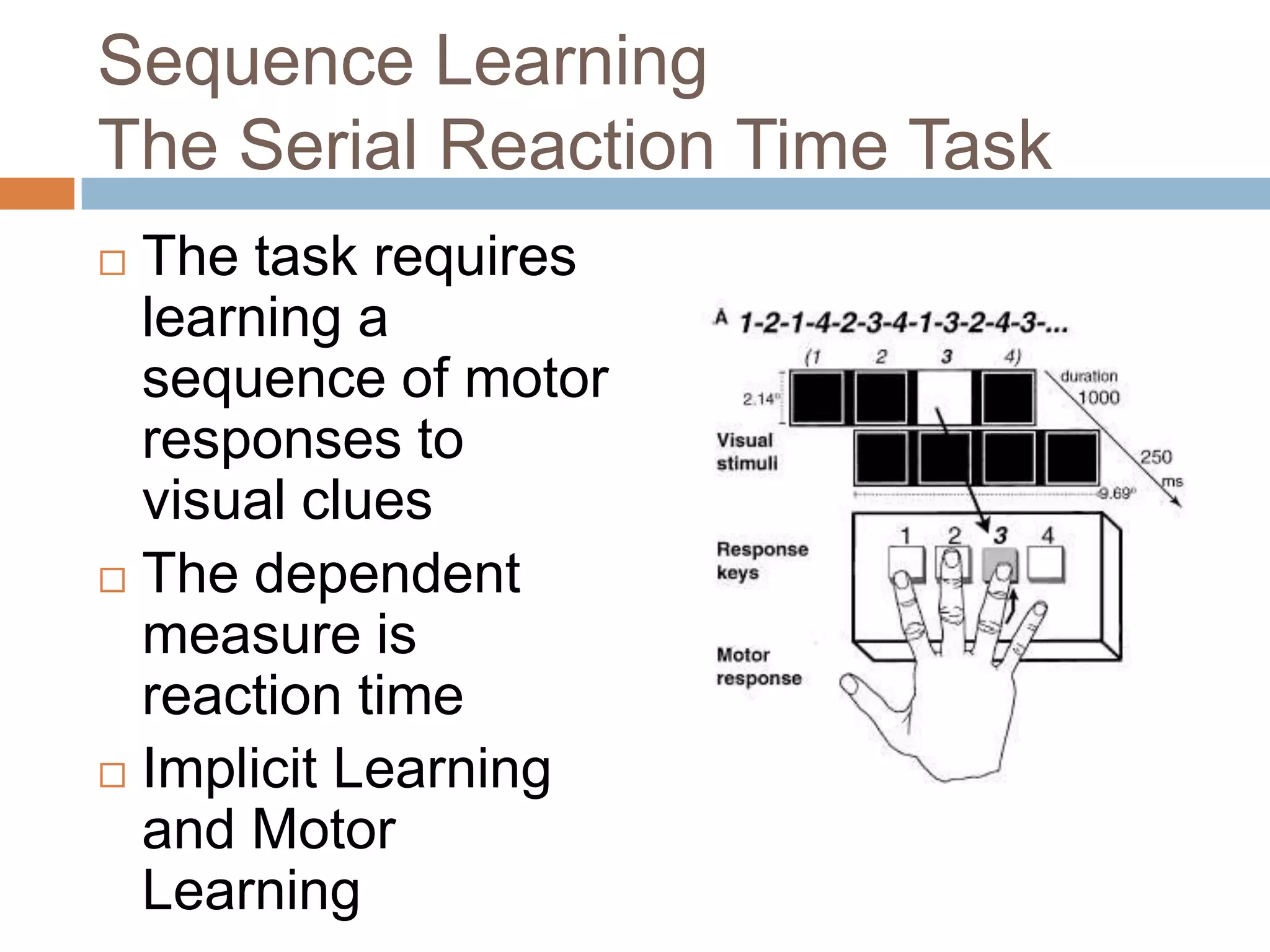
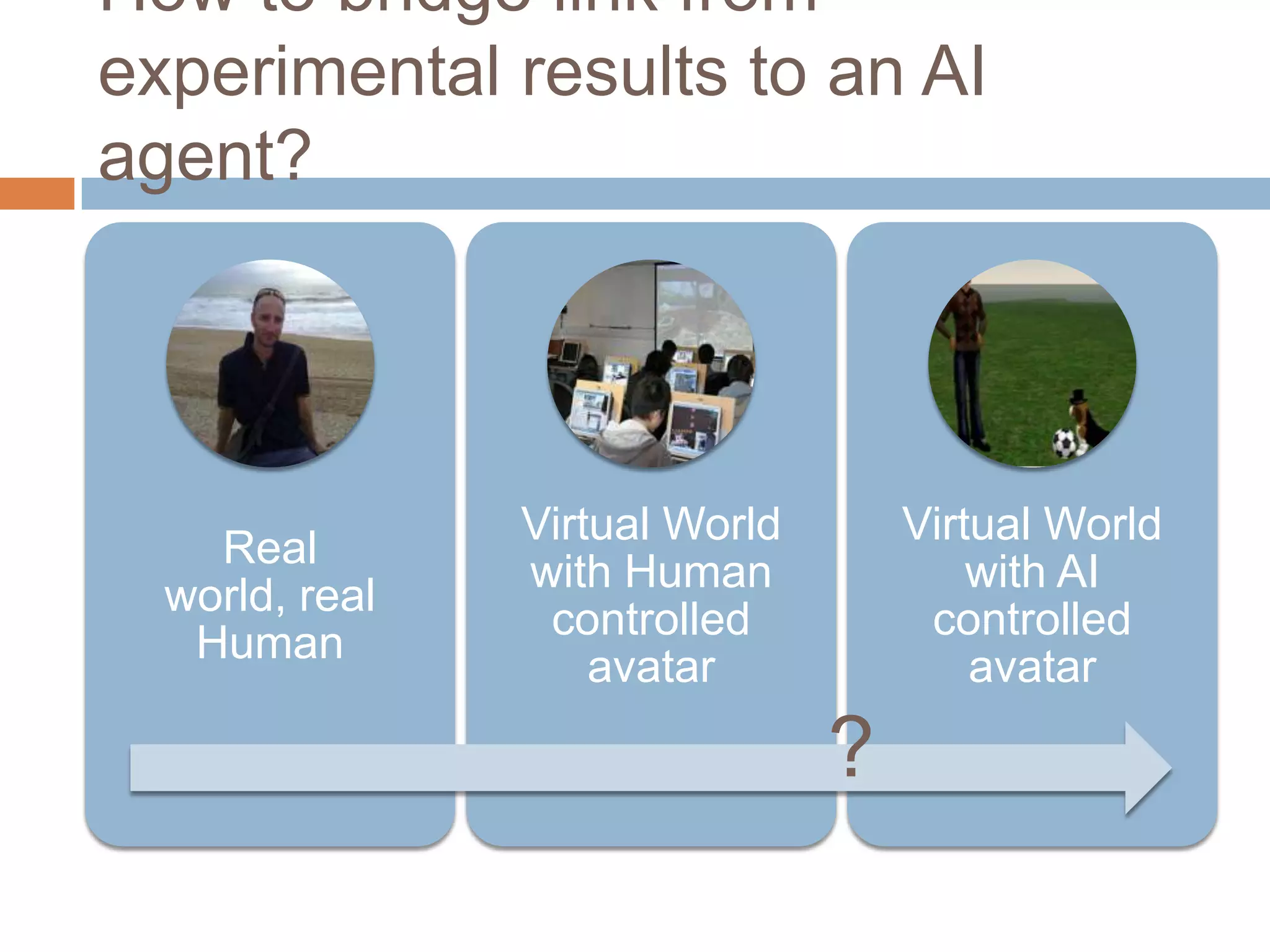
This document discusses cognitive science research in virtual worlds. It summarizes different cognitive architecture approaches like symbolic, emergent, and hybrid architectures. It also discusses memory structures and applications of cognitive architectures like Soar and OpenCog Prime. Finally, it considers how cognitive science experiments could be conducted in virtual worlds and how results could potentially transfer learning to embodied artificial agents.